 Collagen: 9 Reasons Why This Improves Your Health
Collagen: 9 Reasons Why This Improves Your Health
Everyone is talking about collagen these days and for good reason! Collagen is a unique supplement because it has both external and internal health benefits.
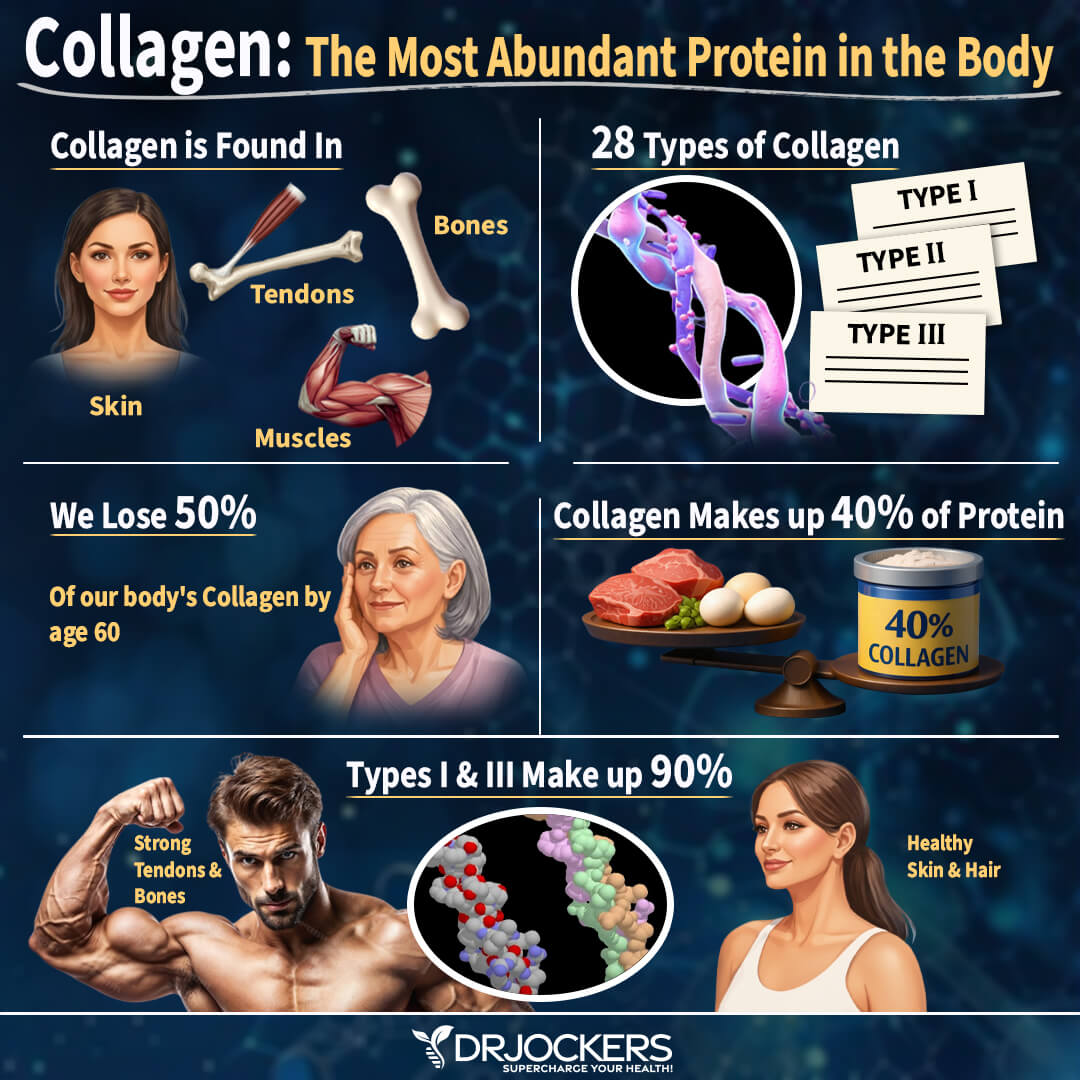
It is the most abundant protein found in the body. In fact, it makes up about a third of the body’s protein content. It also gives structural support to the body and is the primary substance of connective tissue. It is the glue that holds our bodies together.
