 Top 4 Herbs to Reduce Inflammation Instead of NSAIDs
Top 4 Herbs to Reduce Inflammation Instead of NSAIDs
Herbs are powerful healing tools when used to help balance the body. Inflammation is your body’s way to protect itself from injury, infections, and other pathogens. While inflammation can be beneficial when it comes to acute injuries and illness, if it turns chronic, it can also become harmful to your health. Chronic inflammation can last for months or years. It is the underlying reason for almost every major health condition and disease.
In this article, you will learn what inflammation is, what the difference between acute and chronic inflammation is and what its causes and consequences are. I will also share some powerful strategies on how to lower inflammation and reduce the risk of disease with herbs instead of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
What is Inflammation (Acute/Chronic)
Inflammation is your body’s way to fight against any potential harm, such as injuries, infections, and toxins. It is part of your body’s inherent immune response. When your body senses damage to its cells, it releases chemicals to trigger a response from your immune system for your protection. The main goal of inflammation is to protect you from harmful invaders and promote fast healing and recovery.
Inflammation itself is not bad. Without inflammation, wounds would become septic and even minor infections could result in tissue damage and become deadly.
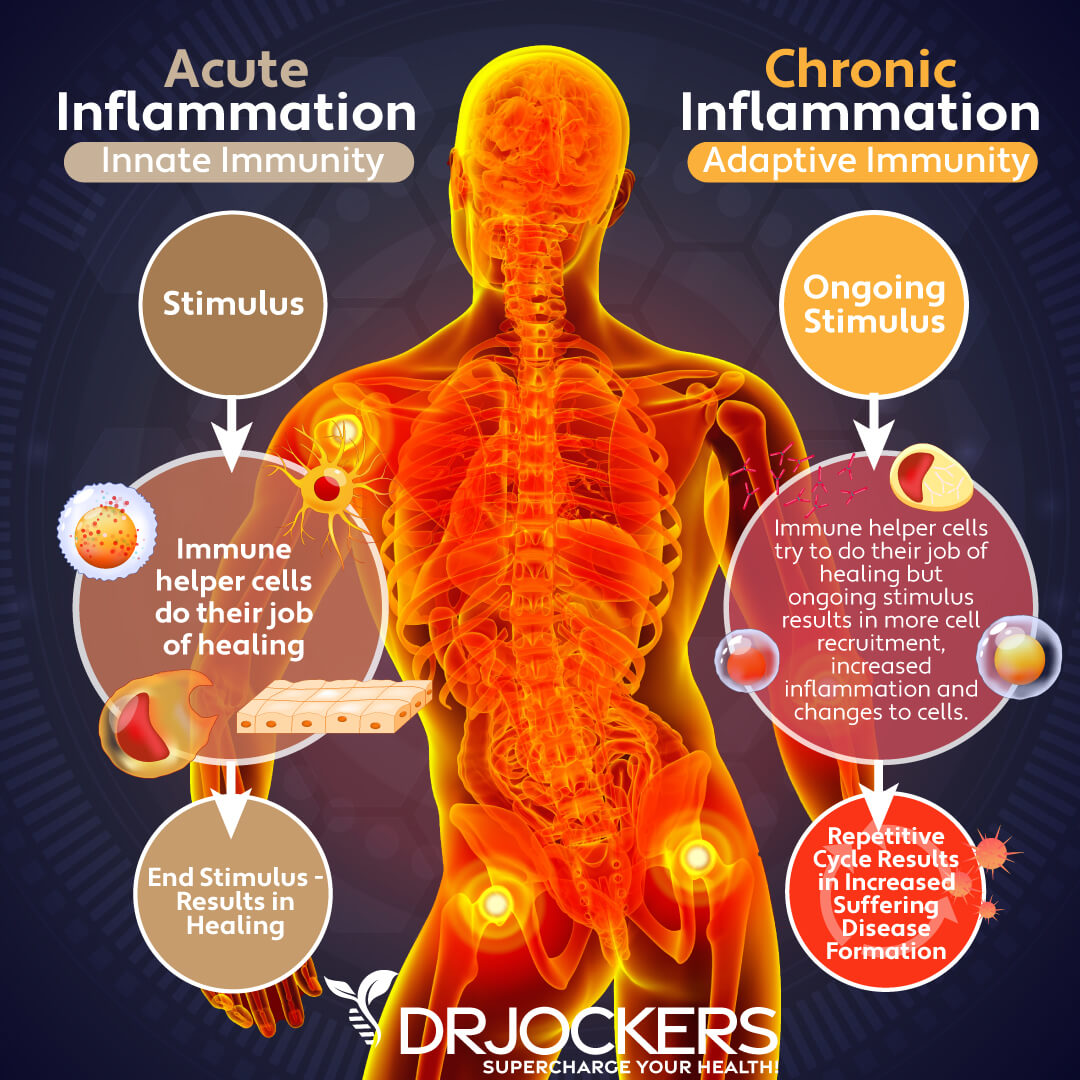
However, not all inflammation is good. There are two types of inflammation: acute and chronic. Acute inflammation can enhance recovery from an injury or short illness, however, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to further health problems, including chronic pain and disease.
Acute Inflammation
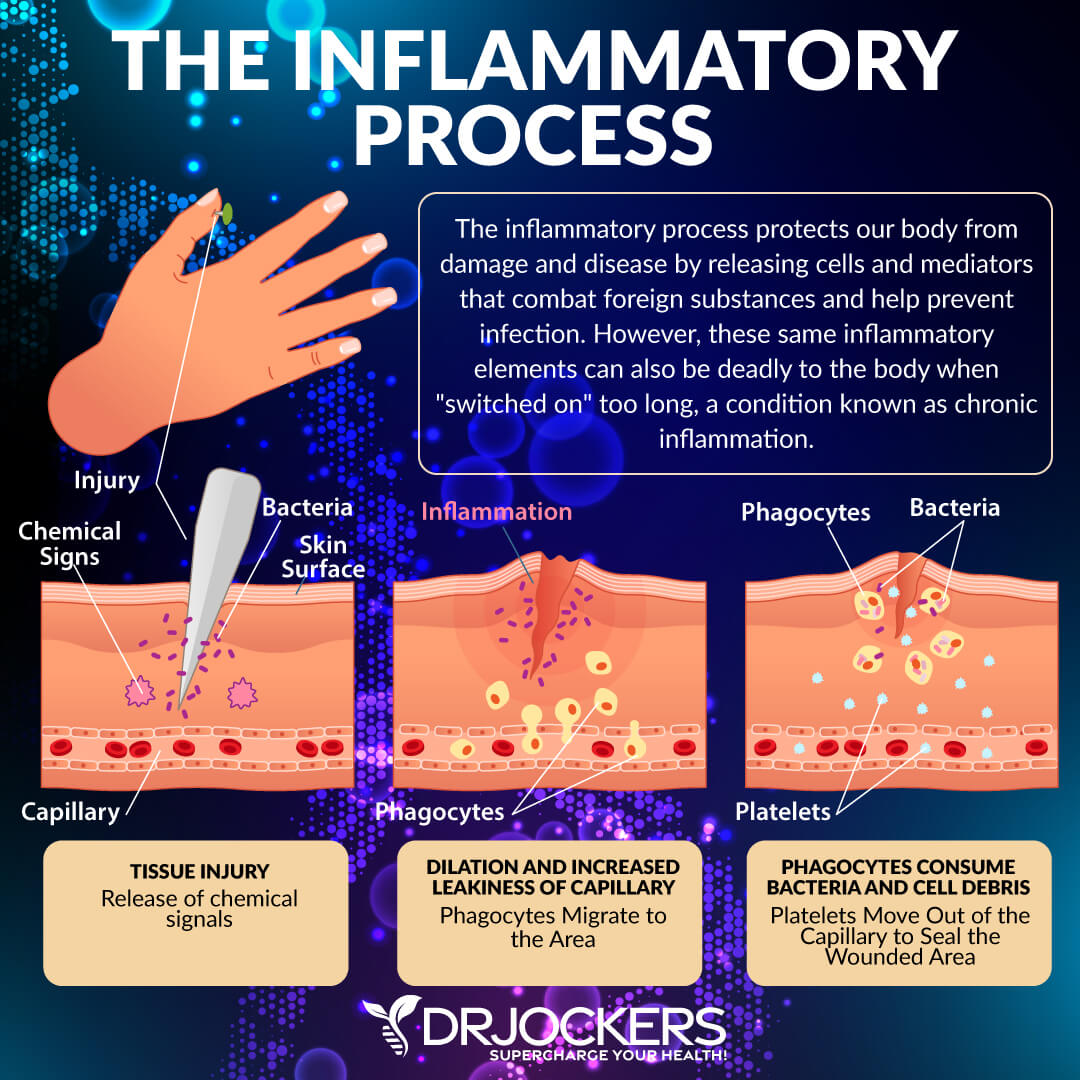
Acute inflammation is your body’s response to short-term, acute injuries, infections, or illness with localized effects. Your cells release chemicals to create inflammation to protect your body, prevent infections from spreading, and aid recovery. Your blood vessels dilate, blood flow increases and white blood cells rush to the affected area to promote fast recovery.
