 Low FODMAPs Keto Diet for Digestive Health
Low FODMAPs Keto Diet for Digestive Health
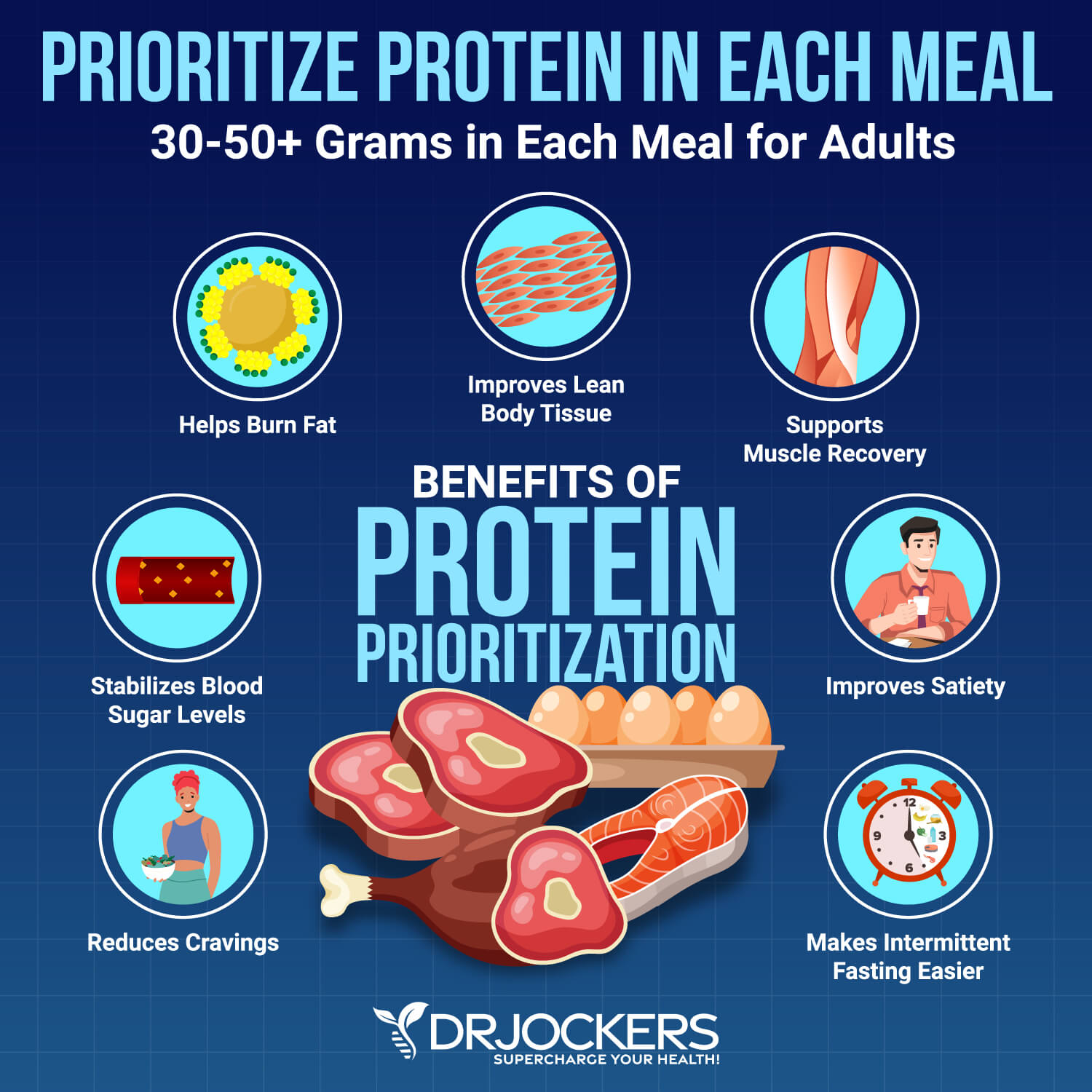
A powerful nutrition strategy for improving digestive and overall health is the ketogenic low FODMAPs diet. This nutrition plan combines two healing diets to eliminate troublesome digestive issues along with reducing inflammation, balancing your blood sugar, stimulating cellular autophagy, improving brain health, and more.
Digestive issues are very common and can be extremely aggravating. They have a wide range of symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, excess gas, bloating, and abdominal pain. Food is a common trigger of digestive symptoms, and even otherwise healthy foods can be problematic for some people.
If you are looking to address your digestive issues while improving your overall health, the low FODMAPs ketogenic diet may be your answer. This high fat, low carbohydrate diet limits FODMAPs (fermentable oligo, di- and monosaccharides, and polyols). These sugar-based carbohydrates include glucose, fructose, galactans, and lactose which are hard on our digestive systems.
Removing high FODMAPs foods helps to reduce digestive symptoms while supporting the overall healing process. By removing FODMAPs and following the ketogenic diet guidelines, you can experience the benefits of the ketogenic diet while improving your digestive health.
