 Female Hair Loss: Causes and Natural Support Strategies
Female Hair Loss: Causes and Natural Support Strategies
When you hear the term hair loss, you may think about men. But hair loss doesn’t only affect men but may affect women too due to menopause, hormonal issues, autoimmunity, or other factors. Female hair loss can be frustrating or even embarrassing. Fortunately, if you understand the underlying root issues behind your female hair loss, you may be able to improve the condition.
In this article, I want to talk about female hair loss. You will learn about the main types of female hair loss. I will discuss the root causes of female hair loss. I will go over the key labs to look at if you have or are at risk of female hair loss. I will share my top natural strategies for female hair loss.
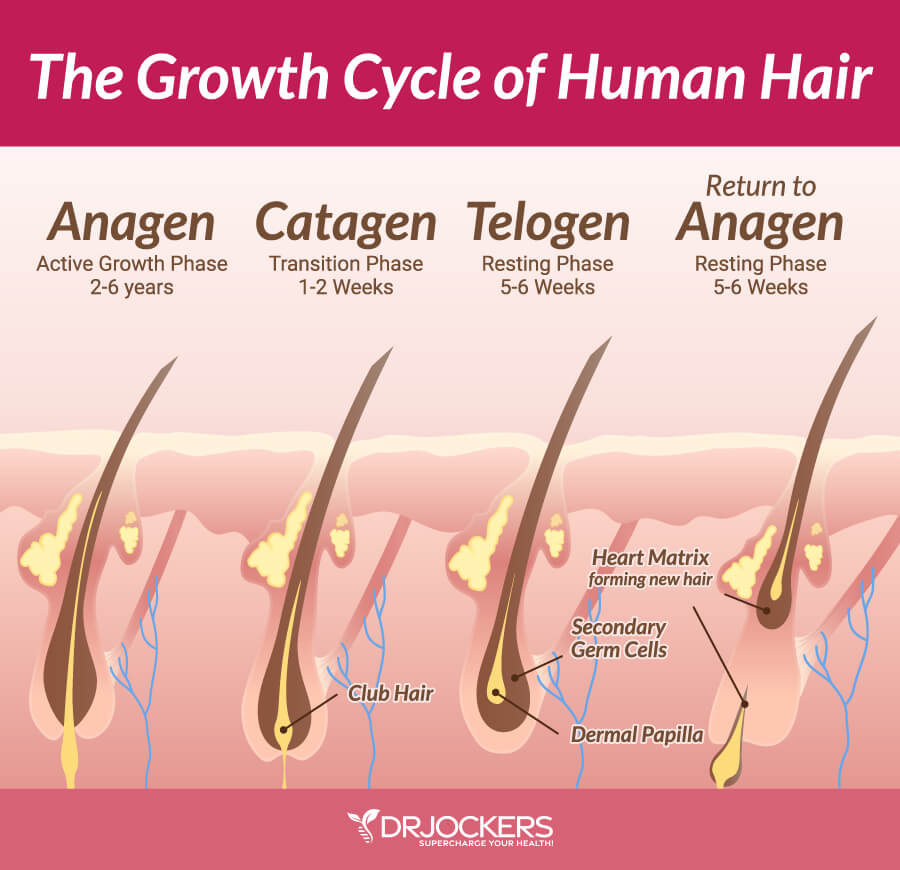
The Hair Growth Cycle:
Before we discuss reasons for hair loss, let’s talk about your hair. Your hair has two separate structures: the follicle and the shaft. The follicle resides in your skin. The shaft is the visible part of your hair that surrounds the follicle. Your hair shaft protects your hair and helps it to grow.
The hair growth cycle has three phases:
- Anagen phase: phase of active hair growth that lasts 2-6 years.
- Catagen phase: 2-3 week transitional or intermediate phase during which growth stops; and,
- Telogen phase: resting phase that lasts up to 100 days.
This cycle may be affected by many factors and result in hair loss. Hair loss can significantly impact a person’s self-image and self-esteem. Let’s look at causes of hair loss.

Types of Female Hair Loss
There are several different types of female hair loss. The most common types of female hair loss include (1):
- Androgenic alopecia: This is the most common type of female hair loss during menopause. It displays patterns of baldness with thinning in the front and tops of the scalp. It’s characterized by insufficient estrogen and/or progesterone.
- Alopecia areata: This type of female hair loss is characterized by patchy hair loss all over the scalp that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles. It is caused by autoimmunity in the hair follicles.
- Telogen effluvium: This is the most common type of hair loss seen in Hashimoto’s disease. It is characterized by diffuse thinning all over the scalp. It is caused by autoimmunity in the thyroid gland.

