How a Fever Benefits Your Health
Is it possible that a fever could actually benefit one’s health? Most of our society lives with the idea that health is a state of “feeling good,” and “not being sick or diseased.” We fear contact with bacteria, virus, and other microorganisms. We use anti-bacterial soap, sprays, pills, potions, & lotions. We are constantly “gearing up,” for the next big flu pandemic, etc.
In traditional cultures, fevers were always well respected and understood. Most people knew that the fever would build up and then break, much like a wave rolling into shore. Now, our society tries to suppress the fever immediately using antipyretics, or substances that lower temperature.
These antipyretics include acetaminophen and ibuprofen (1). These quickly lower the temperature but they also silence the body and hinder the development of the immune system. This allows the invading organisms to survive and contribute to the formation of chronic disease.
Your Immune System is a Muscle:
The immune system functions like a muscle in that must be challenged in order to grow stronger. Without resistance the immune system cannot get any stronger. An appropriate resistance may at times give someone a cold or fever (2). This is a natural adaptive response the body makes in order to allow the immune system to function at a greater level.
Getting a cold or a flu and having feverish symptoms may be the best expression of health for someone. Their individual immune system’s metabolic capacity may have been so weak that they couldn’t handle the natural environmental stressors. So the body became vulnerable and developed a viral or bacterial infection.

Fevers Stimulate the Immune System:
The immune system responds in order to fend off infection and strengthen the body. Microorganisms can only survive at unique temperature ranges (3). The innate intelligence within our body understands this and has adapted since the beginning of time to create an environment that is incompatible for these infectious organisms.
As our core temperature rises, it reduces the microorganism load in the body. The body will not want to elevate temperature to the point of killing off all its good microbes but will if necessary. When the body is under extreme infection the core temperature has to regulate the internal ecosystem by increasing the temperature and killing off microbes.
Our normal body temperature is said to be 98.6 degrees. A fever is defined by an oral temperature that exceeds 100.4 degrees (4). At 101 degrees most bacteria are unable to survive and at 102 degrees the viruses are unable to replicate and spread in the body (5). Fevers are typically self-limiting and short in duration. They are not dangerous until they get up over 103-104 degrees in temperature (6).

Immune Thermal Regulation:
As the core temperature elevates it activates the CD8+ cytotoxic T cell (7). This is a special lymphocyte that is able to destroy cells infected with viruses and cancerous cells (8). Researchers have found that higher body temperatures raise the number of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. This creates a significantly greater immune response against infection.
The increase in core temperature also elevates neutrophils which are unique immune cells that selectively target infectious bacterial cells. The temperature increase also improves enzymatic activity to create an environment that is unkind to the infectious microbes.
According to Dr. John Wherry, Ph D and deputy editor of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology “Having a fever might be uncomfortable, … but research reports show that having a fever is part of an effective immune response (7).”
Over sterilizing our environment and using synthetic chemicals such as drugs, artificial vitamins and fever reducers only makes our body weaker. These products are like a crutch that does not allow the body to adapt and get stronger. So we end up weak and vulnerable and unable to effectively adapt to a challenging environment.

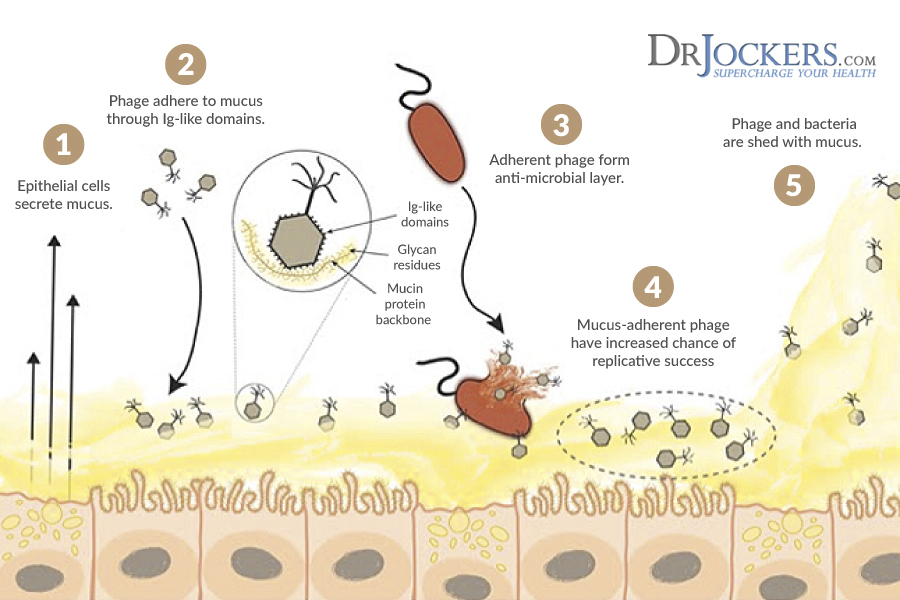
The Role of Mucous Formation:
Mucosal surfaces are the primary entry points into the body for pathogenic microorganisms (9). Until recently most scientists viewed mucus as simply a physical barrier that helped to prevent against the invasion of infectious organisms. It was also thought to play a lubricating role between tissues. However, the latest research shows that mucous appears to be the major home of a unique organism called bacteriophage (9).
Bacteriophages which are also called “phages” are viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria. They selectively target antagonistic microbes and thus enhance the health of the host. Wherever bacteria and other microorganisms reside you will also find phages.
Researchers have found evidence that phages partner with host animals and humans to kill of unwanted bacterial colonies and control the composition of friendly microorganisms in the body (10). This reduces infectious organisms and improves the immune system.
In times of fever the body increases mucous to trap bacteria and enhance the activity of phages in order to reduce infectious organisms. This is an intelligent response by the body to prevent against chronic infection and disease development. Trust the body and trust your symptoms!
When is the Fever Dangerous?
You should always consult your natural health physician when fevers go over 103 degrees or last longer than four days. If the fever causes tremendous discomfort, trouble breathing or convulsions at any time it would be an indication to go to the emergency room.
One should drink tons of clean water and use electrolytes such as fresh squeezed lemon. This will support the body as it uses up fluids and electrolytes quickly in an effort to rid itself of the infectious organisms. If the temperature gets up over 104 degrees an ice bath can help bring it down a bit so as to not cause damage to any of the vital organs.
If you want to know my best action steps for improving your immune health, read this article. If you are interested in cleansing you liver check out my free guide where I show you the best things you can do for optimal liver health!





I believe this is a very important article. Some of the pharmaceuticals mentioned cannot kill the virus or bacteria and some of it can be trapped in our system leading to stagnation (a TCM term). Over time this slows our whole system down. If our immune system is working properly we should get over the fever in a couple of days like any young child. I have friends who can have the flu for 6 weeks at a time but it is difficult to get through to them that they have a weak immune system. I used to be the same but had a TCM doctor unblock the stagnation and then started to follow a probiotic diet. Now if I get the flu it is gone in a few days.
Pediatricians aren’t as freaked out by high fevres as they were when we were kids, which was an incredibly long time ago for me. Nowadays, I believe it’s until they are 3 or so months old that they’re really concerned about any fever, I think b/c of concern about meningitis. After that, I’ve been told, by at least one ped, not to worry about the fever itself unless it hits 106. Worry meaning go to the ER. And even febrile convulsions don’t impress the doctors these days. Our ped in Brooklyn always told us not to bring down the fever, to let it do its work, but I could never stand to see her suffer and always gave her tylenol/motrin. I hope little Trixie beats this bug soon.