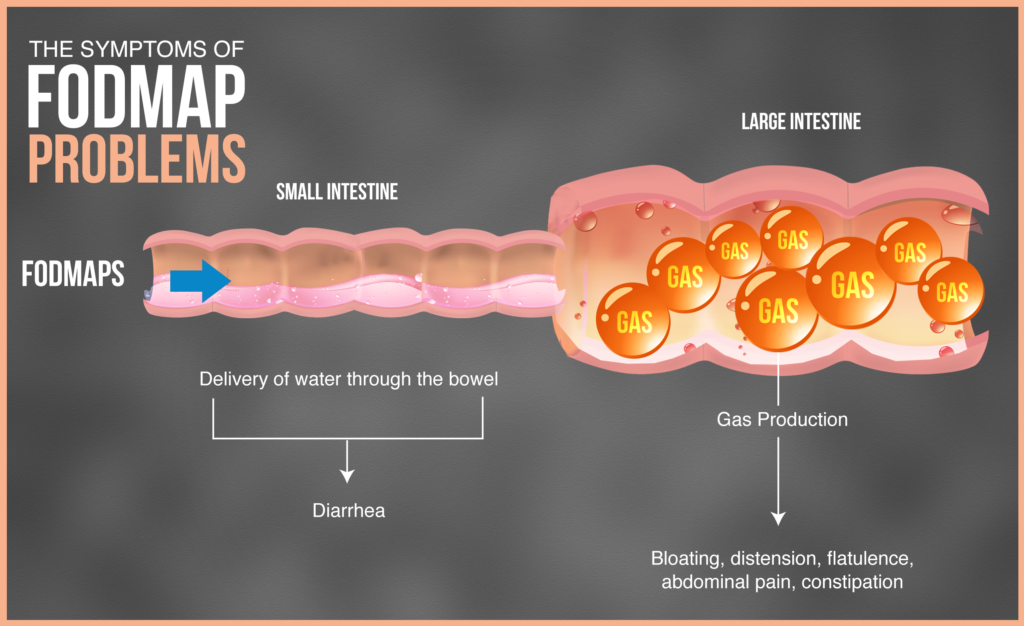
What Are FODMAPs?
FODMAPs are short-chain carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine. They pass along the gut to the large intestine and are fermented by bacteria. This fermentation results in many digestive symptoms like gas, pain, and bloating. A diet high in FODMAPs can contribute to functional gut disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
FODMAPs is an acronym for Fermentable Oligo, Di- and Monosaccharides and Polyols. These fermentable sugar-based carbohydrates include fructose, glucose, galactans, polyols, and lactose. They can be difficult for some people to digest and can lead to gastrointestinal issues.
A diet low in FODMAPs is effective for relieving gut symptoms such as bloating, gas, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation. People with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), IBS, and other digestive conditions can greatly benefit from a low FODMAPs nutrition plan. In fact, a low FODMAPs diet has been shown to significantly improve gastrointestinal symptoms in people with irritable bowel syndrome (1). For more information on the benefits of a low FODMAPs diet for improving digestive symptoms, read this article.
Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet is a nutrition and lifestyle plan that helps your body use fat (both stored fat and dietary fat) rather than sugar for fuel. When the body is in ketosis, it utilizes ketones as an energy source instead of sugar. Ketones are a preferred fuel source for the body and produce significantly more energy than glucose with less metabolic waste.
Transitioning from a sugar burner to a fat burner with a ketogenic diet can have amazing health benefits. The ketogenic diet stimulates cellular autophagy, lowers inflammation, balances blood sugar levels and your mood, improves mental performance, gives you energy, ends cravings, helps you lose excess weight and controls weight gain, and reduces your risk of chronic disease (2).
A major contributor to most chronic health conditions is inflammation. The ketogenic diet lowers inflammation by reducing the amount of free radical production, stabilizing blood sugar levels, and reducing insulin levels. The high fat, low carbohydrate ketogenic diet encourages healthy metabolism and enables your body to function at a more efficient level. To learn more about ketosis and its benefits, read this article.

How to Implement a Ketogenic Low FODMAPs Diet
The keto low FODMAPs diet is a high fat, moderate protein, low carbohydrate diet that eliminates foods that are high in FODMAPs. For the foods included in the diet, you will follow ketogenic diet guidelines: 70-80% of your calories from healthy fats, 15-20% from clean protein sources, and 5-10% from net carbohydrates (total carbs minus fiber).
What Foods to Include on a Keto Low FODMAPs Diet?
Foods included on this nutrition plan include low FODMAPs healthy fats, clean-sourced protein, nuts and seeds, low carbohydrate vegetables, low glycemic fruits, and herbs. These foods help to reduce inflammation and support the immune system.
