 The 12 Best Heart Healthy Foods
The 12 Best Heart Healthy Foods
The heart is a remarkable organ that beats around 100,000 times a day. It is only the size of your fist yet supplies every organ and cell in your body with oxygenated blood. Damage to the heart can reduce its pumping power, forcing it to work harder to keep up with the demands of the body. In this article, you will discover the best foods to support your heart and keep inflammation under control.
Heart disease is the number one killer of men and women in the United States and one of the top killers worldwide. The first step in preventing yourself from becoming a part of this statistic is to live a heart healthy lifestyle.
There has been a great deal of misinformation over past decades regarding the causes of heart disease with much of the blame being misplaced on saturated fats and cholesterol. We now know that chronic inflammation is the root cause of heart disease. While certain dietary components do play a large role in heart disease risk, eating in a way that is anti-inflammatory is one of the best ways to mitigate heart disease risk.
Heart Healthy Diet
The best diet to address this inflammation and reduce your risk of developing heart disease is the anti-inflammatory healing diet. This diet is a plant-emphasized diet of real food, including low glycemic vegetables and fruits, clean meat, and healing fats.
This style of eating helps to address one of the leading causes of chronic inflammation, blood sugar imbalance. In fact, a ketogenic diet may be even more powerful for mitigating your risk of heart disease.
In addition to a meal plan that stabilizes blood sugar, it is critical to consume foods that have been shown to support and protect the heart. This article will discuss the 12 best heart healthy foods and the foods you must avoid if you want to protect your most vital organ system.
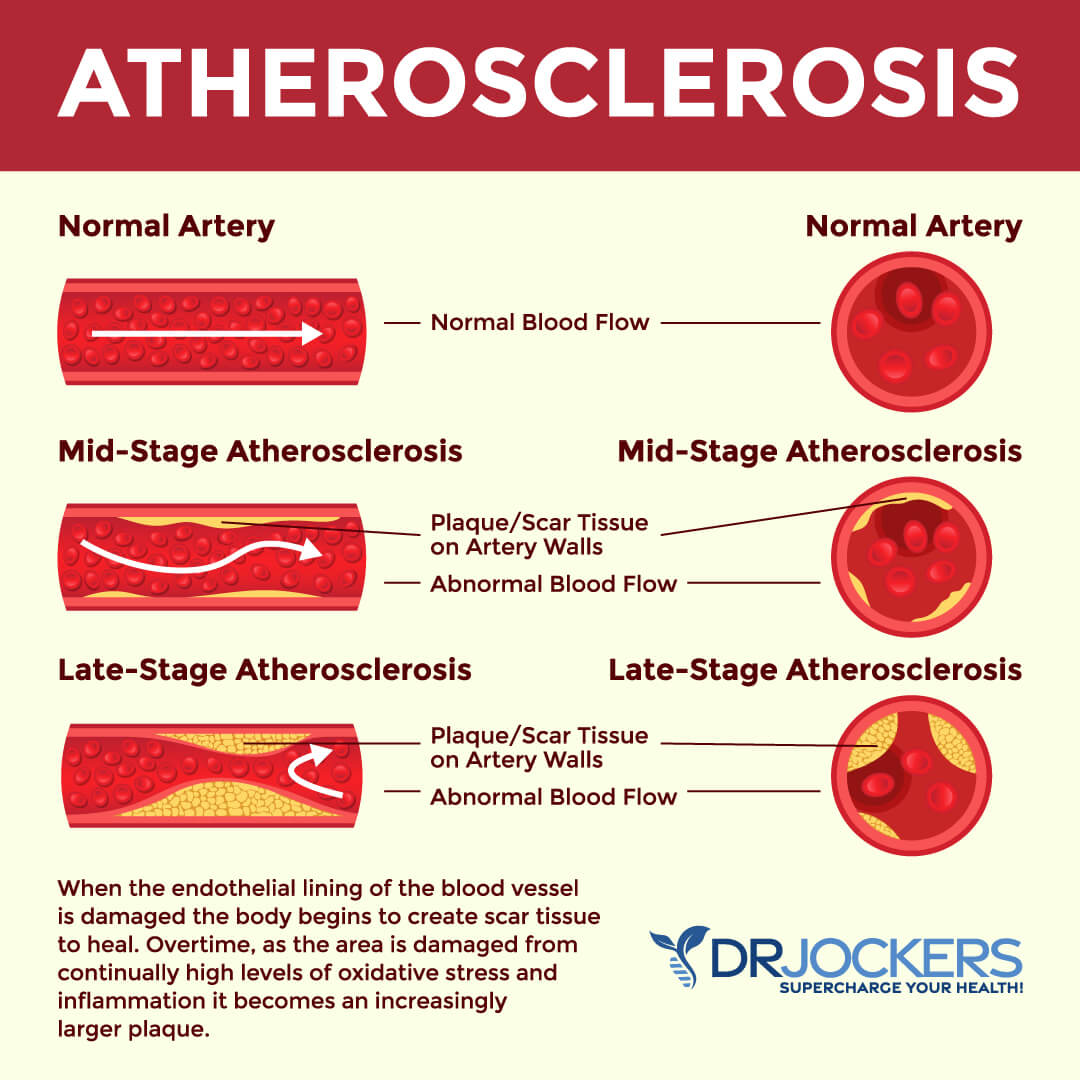
What are the Causes of Heart Disease?
