Is Your Fatigue Related to Acidosis
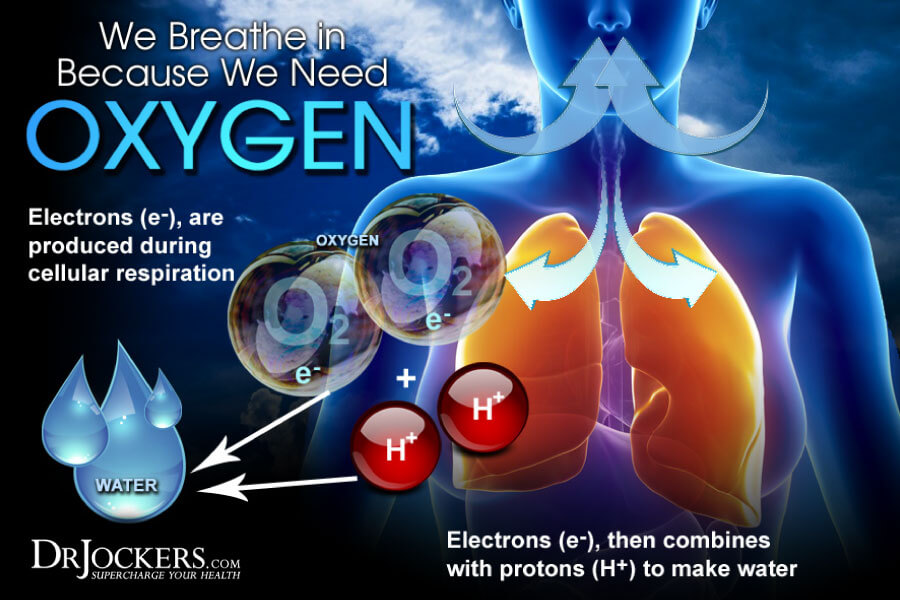
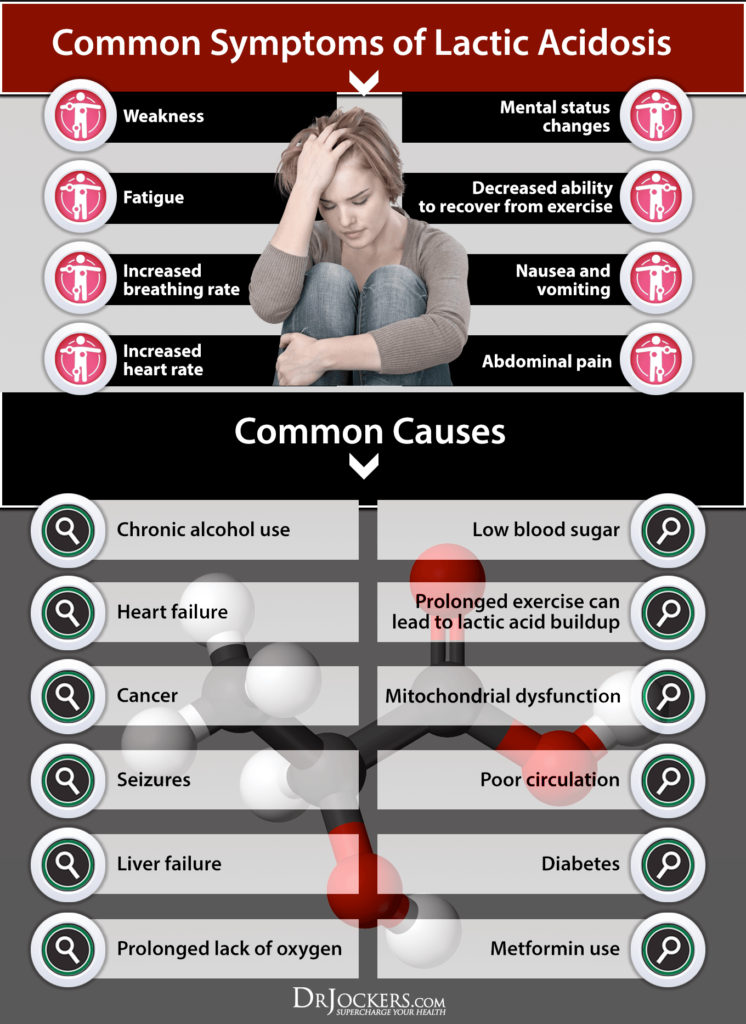
Acidosis can be a serious issue! Have you ever experienced extreme fatigue, felt like you could not recover from exercise, or even get your energy up enough to go exercise? Everyone says exercise is so good for the body! Why can’t I get motivated? It may be because you have excess lactic acid built up in your system. Any impairment in your body’s ability to utilize oxygen efficiently can cause lactic acid to build up in your system and cause dysfunction.