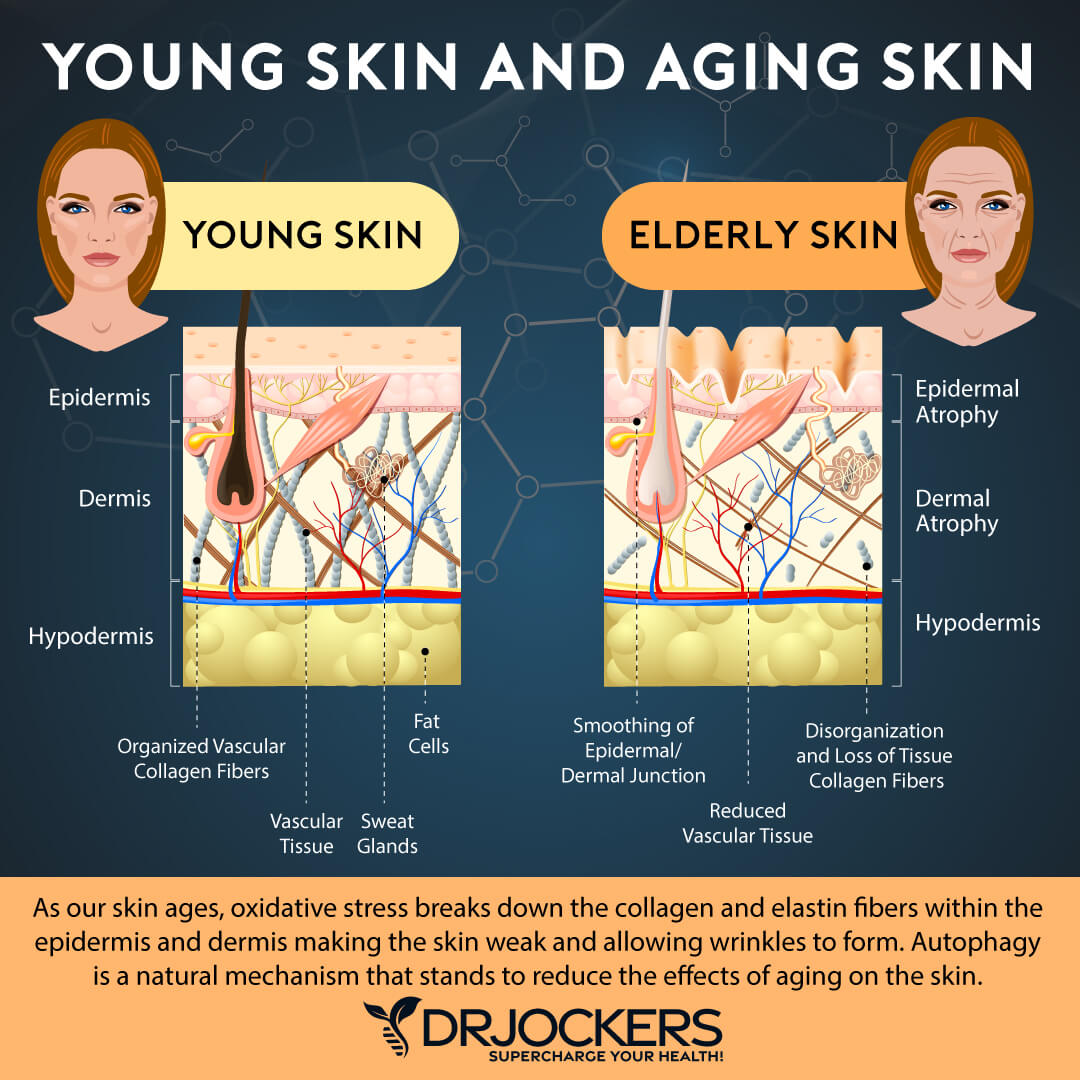
As we age, our body’s natural production of collagen slows down. We notice this in our skin, which is no longer as firm and smooth. In addition to our skin, the decrease in production affects the health of our gut, joints, ligaments, hair, nails, teeth, and bones. A lack of this vital nutrient can even impact vital organs like the heart and liver.
Fortunately, there are steps you can take to improve your levels. Consuming foods rich in collagen-promoting amino acids, vitamins, and minerals and supplementing with a high-quality collagen powder are effective strategies.
This article will discuss what collagen is, including the different types and sources. I will also review the nine ways it improves your health, including healing the gut, supporting metabolism, strengthening bones, joints, and ligaments, and more. Finally, I will discuss the best ways to boost your own production, slow its breakdown in the body, and the best form of supplementation to ensure you have optimal levels.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is a structural protein and the most abundant protein in our bodies. It forms connective fibers in tissues such as skin, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and teeth. It also gives bulk, shape, and support to bones, blood vessels, and organs such as the heart, kidneys, and liver. Finally, it is the intracellular “glue” that holds your body together.
Collagen is manufactured by specialized cells called fibroblasts. These cells are capable of incorporating amino acids into the distinctive strands that constitute this molecule.
The primary amino acids found in collagen are glycine, lysine, and proline, accounting for around 50% of its amino acid content. Lysine and proline are converted to hydroxylysine and hydroxyproline before they are incorporated into the structure. Vitamin C is required for this important conversion. Additional amino acids involved in the process include arginine, leucine, glutamine, and tyrosine.
