 Stem Cells: What Are They and 8 Ways to Activate Them
Stem Cells: What Are They and 8 Ways to Activate Them
Chances are you’ve heard about stem cells and stem cell therapy before. You’ve heard about their potential to treat some serious diseases and some controversies around these therapies. But do you know what stem cells are and how they may benefit your health?
In this article, you will learn about stem cells. You will understand what stem cells are and how they work. I will explain what stem cell therapy is and the reasons for using this form of therapy. I will also share 8 ways you can activate your stem cells naturally.
What Are Stem Cells
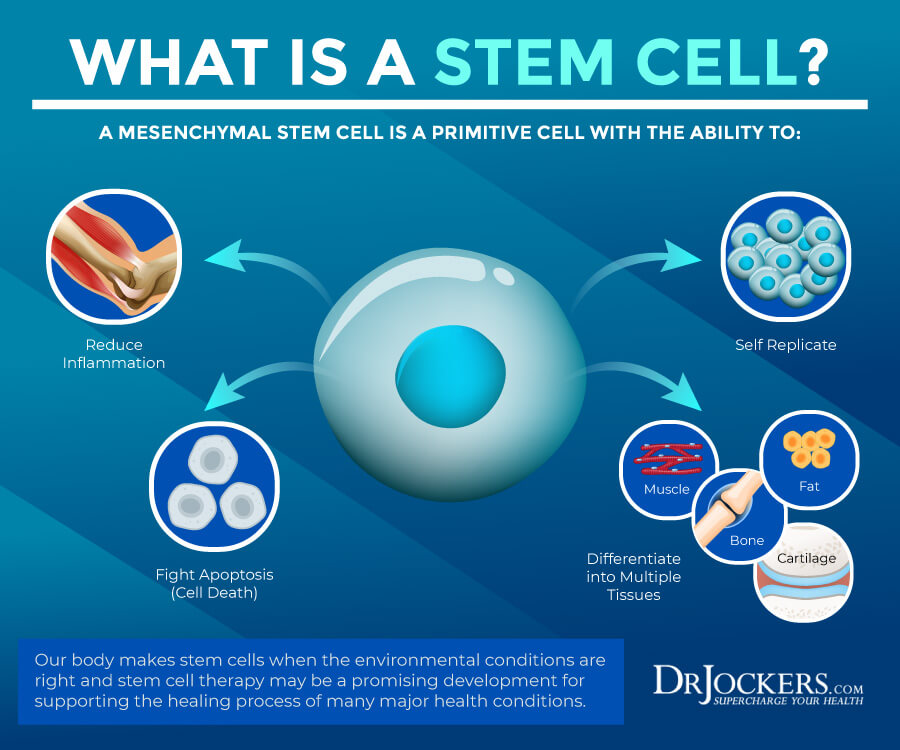
Stem cells are found in your body. While most cells in your body have specific functions, a stem cell doesn’t have a specific purpose and can turn into any cell if needed. They are undifferentiated cells or raw materials that can turn into cells with specialized functions as your body requires them.
When the conditions are right, your stem cells can divide into several daughter cells that can turn into new stem cells through the process of self-renewal. They can also turn into specialized cells, such as blood cells, brain cells, bone cells, or heart muscle cells through the process of differentiation. Self-renewal or differentiation can occur in your body or a laboratory provided the right conditions.
Research scientists and medical professionals are interested in stem cells because they may help them understand how our cells and body function, why and how we get certain diseases, and find potential treatments or cures. Research is ongoing, but stem cells show promise in treating certain diseases with no currently known cure, including spinal cord injury, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, heart disease, and diabetes (1, 2).
Types of Stem Cells
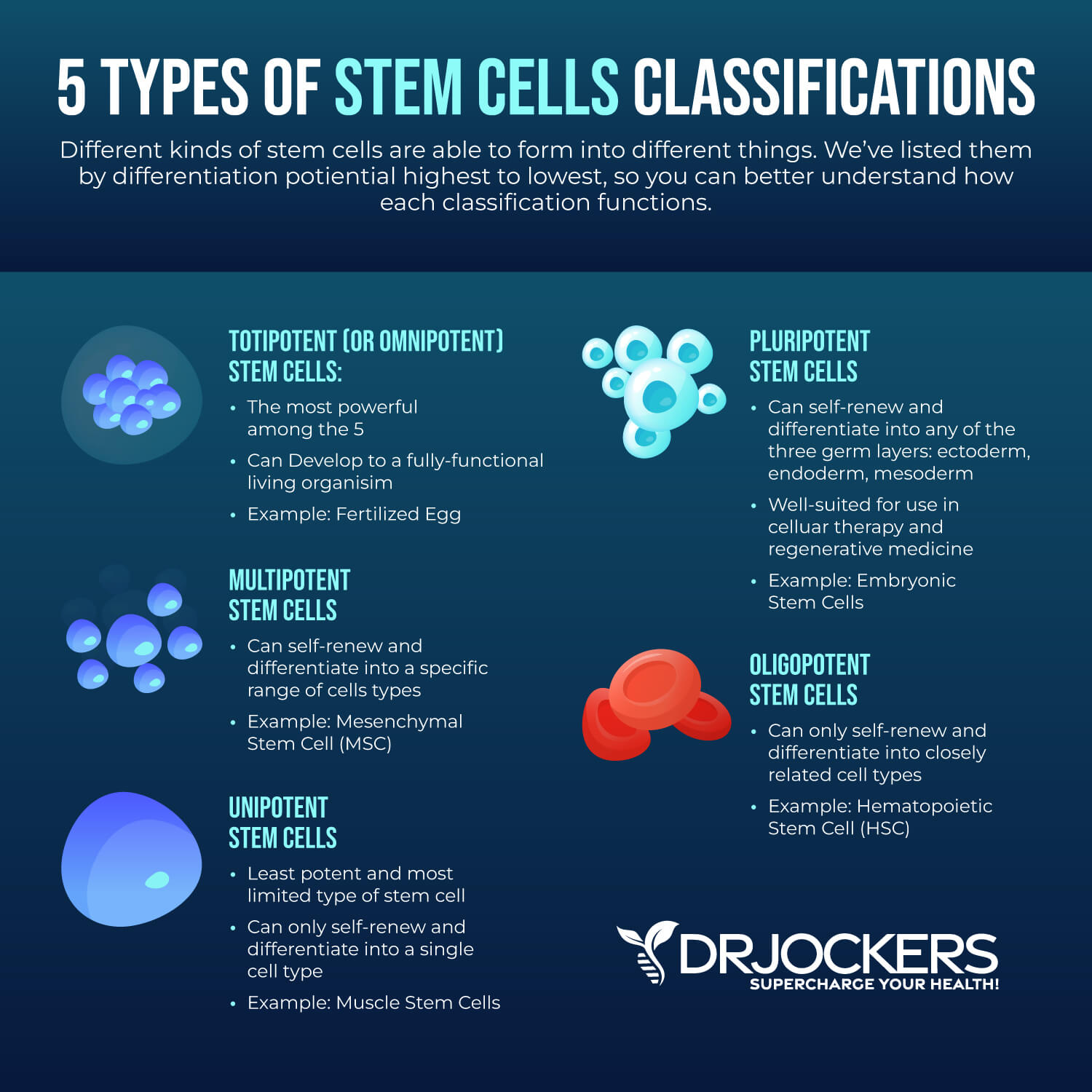
There are several types of stem cells categorized based on their potential to differentiate, including:
- Totipotent stem cells: Totipotent cells first appear at the zygote stage and can differentiate into all kinds of cells.