The body has an incredible mechanism for making energy even when we are oxygen deprived. An example of when we are oxygen deprived, is when we are working out hard and increasing our body’s oxygen demands. When this function becomes overwhelmed, lactic acid can build up in the muscles and tissues and cause extreme fatigue and acidosis. This article will dive into how this works and you will discover if your fatigue is related to acidosis.
Lactic Acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a condition that occurs due to the accumulation of excess lactic acid in the blood. A human body typically has a pH level that is slightly basic or alkaline. Excess acid causes this pH to decrease and makes the pH level acidic.
This is a very dangerous state for the body to be in because the function of each cell, tissue, and organ is significantly impaired. The body has many internal mechanisms in place to tightly regulate the blood’s pH level and the slightest change in this level can result in severe organ dysfunction.
Conditions that decrease blood oxygen levels, interfere with the mitochondria, or decrease the clearance of lactic acid can allow lactic acid to increase to harmful levels (3).
Lactate Metabolism
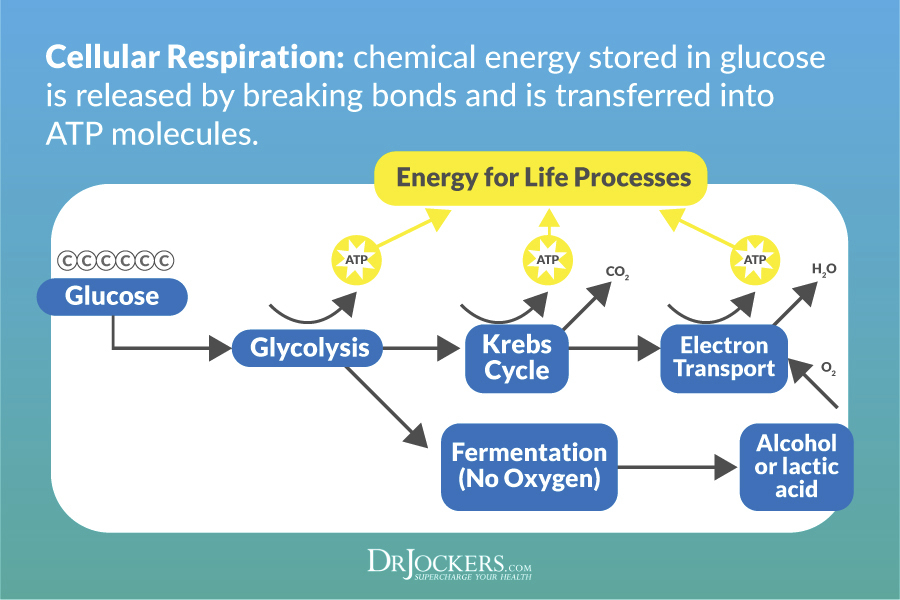
Lactate is produced by anaerobic glycolysis, which means that glucose is metabolized without oxygen through a process known as lactic acid fermentation, in order to produce energy.
This is a deviation from the normal Kreb’s cycle which is used to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl CoA, synthesize NADH, and produce amino acids. The Kreb’s cycle is much more efficient than lactic acid fermentation. It takes place in the mitochondria for human cells.