Healthy Fats
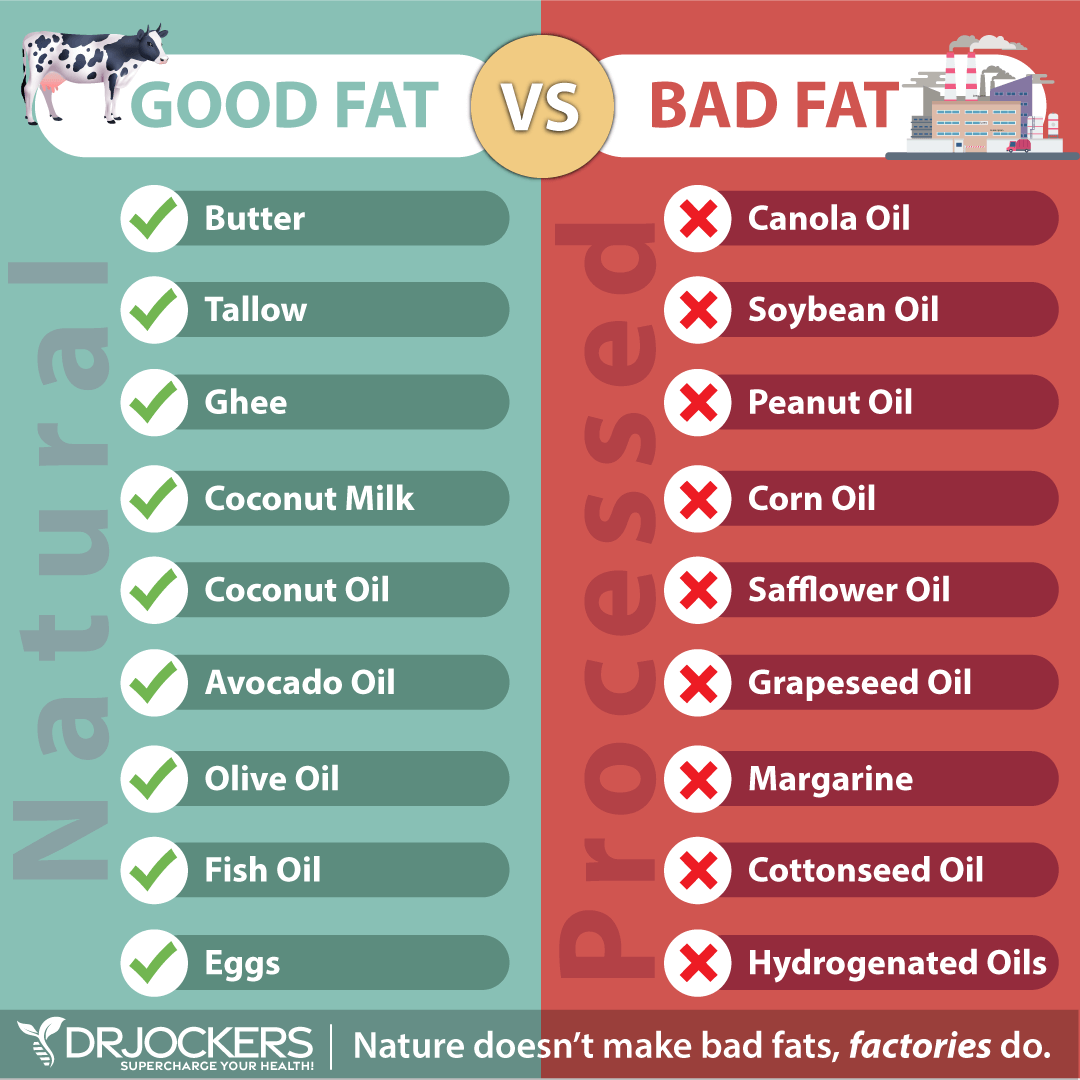
Consuming plenty of healthy fats is very important on the keto low FODMAPS diet. Healthy fats that are low in FODMAPS are found in coconuts, olives, and their oils and in grass-fed butter and ghee. Coconut milk is allowed, but coconut flour and coconut water are high FODMAPS and should be avoided.
Wild-caught salmon and grass-fed beef and dairy contain omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). These healthy fats are low in FODMAPS and an efficient source of fuel for the body to combat inflammation.
Clean Protein
Great low FODMAPS protein sources are grass-fed, pasture-raised, and organic meats. Beef, bison, lamb, buffalo, venison, chicken, pheasant, duck and turkey are all included. Eggs from pastured, organic chickens are an excellent protein source.
In addition to providing healthy fats, wild-caught fish such as Alaskan Sockeye salmon is a good source of protein. I am also a huge fan of drinking bone broth on a daily basis to get more collagen protein into your diet.
My favorite brand of liquid premade bone broth is Kettle & Fire (here) which I have found to be the very best on the market. Getting a great protein powder such as an bone broth collagen powder to provide collagen protein which is the building block for a healthy gut lining and connective tissue can be very helpful as well.
Nuts and Seeds
Pumpkin, flax, hemp and chia seeds are keto-friendly, low FODMAPS sources of protein and healthy fats. Macadamia nuts and walnuts and butters made from these nuts are good options.
Very small amounts of almonds and pecans (less than 15) are low in FODMAPS. Cashews, pistachios, and almond meal are high in FODMAPS and not allowed on this plan.
Low Carbohydrate Vegetables, Low-Glycemic Fruits and Herbs
A variety of lower-carbohydrate, low-glycemic, colorful vegetables and fruits should be included for their abundant antioxidants and phytonutrients. Examples of low FODMAPS keto friendly vegetables are collard greens, cucumbers, green beans, okra, zucchini, and leafy greens like kale, Swiss chard and spinach. Low-glycemic fruits to include on the keto low FODMAPS diet are blueberries, raspberries, strawberries, lemons and limes, and coconuts.
Herbs like rosemary, oregano, basil, cilantro, sage, and thyme have healing properties and should be included in the keto low FODMAPS diet. Black pepper, nutmeg, cinnamon, cumin, ginger, turmeric, pink salt, and nutritional yeast are also included.
Other Foods to Include
Stevia is a natural, low FODMAPS sweetener that you can include in the ketogenic diet. Be sure to check the stevia label for added sugar alcohols which are high in FODMAPS. Apple cider vinegar, almond butter, 80% or higher dark chocolate are low FODMAPS and keto friendly.