- Pluripotent stem cells: Pluripotent cells appear at the early embryo stage and can differentiate into almost any cell.
- Multipotent stem cells: Multipotent cells can differentiate into a closely related family of cells. For example, adult hematopoietic cells can turn into platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells.
- Oligopotent stem cells: Oligopotent cells can turn into a few different cell forms. Lymphoid and myeloid stem cells are two examples of oligopotent stem cells.
- Unipotent stem cells: Unipotent cells can only differentiate into their type of cells. For example, adult muscle stem cells are unipotent.
Sources of Stem Cells
Stem cells mainly come from two main sources: adult body tissues and tissues of embryos. However, scientists are working on other options as well.
Adult Stem Cells
Every person has adult stem cells, also called somatic or tissue-specific stem cells, that have existed in their body from the time they were an embryo. These stem cells can be found in your bone marrow, blood, blood vessels, brain, skin, skeletal muscles, and liver.
They stay in a non-specific state until your body needs them to turn into a specialized cell used for a specific role. Researchers used to believe that adult stem cells can only change based on their tissue of origin, however, it seems like they can turn into other cells as well (3).
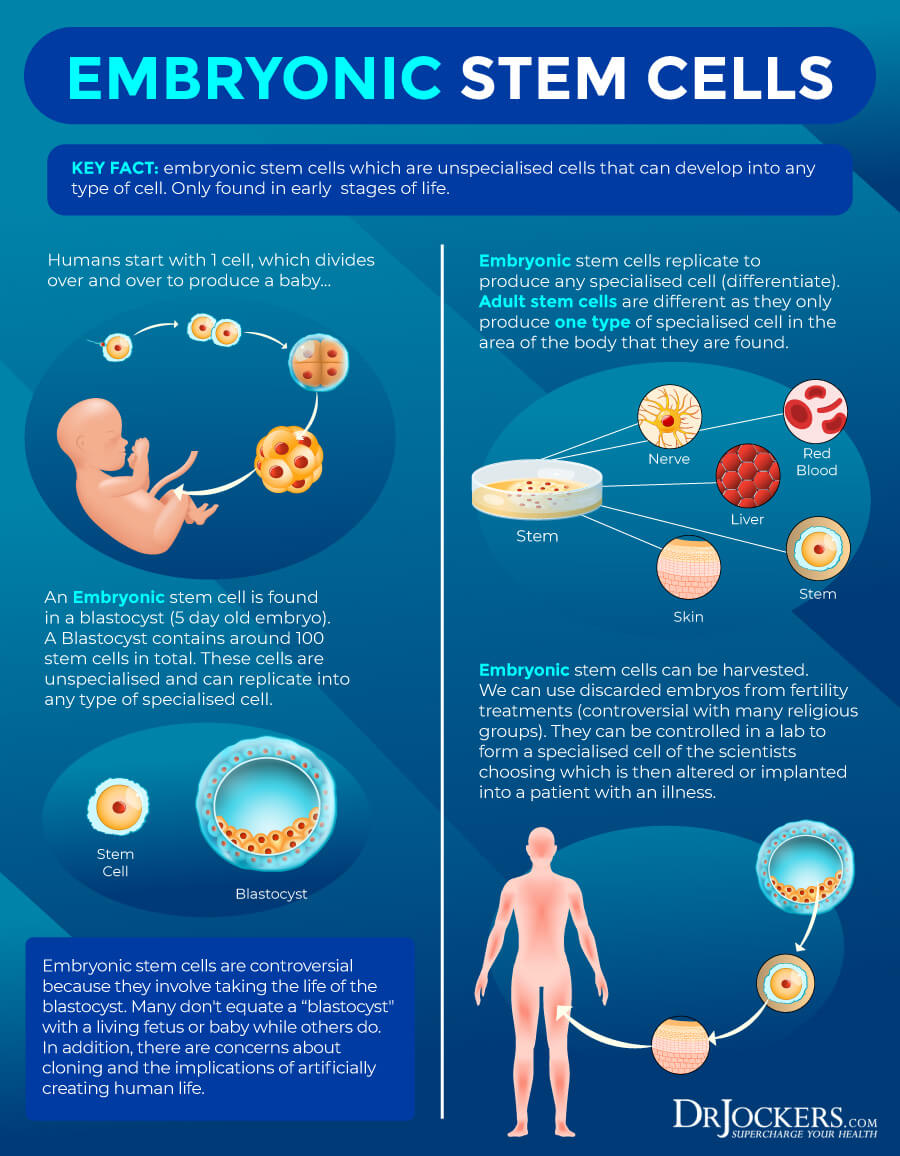
Embryonic Stem Cells
After a sperm fertilizes an egg, an embryo is formed into a ball of cells called a blastocyst. A blastocyst already contains stem cells called embryonic stem cells at 4 to 5 days old. Before implantation, a blastocyst has 150 to 200 cells.