Acute inflammation is usually characterized by pain, swelling, redness, heat or even loss of function.
For example, if you cut your finger while preparing dinner, you may experience swelling, redness, and pain. If a mosquito bites you, it will result in redness, swelling, and itching. During allergy season, you may experience sneezing or redness in your eyes. If you catch a cold, you may have a red, sore throat with swelling, runny nose, and other related symptoms of inflammation (1).
In some cases, acute inflammation may be internal, such as if you have acute appendicitis. Internal acute inflammation may also be characterized by pain or other symptoms.
Acute inflammation must not be mistaken for an infection. An infection caused by harmful substances, such as bacteria, virus, or fungus usually results in inflammation. However, inflammation can happen without an infection. For example, if you twist your ankle or scrape your knee, it will likely turn red, swell up, and hurt due to inflammation but without any infection. If infection and inflammation are both present, as you recover from the infection, your inflammation will subside as well.
Acute inflammation is short-term. It may last for a few hours, a few days, or in case of some more serious injuries, a few weeks.
Chronic Inflammation
Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation is long-term. When you have chronic inflammation, the inflammatory response is on-going leaving your body in a constant state of alert trying to defend you from potential harm.
Instead of acute injuries, chronic inflammation is caused by an excessive stress load on your body, including physical, emotional, and chemical stressors. As a result of these constant stressors, your body ends up trying to constantly defend itself, thus overwhelming your immune system. This chronic inflammatory stimulus results in increased inflammation, more white blood cells, cell changes, and eventually tissue and organ damage.
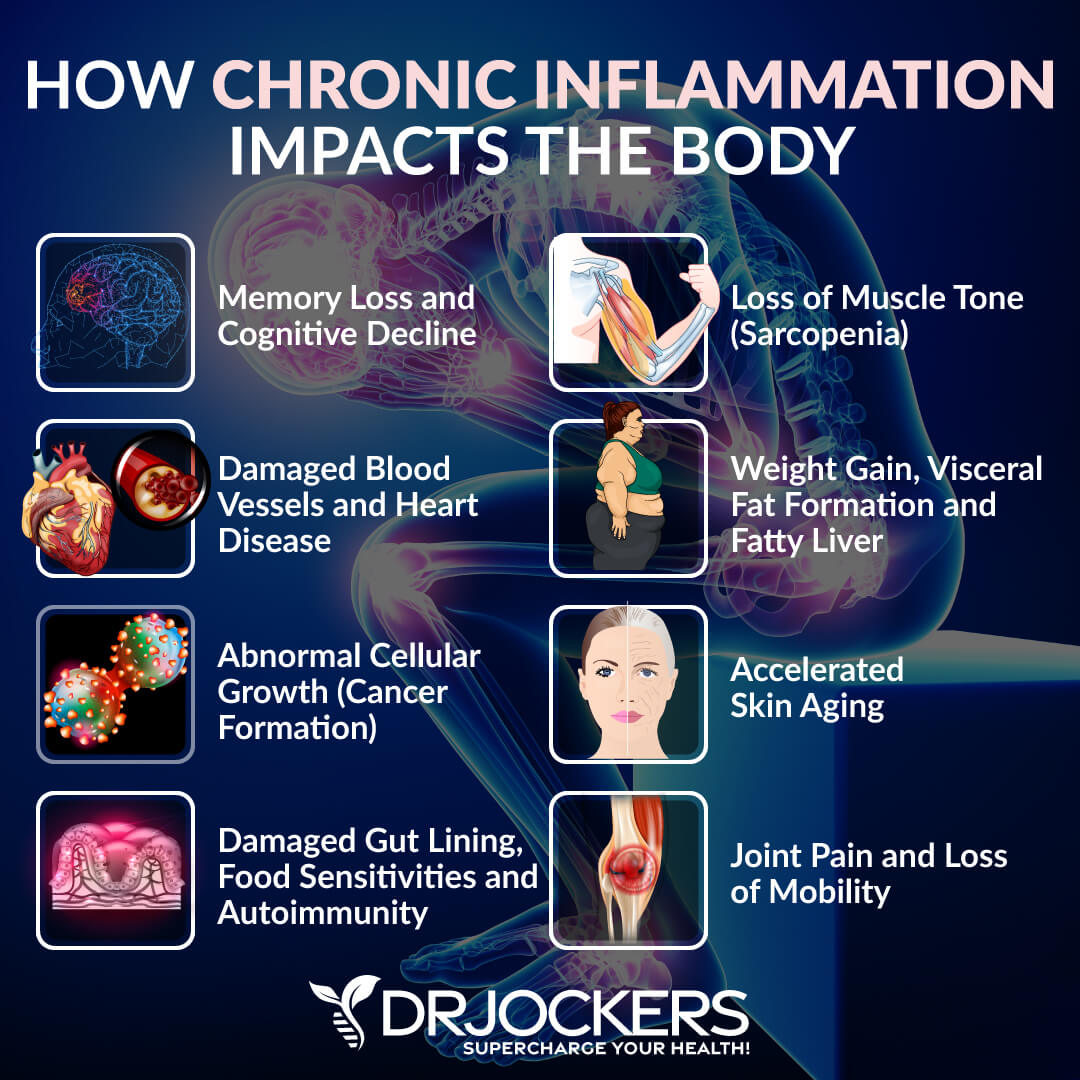
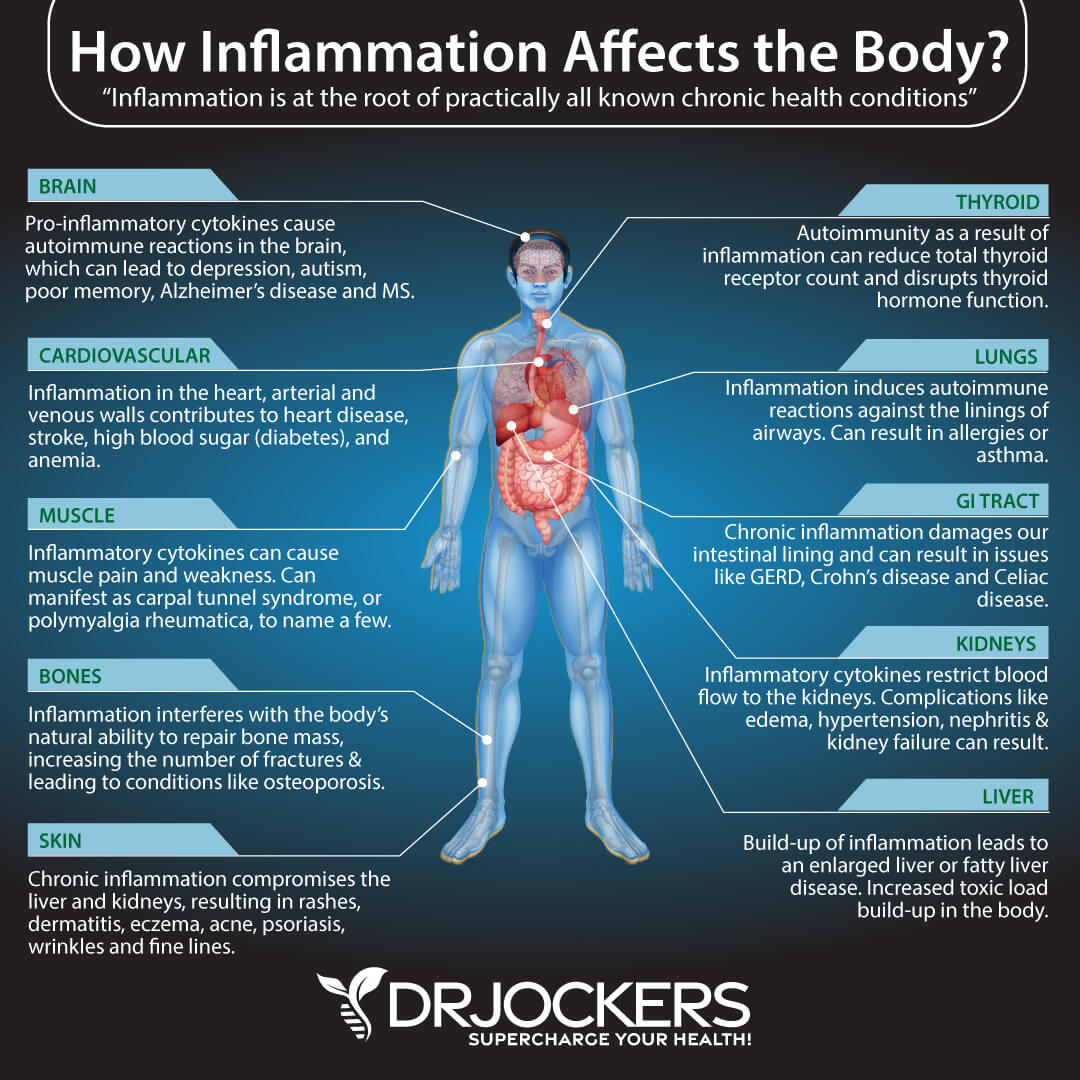
While acute inflammation is necessary and beneficial for your health and recovery, chronic inflammation may have a harmful impact on your health. Chronic inflammation can play a role in a variety of health conditions, including metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer, asthma, Alzheimer’s disease, and heart disease. Chronic inflammation results in 7 out of the 10 leading causes of death (2, 3).
Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation can last for several months or years. It continues until the cause of the inflammation is addressed. You must address the underlying causes of your inflammation in order to stop it and prevent further damage in your body.
What Causes Inflammation
Acute inflammation is caused by an acute injury, infection, or illness. Chronic inflammation is a sign of an overtaxed body. It is caused by excessive stress on your body often due to a combination of reasons, including physical, emotional, and chemical stress.
When your body is under sustained stress due to an inflammatory diet, chronic emotional stress, the burden of chemical toxins and poor sleep, it feels constantly under attack. It cannot differentiate a poor diet or an ongoing emotional battle from the distress caused by a bug bite or banged toe. All it wants to do is to protect you which results in a constant emotional response and chronic inflammation.
Let’s learn more about some of the causes of inflammation:

Inflammatory Diet
An inflammatory diet low in nutrients is one of the top causes of modern-day chronic inflammation. Certain foods are known to trigger your immune system and result in the over-production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the under-production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Cytokines are proteins secreted by your immune system that regulate your immune response (4).
Inflammatory foods include sugar, refined carbohydrates, trans fat, omega-6 fatty acids, mono-sodium glutamate (MSG), gluten, casein, aspartame, and alcohol. Foods that you are allergic to or sensitive to may also cause chronic inflammation (5).

The Standard American Diet
The Standard American Diet (SAD) relies heavily on processed food, refined sugars, starches, and unhealthy fats. It lacks greens, vegetables, and fruits and hence is incredibly low on vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It’s also very low in fiber which is essential for healthy digestion and detoxification. The SAD diet has been linked to increased risk of health conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, all of which are linked to chronic inflammation (6).
To reduce inflammation, make an effort to move away from an inflammatory and SAD diet to an anti-inflammatory one that’s rich in organic whole foods, such as greens, vegetables, fruits, anti-inflammatory herbs, good fats, and high-quality animal products. You can learn more about how an anti-inflammatory, healing diet can better your health in this article.
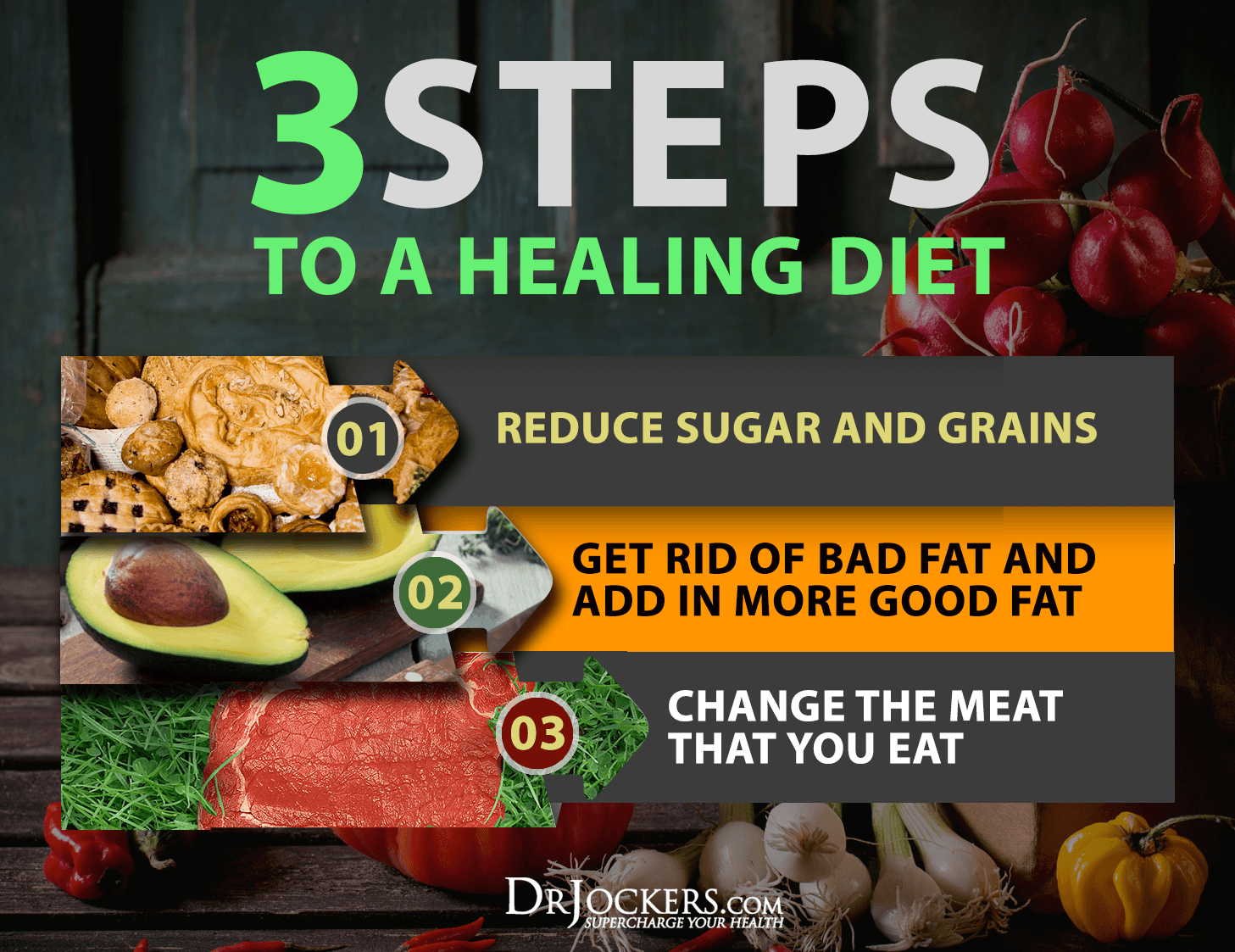
Blood Sugar Imbalances
High blood sugar, insulin resistance, and chronic inflammation have all been linked to chronic health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease, and high blood pressure.
Eating an inflammatory diet and too much sugar can lead to blood sugar imbalances that cause inflammation and the overproduction of inflammatory cytokines. Inflammatory cytokines can lead to increased insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar that only feeds the cycle of continuous inflammation and blood sugar problems. Furthermore, chronically elevated blood sugar levels result in advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that consequently increase inflammation and and produce risk of oxidative stress (7, 8).
If you are looking to balance your blood sugar levels, check out this article to learn about foods that can help you.
Leaky Gut Syndrome
Leaky gut syndrome is a condition characterized by damaged cell lining in the intestines that cannot regulate what goes in and out.
Naturally, your gut is a semi-permeable organ that allows micronutrients to pass through into the bloodstream to help you absorb nutrients from your food. However, inflammatory foods, toxins, infections, and stress can lead to holes in your intestinal wall resulting in leaky gut.
Once your gut becomes leaky, larger particles, including undigested food particles, toxins, and microbes can get through and escape into your bloodstream. Your immune system will recognize them as foreign invaders and pathogens. As an attempt to protect you, it releases an immune response which leads to long-term inflammation.
Leaky gut syndrome is often characterized by gas, bloating, constipation, indigestion, and other digestion problems. However, it can also lead to more serious health issues, including autoimmune diseases (9).

Chronic Stress
Chronic stress plays an enormous role in the development of chronic inflammation. Emotional and life stress may lead to poor eating habits, consumption of alcohol, lack of exercise, and poor sleeping habits that may all increase the risk of inflammation (10).
Chronic inflammation may also increase the risk of depression and anxiety. Chronic stress can put your body in a state of persistent flight-or-fight that may result in digestive disorders and anxiety. This feeds the cycle of further inflammatory behavior, inflammation, and emotional health issues (11, 12).
Poor Sleeping Habits
Getting a good night sleep is non-negotiable when it comes to your health and well-being. Sleep is the time when your body can rest, recover, and promote healing. Poor sleep habits and sleep loss can result in chronic low-grade inflammation.
It may also result in a number of health conditions, such as high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes that are all linked to chronic inflammation (13). Learn more about how to reverse poor sleep in this article.

Environmental Toxins
Environmental toxins are all around you. They can be found in the air you breathe, the food you eat, the water your drink, and the products you use. Air pollution, smoke, heavy metals, and mold exposure are all examples of environmental toxins you may be subjected to. Conventional cleaning and body care products, medications, and even processed foods are filled with ingredients that are unnatural and toxic to your body.
Long-term exposure to environmental toxins can become overwhelming to your immune system and result in increased chronic inflammation which may increase your risk of disease. You can learn how to test for signs of environmental toxicity in your body in this article.