Collagen’s Role in Aging
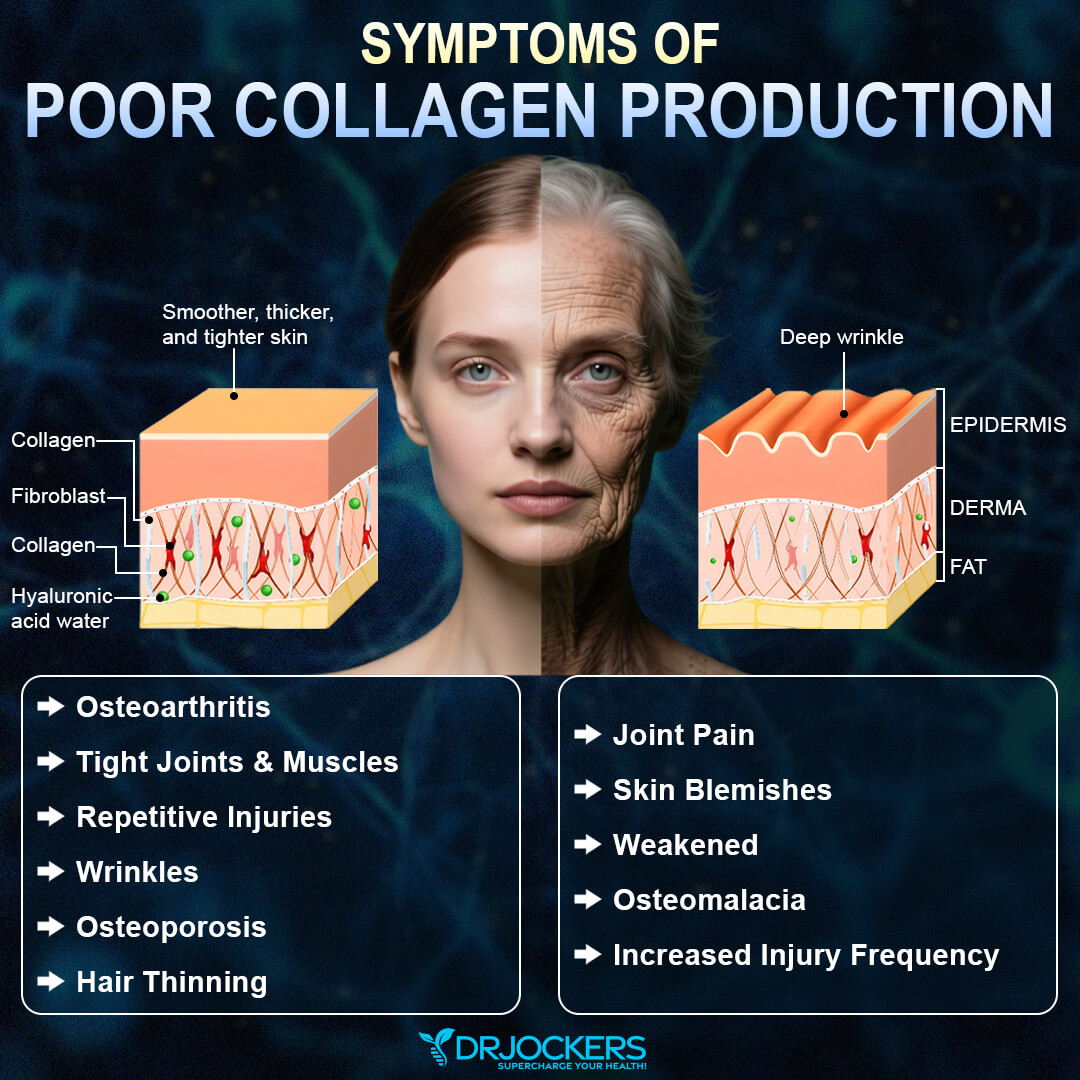
Collagen is constantly destroyed and regenerated as part of our body’s natural cycle. Our bodies are continually making it to maintain and repair connective tissues. As we get older, we get faster degradation on top of slower production from the body. This is when we begin to see and feel the effects of lower collagen.
In addition to the natural aging process, there are environmental causes of reduced collagen. Environmental factors contributing to its destruction include UV rays from the sun, stress, and toxins in food and water. Smoking and eating a diet high in sugar and processed foods also contribute to this.
Antioxidants play a protective role from free radical damage. They also support the formation and incorporation of collagen into various tissues. The most important antioxidant for this is vitamin C which protects and boosts its production. Coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E are also key players.

Types of Collagen
There are at least sixteen different types of collagen in the human body (1). All sixteen types contain a repeating glycine-proline-hydroxyproline sequence and fold into a characteristic triple-helical structure. The various types are distinguished by the ability of their helical and nonhelical regions to associate into fibrils, to form sheets, or to cross-link different types.
The most common types are Type I, II, III, IV, V, and X. Type-I is made of eosinophilic fibers. Over 90% of the collagen in the human body is Type-I.
Type-I collagen helps form tendons, ligaments, organs, and skin. It is the main component of the organic part of bone. Type-I is also found in the gastrointestinal tract and is important for wound healing, giving skin elasticity, and holding tissue together.
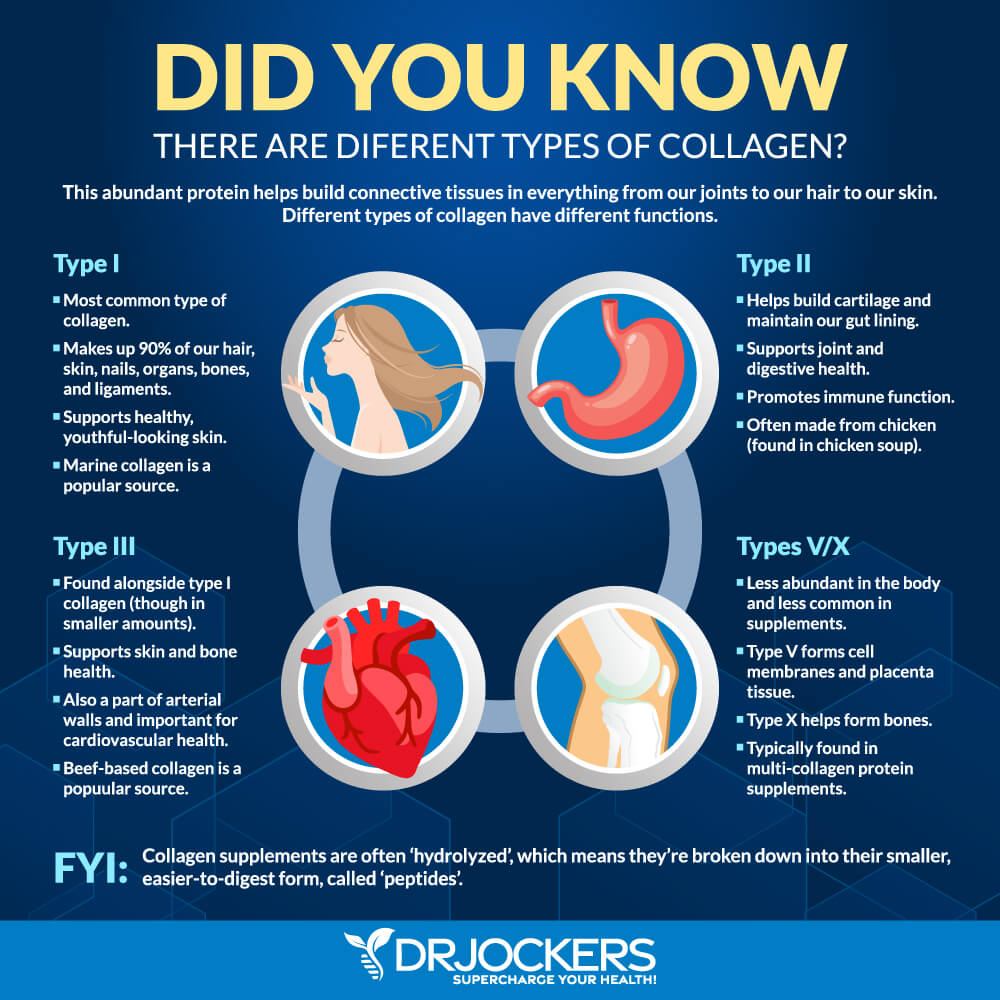
Type-II collagen is fibrous and found in cartilage. Type-III is made of reticular fibers and is usually found along with Type-I in the body. Type-III gives skin its elasticity and firmness. It forms the connective tissues that give shape and strength to organs.