The process happens by taking a glucose molecule and breaking it down into pyruvate, which is then turned into acetyl CoA. The result of one Kreb cycle is 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 GTP, and 2 CO2 (1).
Lactic acid is created when oxygen is not present and glucose goes through fermentation instead of the Kreb’s cycle. Lactic acid is then returned to the liver to be turned back into glucose.
This is a normal and healthy process unless the production of lactic acid exceeds the body’s ability to convert it back to glucose. When this happens, we have a buildup of lactic acid in the system (1).
How Do We Test For It?
One of the best tests we can do to evaluate how our body is functioning while spending as little money as possible, is the Organic Acid Test. This is a simple urine test that looks at complex biomarkers from various metabolic pathways.
Metabolites are produced in various reactions in the body and when we have excess or too little of these biomarkers, this tells us something. This gives us an analysis of nutritional deficiencies, energy production efficiency, neurotransmitter levels, detoxification abilities, and intestinal microbial activity.
This is a great test for looking at mitochondrial function because it looks at many metabolites involved in the process of energy production. Lactic acid is one of these and when this metabolite is elevated, we know that this means the person is acidotic, experiencing oxygen deprivation, and not meeting the body’s energy demands efficiently.
What Do We Do About It?
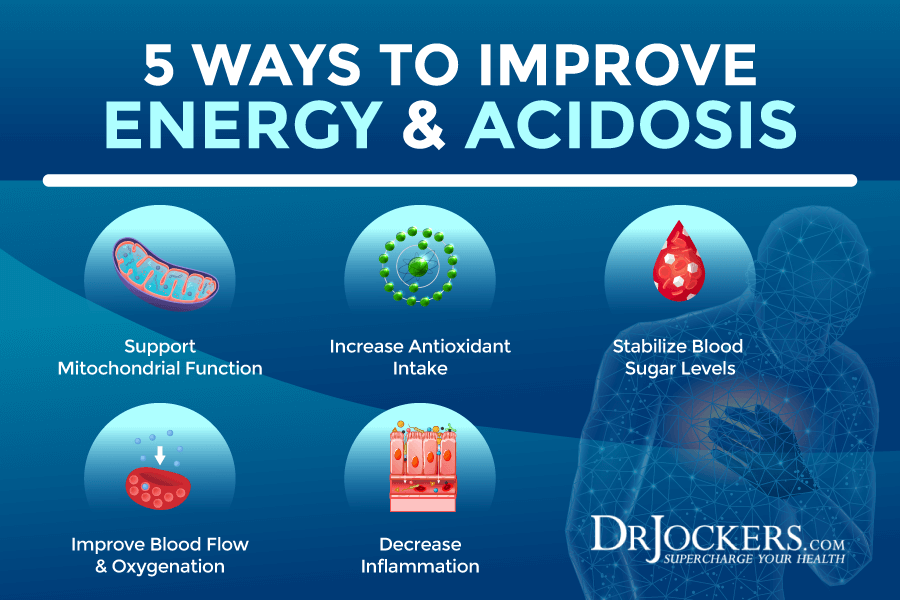
There are a number of things that will improve lactic acid metabolism. These things include supporting healthy mitochondrial function, regulating blood sugar levels, improving blood flow and oxygenation and decreasing inflammation.
All of these things work together, meaning that as you work to support healthy blood sugar levels, you will inherently also improve blood flow, oxygenation and reduce inflammation. As you do this, you will support the development of healthy mitochondria.
In the holistic model of health, healthy lifestyle inputs synergize to help us overcome the challenges of our environmental stressors. Let’s dive into these strategies and see how to best apply them.
1. Support Mitochondrial Function
Mitochondria are organelles in your cells that are responsible for producing energy and essentially lies at the heart of everything that occurs in your body. Dysfunction in their processing quickly leads to disease, inflammation, and deteriorating body functions.
Optimizing mitochondrial function can be done by ensuring that the body gets the right nutrients and precursors necessary for mitochondria function. Healthy mitochondrial function also plays a large role in cancer prevention and reversal.