The other mass of the blastocyst will form the placenta and the inner layer will develop into a human body. Embryonic stem cells, or totipotent cells, are located in the inner cell mess. Through the right stimulation, these totipotent cells can turn into any cells from blood to skin cells as needed. Since embryos have a lot of development to go through, embryonic stem cells can differentiate into more cells than adult ones.
Embryonic stem cells used for research come from extra embryos from in vitro fertilization (IVF). Embryonic stem cell research is a highly controversial issue. In 2001, President Bush banned funding for stem cell research, while President Obama lifted some restrictions. However, researchers started using pluripotent stem cells in 2006, which doesn’t carry the same ethical concerns (4, 5).
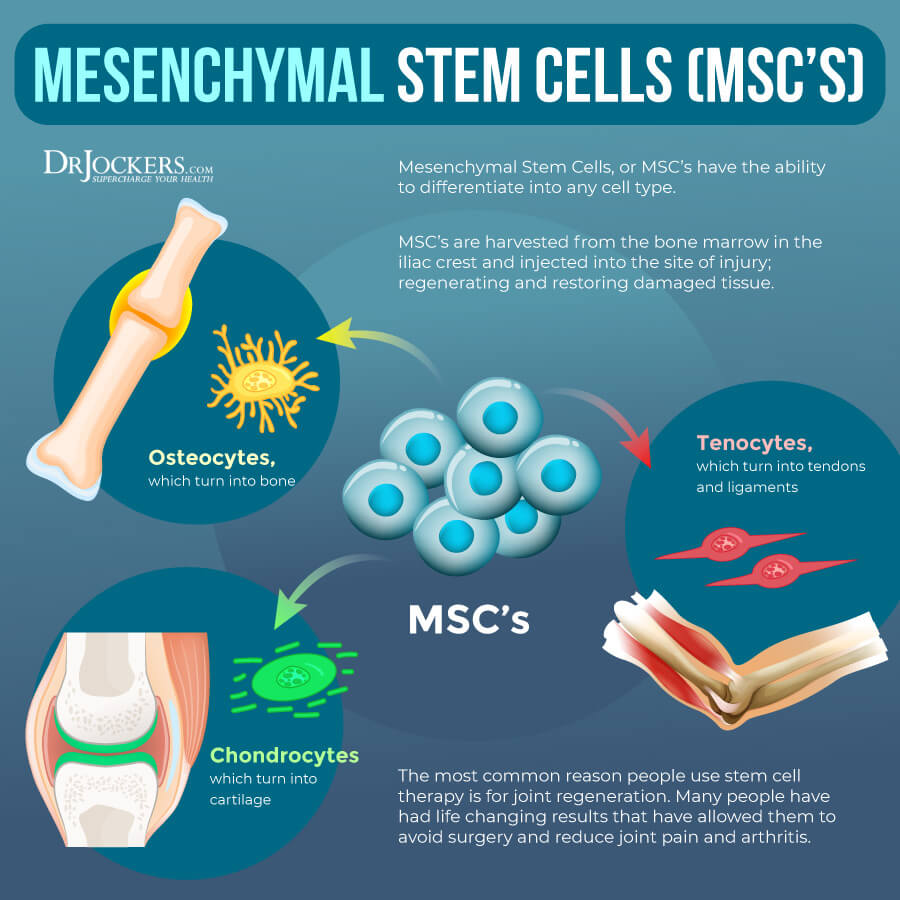
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) originate from the connective tissue or stroma around your body’s organs and tissues. Scientists have explored using them for new body tissues, including fat cells, bone, and cartilage.
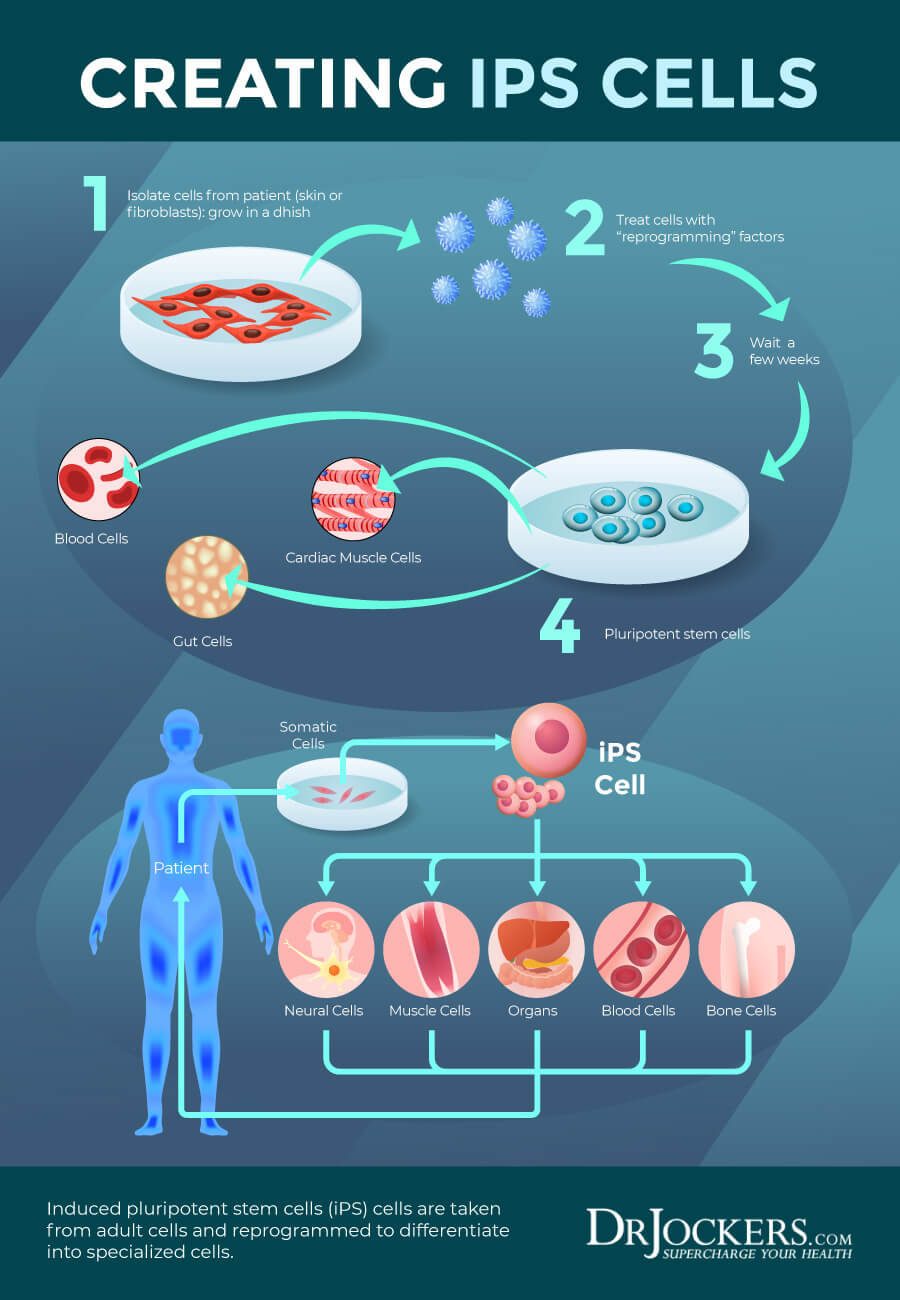
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPS)
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) cells are created from skin cells and other tissue-specific cells in a lab to be used similarly to embryonic stem cells. Samples are extracted from adult or embryonic tissue and are placed in a controlled culture where they can divide and reproduce without specialization.