While it is important to lower your toxic load by buying organic and natural products and avoiding exposure to toxins as much as possible, it is impossible to completely eliminate them. This is why paying attention to other factors, such as your diet and overall lifestyle is incredibly important.
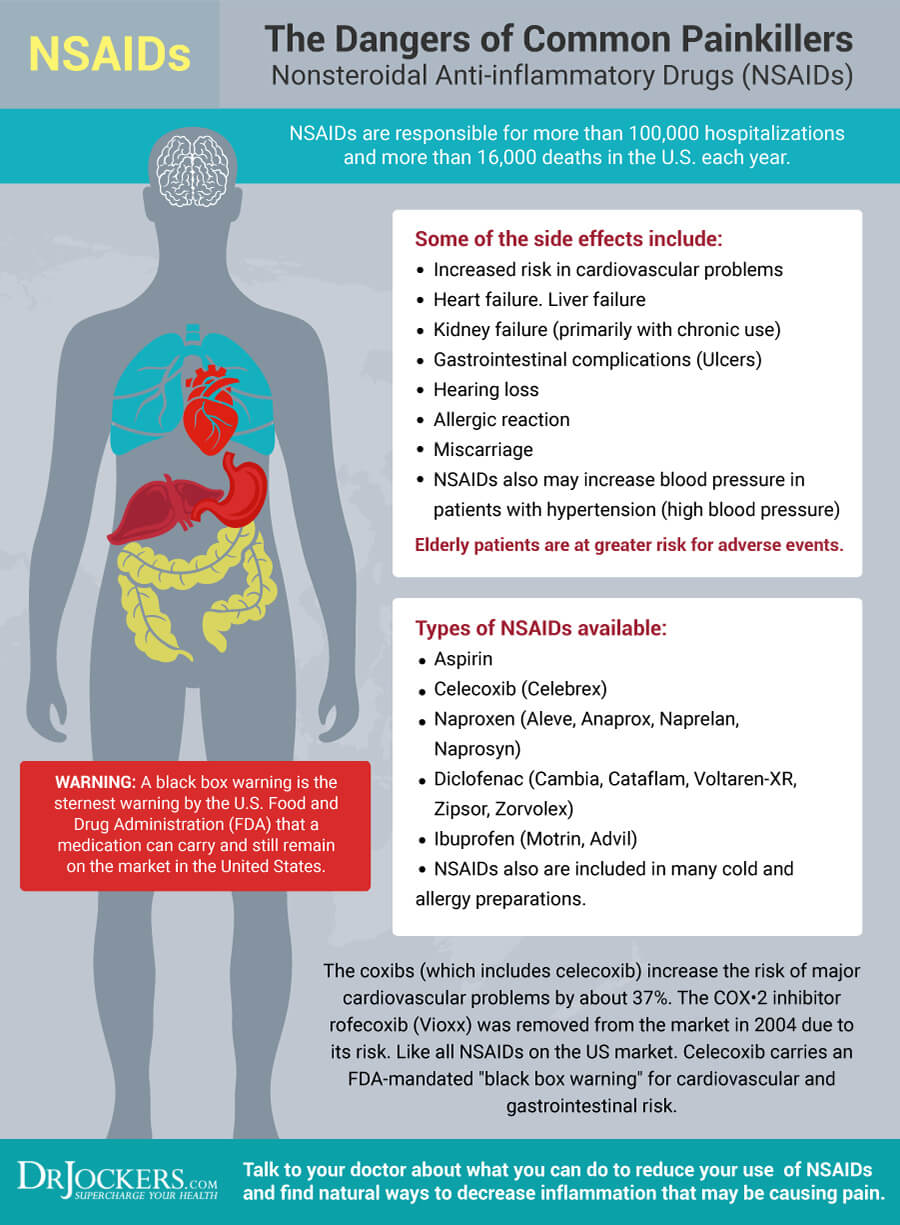
Problem with NSAIDs
Conventional treatment of inflammation often involves over-the-counter medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin.
NSAIDs block the Circulating Immune Complex (CIC) activity in your body. CIC is a protein chain activated by your immune system causing pain, swelling, and redness to promote recovery.
The problem is that NSAIDs affect all CIC’s in your body, including the ones necessary to maintain the lining of your stomach, intestine, kidneys, and liver. As a result, long-term use of NSAIDs can result in stomach ulcers, kidney and liver toxicity, and leaky gut syndrome. NSAID use accounts for 10 to 20,000 deaths a year in the US and many more hospitalizations due to liver and kidney damage or intestinal bleeding (14, 15, 16, 17).
Instead of relying on NSAIDs to lower inflammation, it is important to understand and address the underlying causes of chronic inflammation. Diet and lifestyle factors are both important factors in lowering inflammation and recovering from inflammation-related pain and illness.
The good news is that there are some fantastic anti-inflammatory herbs you can use to fight inflammation. Check out my top 4 anti-inflammatory herbs and supplements.
Top 4 Herbs to Reduce Inflammation
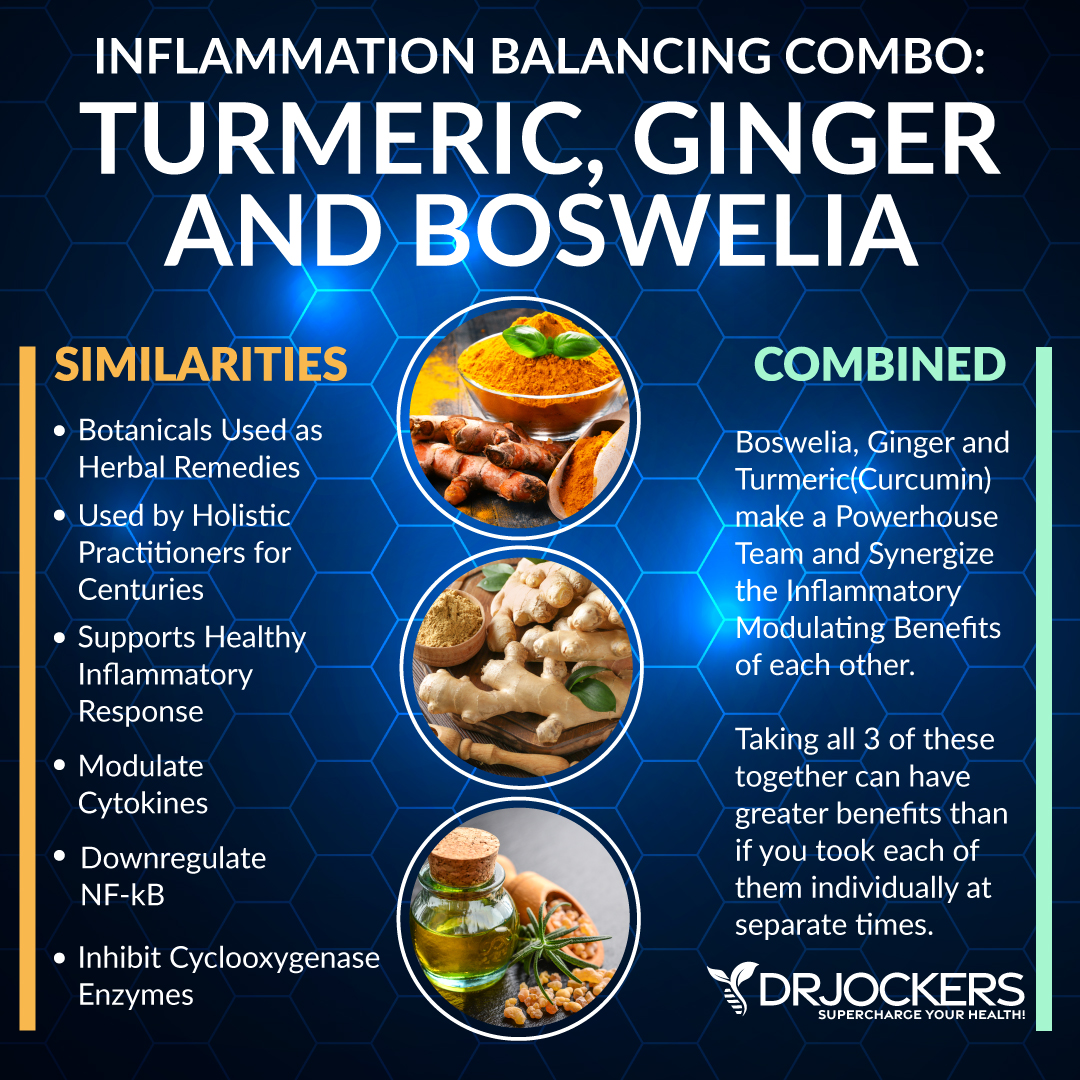
Eating an anti-inflammatory, nutrient-dense diet is crucial to reduce inflammation and prevent or recover from inflammation-related pain and disease. Using anti-inflammatory herbs plays an important role in an anti-inflammatory diet.