Many beverages are high in FODMAPS such as chai tea, ginger tea, coconut water, and many alcohols. Low FODMAPS beverages that are good options on the ketogenic diet are black tea, coffee, green tea, peppermint tea, and water.

Foods Excluded on Keto FODMAPs diet
The keto low FODMAPs diet eliminates foods that are high in FODMAPs and additional highly pro-inflammatory foods.
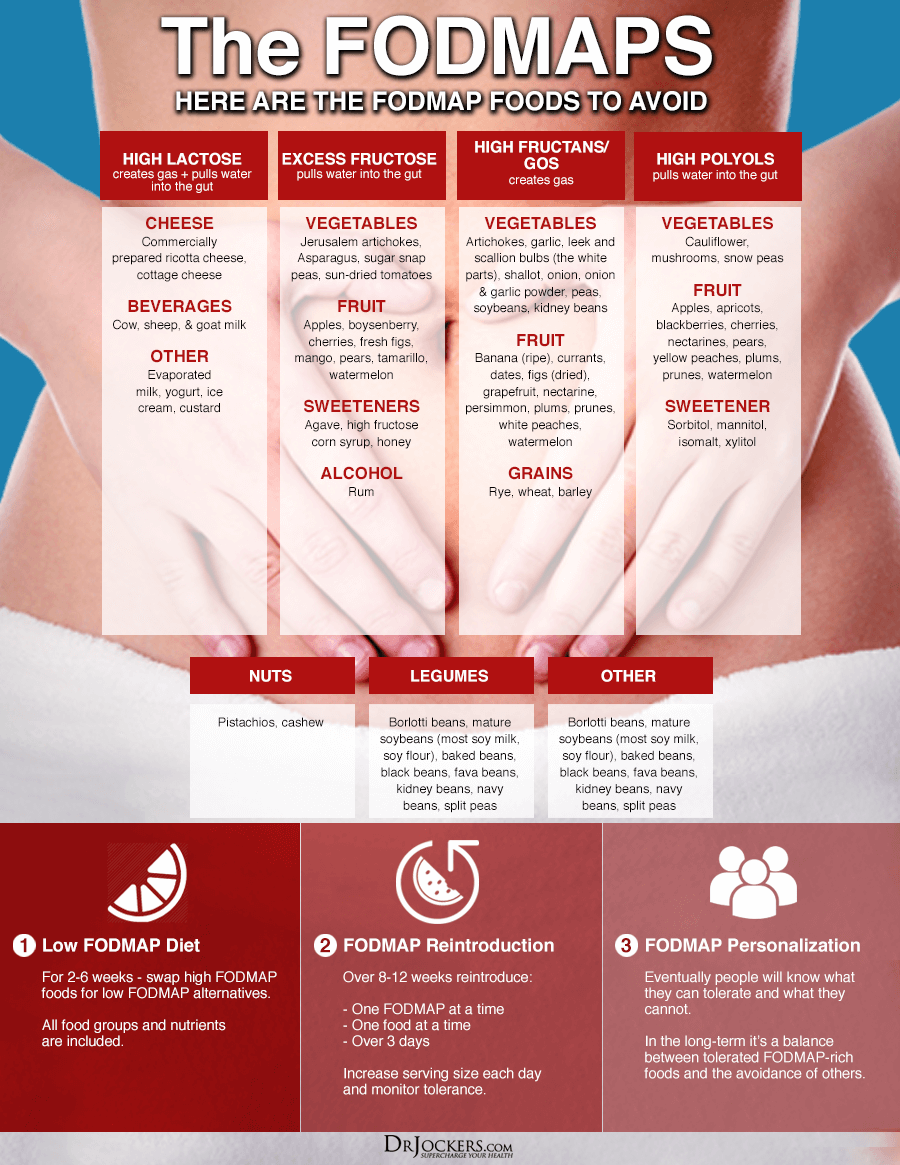
Foods High in FODMAPs
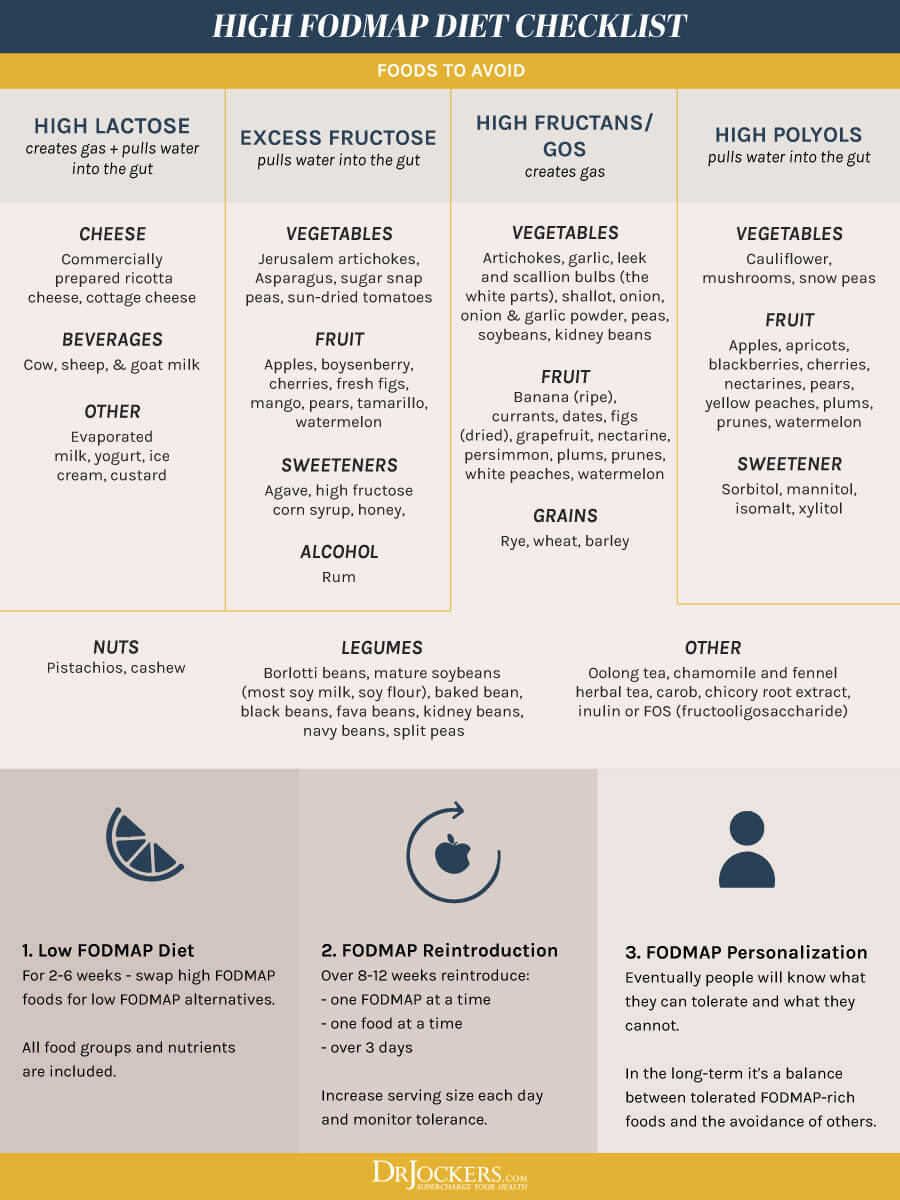
FODMAPs can be found in a range of different foods including some healthy foods (3). The foods that should be avoided are:
- Oligo-saccharides (fructans): found in vegetables (artichokes, beets, asparagus, onions, garlic, mushrooms), wheat, rye
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (galactans): found in legumes and pulses (chickpeas, kidney beans, lentils, butter beans, black-eyed peas, soybeans)
- Disaccharides (lactose): milk, yogurt, and cheeses like cottage cheese, cream cheese, and ricotta
- Mono-saccharides (excess fructose) found in fruits like apples, apricots, cherries, figs, mangoes, peaches, pears, plums, and watermelon, sweeteners like agave nectar, corn syrup, and honey
- Polyols (sorbitol and mannitol) found in fruits (apricots, avocados, blackberries, peaches, cherries), vegetables (cauliflower, mushrooms), sweeteners (sorbitol, xylitol, mannitol)
Inflammatory Foods to Eliminate
In addition to foods high in FODMAPS, it is important to eliminate foods that cause inflammation. These include:
- Gluten
- Sugar
- Refined carbohydrates (white flour, white rice, white potatoes)
- Conventionally raised meat and dairy
- Farm-raised fish
- Processed meats
- Trans fats (partially hydrogenated oils)
- Mono-sodium Glutamate (MSG) and other food additives and preservatives
- Highly processed vegetable and seed oils, such as canola, corn, sunflower, peanut, grapeseed, cottonseed, and safflower
- Artificial Sweeteners