Later they can be stimulated to change into specialized cells through directed differentiation in a lab. While it is easier to grow a large number of embryonic cells, there is progress with both cell types. When it comes to iPS cells, research is ongoing, and further development is still necessary.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy
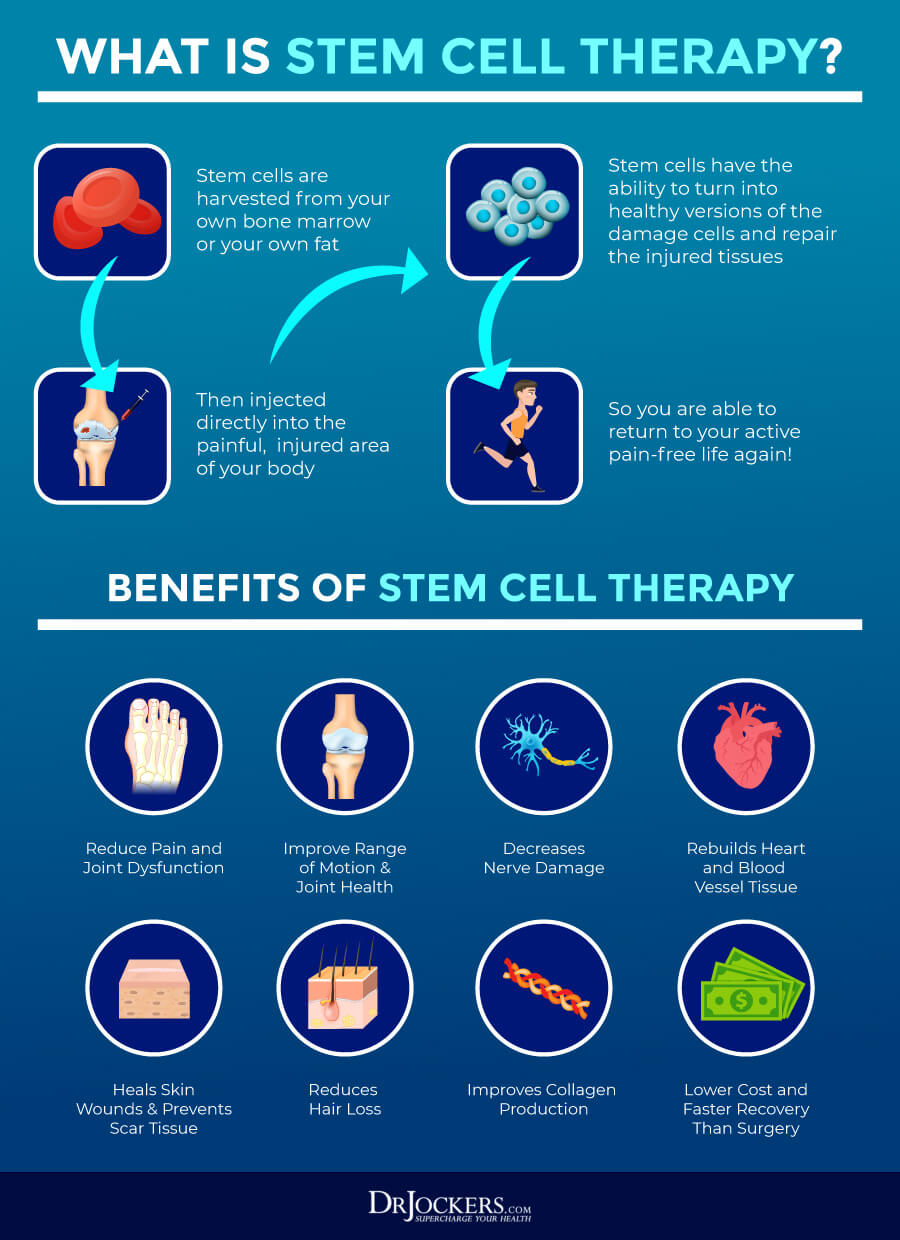
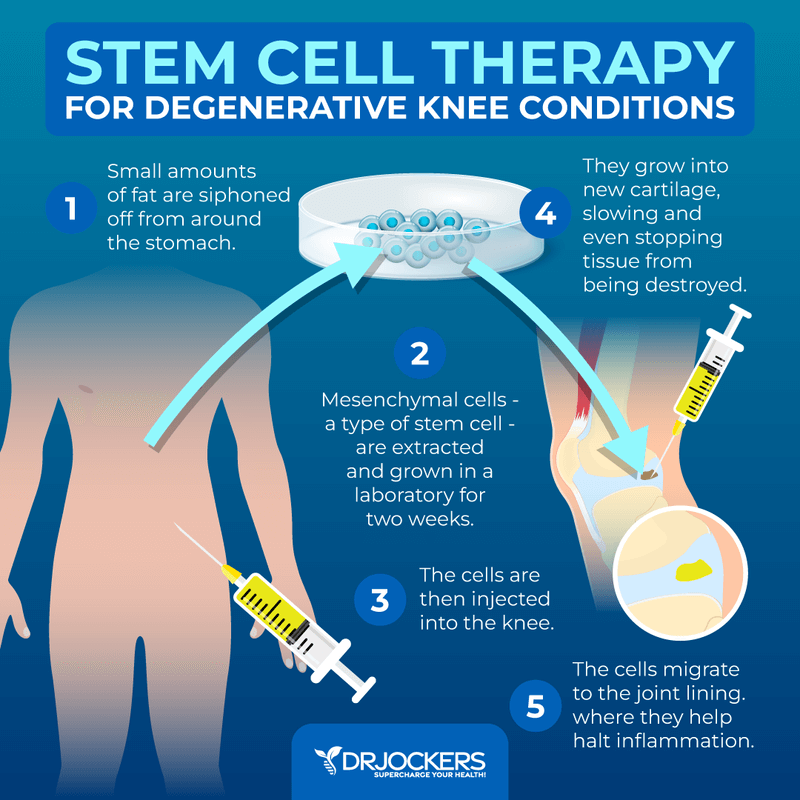
Stem cell therapy (SCT) is a type of emerging regenerative medicine used to repair damaged cells by lowering inflammation and regulating the immune system. Stem cell therapy has been used for a variety of medical conditions, including Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), Crohn’s disease, lupus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and more. While stem cell therapy is not a cure for any disease at this point, it has a premise to help your body repair itself and reduce or eliminate symptoms for long periods of time and increase the quality of life of people receiving stem cell therapy.
Stem cells for stem cell therapy may come from various sources, including adipose or fat tissue, placental tissue, umbilical cord tissue, or bone marrow. Stem cells can be administered intravenously through IV Stem Cell Therapy, directly into the spinal cord through intrathecal treatment, and site injection into affected areas, such as the hips, knees, or hands.
Stem cell therapy is a non-invasive therapy. Its goal is to replace damaged cells and allow repair. This process uses mesenchymal stem cells and has shown great potential for reducing inflammation and becoming a potential therapy option for a variety of diseases. For example, a 2017 study has found that mesenchymal SCT may be an effective therapeutic application for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
What’s fascinating about stem cells is that they have a unique property that lures them to inflammation in your body. They not only find inflammation, but as research has shown they can help to lower inflammation, regulate the immune system, and regenerate damaged or diseased tissue in your body. By allowing tissue repair and reduced inflammation, stem cell therapy can help patients live a healthier and better quality of life (6, 7, 8, 9).