Anti-inflammatory herbs are easy to use in your kitchen. You can also find them in supplements to boost your body’s ability to reduce inflammation and repair any damage. My top four favorite anti-inflammatory herbs include turmeric, boswellia, ginger, and rosemary. I use them regularly, and once you learn their powerful benefits, I’m sure you will utilize them too.

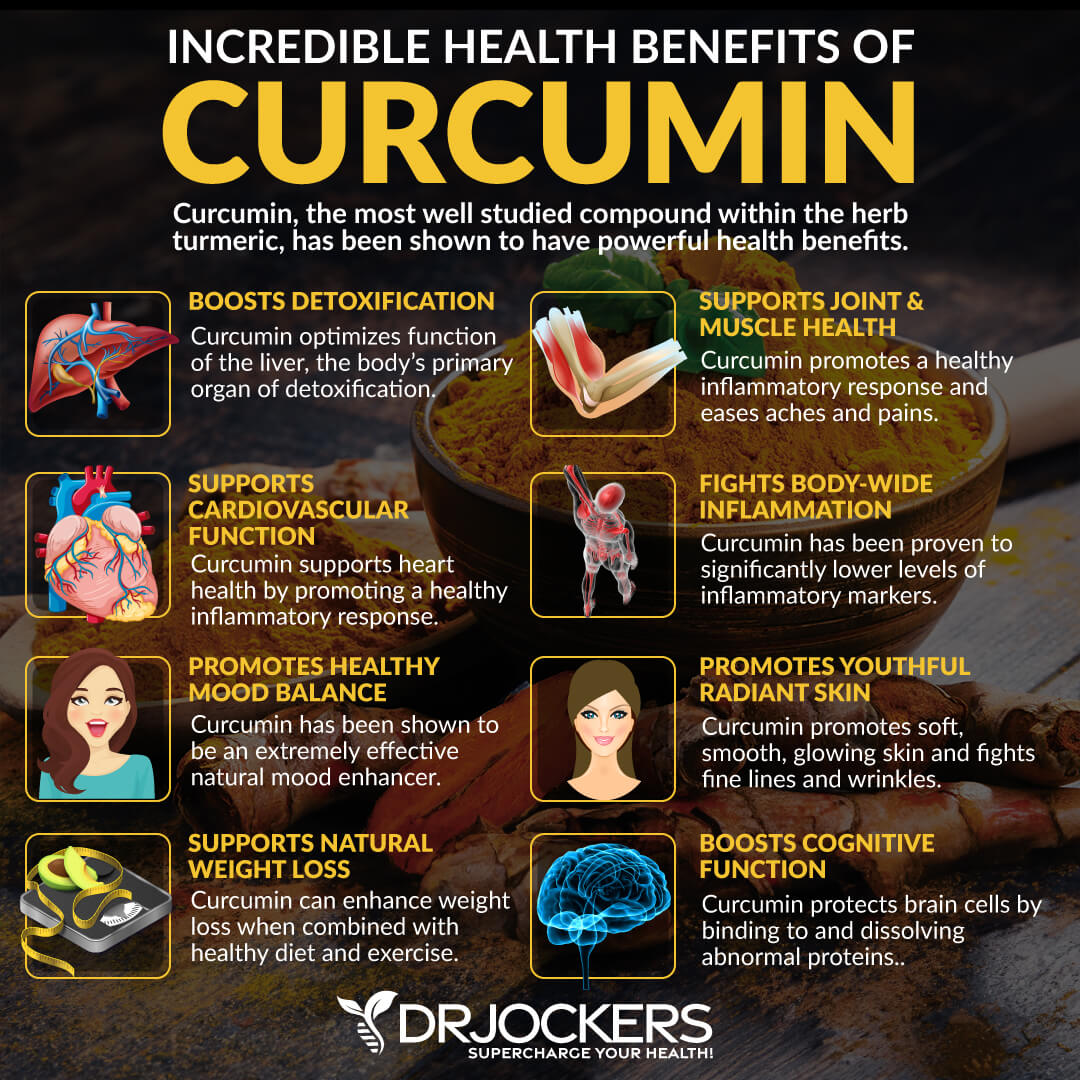
Turmeric/Curcumin
Turmeric is one of the most potent anti-inflammatory herbs. It is a staple in Indian cuisine and is the main spice used in popular curry dishes. It’s known for its unique, warm, and somewhat bitter taste. Turmeric is used to flavor and color various foods and condiments, including curry powder, mustard, butter, and even cheese.
Turmeric is not only an important part of the Indian diet, but it has been used in traditional Indian and Chinese medicine for thousands of years for its health benefits. One of the earliest documented uses of turmeric dates back to 250 bc when Susruta’s Ayurvedic Compendium recommended turmeric to relieve the effects of poisoned foods (18).
Turmeric finally began to gain popularity as a delicious spice and a powerful supplement in the United States and other Western countries over the past 30 years. Turmeric is actually one of the most researched spices. The US National Center for Biotechnology alone has over 6,000 studies available on turmeric and curcumin.
The secret of this anti-inflammatory herb lies in its active compound, a powerful antioxidant, called curcumin. Curcumin is known for its abundant medicinal properties. One of its top benefits is its ability to lower inflammation. Studies show that turmeric is able to reduce pain and inflammation just as well as ibuprofen without harmful side-effects. Other studies have shown that turmeric can improve inflammation in those with ulcerative colitis, diabetes, osteoarthritis, and lupus (20, 21, 22, 23, 24).
Ginger
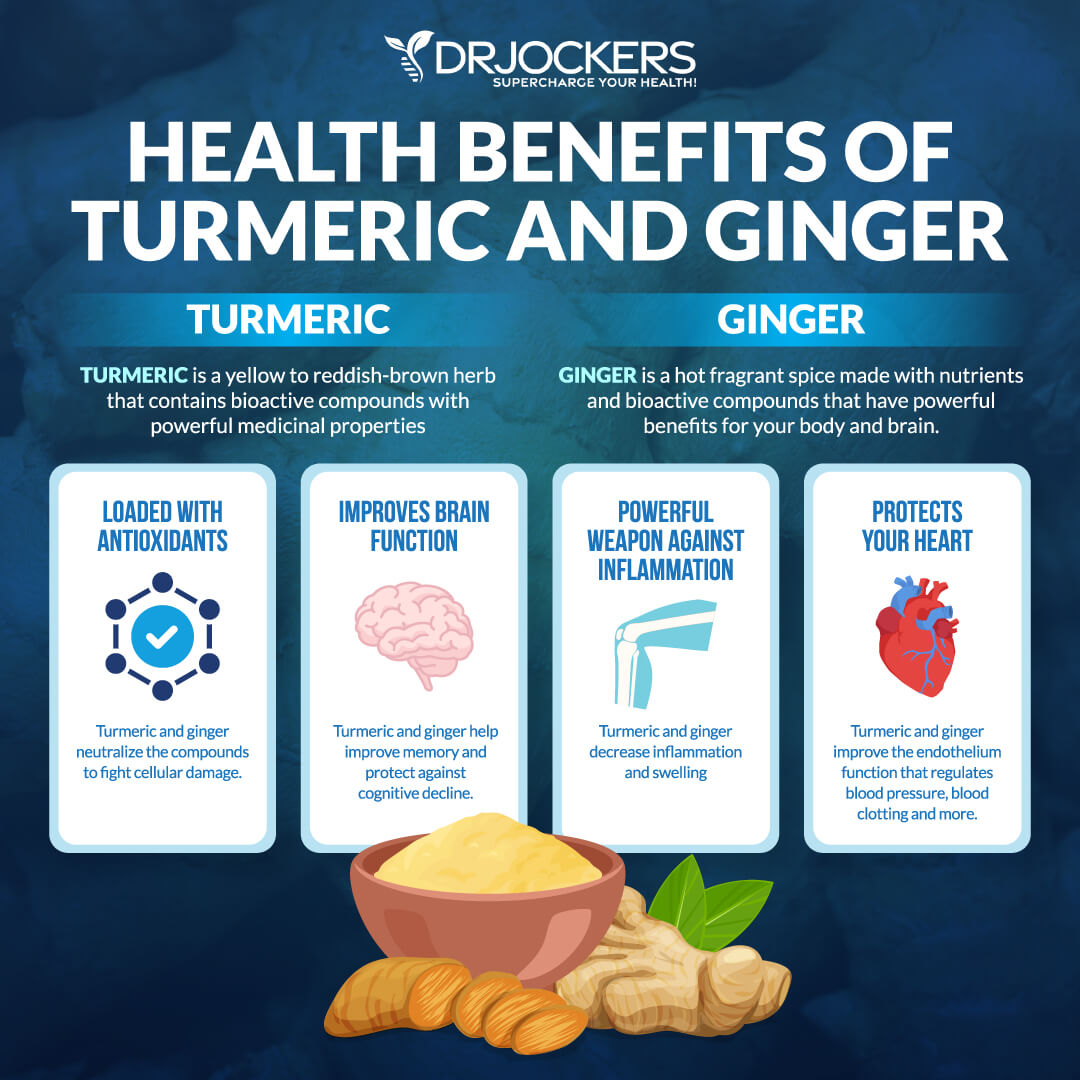
Ginger is similar to another anti-inflammatory herb, turmeric. They both belong to the rhizome family, which means that they have an underground stem that grows horizontally forming roots downwards while growing sprouting stems and leaves above ground.