These foods upregulate inflammation and create extra acidity in the tissues. They also damage the gut lining and alter the gut microbiome.

Foods High in Histamines
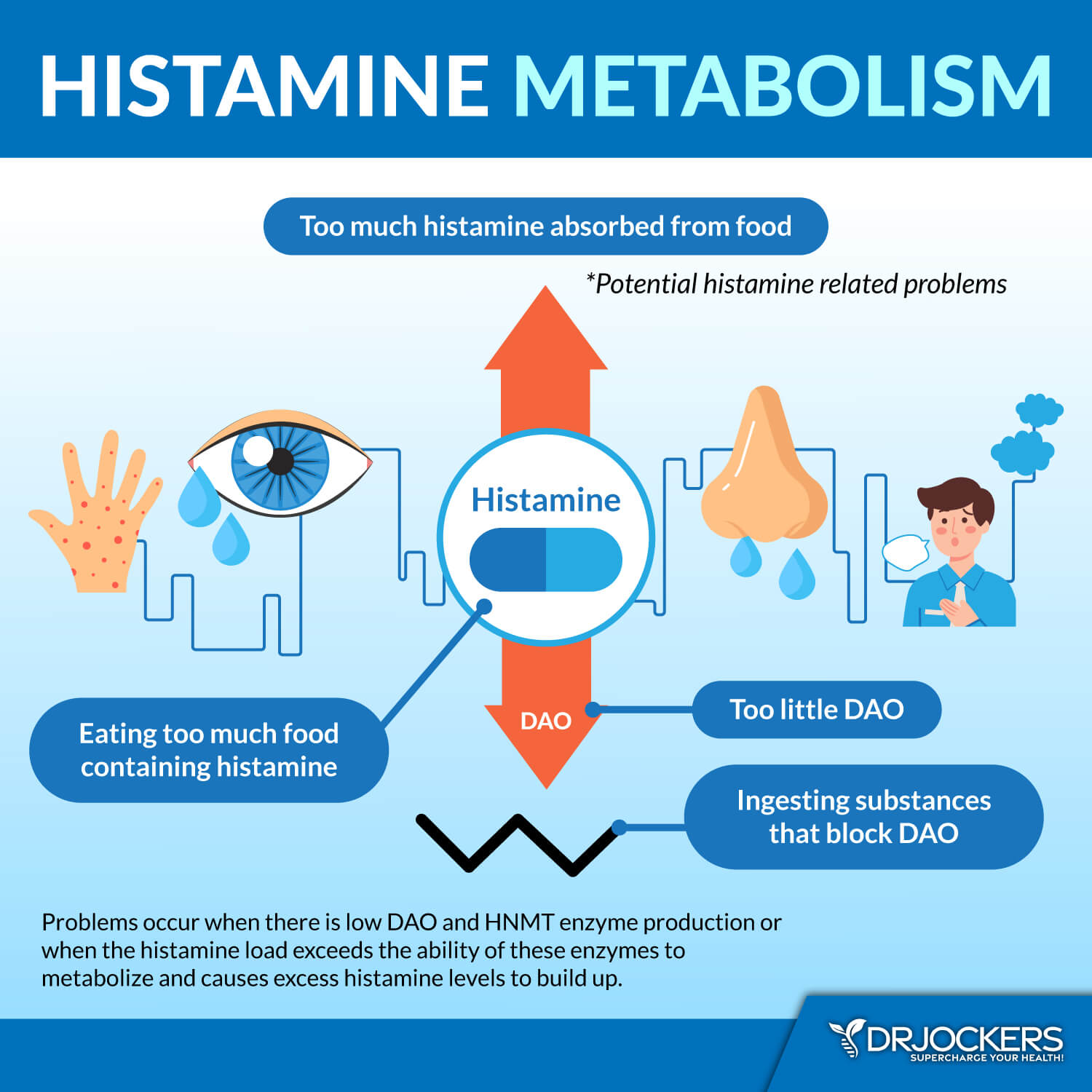
Many people who cannot tolerate high FODMAPS foods are also sensitive to foods high in histamines. Histamine is an inflammatory molecule that helps regulate immunity.
An individual with histamine intolerance has an exaggerated reaction to high histamine foods (such as fermented foods and beverages, vinegar, cured meats, soured foods, citrus fruits, dried fruits, aged cheeses, nuts, and processed foods) or foods that produce histamine (such as alcohol, cow’s milk, avocados, nuts, and bananas).
The causes of the exaggerated reaction to high histamine foods could be insufficient DAO enzyme production (needed for proper histamine metabolism) or elevated histamine levels. A low FODMAPS diet may improve histamine issues by down regulating the histamine overreaction or intolerance. For more information on histamine intolerance, check out this article.
How Long Should You Follow the Ketogenic Low FODMAPs Plan?
The length of time that a person needs to eliminate low FODMAPS foods will depend on the individual and the condition of their gut. Most people should reduce their FODMAPS intake for 4-8 weeks to determine if their digestive symptoms will respond to the low FODMAPS diet. For people with IBS, Crohn’s, or other major digestive disorder, removing these foods for longer periods may be necessary to allow the gut time to heal.
Once your gut symptoms have improved, you can reintroduce foods that contain FODMAPS. You should slowly reintroduce these foods, one at a time, noting any reactions and symptoms you may experience. This helps you to identify which of the high FODMAP foods you are sensitive to and how much of a food triggers your symptoms. After you have determined which high FODMAPS foods contribute to or trigger your symptoms, you can avoid only those foods.