Reasons For Using Stem Cell Therapy
As you’ve learned, SCT can help to lower inflammation and modulate the immune system. It can help your body’s damaged and diseased tissue to repair and regenerate. It basically empowers your body to repair itself and allow a better quality of life.
Researchers believe that in theory there is no limit on what diseases may be treated with stem cells. SCT shows great potential for the treatment of certain cancers and blood-related disorders, such as leukemia, neuroblastoma, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, a variety of autoimmune conditions and digestive health issues, such as Crohn’s disease, irritable bowel syndrome, MS, and lupus, neurodegenerative issues, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkison’s disease, spinal cord injury, COPD, heart disease, diabetes, tooth regrowth, blindness and vision impairment, arthritis, musculoskeletal issues, and more. It may have potential in veterinary medicine as well in bone, tendon, joint, muscle, and neurodegenerative repair.
At this point, the FDA has only approved certain blood-forming stem cells (hematopoietic progenitor cells) derived from cord blood for certain health issues. However, research is ongoing and we are likely going to see many advancements in stem cell therapy and research in the upcoming years (10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22).
8 Ways to Naturally Activate Stem Cells
What’s exciting about stem cells is that they are already in your body and ready to help with repair and healing. You can activate them naturally to improve your health. These strategies are not as therapeutic or powerful as stem cell therapy but they are very helpful for the body’s healing process.
While research is still ongoing in this area, we know enough to recommend certain lifestyle and nutritional factors. Here are 8 ways to naturally activate your body’s regenerative cells:

Get Into Ketosis
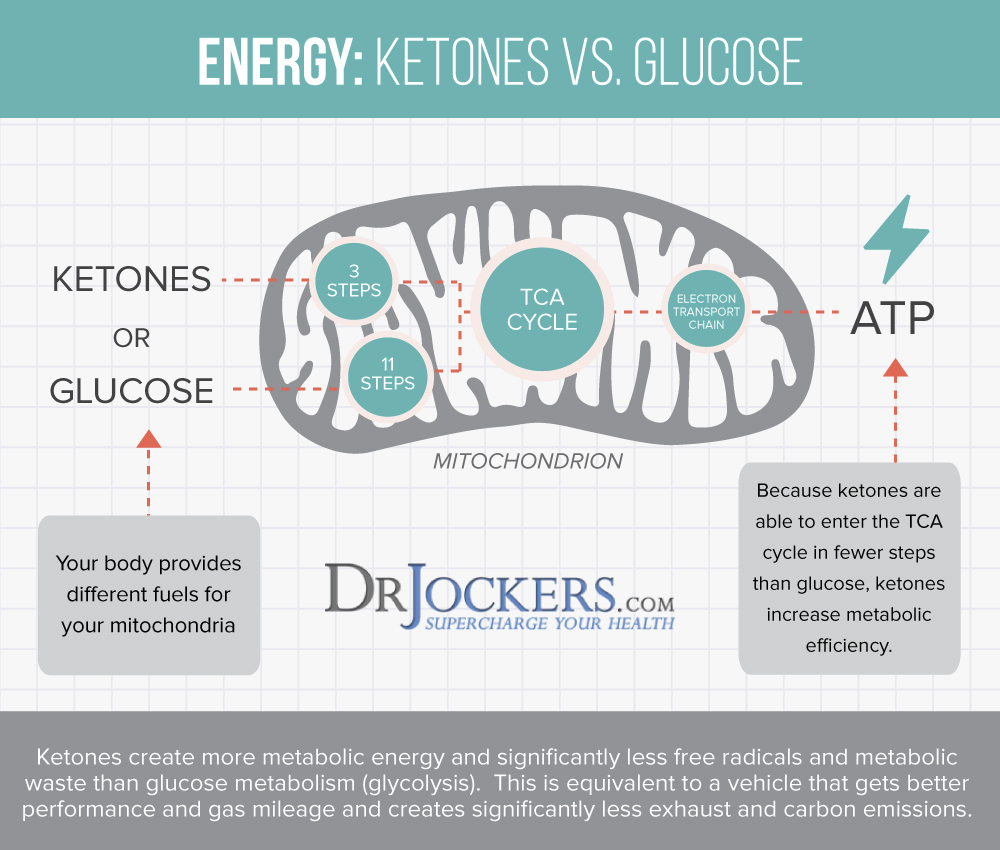
Under regular circumstances, your body gets its energy from glucose (sugar) through carbohydrate-rich foods you consume. However, if you are fasting, following a low-carb ketogenic diet, or experiencing glucose deficit for any other reason, your body will learn to rely on and get energy from the fat you consume and store fat.