Root Causes of Female Hair Loss
To address female hair loss or reduce your risk factors, we have to understand the potential underlying causes of the issue. Let’s look at the potential root causes of female hair loss.
Chronic Inflammation & Autoimmunity
Chronic inflammation and autoimmunity are two major underlying issues behind female hair loss. A 2020 review published in the Journal of Inflammatory Research has found that perifollicular inflammatory infiltrates, such as histiocytes and lymphocytes, may be found in female pattern hair loss, as well as male pattern hair loss (2). They also found that inflammatory genes, including TNF and CASP7 may also play a role.
Chronic inflammation and other factors, including leaky gut syndrome, may also increase the risk of autoimmunity, which may lead to female hair loss. Alopecia areata is caused by autoimmunity, and Telogen effluvium is due to autoimmunity of the thyroid gland.
A 2023 review article published in Skin Appendage Disorders suggests that underlying and often undiagnosed autoimmunity is often the reason behind hair loss and should be considered as an option (3). The authors found that hair loss may be seen in dermatomyositis, scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, acute lupus erythematosus, and discoid lupus erythematosus.
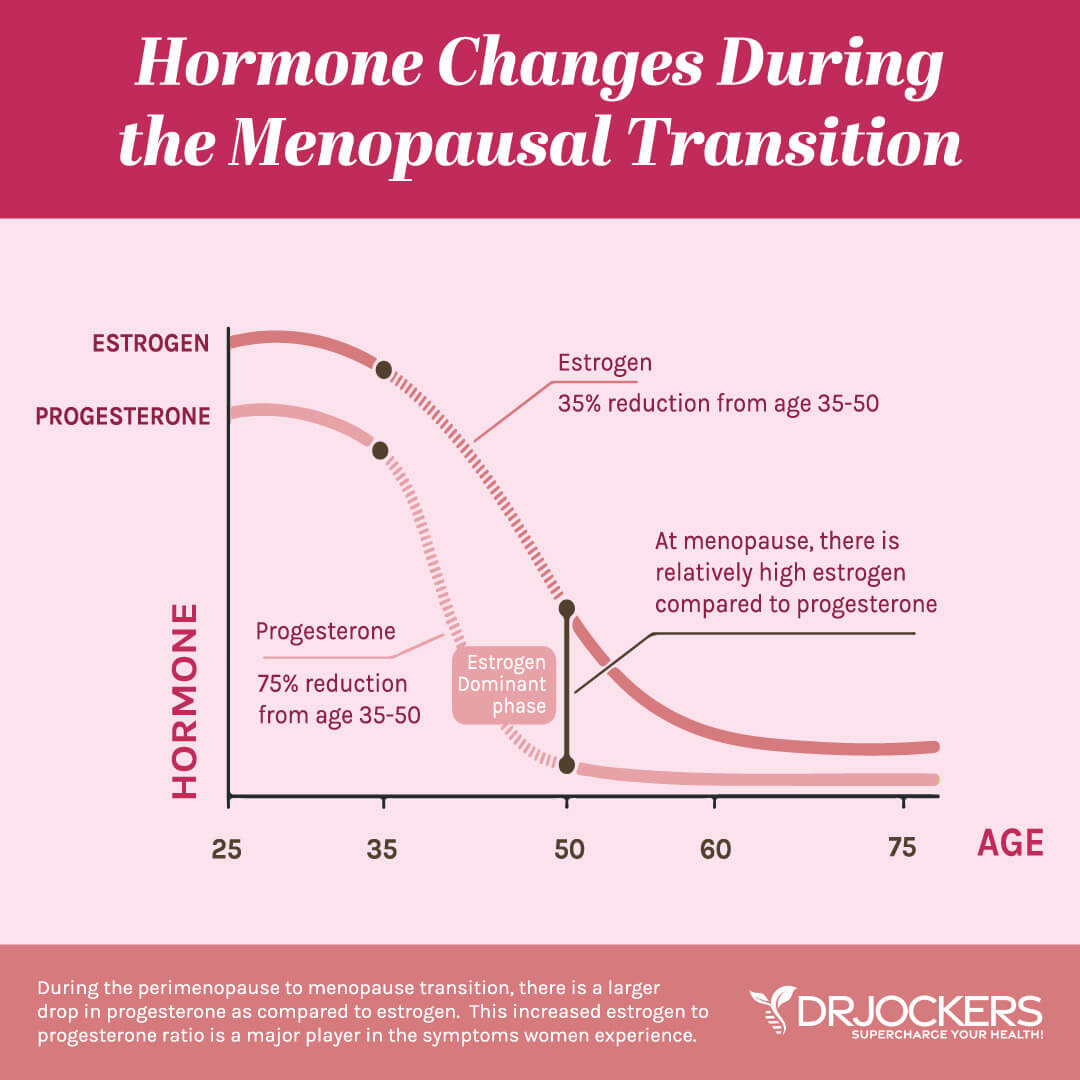
Hormone Changes During Menopause
Hormonal changes during menopause may also lead to hair loss. Androgenic alopecia is the most common type of female hair loss during menopause.
A 2022 cross-sectional study published in Menopause has found that female pattern hair loss is prevalent in postmenopausal women (4). Researchers looked at 200 postmenopausal women between 50 and 65 years. They found that 52.2 percent of participants had female pattern hair loss.
Chronic Stress & Poor Sleep
Chronic stress and poor sleep may also contribute to female hair loss. They both may increase chronic inflammation, which is a common root cause factor behind female hair loss. They are also commonly seen in autoimmunity and hormonal issues, which are also root cause factors.
Moreover, a 2021 study published in Nature has found that stress may cause hair loss (5). They found that in rodents, stress hormone corticosterone may play a role in regulating the hair follicle stem cell (HFSC). Corticosterone is the equivalent of cortisol in humans. Under chronic stress, it may put hair follicle stem cells into an extended resting phase, leaving their hair without regeneration and causing hair loss.
A 2022 cross-sectional study published in Health Science Report has found that sleep disturbance may play a role in hair loss (6). Researchers looked at 51 patients with alopecia areata and 51 without. They found that sleep disturbance is more prevalent in those with hair loss. They also found that anxiety and depression were also more common in participants with hair loss.
High Toxic Load
Environmental toxins are all around us, including air pollution, cigarette smoke, mold, plastics, toxins in municipal tap water, chemicals in cosmetics, body, hygiene, and cleaning products, heavy metals, and so on. A high toxin load may increase the risk of chronic inflammation, gut health issues, and autoimmunity and, as a result, may contribute to hair loss.
A 2018 systematic review published in Skin Appendage Disorders has found that a number of toxic agents may lead to hair loss, including mercury, arsenic, colchicine, boric acid, and Botulinum A (7).

Chronic Infections
Chronic infections may also increase your risk of female hair loss. They may result in chronic inflammation, autoimmunity, hormonal issues, and chronic symptoms. A 2022 study published in the Journal of Medicine and Life has found that people may develop hair loss after a COVID-19 infection and as a long-COVID symptom (8).
2022 research published in the American Journal of Dermatology has found that hair loss may be associated with cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and swine flu virus due to the inflammatory response induced by immune cells (9).
Nutrient Deficiencies
Various nutrient deficiencies due to a poor diet, eating disorders, malabsorption issues, underlying health issues, certain medications, or other factors may also contribute to female hair loss. Here are the common nutrient deficiencies that may play a role in female hair loss:

Low-Calorie Diet
Frequent extreme dieting and following a low-calorie diet may cause nutritional deficiencies and low thyroid function that may lead to hair loss. Studies on the link between low-calorie crash diets and hair loss date back to the 1970s (10).
As you will learn in the later sections, nutrient deficiencies due to a low-calorie and/or low-nutrient diet may increase the risk of female hair loss. A 2007 study published in the McGill Journal of Medicine has found that anorexia nervosa, which is associated with a low-calorie diet and malnutrition, may lead to hair loss and other health issues (11).
B Vitamin Deficiencies
B vitamins, especially biotin, are key for healthy blood flow and proper hair follicle function. A 2017 review published in Skin Appendage Disorders has found that biotin supplementation may be beneficial for hair growth and nail health (12).
2017 research published in Dermatology Practical and Conceptual has found that biotin is essential for protein synthesis, which is critical for hair health, as you will learn in the next section (13).

Low-Protein Diet
Your hair is made of protein. Protein comes from your diet, and a low-protein diet may cause hair loss. 2017 research published in Dermatology Practical and Conceptual has found that protein malnutrition may result in hair changes and hair loss (13).
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with autoimmunity to the hair follicle and may result in hair loss. 2017 research published in Dermatology Practical and Conceptual has found that vitamin D is also critical for hair follicle cycling, and deficiencies may result in hair loss (13).

Low Iron
Iron is key for blood cells and oxygen delivery to your hair follicles. Low iron may increase the risk of female hair loss. A 2015 study published in The Journal of Clinical & Diagnostic Research has found that iron deficiency may increase the risk of hair loss (14).
Zinc Deficiency
2017 research published in Dermatology Practical and Conceptual has found that zinc is critical for protein synthesis and cellular function (13). Since protein is critical for hair health, zinc deficiency may increase the risk of hair loss.