Ginger is a powerful anti-inflammatory herb that has been used in China and India as a natural remedy for 5,000 years. Thanks to the Roman Empire trade, ginger became popular in Europe as well. It is commonly used for dishes, teas, and juices, as well as a supplement.
While ginger has over a hundred different chemical components, gingerol is its most important active compound providing its powerful health benefits. One of the most important qualities of this anti-inflammatory herb is its ability to reduce inflammation (29).
A 28-day study, for example, has found that patients who were given two grams of ginger experienced a significant reduction in colon inflammation markers compared to the placebo group. This suggests that ginger is a powerful anti-inflammatory herb that can play an important role in colon cancer prevention. Other studies showed that the anti-inflammatory herb can lower inflammation in osteoarthritis, exercise-induced muscle pain and inflammation related to obesity and metabolic syndrome (30, 31, 32, 33).
Boswellia (Frankincense)
Boswellia, or otherwise known as Indian Frankincense, is a potent herbal extract that comes from the Boswellia serrata tree. It has been a popular anti-inflammatory herb used by Asian and African cultures for its medicinal properties to treat a number of health conditions, including. chronic inflammatory illness.
You can take advantage of this anti-inflammatory herb in various ways. Boswellia is commonly used as a pill, resin, or cream.
Research has found that boswellia can reduce inflammation in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. It may be beneficial in lowering inflammation and inhibiting cancer growth in cancer patients (25, 26, 27).
Boswellia is particularly beneficial when used in combination with another anti-inflammatory herb, curcumin. According to a comparative, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study on osteoarthritis patients, boswellia and curcumin can be used together safely and effectively. They synergize together to reduce inflammation (28).
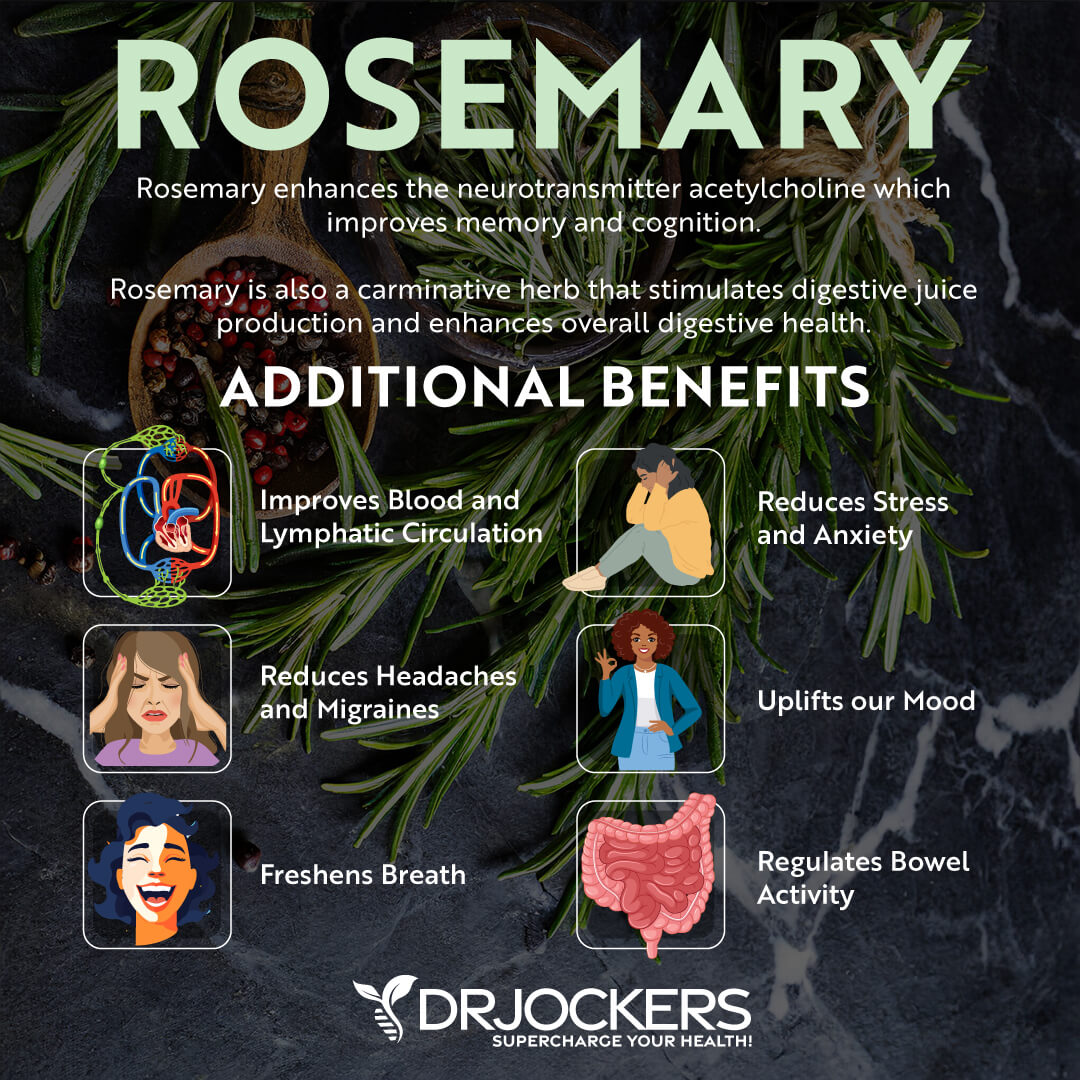
Rosemary
Rosemary is a fragrant, delicious, anti-inflammatory herb native to the Mediterranean and popular all over the world. It belongs to the same herb-family as oregano, thyme, basil, and lavender, and is often used alongside them in a variety of dishes.
Rosemary is not only a delicious herb commonly used in the kitchen, but it is also incredibly powerful. Rosemary is a rich source of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds. It has been celebrated as a beneficial anti-inflammatory herb for its medicinal properties for centuries.
Research has found rosemary to be a potent anti-inflammatory herb that may reduce inflammation in various conditions. One study has found that rheumatoid arthritis patients who were given a 15-minute massage with rosemary oil for three weeks experienced a 50 percent reduction in pain and inflammation compared to the control group which experienced only a 12 percent reduction, and which was only given a massage without the rosemary oil. (34, 35)
Additional Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
Besides anti-inflammatory herbs, you can benefit from some additional anti-inflammatory compounds such as bioflavonoids and systemic enzymes.
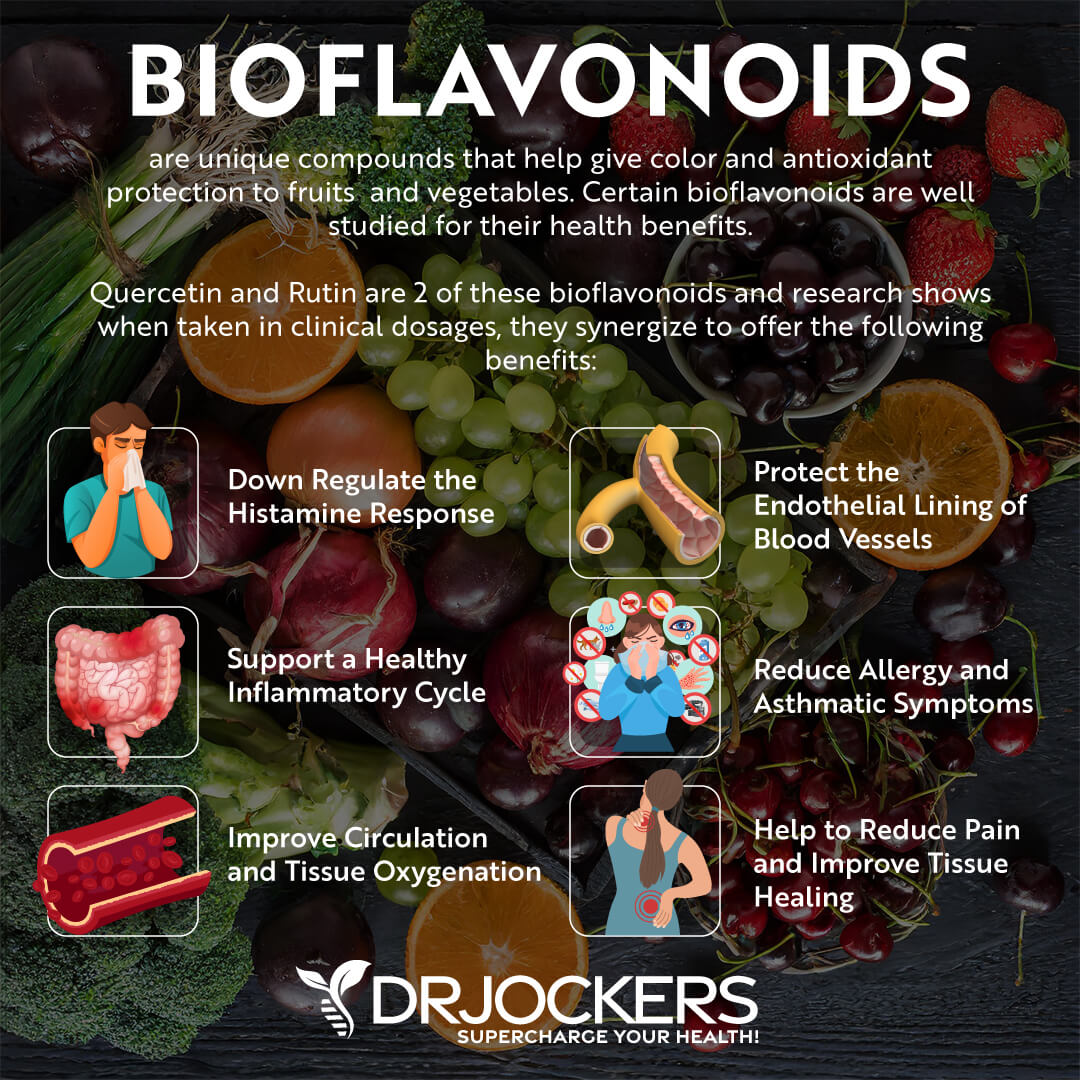
BioFlavonoids
Bioflavonoids, or flavonoids, are a group of plant pigments that can provide protection against many diseases. They are known for the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, anti-carcinogenic, and anti allergic properties. There are over 4000 known bioflavonoids. Two of my favorites are quercetin and rutin which I love for their anti-inflammatory benefits.