Type-IV collagen forms extracellular structures called basal lamina. Basal lamina supports epithelial and endothelial cells and surrounds muscle and fat tissues. Type-V is found in cell surfaces, hair, and the placenta. Type-X collagen aids in bone formation and the growth, development, and remodeling of articular cartilage (2). These different types of collagen are found in certain foods or collagen supplements. As you can see, they all play fundamental structural roles in the body.

Where Can We Get it?
Collagen comes from different high-protein food sources including chicken, beef, fish, and eggs. Depending on the source, each type has unique benefits. Chicken is highest in type-II and provides chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate. This makes it beneficial for joint health and anti-aging effects.
Bovine collagen from cows is made mostly of type-I and type-III. It is rich in the amino acids glycine and proline. Bovine collagens are great for creatine production, building muscle, and aiding in the body’s own production.
Fish collagen provides mostly type-I and the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. Fish collagen is easily absorbed and benefits digestion, organs, blood vessels, bones, joints, and skin.
Egg collagen is found in the shells and white of eggs. It contains different types but is mostly type I. Egg collagen provides glucosamine sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid, and other amino acids. Egg collagen helps build muscle mass, reduce pain and stiffness, build connective tissue, and heal wounds.

9 Ways Collagen Can Improve Your Health
Collagen is the main protein in connective tissue. Connective tissue is the material that forms the structural framework for organs, bones, eyes, tendons, muscles, skin, blood vessels, lymphatics, tendons, cartilage, and bones. Along with this important role, collagen has numerous health benefits.

Supports a Healthy Metabolism
Collagen supports a healthy metabolism. It provides co-factors such as glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid, and key electrolyte minerals.
It also provides a good amount of the amino acid glycine. Glycine has the important role of helping form muscle tissue by converting glucose into energy to feed muscle cells. Because of this, it can add lean muscle mass and help with the conversion of essential nutrients.
Containing the amino acids arginine and glutamine, it also supports the metabolism in another way. Arginine boosts the body’s ability to make protein from other amino acids while glutamine provides carbon and nitric oxide which are important for building and maintaining muscles (3). Glutamine also provides fuel to our cells to maintain energy levels.
For anyone trying to lose weight, collagen can support your weight loss efforts. It stimulates the release of satiating hormones into the bloodstream which can help reduce appetite.
Collagen can also support weight loss efforts by being very filling. One study found collagen to be 40% more filling than other protein powders. Participants also consumed 20% less at their next meal than individuals who consumed whey, casein, or soy protein powders (4). Using a high-quality collagen powder can be an effective metabolism-boosting and weight-loss strategy.