Selenium and Iodine Deficiency
Selenium and iodine are both necessary for proper thyroid function. Low thyroid hormone levels are associated with hair loss. Thus, thyroid issues from low selenium or iodine deficiency may lead to female hair loss. 2017 research published in Dermatology Practical and Conceptual has found that selenium is critical for hair health (13).
Low Antioxidants and Omega-3s
2017 research published in Dermatology Practical and Conceptual has found that antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids are key for proper cellular function (13). They may help to lower oxidative stress and inflammation. As a result, low levels may increase the risk of female hair loss.
Key Labs To Look At
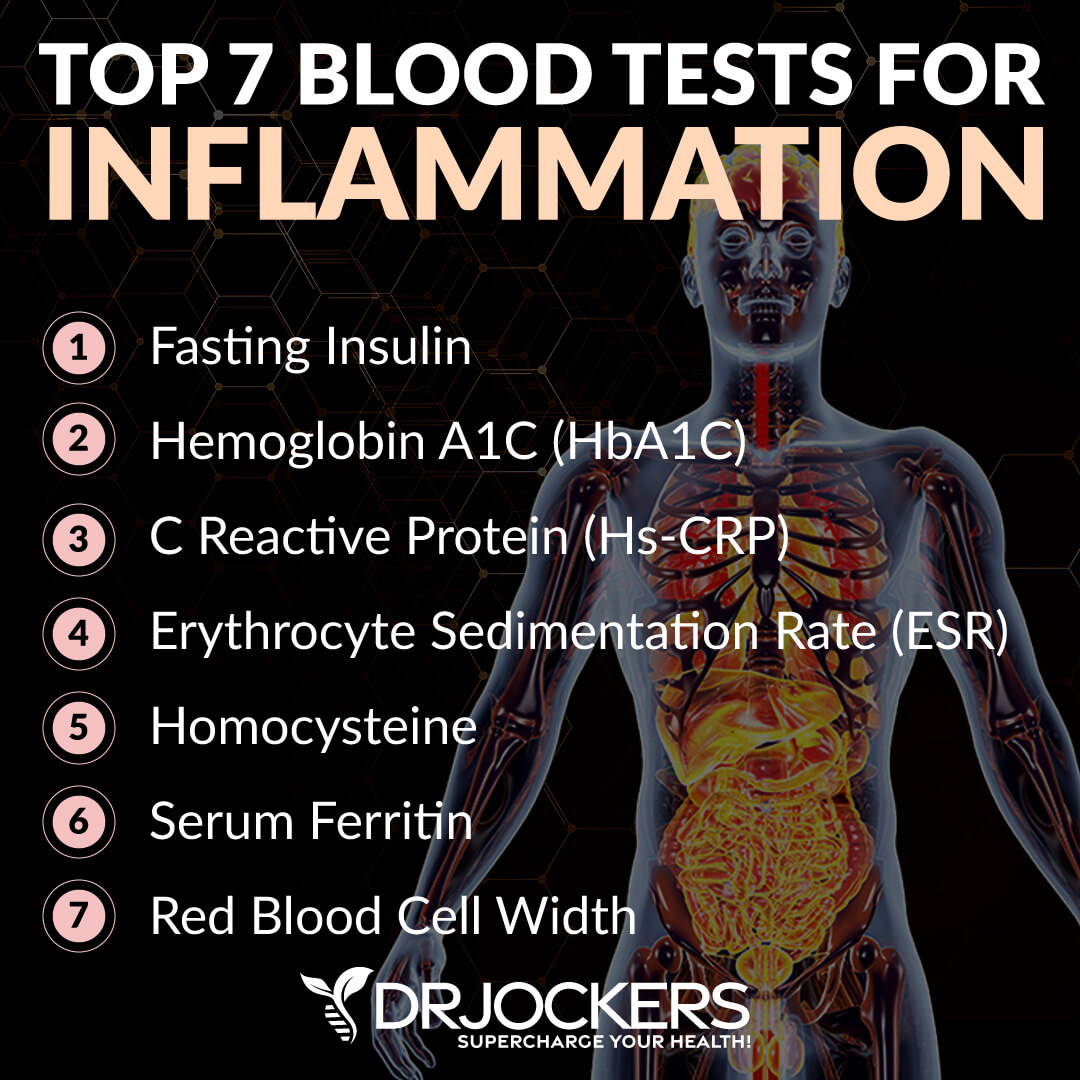
To look at the risk factors and potential underlying issues behind female hair loss, I recommend looking at certain lab markers. Here is what I recommend.
Inflammatory Markers
I recommend looking at some inflammatory lab markers.
ESR