Quercetin is a flavonoid that can be found in vegetables and fruits, such as leafy greens, broccoli, tomatoes, and berries. It is rich in antioxidants, full of anti-inflammatory benefits and can fight free-radical damage. Research shows that it is a powerful anti-inflammatory compound that can effectively reduce inflammation and improve your immunity (36).
Rutin can be found in various vegetables and fruits, including apples, citrus, figs, green tea, black tea, and buckwheat. Rutin has powerful antioxidants that can help your body to use vitamin C better and which helps to produce collagen. Research shows that rutin can reduce inflammation and pain in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases (37).
Systemic Enzymes
Your body uses systemic enzymes to carry out virtually every metabolic function. They are essential for an immune system and for optimal digestion. They are powerful biocatalysts that carry out and speed up chemical reactions in your body. More importantly, according to research, they have full-body anti-inflammatory benefits (38, 39).
You can receive the benefits of enzymes by eating lots of raw, sprouted and fermented fruits and vegetables. However, you may also benefit from supplementing with enzymes, especially if you are dealing with chronic inflammation. Enzymes can be used in combination with anti-inflammatory herbs and bioflavonoids.
Proteo Enzymes are my favorite enzymes which I recommend to my patients all the time. They are absolutely fantastic in reducing inflammation and in aiding recovery.

Try Inflam Defense for Inflammation
Inflam Defense™ is my favorite supplement to support a healthy inflammatory response and to protect you from health issues which may result from inflammation.
Inflam Defense™ is a powerful combination of anti-inflammatory herbs, such as curcumin, boswellia, ginger, and rosemary extract as well as nutrients from quercetin and rutin, and proteolytic enzymes. I love this product because it can help downregulate the inflammatory process. It can help you if you are dealing with the negative impact of acute or chronic inflammatory conditions.
If you are looking to keep inflammation under control and have a healthy immune system, choose Inflam Defense™. Take one capsule twice a day between meals or for advanced protection take two or more capsules twice a day between meals or as directed by your health care practitioner.
Final Thoughts
Inflammation is both important and beneficial and can promote recovery from injuries, infections, and other pathogens. However, when inflammation turns chronic as a result of inflammatory diet, blood sugar imbalances, leaky gut syndrome, chronic stress, or lack of sleep, it can lead to pain and disease.
Taking NSAIDs is commonly suggested by healthcare professionals and regularly used by those who suffer from chronic inflammation and pain. The problem is that the long-term use of NSAID’s can result in stomach ulcers, kidney and liver toxicity, and leaky gut syndrome.
Luckily, there is a better and more natural way to lower inflammation in your body and to protect yourself from disease. Anti-inflammatory herbs, such as turmeric, boswellia, ginger, and rosemary, bioflavonoids, such as quercetin and rutin, and proteolytic enzymes are incredibly powerful in fighting inflammation and improving your health.
This is why I recommend Inflam Defense™ to anyone dealing with inflammation. This supplement is a powerful combination of anti-inflammatory herbs, nutrients, bioflavonoids, and proteolytic enzymes. It can help downregulate the inflammatory process.
Give Inflam Defense™ a try to lower inflammation, reverse its negative impacts, and to regain your health.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!







Some what confused, you say “If you are looking to keep inflammation under control and have a healthy immune system, choose Inflam Defense™. Take one capsule twice a day with meals or for advanced protection take two or more capsules twice a day or as directed by your health care practitioner.
The label directions state: As a dietary supplement, take two capsules per day between meals, or as directed by your health care practitioner (check spelling on the label!) Are the label directions to address an already inflamed condition? Please advise? thanks!
Yes we just changed it. It is better to take this between meals as the systemic enzymes will have the impact that way.
Hello, do you consult online? How do I access this option?
Yes we have several health coaches you can work with. We go over how to find a good health coach to work with in this article: https://drjockers.com/functional-nutrition-tips-to-find-a-great-health-coach/
Dear dr. Jocker,
Please is it possible to mixed these 4 herbs together Tumeric
Ginger
Boswella
Rosemary
Br.
Ola
Yes you can do this!
Can I ask how is the best way to take these four ingredients- Turmeric, ginger, rosemary and boswella.
How much of each daily please?
Hi Kate, You can add herbs to everyday meals, juices and smoothies and even desserts! This is one of my favorite recipes: https://drjockers.com/turmeric-milk/. This article also has useful information: https://drjockers.com/skin-autophagy/
How much of each?
I would recommend at least 200-500mg of each.
Dr. Jockers, I’d try this formula if not for the titanium dioxide and microcrystalline cellulose. I’d love to find an anti inflammatory for my joint pain, but those two ingredients cause me kidney pain and digestive distress. (Titanium Dioxide is a whitener/ flow agent and microcrystalline cellulose is a filler/bulking agent.) If you take a lot of supplements (like I do) the amounts of these additives add up quickly, as they’re in most supplements; a low dose with negligible effects becomes a big dose with major side effects when you’re taking multiple supplements that have it. I watch out for them.
Hey Noraq, A healing diet in the article above can help reduce inflammation. This article offers 10 anti-inflammatory foods: https://drjockers.com/anti-inflammatory-foods/
First, I must say that I’m more than a little bit skeptical of the Arthritis Foundation’s blanket statement (reference #5) that eating saturated fat causes inflammation. I’m sure that eating some kinds of saturated fats can be harmful, but it depends more on what type of saturated fat, e.g. the natural fats found in butter or the artificial trans-fats (hydrogenated vegetable oils) found in margarine, and on the source of any natural fat, such as butter made from the milk of healthy 100% grass-fed cows of from the milk of sick cows fed glyphosate-soaked GMO soy and Bt toxin-laden corn in a factory farm dairy. It also depends on whether the originally-healthy fat is damaged by a food processing company on its way to our tables, such as by refining coconut oil. So I fully endorse Dr. Jockers’ listing of organic butter and unrefined organic coconut oil as healthy saturated fats that either reduce have no significant effect on inflammation instead of increasing inflammation.
Because chronic inflammation is part of the body’s attempt to deal with some kind of ongoing disruption of normal cell functions, I believe that treating the symptoms directly, even with natural substances found in healthy foods, should generally be considered only a temporary stop-gap measure to alleviate suffering while the underlying functional cause of the problem is identified and treated directly. And as I personally learned the hard way, the functional cause may very well be somewhere in the body far removed from where the symptom appears.
In my own case, I had three heart attacks over the course of 7 years, and the only thing that either of my cardiologists ever did was to treat the symptoms themselves with prescription medications like statins that ended up doing far more harm than good, while totally ignoring the functional cause of the problem, not even taking a stab at trying to identify it.
As I eventually discovered, fortunately in time to completely cure my heart disease before it killed me, I had inflammation in my cardiovascular system, especially in my heart, caused by toxins that were being produced in a “quiet” (no pain or swelling) chronic infection of anaerobic bacteria in my jaw which was ultimatly caused by an infected root-canalled tooth. After my third heart attack I finally wised up, fired my cardiologist, stopped taking all the toxic medications I was told that I would have to continue taking for the rest of my life, and stopped following what I was told was a “heart heathly” diet which, for example, replaced the healthy saturated fats in butter with the unhealthy saturated fats in margarine and deprived me of all the health benefits of eating pasture-raised eggs because they contained the “demon” cholesterol.