Helps to Repair and Heal Leaky Gut
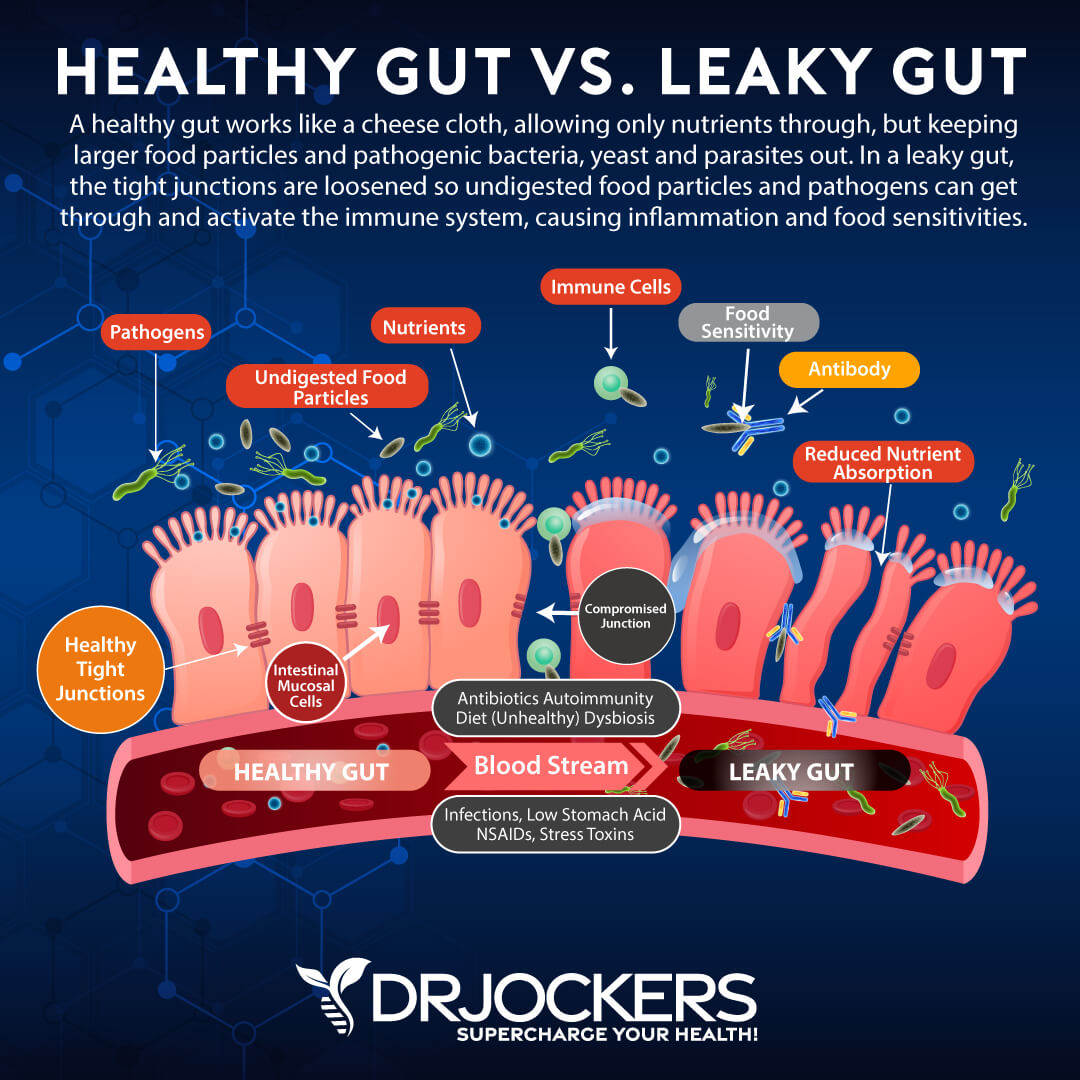
A huge benefit for today’s society is collagen’s ability to repair and heal the gut. Leaky gut syndrome, or intestinal hyperpermeability, is a condition in which the tight junctions in the gut lining become too large and abnormally permeable. Undigested food particles and toxins can pass through these holes in the intestinal wall and into the bloodstream. This causes the immune system to overreact which results in chronic inflammation.
There are several mechanisms by which it repairs and heals the gastrointestinal system. First of all, it makes up the villi, small finger-like structures on the intestinal wall. The amino acids glycine and glutamine are essential for healing the protective lining of the gastrointestinal tract. These amino acids seal the holes in the gut by healing damaged cells and building new tissue.
Collagen can also benefit other gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It soothes and heals the gut and can also assist with water absorption in the intestines. For anyone suffering from leaky gut or other gastrointestinal issues, supplementing with collagen is an effective healing strategy.
Collagen Strengthens Bones, Teeth, and Nails
Did you know that bones are around 1/3 collagen? It actually gives bones their flexibility. Adding more of this protein to your diet can make your bones stronger by increasing bone mineral density. Improving bone mineral density is also vital for ensuring that your teeth stay securely in your jaw.
It can also strengthen bones by stimulating osteoblasts. Osteoblasts are the cells that make bone. Because of this ability, supplementing with collagen has been shown in numerous studies to prevent and even reverse osteoporosis (5).
It helps maintain healthy teeth and gum tissue. In fact, collagen fibers help anchor our teeth to our gums. Collagen is present in the dental papilla, the part of the gum that sits next to the teeth, in the tooth germ, and in the enamel of the teeth (6). Finally, supplementation can also prevent brittle and broken nails and support nail growth.

Collagen Improves the Quality of Skin and Hair
Collagen is an essential building block of the skin. In fact, 70% of the protein in our skin is made of it. With collagen’s unique ability to help renew and repair cells, good skin integrity depends on higher levels of this vital building block.
It is one of the few anti-aging supplements that has research supporting its claims (7). It helps form elastin and other compounds within the skin, improving skin elasticity and skin moisture. The hyaluronic acid in it holds water and forms a gel-like substance that hydrates the skin and hair. It is one of the best ways to maintain your skin’s youthful tone, texture, and appearance.
It is also essential for healthy hair as it is part of your hair follicle stem cells, which help create new hair. A deficiency can trigger premature hair loss. The collagen in your hair also gives it structure and a healthy bounce. When there is not enough, hair is weak, brittle, and dull.