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a common hematology test to look for inflammation and related health problems. Optimal ESR rates for women under 50 are between 0 and 20 mm/hr, men under 50 are between 0 and 15 mm/hr, women over 50 are between 0 and 30 mm/hr, men over 50 are between 0 and 20 mm/hr, and children between 0 and 10 mm/hr.
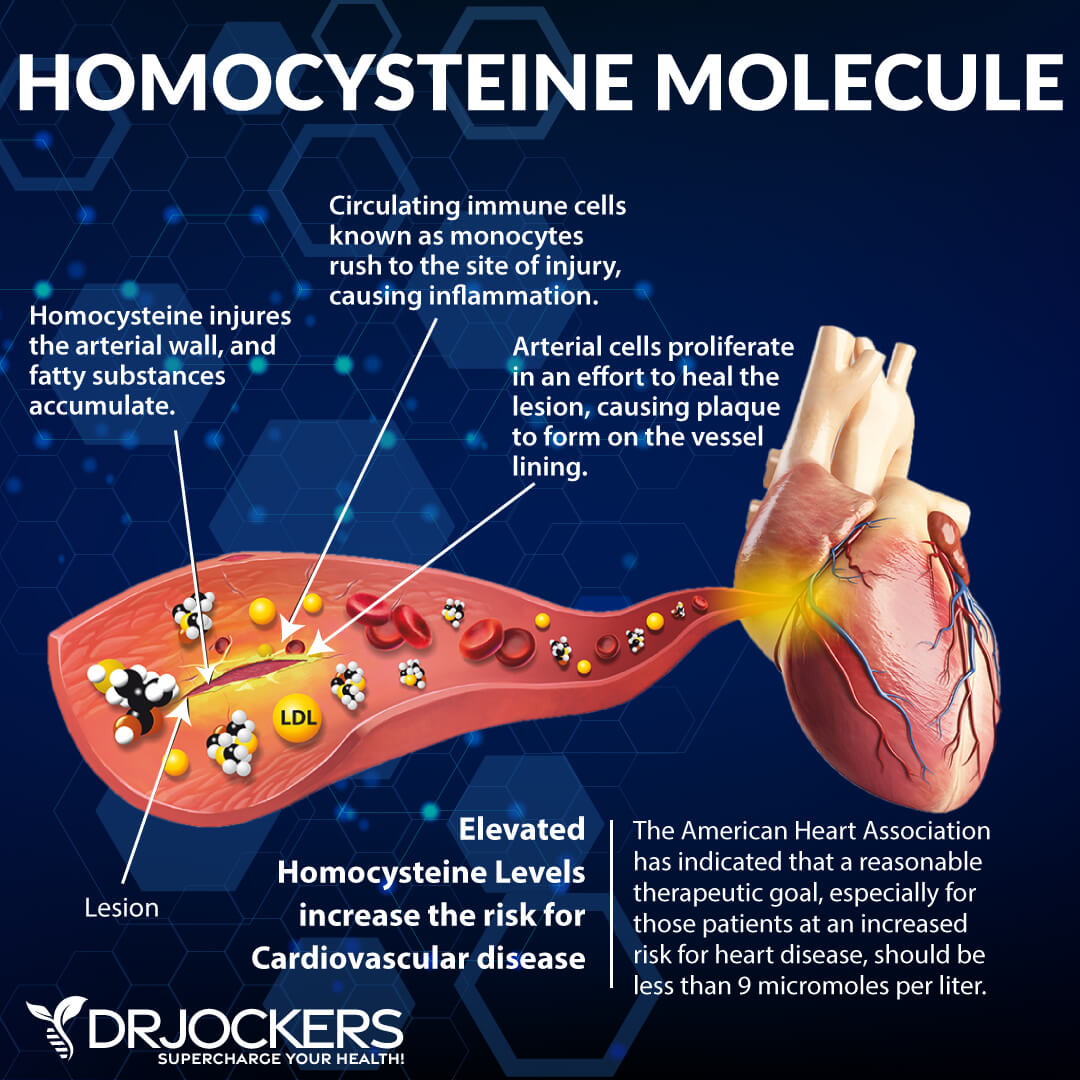
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is a common amino acid in your blood that you mostly get from eating meat. Homocysteine is particularly a good marker for cardiovascular issues. The optimal range for homocysteine is between 6 and 9.
Serum Ferritin
Serum ferritin measures the level of ferritin in your body to detect iron deficiency anemia and other health issues. Elevated serum ferritin levels may indicate inflammation, liver disease, autoimmune disease, or even cancer.
The clinical range is 30 to 400, and the optimal range is 25 to 100 for females and 50 to 150 for males.
Hs-CRP
The C-reactive protein or CRP test is a key test I recommend. The clinical range is between 0 and 3 mg/L, while the optimal range is 0 to 1 mg/L. When I see levels over 1 mg/L, I know the individual is having an inflammatory response that could be due to acute trauma or chronic conditions.