Additional Strategies to Heal the Gut
To speed up the gut healing process, you should consider using liquid nutrition and adding gut enhancing supplements.
Fasting and Liquid Nutrition
Fasting and using liquid nutrition can speed up the healing process. Digesting solid foods creates significant stress on the digestive system, irritates the gut lining, and leads to inflammatory processes.
When we fast or use liquid nutrition, our bodies can conserve the energy used in digesting, processing and assimilating solid foods. Instead, the body can use this energy for healing and detoxification. Consuming liquid meals through shakes and smoothies is called a semi-elemental diet and has been shown to greatly improve the digestive health of individuals who struggle to digest FODMAP groups.
We can also do things like a water or bone broth fast to take stress off of the gut and reset the microbiome. Here is a helpful article on bone broth fasting and here is one on how to use fasting and liquid nutrition to heal your gut.

Gut Enhancing Supplements
Certain supplements can help to destroy pathogens, improve the microbiome, and repair the gut lining. Some of my favorites are:
Super DZyme: Key digestive enzymes to help assist the body to metabolize and digest food and absorb the nutrients within. Can assist with bloating and gas due to poor digestion.
L-Glutamine Powder: Key amino acid that is needed to repair the gut lining. L-glutamine reduces food sensitivities and gut inflammation. This also helps to reduce muscle tension and soreness and aids in detoxification.
Oxy-Powder: Oxy-Powder is a scientifically formulated, all-natural oxygen colon cleanser that safely relieves the bloating, irritation and constipation associated with a toxic colon. By using Oxy-Powder you can safely and effectively melt away the compaction from your small intestine, large intestine, and colon.