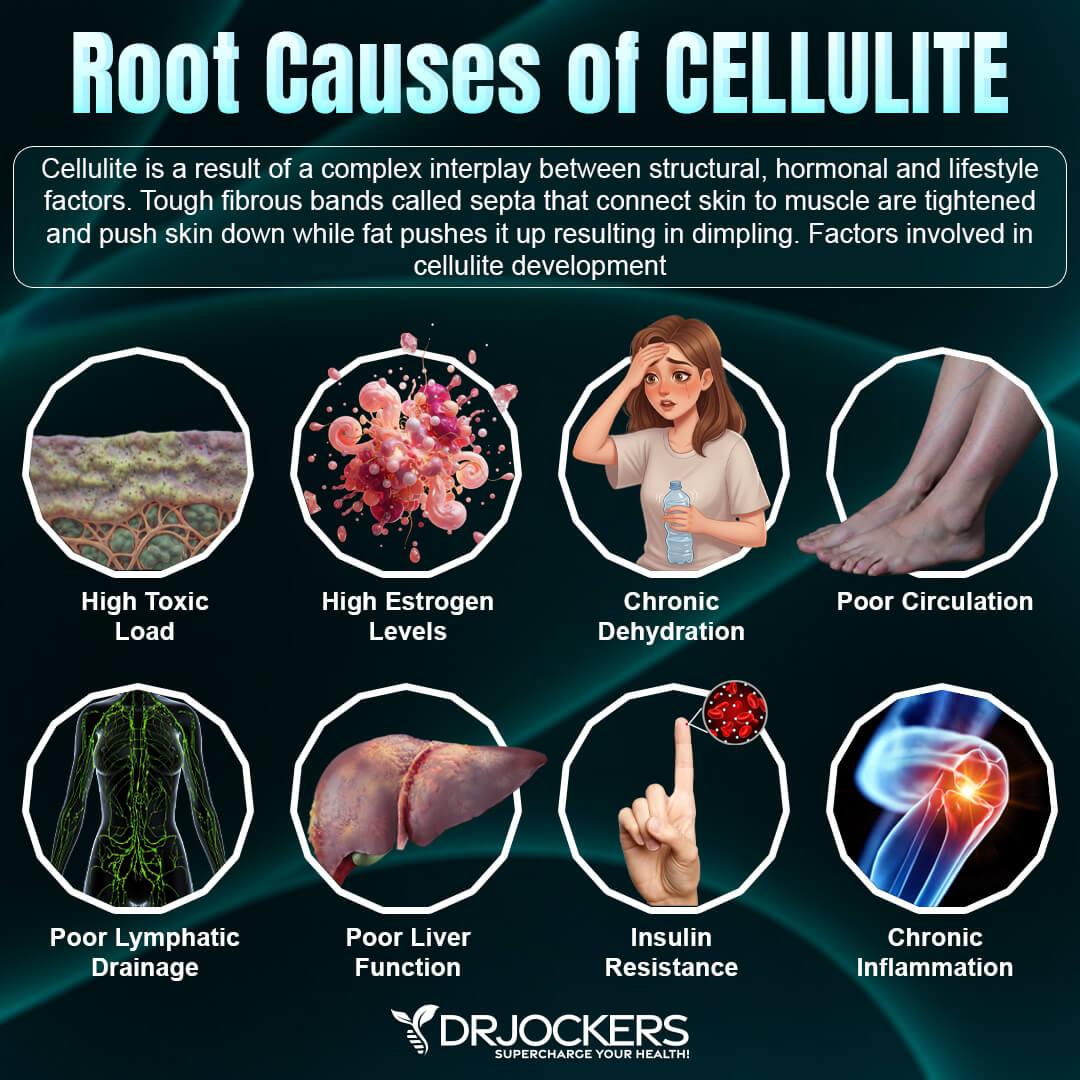
Reduces Cellulite and Stretch Marks
Collagen helps reduce the appearance of cellulite and stretch marks. When our levels are low, skin loses its elasticity and becomes thinner. This makes cellulite and stretch marks more obvious.
By strengthening the dermis layer of our skin, collagen plays an important role in hiding cellulite. Supplementation has been shown to increase skin-collagen expression and improve elasticity and thickness (8). This is important for hiding fat cells underneath the skin and reducing the appearance of cellulite and stretch marks.
Protects the Heart
Collagen keeps your heart healthy. Being the most abundant protein in the heart, it provides a structural framework for cardiac muscle cells. It also provides stiffness to the walls of the heart and aids force transmission so that the heart can pump blood (9).
In addition to being abundant in heart tissues, the walls of blood vessels are made of collagen and elastin. It keeps blood vessels strong, the inside of arteries and veins smooth, and blood pressure controlled. Its amino acids proline and lysine help to disintegrate plaque deposits and repair tissue in the arteries (10).