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States for both men and women. “Heart disease” actually refers to several types of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease which is the most common type. Coronary artery disease occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. Heart failure, irregular heartbeat, and heart valve problems are also types of heart disease.
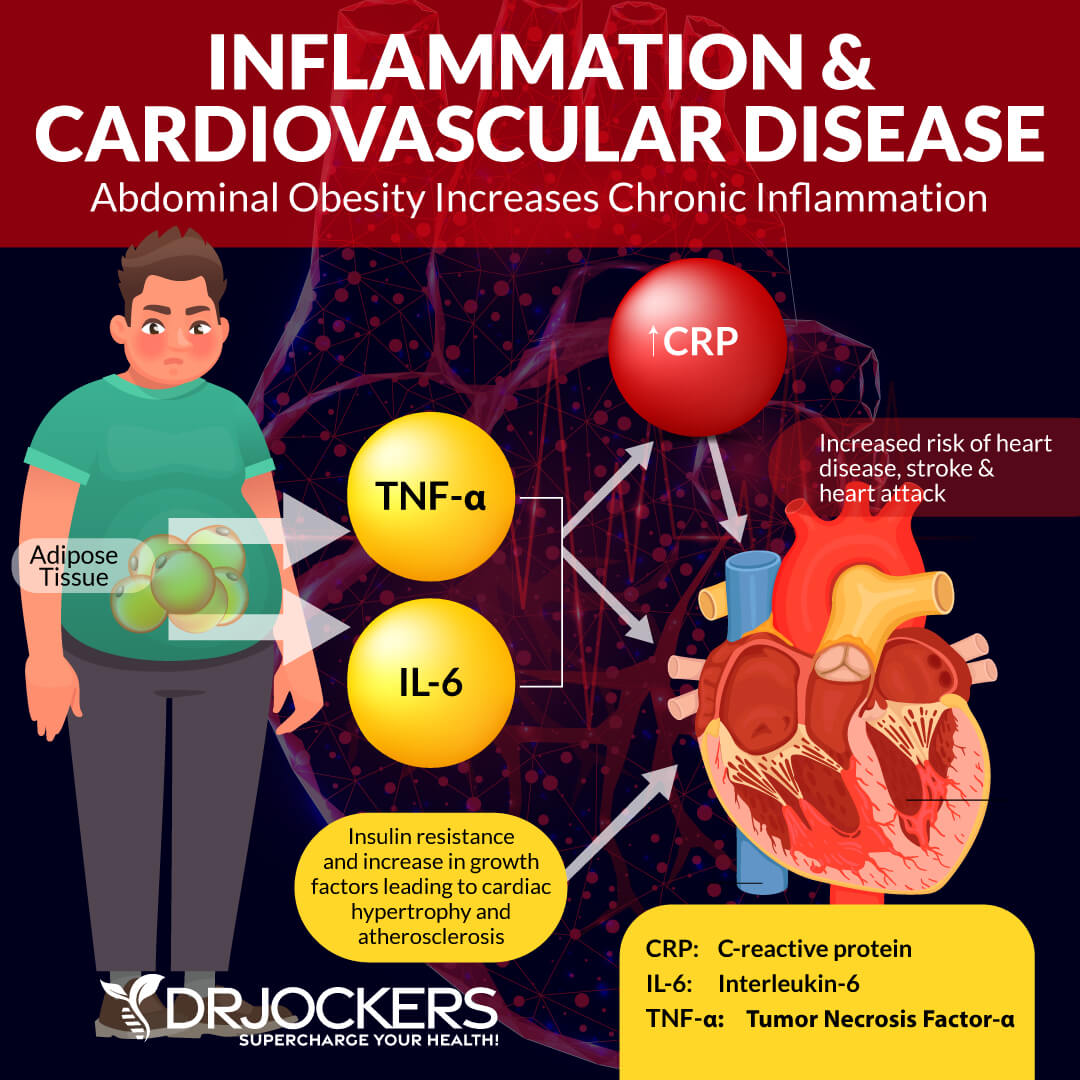
Chronic inflammation is at the root of most, if not all chronic diseases including cancer, ALS, and heart disease (1). Chronic inflammation is systemic inflammation that can last for months or years. Many things can contribute to chronic inflammation including inflammatory foods, environmental toxins, excess weight, and stress.