Mitochondria can be supported by practicing intermittent fasting. Intermittent fasting decreases the window for oxidative stress induced by caloric intake. When the mitochondria are working to produce energy, some electrons leak from the electron transport chain to react with oxygen and form the free radical superoxide.
This is a precursor to other reactive oxygen species and a mediator in oxidative chain reactions. These free radicals then attack your cell membranes, receptors, enzymes, and DNA. This can eventually kill your mitochondria.
This problem arises when we have too many free radicals present. An effective way to decrease the amount of free radicals we have, is to reduce the amount of free radical production by decreasing caloric intake.
The best way to practice intermittent fasting is to eat your last meal several hours before bedtime and drink water and herbal tea with coconut oil, ghee, MCT oil, lemon, or essential oils while fasting in the morning. These things are very easy to absorb for energy and also provide anti-oxidants for the body to continue fighting off free radicals.
2. Increase Antioxidant Intake
Another effective way to decrease free radicals is to increase antioxidant intake. This can be done through diet and supplementation (4).
Some of the best sources of anti-oxidants can be found in the following:
- Green Tea
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Cinnamon
- Oregano
- Berries
- Dark Green Leafy Veggies
- Thyme
- Rosemary
- Raw Cacao
I also discuss some of the best anti-inflammatory foods in the video below
Essential nutrients and enzymes that we must get through the diet or supplementation to get the mitochondria functioning optimally include:
- CoQ10
- L-Carnitine, which shuttles fatty acids to the mitochondria
- D-ribose, which is raw material for ATP molecule
- Magnesium
- Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA)
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- All B vitamins, including riboflavin, thiamine, and B6 (4).
To learn more about our supplement that contains L-carnitine, Alpha-lipoic acid, CoQ10, and antioxidants, read here.
3. Blood Sugar Regulation
Controlling blood sugar levels has been shown to decrease the amount of lactic acid present in the body (5). This is due to increased insulin sensitivity, which means that the cell is able to uptake glucose that is ingested and created by the liver.
When the cells uptake glucose efficiently, energy is produced more efficiently and the body becomes less acidic. Elevated blood sugar levels result in insulin resistance, an acidic environment, and deficient energy use.
Regulate blood sugar levels by eating high amounts of good quality fats, proteins, and phytonutrient dense vegetables, limiting fruit intake, and eliminating grains, starchy foods, processed foods, trans fats, etc. See this article to learn more about blood sugar regulation.
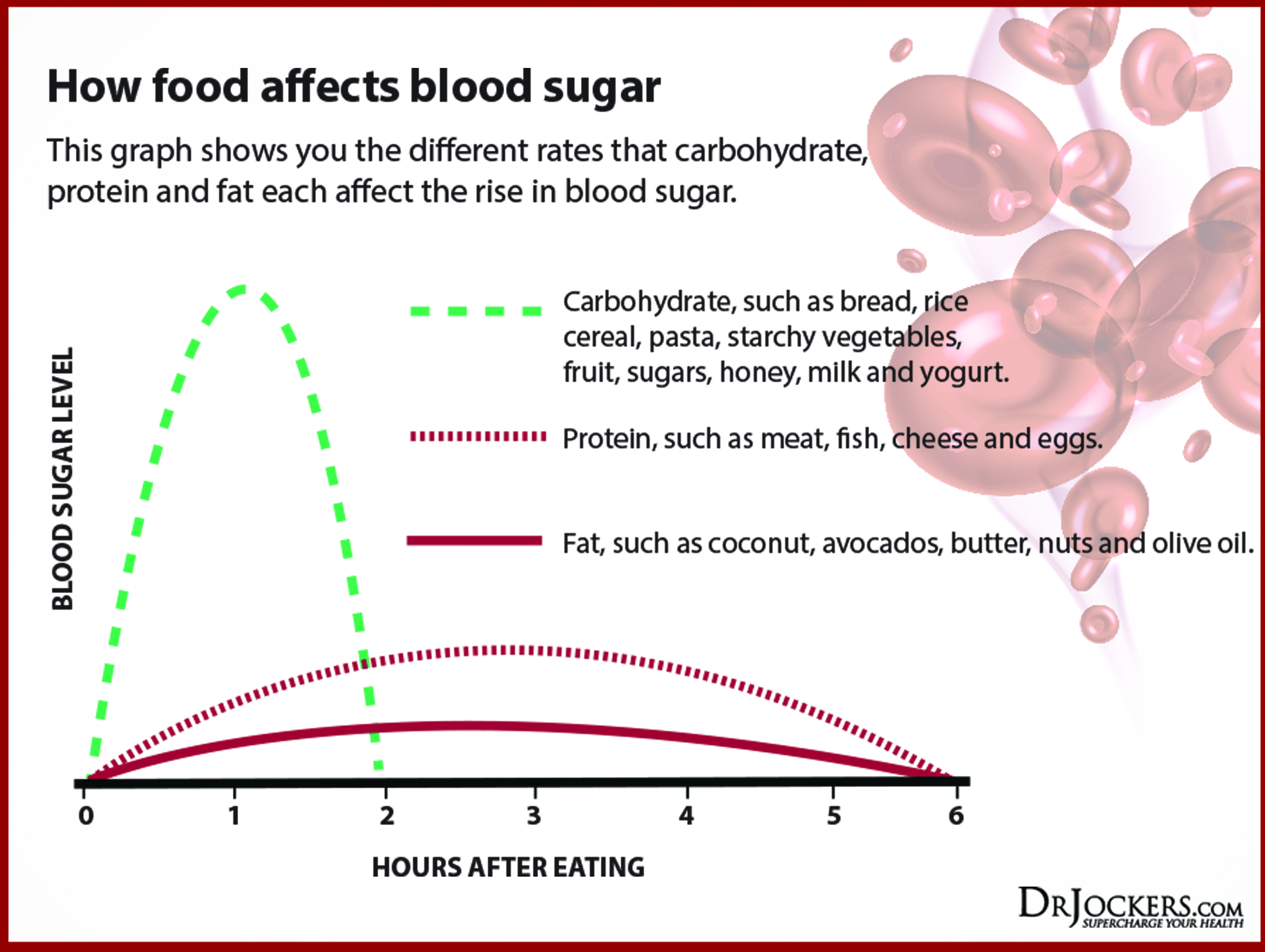
4. Improve Blood Flow & Oxygenation
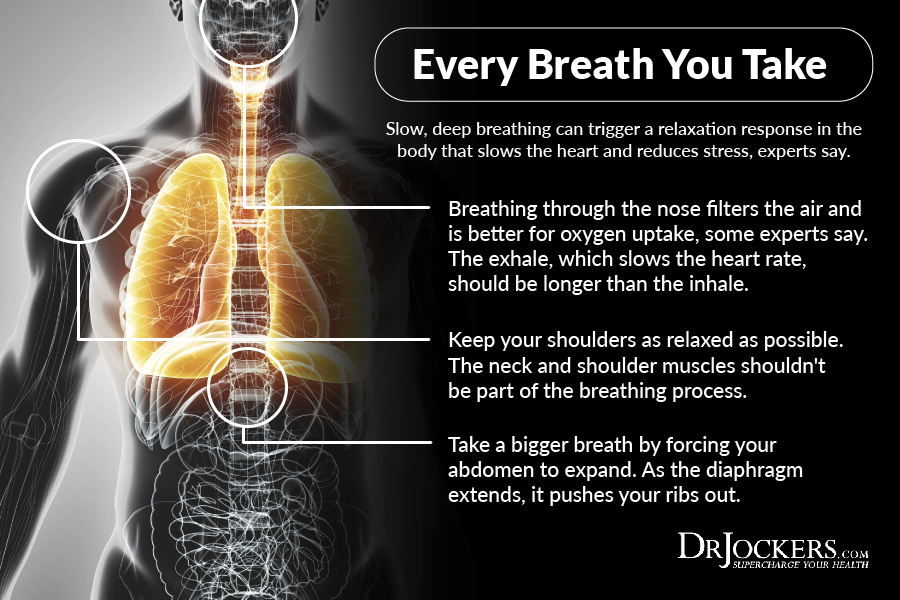
There are many ways to improve blood flow and oxygenation. The most important things to remember are to move the body regularly by engaging in exercise, deep breathing and following a healthy, blood sugar regulating nutrition plan. Here are the key steps:
Regulating blood sugar
Controlling blood pressure
Increasing muscle mass