Not long after that I had the very good fortune of finding a really good holistic dentist who discovered that infection in my jaw bone on my first visit. (My old conventional dentist, who even had all three of my heart attacks in his records for me, never found or even looked for the infection because he was never trained to.) I promptly had my new dentist properly extract the dead tooth and clean out the infection in the bone. With the infection in my jaw gone, the bacterial-produced toxins were gone from my bloodstream. At that point the inflammation in my heart successfully accomplished what it was trying to do all along, which was to heal the damage that had been done to my entire cardiovascular system by a never-ending stream of bacteria-produced toxins. Then, once the healing was done, the inflammation went away completely along with my heart disease. What took a lot longer than healing my heart was recovering from all the damage like intermittent claudication (damage to my legs) that the prescription meds, especially the statins, had done; but that’s another story.
Hey Greg, I am so sorry to hear that your journey to health was a long road. I am glad that you found this holistic dentist! I always appreciate your feedback and your willingness to share Greg! Blessings!
I would love to try this I have to try everything I’m desperate I have rheumatoid arthritis and it sucks
Greg Hill who and where is this holistic dentist? I’m in Oregon.
Lynda
Hello Lynda, you can find holistic dentists all over the world here: https://iaomt.org/
dear DR Jockers I have just had cataract surgery on both eyes and y blood pressure was very high 212 can’t remember the other one.it happened with the 1st one and the same with the other one.
I have been on the ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting since august last year and got off all medication felt great and lost 25 kg in the process.my blood pressure was in the 120 over 70 most off the time.now they want me to go to the GP to get medication!
can I do more than Keto and IF to lower it again or is there more I can do?
Hey Brigitte, I am sorry to hear this. These articles offer more information on improving your blood pressure: https://drjockers.com/doctor-high-blood-pressure/ & https://drjockers.com/12-best-heart-healthy-foods/
I know someone who didn’t eat meat for around 7 years, the result was chronic inflammation of the joints! the joint shoulder would inflame and blood would flow less to the arm, forcing it to go upwards, which would cause the tongue to swell and more than double in size . the solution: after that he started eating meat again and that made the anemia go away, but the joint pain persisted, this in turn was bettered by having sulfur, which helps regenerate joint and muscle tissue. of course foods rich in collagen is needed to restore the joints..to alleviate the symptoms of joint pain and tongue swelling, he went to a homeopath which prescribed him 3 medicines among which was rus, which acted as a driver for the blood to the arm when the symptoms were about to occur!
Thanks for sharing Vacheslav! Blessings!
thanks very much for a thorough article on inflammation and natural therapies to treat it. over 3 decades, i have chronic inflammation resulting in autoimmune disease (sjogrens). recently had 2 occasions of pericarditis and a butterfly rash for a week including over 10 years of enlarged blood cells (haemolyptic anaemia) which i suspect it could be lupus (also another autoimmune disease cause by inflammation)! relieved to hear that inflammation is not all that bad if it is kept under control. it is also part of a evolution process in adapting to the changing environment we are living in these modern times.
Sorry to hear this! Praying for full healing for you!
Thanks so much for the information. Yet I miss a mention of – – vaccines. As vaccines are designed to cause permanent – or at least prolonged – stimulation of the immune system – I would like to learn more about it. Wuold you consider vaccine-derived irritation of the immune system as infection? or inflammation? or none of them? And given that the vaccine ingredients are staying in the body – and the immune system is stimulated permanently – will it be smart/beneficial to consume these 4 herbs (or others)? (The cause of the problem is still there..)
Thanks, again/
Yes unfortunately vaccines and other toxins are a major cause of inflammation! But we can help rebalance the immune system through the proper strategies!
is very goog information
thank you for the article.
How is the best way to take Boswellia (Frankincense)?
I have some resin as well as the essential oil.
Do you soak the resin in hot water & drink it? or what.
Previously i had been putting frankincense essential oil under my tongue. not the greatest taste.
thanks. Stuart
Here is a helpful article Stuart https://drjockers.com/frankincense/
I noticed that you don’t mention the vagus nerve. I’ve been reading how it is connected to every part of the body and there has been studies done on it’s connection to several of the mentioned problems.
Yes the vagus nerve is extremely critical to parasympathetic tone and overall health!!
a wise man once said: tell me who you are afraid to criticize and i tell you who your master is!
Thanks for sharing!
How much tumeric, rosemary, ginger and boswellia should I take a day
200-500+ mg of each!
Hi
In regards to “Inflam Defense”…. Are there any drug interactions that I should be aware of? Just inquiring before I purchase. Thx
Heather
Hey Heather – it can interact with blood thinners as ginger, proteolytic enzymes and turmeric all have mild blood thinning properties. So if you are on blood thinners I would consult with your physician on this. Otherwise, you should be fine but always good to consult with your physician on any change in diet, lifestyle and supplementation.
CAN WE GET THE EXACT AMOUNT OF THESE 4 HERBS
THANK YOU
200-400 mg daily is a good amount!
Hello Dr would this be helpful to reduce nasal polyps?
Also do you have any articles on how to get rid of nasal polyps.
Thank you
Hey Tracey – yes here is a helpful article for you: https://drjockers.com/nasal-polyps/
Thank you, an excellent review on the inflammatory process, the “gift that keeps on giving”.
Actually it is Nature’s way to call attention to take care of our Immune System. I used to lecture on “How to boost your Immune System, naturally” and the folks would tell me that they did not need to know all this “stuff” because they had antibiotics….
Dr. Karla
While I appreciate most of the content, whoever puts meat as the no 1 anti-inflammatory food discredits herself. I am sorry, another unsubscribe.
Hello Bettina, we are actually very pro meat eating, but it is important to get grass-fed meats and wild-caught seafood!
I wonder if there are any herbs that help combat Alzheimer’s disease. If there are any proven herbs including turmeric, please let us know.
Thank you.
Hello Ranga, yes here is a helpful article for you: https://drjockers.com/alzheimers-disease/
What are good herbal treatments for early kidney disease?
Here is a helpful article Ian: https://drjockers.com/kidneys-health-natural-remedies/
Why are vaccines not on your list of things that cause inflammation? Is this a gross oversight or what!? I was badgered until I gave in to the Hep B vaccine series in 1986 and have suffered inflammation and the resulting pain and physical damage for 36 years now. I am a medical professional who has turned my back on allopathic medicine as much as I am able in favor of naturopathy and other more functional health options. I have refused all vaccines since but the damage is done. I am constantly reading articles like yours looking for someone to talk about the damage done by vaccines looking for ideas as to how to deal with the pervasive inflammation, but am nearly always disappointed.
Robert S. Mendelsohn, MD (deceased) wrote in his book “How to Raise a Healthy Child…In Spite of Your Doctor” (1984) about his concerns regarding immunizations in chapter 19 entitled ‘Immunization against Disease: A Medical Time Bomb?’ I thought he was right then and I still believe he was correct.
Hello Jenifer, yes vaccines are definitely a “toxin” that alters the immune system and drives up inflammation!
Dr Sally LaMont, ND, Lac from the “Natural Approaches to Osteoporosis and Bone Health Summit” has come up with alternative saying to the SAD diet, it is the MAD diet, “Modern American Diet”. (love it)
Why not make it a global issue and call it “Modern Abusive Diet”.
Please comment on oxalate poisoning and its causes. I am trying to avoid turmeric which is high in oxalate. I just recovered from a severe case of oxalate poisoning.
Few doctors have in depth knowledge on the subject. I learned from Sally K Norton,
you tube videos and website.
Hello Don – while limiting oxalates can be an important process for good health, I haven’t found that using turmeric or supplemental curcumin being an issue here. I would focus on reducing spinach, chocolate, nuts, seeds, beets and sweet potatoes.
I take the blood thinner Eliquis. What natural foods, herbs, etc. have a negative interaction with it?
That is a question you need to discuss with your prescribing physician as we are unable to give advice on medication usage.
The last food sensitivity panel I took, several years ago, it showed I was moderately sensitive to both Ginger and Turmeric. I recently started taking Turmeric because I have Sjogrens/Hashimoto’s and Raynaud’s and wanted to reduce my inflammation. I also started taking 0.5mg of Melatonin for sleep and it helped immensely. I ended up getting dermatitis on my eyelid, first time ever. Do you think it is possible that any of these treatments would or could cause that reaction? Thanks so much Dr. Jockers. Blessings to you and your family. Cindy
I found over the years that a good amount of good fats will keep the toilet paper usage to minimum while bad fats would escalate the amount of paper needed.
The big question is, if Gods recipe to making monkeys and Gods recipe to making humans is very close, How come monkeys do not need toilet paper? ANSWER: Their diet is not from a fast food outlet in the jungle.
I read above someone is making a issue of “saturated fats” I am sure you could use the “rule of thumb” God made saturated fats is good for you, factory made saturated fats or factory modified fats is bad for you.