GI Clear: This is a blend of botanical extracts with a long history of use for supporting a healthy gastrointestinal microbial balance. The botanical substances in GI Clear™ are commonly represented on sensitivity testing provided by the major functional laboratories performing stool analysis.
These herbs can be used to reduce the microbial load and be an important part of reestablishing a healthy microbial balance. GI Regulator is great for helping to reduce pathogenic bacteria, yeast, and parasites.
Tips for Success on the Keto Low FODMAPs Diet
1. Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting while on the keto low FODMAPS diet is a fantastic strategy for improving your results. In addition to supporting the digestive healing process, intermittent fasting boosts the immune system, stimulates cellular autophagy, improves genetic repair mechanisms, improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases (8).
Start with a simple fast of 12 hours for 1-2 weeks and see how your body responds. This short fast is basically from dinner until breakfast the next day. You can increase your fasting time as your body adapts to not eating at certain times of the day. For the best intermittent fasting strategies and information on how to fast, check out this article.

2. Use Specific Enzyme Formulations
Digestive enzymes help support our body’s ability to break down carbohydrates, fiber, protein and fats from our diet. When our digestive system is stressed, we often under produce these key enzymes and this further compromises our digestive function.
When it comes to digestive enzymes, there are many different types. For an example, the enzyme cellulase breaks down plant cellulose fibers and the enzyme amylase breaks down starch and sugars. Lipases break down fats or lipids and proteases break down proteins into amino acids.
To better break down and digest FODMAPs, I recommend a specifically formulated enzyme mix. FODMATE™ is an innovative enzyme formula designed for short-term use that can help support digestive health, including relief from occasional cramping, bloating, gas, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation that may result from the consumption of high FODMAP foods.
3. Carb Cycling
After 2-3 weeks on the keto low FODMAPS diet, your body will become keto adapted. At that time, you can begin carb cycling to optimize your body’s metabolic needs. Carb cycling is alternating periods of lower and higher carbohydrate content in your diet.
To cycle carbohydrates, you eat 6 days of very low-carb meals and 1 day of higher-carb meals. If your body is signaling that it needs more carbohydrates, you can do a higher carb day every fourth day. For example, low-carb for 3 days, higher-carb for 1 day, low-carb for 3 days, etc.
On the higher carbohydrate days, you should consume 80-100 grams of carbohydrates. These carbohydrates should come from low FODMAPS foods with a low glycemic index and high nutritive value such as organic berries and sprouted quinoa.

3. Transition to Keto Slowly if Needed
If you are new to a low-carbohydrate lifestyle, it is helpful to slowly transition to a high fat, low carbohydrate ketogenic diet. However, you should immediately eliminate the high FODMAPS and highly inflammatory foods discussed above. For people who are already on a lower-carbohydrate diet, you can transition most quickly into the low FODMAPS ketogenic diet.
The best way to start if you are new to a low-carbohydrate lifestyle is to replace the sugars, refined carbohydrates, grains and starches with healing root vegetables like carrots and low glycemic berries. You should also increase your healthy fat intake with the good fats listed above. By increasing your intake of healthy fats and decreasing your intake of carbohydrates, your body will adjust to this beneficial way of eating.

4. Bonus Tips
More tips for being successful on the ketogenic low FODMAPS Diet are:
- Optimize Your Hydration: It is critical to stay hydrated when on a ketogenic diet. Drink at least half of your body weight in water. A great strategy is to super hydrate first thing in the morning.
- Get Plenty of Sodium and Minerals: On a low carbohydrate diet, your body will not retain sodium as it does on a high-carb diet. You will need to get plenty of sodium from generous amounts of pink Himalayan sea salt. Cucumbers are an excellent low carb source of natural sodium.
- Prioritize Good Sleep and Rest so your body can heal properly. You need at 7-9 hours of high quality sleep and every hour of rest before midnight is equivalent to 3 hours of sleep after midnight. Aim to be in bed by 10pm each night. If you struggle to sleep, read this article to improve your sleep quality.
- Supplement with Digestive Support such as Betaine HCL, ox bile and digestive enzymes for proper digestion.
- Consider Using Keto Support Supplements: This includes things like MCT oil to support ketosis. MCT oil is refined from coconut oil and provides a readily absorbed source of ketones.
- Healthy Mindset: Don’t make a big deal about the foods you are eliminating but instead stay focused on the foods you can consume. If you keep thinking about what you cannot have then it makes this plan so much harder to follow. Enjoy the foods you are able to eat and stay focused on those!
- Consume Enough Calories: Make sure you are consuming enough calories in your meals. Calorie restriction for a prolonged period can shift your body to a state of conservation and negatively affect hormone levels. Eat until you are comfortably full.

Testing for Digestive Health
If you are struggling with digestive symptoms, there are several tests you can do to assess your digestive health.
Organic Acid Test
The OAT is a valuable test for people with a variety of health conditions. If you have sleep abnormalities, fatigue, accelerated aging, autoimmune disorders, digestive challenges, chemical sensitivities, weight gain, and blood sugar dysregulation, you could benefit from the Organic Acids Test.
This test can be helpful for people with symptoms of depression, anxiety, ADHD, autism, and mood changes. People with skin issues such as acne, eczema, dermatitis or gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, gas, distention, nausea, and acid reflux should consider this test. You can find information about ordering this test here: Comprehensive OAT.