This is when you experience ketosis, a metabolic state in which your body gets most of its energy from fat. Ketosis has many benefits. For example, according to a 2018 study, a ketogenic diet can improve your cognition.
A 2019 diet also found that ketosis helps to achieve intestinal stem cell homeostasis and adaptation allowing self-renewal in your body. You don’t have to be in ketosis all the time to get these benefits.
If you aim to get into nutritional ketosis a few times a year for a few weeks or so at a time, you can drive up stem cell production during that window. To learn more about ketosis and how to achieve it, I recommend reading this article. To learn more about the ketogenic diet I recommend, reading this article (23, 24).
Intermittent and Extended Fasting
Fasting is another great way to achieve ketosis and also activate your stem cells. Fasting stimulates a process called autophagy, which means self-eating. During the autophagy process, the body recycles its cellular components to make new healthier cells. This mechanism of self-renewal is also associated with the development of stem cells.
According to a 2015 study, prolonged fasting may support stem cell-based regeneration, cellular renewal and reverse immunosuppression. According to a 2018 study, even a 24-hour fast can boost stem cell regeneration.
Extended fasting can last for a few days to several weeks when you are not consuming anything else but water and perhaps certain liquids, such as herbal tea. Intermittent fasting cycles between periods of fasting and eating within one day. Most people find the most benefit when fasting for 16 hours and leaving an 8-hour eating window.
To learn more about the benefits of intermittent fasting and the best intermittent fasting strategies, I recommend this article. To learn more about extended fasting and water fasting, I recommend reading this article (25, 26).

Partial Fast or Fasting Mimicking Diet
If you are not ready to embark on an intermittent fasting or extended fasting journey, you can try partial fasting or The Fasting Mimicking Diet® (FMD®). FMD® is a high-nutrition, low-protein, low-carbohydrate meal plan in which calories are restricted for five days out of a month.
Through this diet, you can experience the benefits of fasting, including stem cell activation, without depriving yourself of food. FMD® is a form of partial fasting. Other partial fasts with similar benefits include the Daniel Fast, bone broth fasting, keto fasting, and juice fasting. To learn more about FMD®, I recommend reading this article. To learn more about the other partial fasting strategies, I recommend reading this article (25, 26).

Regular Movement and Exercise
Exercise is critical for your health and well-being. According to a 2008 review, exercise helps the activation, mobilization, and differentiation of various types of stem cells, as well as tissue regeneration and function. I recommend that you exercise 5 days a week for 20 to 30 minutes at least.
Try a mix of cardiovascular, strength- and resistance training, and low-impact exercise. Stay active throughout the day by taking regular walks, playing with your kids or pets, stretching regularly, taking the stairs, opting for walking or biking instead of driving when possible, taking breaks during work for a quick stretch, going for hikes, gardening, and dancing to your favorite song (27).

Prioritize Good Sleep
Sleep is one of your basic human needs. A 2018 study found that sleep helps the regeneration capacity of stem cells and tissue regeneration. Make sure to get 7 to 9 hours of sleep a night. Go to bed and wake up around the same time every day to support your circadian rhythms.
Avoid electronics, foods, stress, caffeine, and alcohol in the evening. Develop an evening routine and engage in relaxing activities. Make sure that your bedroom is a peaceful, comfortable, and sleep-promoting sanctuary (28).

Avoid Harmful Medications
Medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, corticosteroids, and immune suppressants, can be harmful to your body. Most come with unwanted side effects. They may interrupt your gut flora, which leads to inflammation, reduces regeneration, and increases the risk of disease.
While in certain cases, medications may be appropriate or necessary, in most situations, there are usually better solutions. Working with a functional medicine doctor can help you uncover the root cause of your symptoms and find natural solutions without medication. If you are on any medications, don’t just stop it, but work closely with a doctor to reduce or stop medication use safely under medical guidance and supervision.