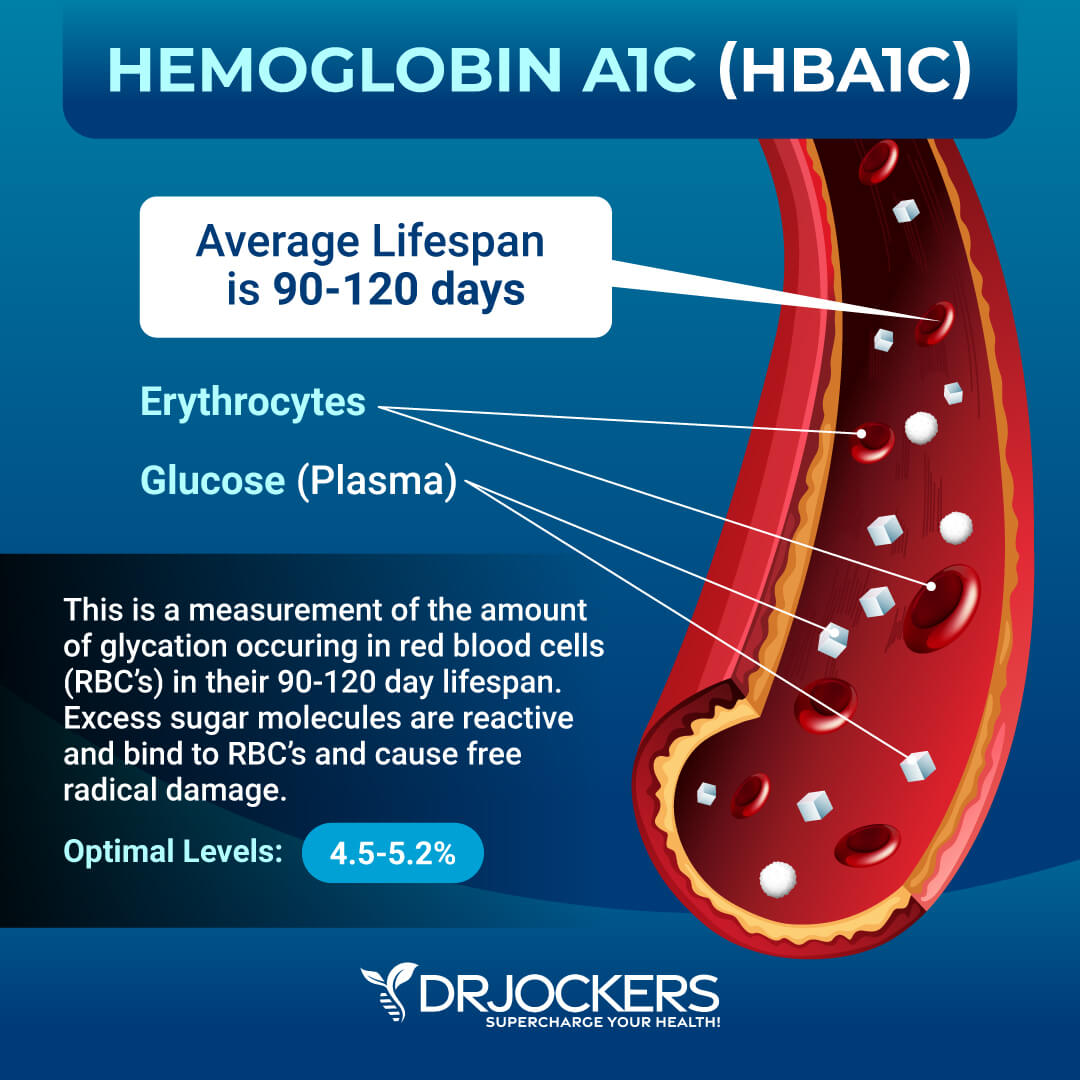
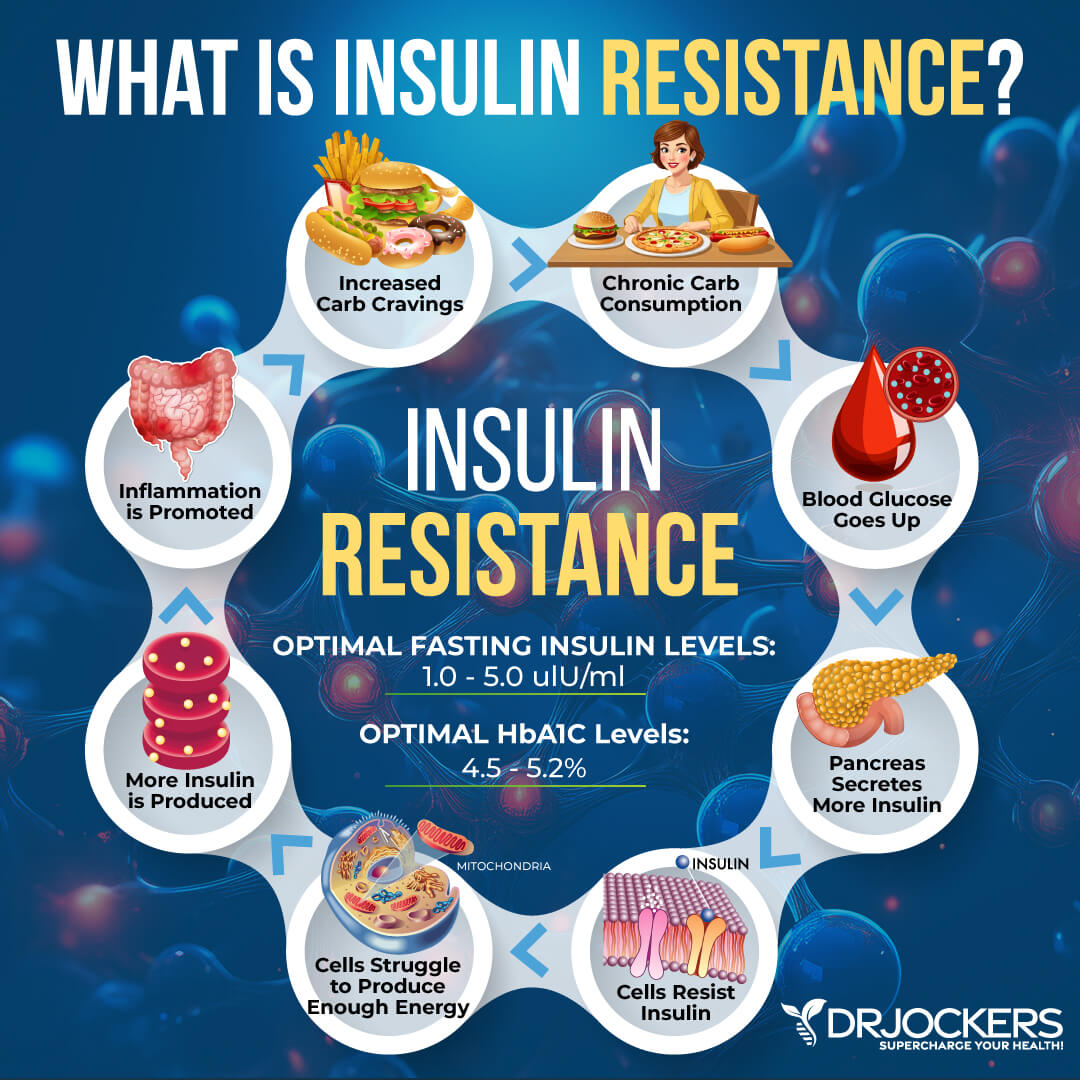
HbA1C
In addition to fasting insulin, I recommend checking your hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) levels. Your HbA1C levels measure your average blood sugar over the past 2 to 3 months.
Hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) gives the average amount of glucose in your blood or blood sugar over the past 3 months, making it one of the top tests for inflammation and diabetes. The clinical range is between 4.8 and 5.6, while the optimal range is 4.5 – 5.2.
Fasting Insulin
Blood sugar imbalances may increase your risk of inflammation and related health issues. In addition to testing your HbA1C levels, I recommend checking your fasting insulin levels.
Testing your fasting insulin can recognize elevated blood sugar levels and can detect inflammation, insulin resistance, blood sugar issues, and diabetes. The clinical range for fasting insulin is 2.6 – 24.9 uIU/ml, and the optimal range is 1.0 – 5.0 uIU/ml.
Nutrient Levels
I also recommend looking at certain nutrient levels.
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is an important vitamin that most of our population is deficient in. Poor levels may indicate inflammation. Normal levels of 25-OH vitamin D are 50 ng/ML (125 nmol/L) or more, while optimal levels are over 60 ng/mL (1500 nmol/L).