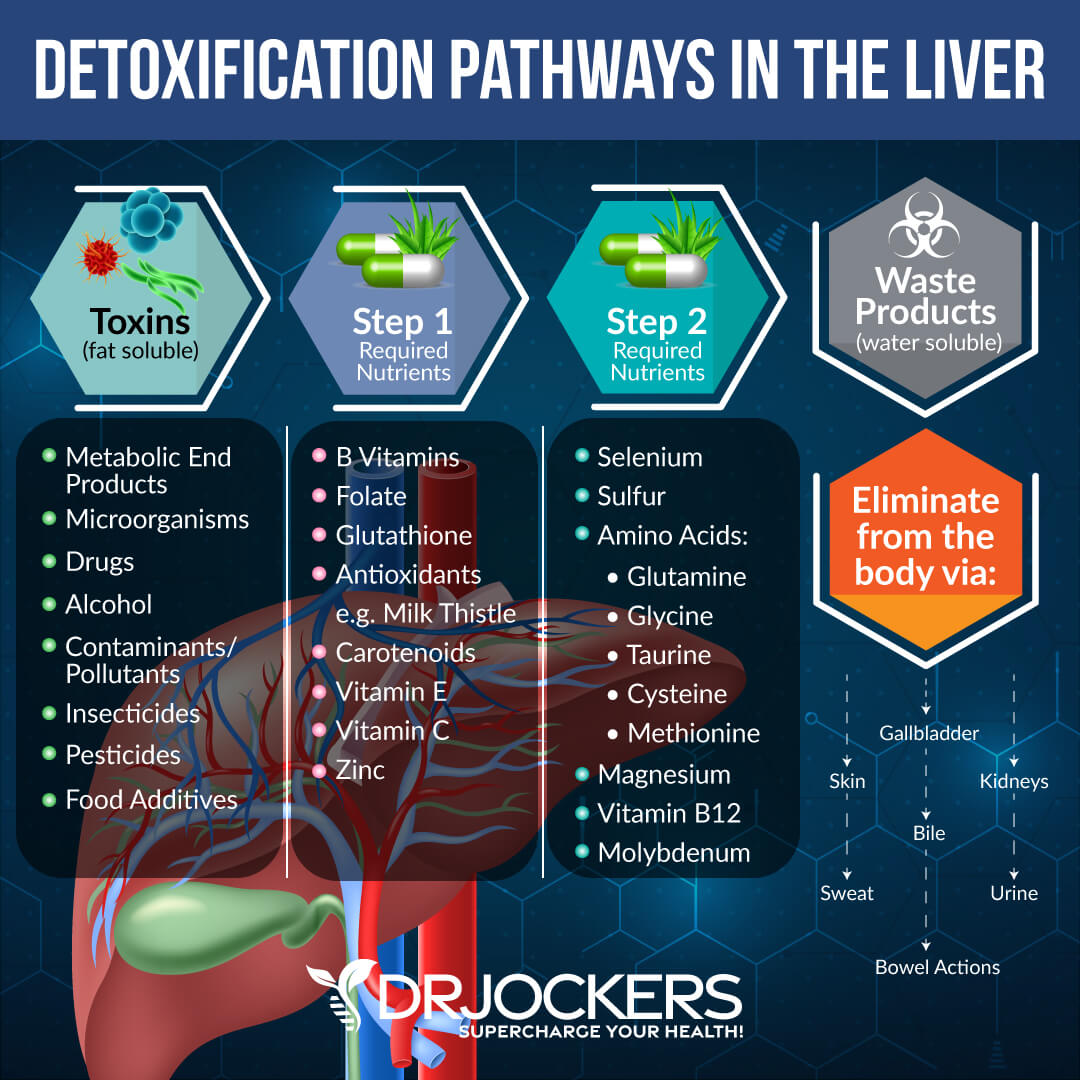
Supports the Liver and Detoxification
The liver is the largest organ in the body and the primary organ for detoxification. It has detoxification pathways that filter the blood to remove large toxins and enzymatically break down unwanted chemicals. It is also designed to transform toxic substances into compounds that can be excreted from the body. As you are exposed to more toxins, the liver’s ability to detoxify can be weakened. This can result in toxins being stored in our tissues and cells rather than eliminated.
The glycine found in collagen can help with detoxification and reduce damage to the liver from toxins. In fact, glycine has been found to prevent liver damage and minimize liver damage from alcohol (11). It also helps the digestive system expel waste and improves the body’s use of antioxidants. Antioxidants aid the body’s detoxification system.
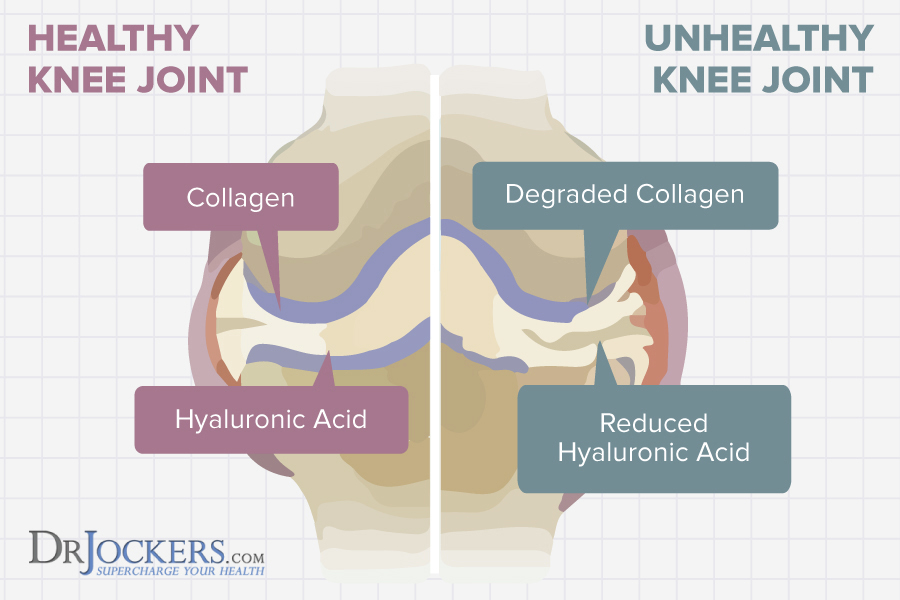
Repairs and Strengthens Joints, Tendons and Ligaments
Collagen is gel-like and smooth. It covers and holds our joints together, helping our joints move more easily. It also makes up ligaments and tendons, the connective tissue that attach and hold together bones and muscles. When our ligaments or tendons are injured, the body produces more of it to heal them.
Collagen supports the body’s ability to produce chemicals that naturally support healthy joints. It also provides chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate which support healthy joints and the body’s ability to build and repair cartilage. The hyaluronic acid in it holds water and forms a gel-like substance that surrounds the tissues around nerves and is found in the synovial fluid between joints. This hyaluronic acid lubricates and cushions joints, serving as a “shock absorber”.
It may also benefit the small cells found within the cartilage of joints. These small cells are called chondrocytes. Chondrocytes produce new collagenous tissue and mucopolysaccharides (glycosaminoglycans) to keep joints cushioned and lubricated.