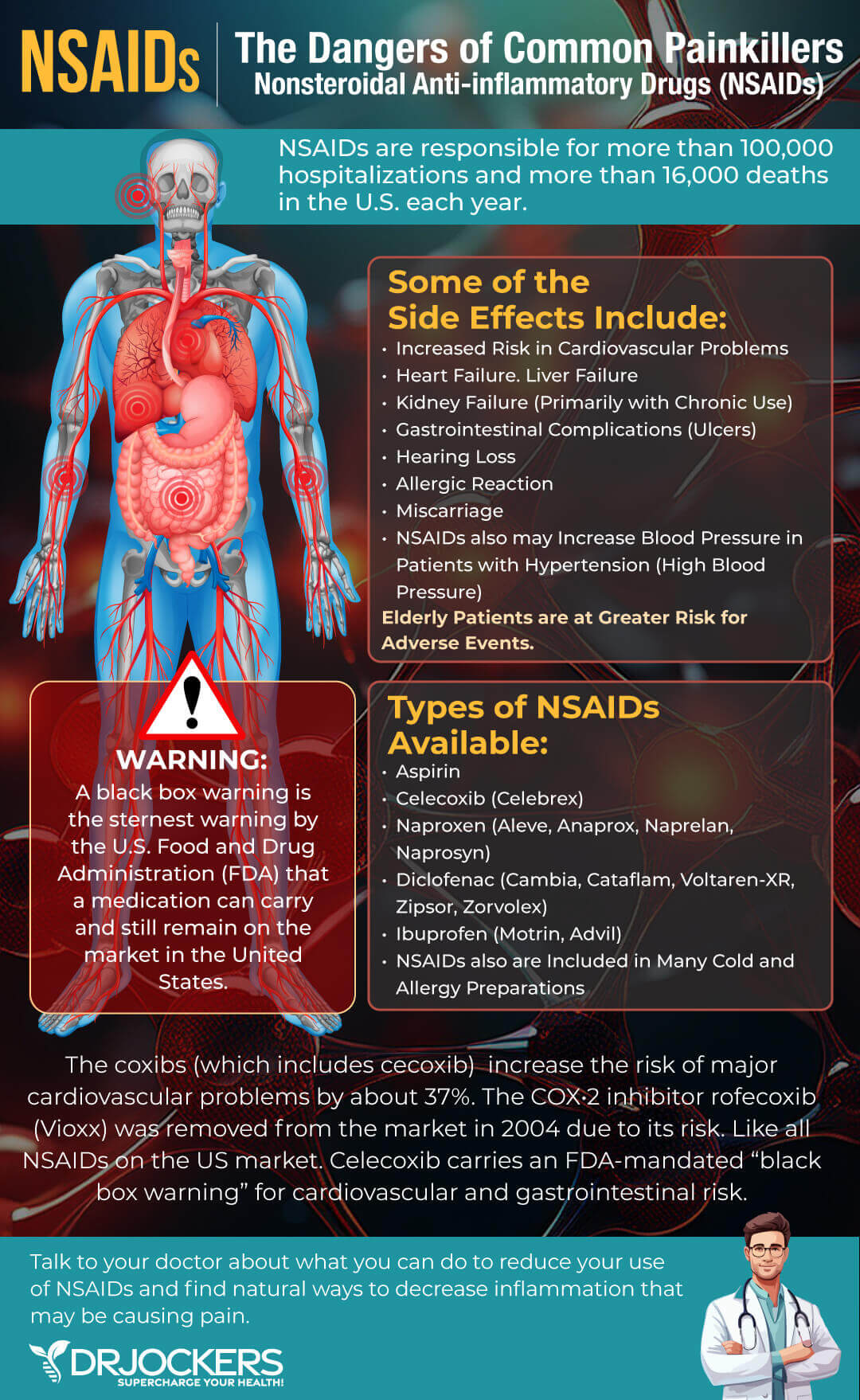
Polyphenolic Compounds
Research has shown that polyphenolic compounds may also help to activate your stem cells. They do this by controlling the activation of inflammatory cytokines, reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis, turning on autophagy, protecting and enhancing mitochondrial function, and regulating migration and differentiation of stem cells (29).
While there are many polyphenols the most well-studied ones include resveratrol, quercetin, EGCG, and curcumin. Here are the studies that support these nutrients to enhance self-healing in the body.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a natural polyphenol and antioxidant found in the skin of grapes. According to a 2019 study, resveratrol may help the survival, self-renewal, lineage commitment, and anti-aging effects of stem cells.
According to a 2014 study, resveratrol taken only for three weeks may increase the frequency and total numbers of normal bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in the body. Using a resveratrol supplement may help to improve your health (30, 31).

Quercetin
Quercetin is a powerful flavonoid found in various plants and food. According to a 2017 rat research, quercetin may help the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into β-cells.
A 2018 study found similar results, that quercetin may help bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) differentiation in mice. Supplementing with quercetin is a great way to support your health (32, 33). One product I use daily to support autophagy, a healthy inflammatory and immune response, and stem cell production is Resveratrol Power.
Curcumin
Curcumin is the active compound of the spice turmeric. It is full of anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial properties. According to a 2008 study, curcumin helps adult hippocampal neurogenesis and promotes neural plasticity and repair. A 2019 study has found that curcumin helps the differentiation of stem cells (34, 35).
To experience the benefits of curcumin, it is a great idea to add turmeric to your soups, stews, vegetable dishes, curries, smoothies, juices, and dressings, and to sip on turmeric tea regularly. Additionally, taking a curcumin supplement is a great way to boost your health.
To experience the benefits of resveratrol, quercetin, and curcumin, I recommend taking Inflam Defense. This supplement supports a healthy inflammatory response, protects you against oxidative stress, offers antioxidant benefits, and supports your healthy circulation and lymphatic function.