Zinc/Copper Ratio
Zinc is a mineral that’s incredibly important for your immune system and metabolic function. The copper-to-zinc ratio is just as important as your zinc levels. Zinc and copper compete against one another as antagonists in order to properly regulate the physiological pathways in your body.
The proper balance between the two trace minerals is critical to maintaining health. Ideal range of plasma zinc is between 90 to 135 ug/dL and for serum copper, it’s 70 to 110 ug/dL. The ideal zinc: copper ratio is 1.0 to 1.2.

Serum B12 and Folate
B vitamins are essential for cellular health, energy levels, brain function, mental health, nerve function, and digestion. I particularly recommend looking at your serum B12 and folate levels if you have female hair loss.
Normal B12 levels are between 160 to 950 pg/mL, or 118 to 701 pmol/L. For folate, normal levels are between 3.1 and 17.5ng/ml.
Thyroid Levels
Since autoimmune thyroid issues may also cause female hair loss, I recommend looking at your thyroid levels. Looking at your TSH levels is not enough. I recommend looking at your TSH, T4, T3, Free T4, Free T3, TPO & TG antibodies, and rT3 levels.

Serum Iron
Iron is a main component of hemoglobin, which helps to carry oxygen from your lungs across your body. Serum is important for red blood cell production, energy, focus, and many other functions. Ideal iron levels are between 60 to 170 mcg/dL.
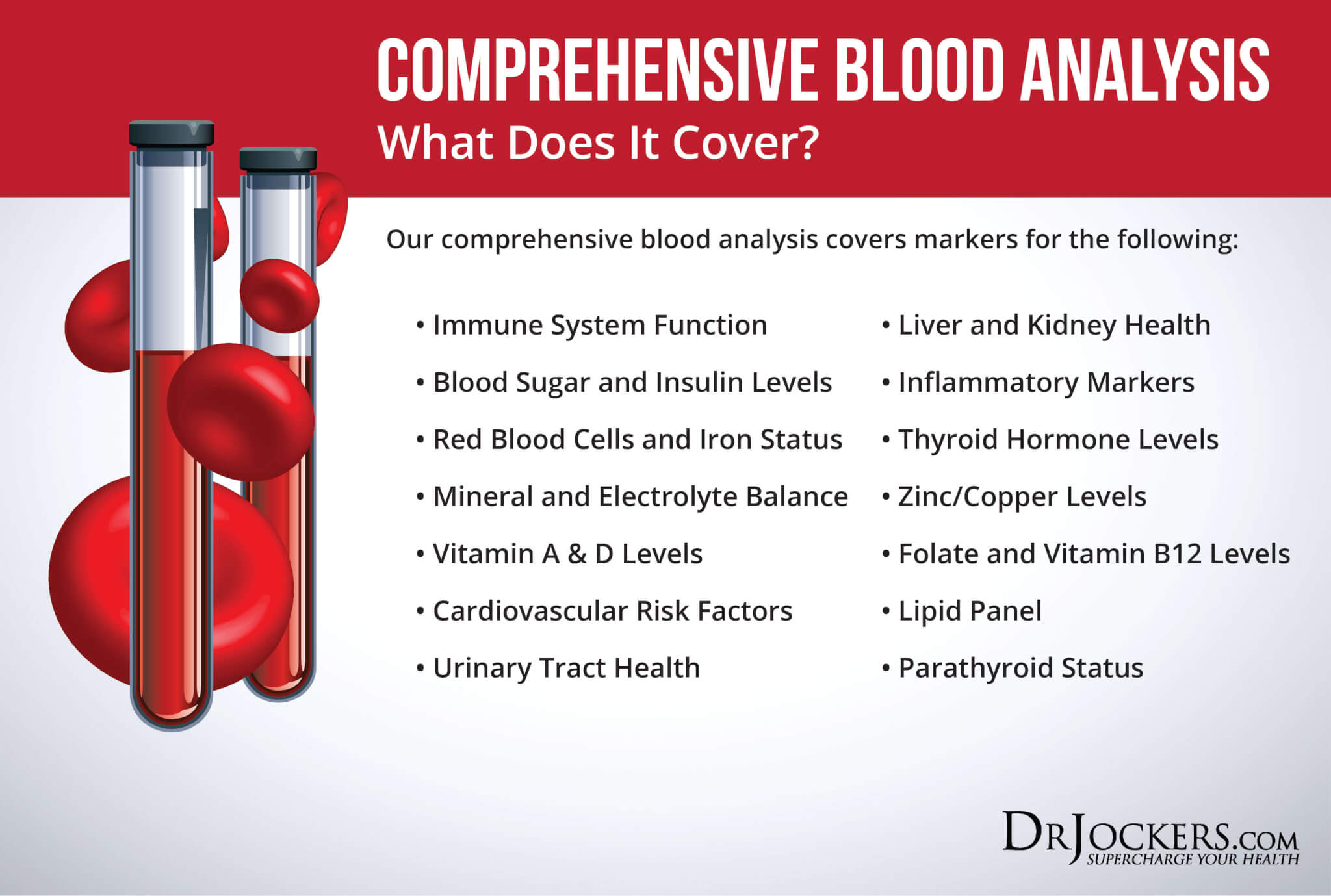
Comprehensive Blood Analysis
To check for these lab markers, I recommend a Comprehensive Blood Analysis (CBA), which is a very detailed blood test that looks at all of these markers of inflammation. This test is more sophisticated than most conventional doctors run.
It examines all parameters for inflammation, blood sugar levels, thyroid function, zinc and copper ratio, vitamin A and D levels, a complete metabolic panel, complete blood count, liver function, nutrient deficiencies, and more. I recommend getting the Comprehensive Blood Analysis done regularly both as a preventative measure and to monitor your inflammation levels and progress if you are on a treatment plan.
DUTCH Hormone Panel for Hormone Levels
To look at your thyroid and other hormone levels, I recommend a DUTCH hormone panel. The DUTCH Test™ — Dried Urine Test Comprehensive Hormones. Precision Analytical developed this new method of urine cortisol measurement that involves the collection of a small amount of urine on filtered paper four times a day.
In this way, the DUTCH Test™ is able to estimate diurnal production, like saliva, but also provide information on both total free cortisol and overall cortisol using metabolites, as well as free cortisone and metabolized cortisone. The DUTCH Test™ is well-recognized for its ease of collection, coupled with comprehensive reporting that is not available from other laboratories.
Natural Support Strategies
You may decrease your risk of and reduce female hair loss with some natural support strategies. Here is what I recommend:
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition Plan
A low-nutrient or low-calorie diet and related nutrient deficiencies may increase your risk of female hair loss (10, 11). Following an anti-inflammatory nutrition plan is critical.
Avoid inflammatory foods, including refined sugar, refined oil, additives, artificial ingredients, junk food, and overly processed food. Don’t forget about inflammatory drinks, such as sodas, fruit juices, energy drinks, other high-sugar drinks, and alcohol.
Focus on nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods, including greens, vegetables, herbs, spices, sprouts, fermented food, low-glycemic index fruits, seeds, grass-fed beef, pasture-raised poultry, pasture-raised organic eggs, grass-fed butter and ghee, wild-caught fish and seafood, and wild game.
Eat lots of healthy fats, including avocados, coconut oil, coconut meat, olives, extra-virgin olive oil, and grass-fed butter and ghee. Eat plenty of protein from clean animal protein sources.

Reduce Stress & Prioritize Good Sleep
Chronic stress and poor sleep may increase your risk of female hair loss (5, 6). I recommend reducing your stress levels and prioritizing good sleep if you are experiencing female hair loss or want to reduce your risk factors.
I recommend practicing breathwork, mindfulness, gratitude, meditation, and other relaxation strategies. Reduce your exposure to stressful activities and people that bring you down. Choose to spend time with uplifting activities and supportive people.
Avoid electronics, caffeine, sugar, and heavy foods close to bedtime. Avoid stress in the evening. Choose relaxing activities. Reading, listening to calming music, board games, taking a bath, and relaxing family time are great options. Create a supportive, relaxing sanctuary in your bedroom. Choose relaxing colors, including light clay browns, soft oranges, earthy greens, dusty yellows, and natural pinks.
Choose a supportive bed, bedding, and pillows. Eye masks and black-out curtains may create the darkness you need to sleep, supporting your body’s natural circadian rhythms. Some essential oils, such as lavender, or using a Himalayan Sea salt lamp may also help to relax and sleep.