One study found that collagen improves pain and function in people with osteoarthritis and other arthritic conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis (12). It has also been shown to improve joint pain in athletes (13). Supplementation can be an effective strategy for repairing and strengthening joints, tendons, and ligaments and reducing joint pain.
Improves Sleep Quality
Many people are looking for natural ways to improve their sleep. One solution may be collagen. It is high in the amino acid glycine. Glycine has been proven to be a therapeutic option for improving sleep quality (14).
Glycine is important for modulating cortisol at night and helping promote healthy relaxation. When cortisol levels are high at night, this can interfere with sleep. Using collagen before bed can help buffer high cortisol and promote relaxation.

How to Improve Your Levels
To improve your collagen levels, it is important to remove the environmental factors that encourage the breakdown, eat a healthy diet full of vitamins and minerals, and use a supplement. There are foods with vitamins and minerals that promote the body’s production, but the best way to ensure you are getting optimal amounts is with supplementation.

Vitamins, Minerals, and Amino Acids
Vitamins, minerals, and amino acids can promote the creation of collagen and slow its breakdown. Amino acids, including glycine, proline, lysine, and arginine, are needed for its synthesis. Around 21 amino acids are needed to form it and can be found in protein-rich foods. Some of the top amino acid protein sources are salmon, venison, beef, lamb, bison, and chicken. Bone broth is full of amino acids and rich in collagenous proteins. You can make bone broth at home with organic, pasture-raised, grass-fed bones.
A diet rich in vitamin C is also necessary for the body to produce collagen effectively. Vitamin C activates key enzymes needed for its synthesis, increases its production, and releases enzymes that inhibit its destruction. Foods rich in vitamin C include bell peppers, grapefruit and other citrus fruits, kiwifruit, broccoli, strawberries, and mangoes.
Wild-caught salmon and pumpkin seeds contain zinc, a trace mineral that has been shown to increase the cellular concentration of collagen (15). Berries and pomegranates contain ellagic acid which helps to prevent damage from UV rays (16).

Supplementation
Supplementing with a high-quality, organic collagen powder is an excellent way of ensuring you have optimal levels. This protein is different than whey and casein proteins because it contains a different balance of amino acids.
You will usually find these supplements in a form that is referred to as hydrolyzed. When hydrolyzed, it is reduced to small peptides which can be ingested. The hydrolyzed form contains 20 amino acids, predominantly glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline.
Up to 90% of the hydrolyzed form is digested and available as small peptides in the bloodstream. The peptides are then transported from the blood into the tissues where they act as building blocks for cells and boost the production of new collagenous fibers.
One of the best supplements on the market is the Multi-Collagen Protein which is rich in type I through V collagen to support healthy joints. This powder provides joint healthy chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate. Glucosamine and chondroitin support the body’s process of manufacturing collagenous tissue.
Vegetarian Collagen Source
The great news is that we have developed a technology that allows vegetarians to get the benefits of collagen boosting without having to consume bone broth or collagen proteins.
For years, orthosilicic acid was the focus of intense research because it was viewed as a potential collagen generator. As a result of that research, the molecular complex known as choline-stabilized orthosilicic acid (ch-OSA®) was created.
CollagenMax™ provides ch-OSA® (choline-stabilized orthosilicic acid), that helps naturally nourish your body’s beauty proteins. Regular orthosilicic acid is highly unstable, leading it to form polymers.
These polymers are too large for the human body to absorb. However, the patented “choline stabilization” technology in CollagenMax prevents the polymers from forming, ensuring optimal absorption. CollagenMax has been formulated with clinically proven ch-OSA for your assurance.
Conclusion
Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body. It helps give shape, strength, and integrity to many tissues, including your skin, bones, tendons, and heart. As we age, our bodies do not produce as much. This can affect our appearance and our health in many ways.
While there are many types, around 90% of that in your body is type-I. There are also different protein sources including chicken, beef, fish, eggs, and bone broth.
Its health benefits of include supporting a healthy metabolism, repairing and healing leaky gut syndrome, protecting the heart, supporting the liver and detoxification, and improving sleep quality. It also strengthens bones, teeth, and nails, improves the quality of skin and hair, reduces cellulite and stretch marks, and repairs and strengthens joints, ligaments, and tendons.
There are several strategies you can use to improve your own levels. You can remove the environmental factors, such as smoking and processed foods, and eat a nutrient-dense diet with amino acids, vitamin C, and minerals. One of the best ways to ensure optimal levels is to use a high-quality supplement.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and thrive in life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!







How do you use collagen when taking exogenous ketones?
However you would like! I like to put collagen in my shakes or coffee while I take Exogenous Ketones separately. There would be nothing wrong with taking them together if you wanted to.
Is there an effective pill form of collagen for those who do not like the taste?
Yes there is Kate!: https://amzn.to/2OfphUj
How much is the bone collagen
Thank you
You can find that here Rosa: https://store.drjockers.com/products/organic-bone-broth-collagen
Do you prefer the pill over the powder? You email Ed putting the powder in your coffee does it have a taste?
Hey Jennifer, No, the collagen peptides is tasteless and dissolves easily into hot or cold liquids! I recommend it!
How can I get all of these benefits if I’m histamine Intolerant? I’m so sad that I have this issue! 🙁 I want to be able to use collagen and eat these foods!
Hello Jann – this is the collagen boosting product we use for those who struggle with collagen proteins. It works really well: https://store.drjockers.com/products/regenmax-liquid
Dr. Jockers, thanks so much for an excellent article. Do the Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides rebuild cartilage? Maranatha!
Yes collagen peptides have been shown to help improve joint healing processes.