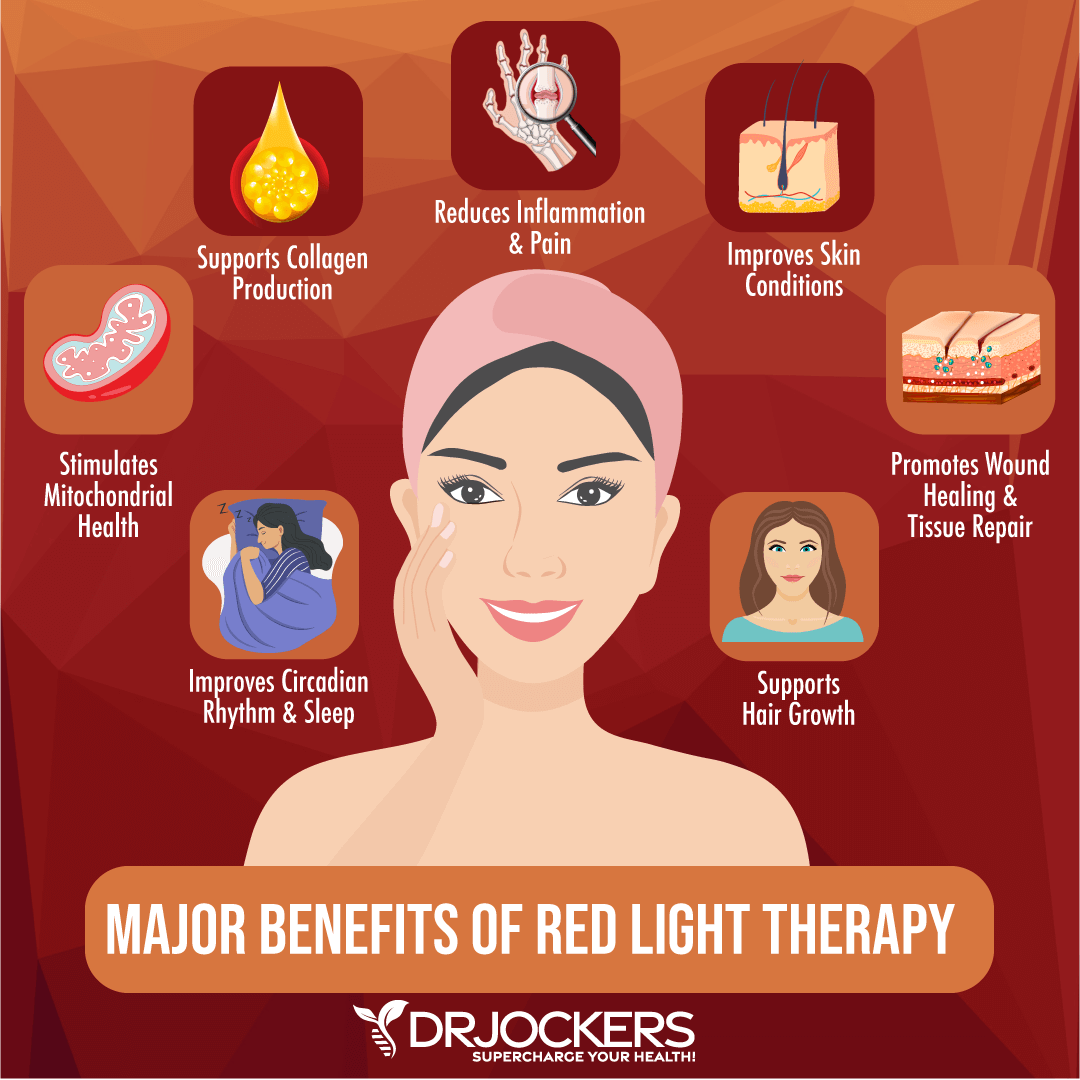
Use Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy (RLT) is a powerful therapeutic technique and an alternative healing method. It uses red low-level wavelengths of light for a variety of therapeutic purposes. It may help with wound healing, scars, and other skin issues, inflammation, pain, hair growth, and sleep quality. According to a 2007 rat study, red light therapy may support mesenchymal cell differentiation.
According to a 2014 study’s experimental findings, 660 nm red light therapy may help the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and increase cell transportation in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage treatment. If you want to experience the benefits of red light therapy for stem cell activation and healing, I recommend Mito Red Light Therapy Device.
Use the coupon code DRJOCKERS at checkout to save 5% on the MitoRed product line. To learn more about the benefits of red light therapy, I recommend reading this article (36, 37).
Final Thoughts
Stems cells are found in your body. They don’t have a specific purpose and can turn into any cell with specialized functions as your body needs them. They help cellular and tissue repair, rejuvenation, and healing.
Follow my 8 tips to activate this powerful self-healing technology and improve your health naturally. If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. On our website, we offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!







Asparagus kicks stem cells into hyper drive. Got damaged nerves, Do the fasting and then get asparagus to kick in the repair of the nerve cells. (big Korean study). It greatly promotes nerve regeneration. Asparagus tea has been known for a long time to help eliminate nerve pain in the body. Older folks with shaky hands or feet taking asparagus tea have reduced or eliminated the neuropathy problems. The garden plant can grow over 8-inches in one night. It’s also touted as aiding the scalp to regenerate NEW hair follicles via the stem cells for the hair roots.
Other studies and ones in progress are showing how the yoke of a chicken egg with Biotin has plenty of stem cell boosting benefits. Biotin helps stem cells to split into two cells and grow. Biotin aids greatly in stem cell muscle regeneration.
Thanks for sharing!
My sister would like to try stem cell therapy because she heard that this may help keep her healthier and younger-looking. Well, it also never occurred to me that stem cells could help cure spinal cord injury and Alzheimer’s disease. Thank you for also sharing here that the multipotent cells have the ability to self renew.
Yes the science is still evolving but these therapies are showing promise.
I did stem cell therapy 3 weeks ago. Doctor said to me: no tumeric, no boswellia, no direct heat, no sauna, no anti-inflammatory supplements for 3 months.
Did the doctor explain why not?
I received umbilical stem cells plus my own adipose stem cells via intravenous injection in an attempt to restore my blindness caused by glaucoma. Didn’t do much though. I’m taking a lot of nutritional supplements, herbs, antioxidants, enzymes, and other stuff to restore my lost vision to no avail. Ha several eye surgeries to install stents to reduce eye pressure. Can you please help me? Any advice will be a blessing for you. God bless…..Ariel
So sorry to hear this! I would recommend working with a functional health practitioner to address the root cause of these issues. https://drjockers.com/functional-nutrition-tips-to-find-a-great-health-coach/
Hi, I read this great article and I have a question:
Could you please recommend some clinic or research org. that can do this treatment as the one in “stem cell therapy for degenerative knee conditions” in this article ?
My uncle is a cancer survivor but his spinal cord is torturing him after the chemo. In my understanding if successful after this in vitro treatment , he would be able to walk on his own. He is willing to be an experimental subject if necessary. That would bring him some hope to walk again.
Thanks and look forward to your reply!