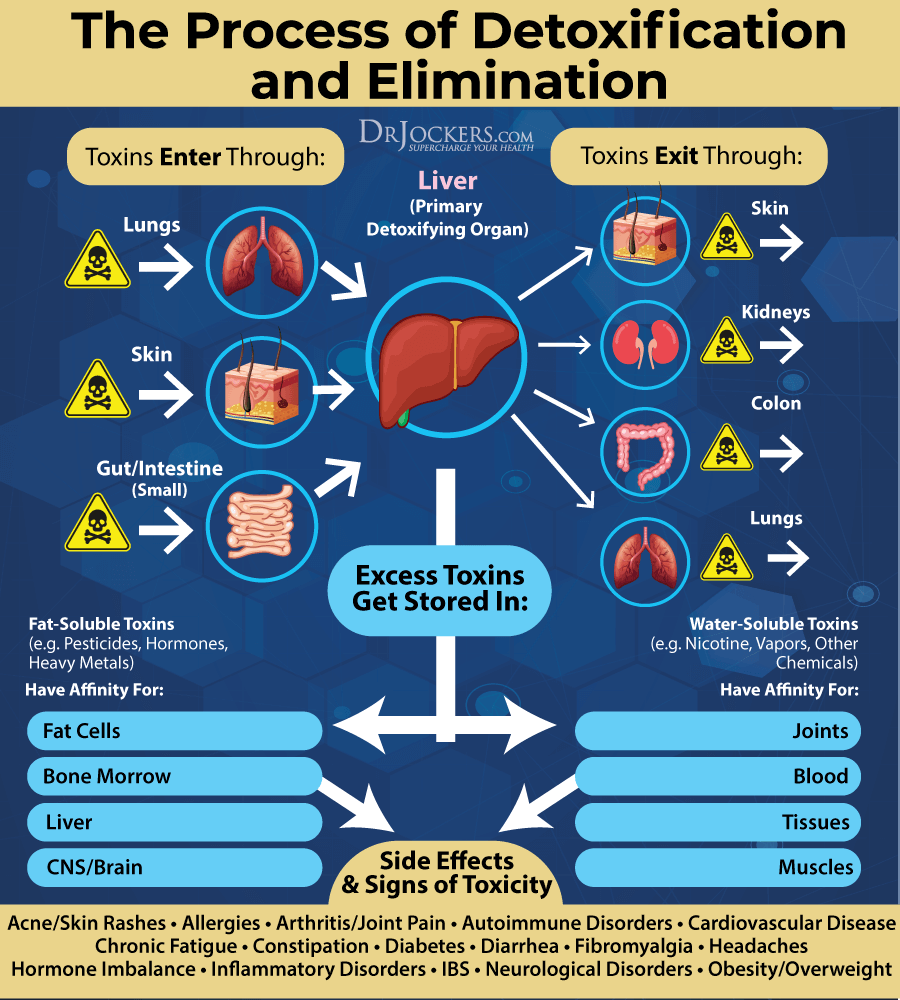
Reduce Toxic Load
A high toxin load may increase your risk of female hair loss (7). I recommend reducing your exposure to environmental toxins. Check your home for mold and address any mold issues. Use an indoor HEPA filtration system to improve your indoor air.
Choose organic, natural, or homemade body, beauty, personal hygiene, and cleaning products over chemical-filled ones. Reduce your use of plastics. Avoid smoking or second-hand smoke. Address any heavy metal toxicity issues. Focus on supporting your detoxification pathways.
Support Gut Health and Stomach Acid Levels
Chronic inflammation and autoimmunity may increase the risk of female hair loss (2, 3). Gut dysbiosis and leaky gut syndrome may increase the risk of chronic inflammation, autoimmunity, and nutrient deficiencies.
Chronic stress, poor sleep, poor diet, and nutrient deficiencies may increase the risk of gut problems. Chronic infections, which may also be linked to female hair loss, may also increase the risk of gut imbalances, chronic inflammation, and related problems (8, 9).
Supporting your gut health and stomach acid levels is critical. Follow an anti-inflammatory, gut-friendly diet. Eat plenty of probiotic-rich foods and take a daily probiotic supplement. Try Gut Repair, a supplement made with gut-supporting L-glutamine, aloe vera, arabinogalactan, and licorice extract to improve your gut lining.
To reduce stomach acid, consider taking Betaine HCL with meals. I recommend Super Digest HCL. Take it regularly with your meals. Eating slowly and mindfully may also reduce symptoms of low stomach acid and aid digestion. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
However, when you are eating meat or any sort of heavier food, you should stop drinking water or other liquids at least 30 minutes before the meal, except if you need to take a supplement with 2 ounces of water. Holding off water during these meals will reduce any potential dilution of the gastric juices and allow for better digestion. Drink ginger tea regularly to improve your digestive juices.
Lemon water or apple cider vinegar mixed with water may also help to improve stomach acid levels. Try fermented foods and drinks, such as sauerkraut, kimchi, fermented vegetables, kombucha, coconut kefir, and coconut yogurts.

Optimize Vitamin D Levels
Vitamin D deficiencies may increase the risk of female hair loss (13). To improve your vitamin D levels, I recommend spending time out in the sun and eating vitamin D-rich fatty fish, egg yolks, and beef liver. Most people are not getting enough sunshine or consuming enough vitamin D from food. Therefore, most people need supplements to optimize their vitamin D levels.
Pairing vitamin D3 with vitamin K2 helps improve calcium absorption and inflammation control. I recommend taking a vitamin D3 supplement with at least 3,000-5,000 IU’s of vitamin D3 and at least 90 mcg of vitamin K2. I highly recommend Vitamin D3/K2 Power. Both of these supplements support your immune, skin, cardiovascular, and bone health.
Typically, taking 1,000 IU per 25 lbs. of body weight will help you get your levels into a healthy range. You want to test your vitamin D levels at least 1-2 times each year and get your levels between 50-100 ng/ml. It has been hypothesized that a therapeutic level for major health conditions is going to be between 70-100 ng/ml.

Consider Adaptogens & Bioidentical Hormone Support
If hormonal issues are the underlying issue behind your female hair loss, you may benefit from using adaptogens and bioidentical hormones. Adaptogens may help to maintain homeostasis in the body, improve physiological functions, and support hormonal health. Some of the most common adaptogens include ashwagandha, rhodiola, and ginseng.
According to a 2023 study published in Drug Design, Development, and Therapy, adaptogens may help to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation and, as a result, may help to lower the risk of androgenetic alopecia and various skin conditions and may serve as anti-hair loss supplements (15).
Hair loss is a common symptom of menopause, and adaptogens may help. A 2021 review published in Nutrients has found that Schisandra chinensis extract may be beneficial for menopausal symptoms (16).
Adaptogens may also help to improve thyroid issues, which may lead to female hair loss. According to a 2010 paper published in Botanical Medicine for Women’s Health, ashwagandha may be helpful for thyroid support (17).
Bioidentical hormone therapy, also known as natural hormone therapy or bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT), uses hormones that are identical to your natural hormones on a molecular level. It is used to improve hormonal imbalances and hormone-related symptoms, for example, during menopause.
It may help with thinning hair and female hair loss. According to a 2021 review published in Dermatology, hormone therapy may be beneficial for hair loss, however, we need more research to understand the potential effects of various hormone therapies, including bioidentical hormone therapy (18).