GI-MAP™ DNA Stool Analysis
The GI-MAP is the most thorough stool test on the market. It is a comprehensive stool analysis that identifies the presence of multiple pathogenic microorganisms. It shows Candida and other fungi, parasites (both protozoa and worms), and opportunistic bacteria.
The GI-MAP is the only FDA-approved DNA test for gastrointestinal microbes and pathogens available. The GI Map also tests for H. pylori, viral pathogens, levels of normal bacteria, potential autoimmune triggers, and viruses, including cytomegalovirus and Epstein Barr virus. The GI Map reveals the health of your intestines with digestion, gastrointestinal, Secretory and Anti-gliadin IgA (immune response), and calprotectin (inflammation) markers.
Another great thing about the GI Map is that the test gives actionable biomarkers. The GI Map looks at all the major factors that can influence the health of the gut. For more information on the GI Map and a sample report, you can look here.
SIBO Breath Test
A low FODMAP ketogenic diet is very helpful for people with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). SIBO occurs when abnormally large numbers of bacteria are present in the small intestine. This can affect digestion and absorption of nutrients and lead to many acute and chronic conditions. Symptoms of SIBO include food allergies and intolerances, joint aches and muscle pains, mood swings, brain fog, weight loss, deficiency diseases, gas, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, fatigue and immune system dysfunction.
The Bio-Health SIBO Breath Test measures hydrogen and methane in the breath. These gases are produced by bacteria in the small intestine. Excess amounts of these gases indicate SIBO. Click here to learn more about this test.
Final Thoughts on the Keto Low FODMAPs Diet
A fantastic strategy for improving digestive issues and overall health is implementing a ketogenic low FODMAPS diet. With this healing nutrition plan, you can improve your digestive symptoms while experiencing all of the benefits of the ketogenic diet.
On the keto low FODMAPS diet, you eliminate foods that are high in FODMAPS and pro-inflammatory foods. You replace these foods with low FODMAPS healthy fats, clean-sourced protein, low carbohydrate vegetables, low glycemic fruits, herbs, and nuts and seeds.
The keto low FODMAPS diet can help improve digestive symptoms and help you to identify which high FODMAPS foods may be triggers. By removing these foods, your body has time to heal. After the elimination period, you can slowly reintroduce higher FODMAPS foods, noting any reaction.
Additional healing strategies to implement while on the keto low FODMAPS diet are fasting and liquid nutrition. You can also use gut enhancing supplements to speed up the healing process.
For anyone with digestive issues, there are options for testing to help determine the underlying cause of your issues and the overall health of your gut. The digestive health panel, GI Map, and SIBO breath test are excellent digestive health tests.
The keto low FODMAPS diet is a powerful strategy for anyone with digestive issues who also wants to reap the amazing benefits of the ketogenic diet. You can check out my Digestive Health Restoration program which helps to reshape and recondition your gut for optimal health.
Sources For This Article Include:
1. Staudacher J, Lomer M, et al., A Diet Low in FODMAPs Reduces Symptoms in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and A Probiotic Restores Bifidobacterium Species: A Randomized Controlled Trial, 2017 Oct., Gastroenterology, Vol. 153, Issue 4, p 936-947. Link here
2. Roberts, M., Wallace, M., et al., A Ketogenic Diet Extends Longevity and Healthspan in Adult Mice. 2017 Sept., Cell Metabolism, Vol. 26, Issue 3, p 539-546. Link here
3. Low FODMAP Food Chart, IBSDiets.org. Link here
4. Mattson MP, Longo VD, Harvie M, Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. 2017 Oct, 39: 46-58; PMID: 27810402








Thanks for sharing with us your knowledge. I really need to start a keto low FODMAP diet for my IBS and other problems related to the gut. Is black pepper low fodmap?
Hi Eleanor, Yes, I recommend black pepper and other herbs and spices referenced above as part of a keto low FODMAPs diet.
Are all the recipes on your website low fodmap and keto? I need to do both at the same time and I wanted to make that all the recipes wre both low fodmap and keto. Thanks for your help!
No they are not all low FODMAP and keto, you will need to go through them and figure out which ones will work!
Is there a way to figure them out quickly and easily? Is there a formula or method I can use? I am confused and the task seems very difficult. Thanks
Yes here is a helpful article: https://drjockers.com/beat-digestive-problems-low-fodmap-plan/
I think what you are presenting on your site, the keto diet along with low fodmops would be ideal for me. I definitely cannot tolerate high fodmops foods, have gluten sensitivity, increasingly worse IBS symptoms, etc. Is your special program that you are offering for $97 a keto/low fodmop diet, assuming? Would it be easy enough for me to follow a keto/low fodmop diet on my own based on your guidelines, without doing your special program?
Hey Elizabeth, our digestive health program isn’t a keto low FODMAP plan but does go over a lot of helpful strategies. You can try following this based on the guidelines in the article.
Excellent article. You mentioned worms and other bad bugs and I wondered what you think of taking Demetrius Earth (food grade)? Also, are raw milk products from a certified company better than pasteurized milk products. What about beet powder and the veggie and fruit supplements. Thank you so much.
Yes, Food grade Diam Earth can be helpful. Yes raw, grass-fed milk is best. Beet powder can be helpful as can greens powders in some cases.