Moving the body and avoiding long periods of sitting
Deep breathing
Yoga/exercising
Eating iron rich foods such as grass fed beef to support red blood cell formation

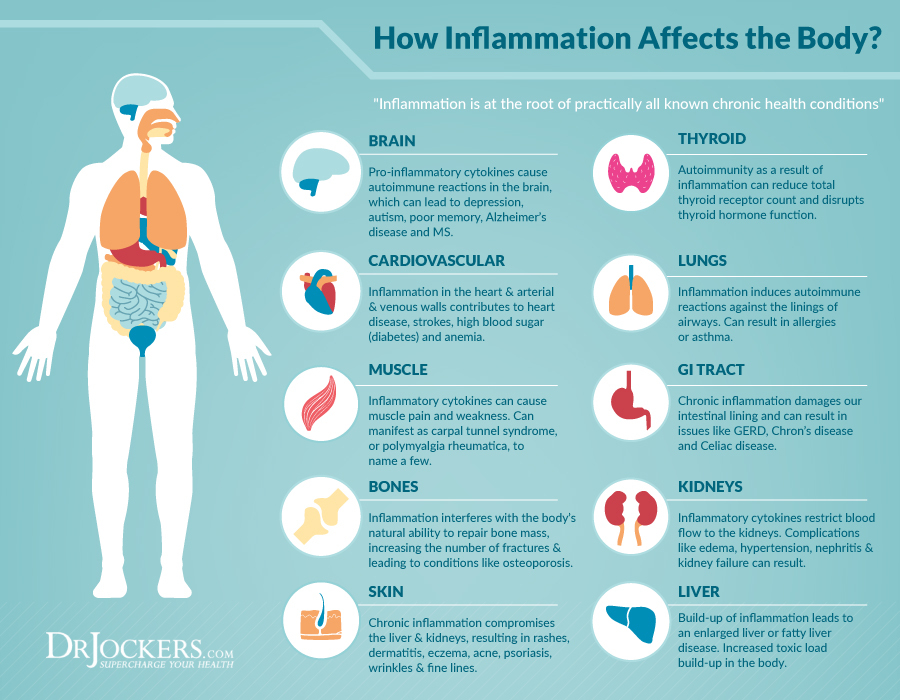
5. Decrease Inflammation
Inflammation has proven to be the underlying reason for nearly every health problem that we encounter. Try adding foods into your diet that de-inflame the body.
These include foods such as apple cider vinegar, avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, ginger, blueberries, lemons and limes, grass fed beef, garlic, etc.. The list goes on. You can read more about anti-inflammatory foods here.
Conclusion
You can improve your lactic acid metabolism by following lifestyle strategies to accomplish the following:
- Reducing free radical production
- Increasing antioxidant intake
- Improving blood sugar regulation
- Decreasing inflammation
- Improving sleep
- Increasing oxygenation and blood flow






I have an extremely low Controle Pause (the most important measure in the Buteyko breathing method), this supposedly means that the CO2 in my blood is too low: hypocapnia. Because of this, less oxygen can be absorbed from the blood into the tissues (Bohr effect), less ATP can be made aerobically (this is also why breathing less is healthier, we should not increase the volume of our breath on purpose for long periods of time, because it makes us breathe out more CO2).
Anyway, I’m also on a keto diet and I read that for anaerobic energy production, only glucose can be used. Not fats or ketones. Is this true? If so, it might not be the best diet for me as long as I have hypocapnia.
Also, I read that ketones are acidic: wouldn’t this make the body more acidic?