Support Key Nutrients
Finally, you may also benefit from adding some key nutrients to your regimen to improve female hair loss.
Zinc
Zinc deficiency may play a role in problems with protein synthesis and cellular function, which may increase the risk of female hair loss (13). Zinc-rich foods include oysters, poultry, red meat, lentils, and beans. You may also benefit from zinc supplementation. I recommend Zinc Charge.
Selenium
Selenium is essential for hair health, and deficiencies may increase the risk of female hair loss (13). You may benefit from increasing your selenium intake. Eating 2 Brazil nuts a day may help to take care of your daily selenium needs.
Muscle meats, seafood, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, asparagus, and mushrooms may also help to improve your levels. In some cases, supplementation may be necessary to correct deficiencies.

Omega 3’s
Omega 3 fatty acids may help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. They support proper cellular function. Low levels may increase the risk of female hair loss (13). Improving your omega-3 levels may help to reduce your risk factors.
Fish and seafood are rich in omega-3s. Additionally, I recommend using an omega-3 fish oil supplement such as Pro EPA.
B Vitamins
Biotin and other B vitamins are key for healthy blood flow and proper hair follicle function. They are essential for protein synthesis, which is key for hair health.
Deficiencies may increase female hair loss (12, 13). Improving your levels may reduce female hair loss. Foods rich in B vitamins include liver, meat, seafood, poultry, eggs, leafy greens, and nuts. Additionally, I recommend supplements, such as B Strong and B12 Power.

Antioxidants
Antioxidants may help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. They support proper cellular function. Low levels may increase the risk of female hair loss (13). Improving your antioxidant levels may help to reduce your risk factors.
I recommend using vitamin C, quercetin, resveratrol, curcumin, and N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC). Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, pineapple, strawberries, tomatoes, guava, broccoli, and cauliflower.
Quercetin-rich foods include blueberries, blackberries, bilberries, cherries, grapes, black plum, cruciferous vegetables, peppers, sweet peas, asparagus, red onions, kale, lettuce, cabbage, some herbs, and olive oil.
Resveratrol-rich foods include grapes, mulberries, blueberries, and raspberries. Curcumin is the active ingredient of the spice turmeric. NAC may be found in meat, fish, seafood, chicken, turkey, eggs, sunflower seeds, broccoli, onions, and legumes.
You may also benefit from supplementation. ImmunoCharge is a great supplement with quercetin, resveratrol, vitamin C, N-Acetyl Cysteine. Pro Omega Curcumin is a great antioxidant support supplement with NAC, curcumin, L-glutathione, and omega-3. Resveratrol Power is a great option for resveratrol and quercetin supplementation. Super C may help to boost your vitamin C levels.

Key Supplements
I recommend some key supplements that may help to reduce your risk factors for female hair loss.
Immunocharge
I recommend using ImmunoCharge to support your immune health. ImmunoCharge is specifically designed to provide you with optimal dosages of these key immune-modulating nutrients and compounds. The synergy of these key nutrients and compounds strengthens immune function and improves the process of inflammation.
Each ImmunoCharge capsule contains the same amount of powerful immune-modulating compounds. These include quercetin, resveratrol, vitamin D, vitamin A, selenium, zinc, vitamin C, N-Acetyl Cysteine, vitamin K2, and magnesium. These ingredients support the body’s natural immune mechanism to help maintain good health.
Rather than taking multiple different supplements to get these key nutrients, you can get the clinical doses within 4 capsules daily of ImmunoCharge. Take 2 capsules, 2 times daily with meals for optimal absorption or as directed by your healthcare practitioner. For advanced doses, take 3 to 4 capsules, 2 times daily with meals for optimal absorption or as directed by your healthcare practitioner.
Thyroid Strong
I recommend taking Thyroid Strong for better thyroid health and reducing thyroid-related female hair loss. It is a comprehensive freeze-dried, BSE-free, bovine, multiglandular, mineral, and herbal formula to support healthy thyroid function. It provides essential nutrient, herbal, and glandular support for the production of thyroid hormones.
Clinically, I use this product when I see that the patient is struggling to produce thyroid hormones. This can be indicated by an elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) or low T4 or T3.
Take 1 to 2 capsules first thing in the morning, away from food or as directed by your health care practitioner. For advanced doses take 3 to 4 capsules first thing in the morning, away from food or as directed by your health care practitioner.
Pro Omega Curcumin
To reduce inflammation, I recommend Pro Omega Curcumin. This unique formulation is the most powerful nutraceutical on the market for down-regulating inflammation and oxidative stress quickly.
It offers a powerful new solution for systemic cellular stress. This unique formulation combines concentrated omega-3s plus optimized curcumin and the potent antioxidants L-Glutathione and N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) to achieve complete functional support for long-term health.
This combination of nutrients synergizes to impact all the major inflammatory pathways while strengthening both the inside cellular mechanics and the outer cell membrane. The omega 3’s and curcumin help to reduce inflammation on the outer cell membrane. The L-glutathione and N-Acetyl Cysteine help to balance the immune system and protect the mitochondria and DNA.
Each nutrient plays a unique and yet complementary role in promoting a balanced immunological response by supporting optimal cell function. Together, these nutrients work within cells, tissues, and organs to improve antioxidant status, normalize metabolic activity, and fine-tune the critical cell signals.
Additionally, they help to strengthen the body’s detoxification capabilities. Use 3 capsules once daily with food or for advanced doses 3 to 6 capsules twice a day with food or as directed by your healthcare provider.
Menopause Hormone Support
I recommend using Menopause Hormone Support if you are experiencing menopause-related female hair loss. Menopause Hormone Support™ is a unique combination blend that is formulated to provide nutritional targeted nourishment for women during menopause.
It features specially selected herbs and nutrients that support the adrenal glands’ adaptive response as well as support circulation, relaxation, and overall well-being. Featuring a non-soy derived source of isoflavones, Menopause Hormone Support beneficially influences estrogen receptor function.
As a clinician, I see so many men and women struggling with estrogen dominance and the related symptoms. This supplement gives me confidence as a practitioner that I can help these individuals get over these issues much quicker than by simply making lifestyle changes. Use 1 capsule twice a day, for advanced dose 2 capsules twice a day, or as directed by your healthcare provider.
Final Thoughts
Hair loss doesn’t only affect men, but women too. Female hair loss can be frustrating, but fortunately, there are strategies to lower your risk or reduce hair loss. I recommend considering the lab tests suggested in this article to uncover underlying imbalances. I also recommend that you follow the natural strategies in this article to improve female hair loss.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. Our website offers long-distance functional health coaching programs with our world-class team of health coaches. For further support with your health and other goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!









There is some thing called G6PD where beans/peas etc.. kill the blood and make it die early causing the body to crash. There is a long list of triggers for the blood to die…peanuts/aspirin etc. A person may think they survived the food, but the next day they may be very sick. A person maybe low in iron and taking iron may clog blood vessels. A person may not know what to eat due to also having gluten etc.. issues. A person may lose hair fast due to the crash in health.