Chronic inflammation occurs when our bodies are repeatedly exposed to these influences, and inflammatory mediators are produced throughout the body. The immune system becomes overwhelmed as the ongoing stimulus results in more cell recruitment, increased inflammation, and changes to cells.
White blood cells will eventually start attacking internal organs or other necessary tissues and cells. This inflammatory response continues unless and until the cause of the inflammation is addressed.
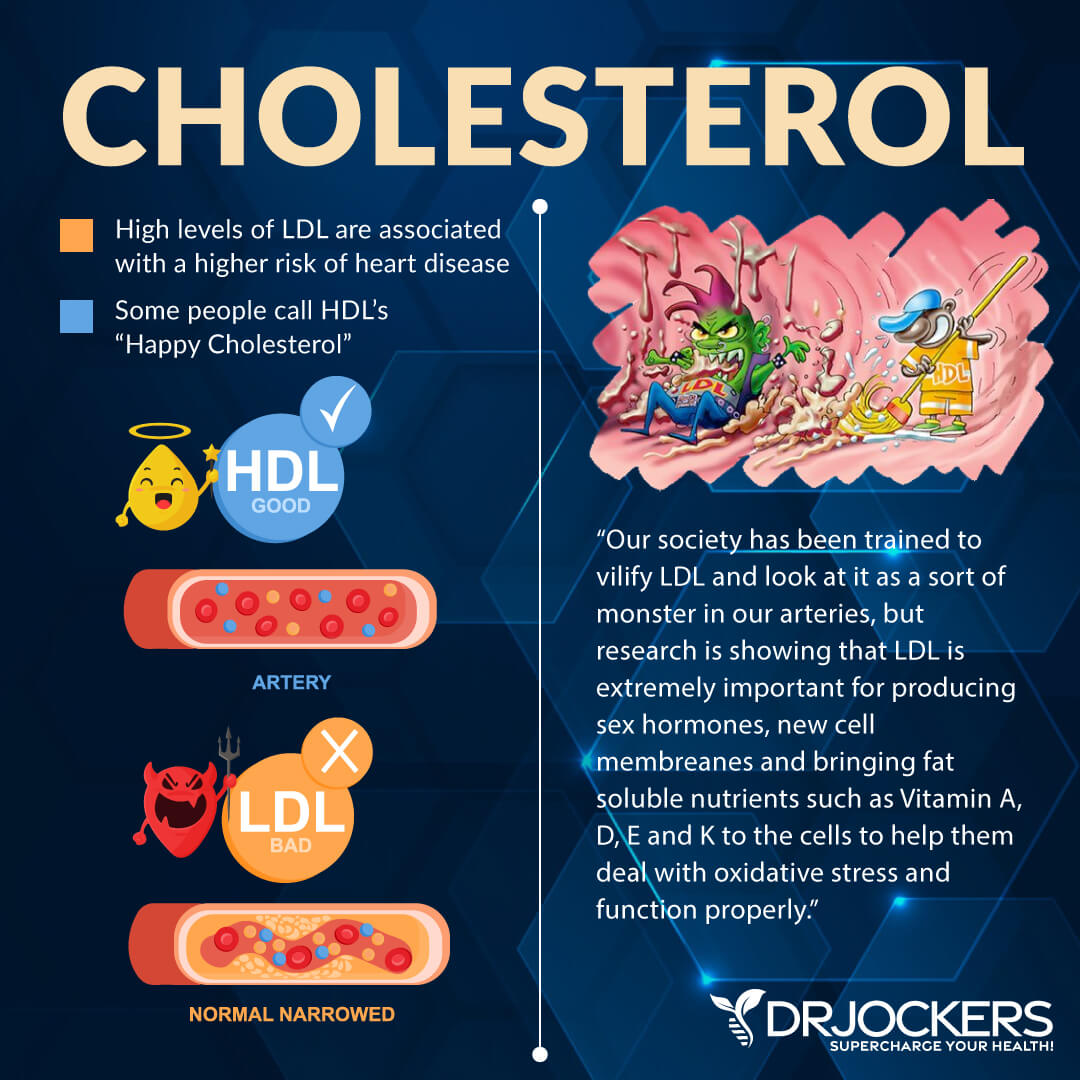
Heart Healthy Cholesterol?
After years of misinformation from flawed theories, we now know that saturated fat and cholesterol do not cause heart disease. In fact, some of the healthiest foods for your heart contain saturated fats and cholesterol.
Dietary saturated fat and cholesterol have been shown to improve hormone regulation and cell membrane function, raise HDL (good) cholesterol levels, and change LDL particles from the dangerous to benign particles (2). In fact, a large portion of the brain and myelin sheath (nerve insulation) is made up of saturated fat and cholesterol. Cholesterol is also necessary to protect the internal lining of the arteries from damage caused by inflammation and oxidative stress.
Lifestyle & Heart Disease
Rather than focusing on saturated fat and cholesterol for heart disease prevention, it is important to consider lifestyle factors that contribute to heart disease. A 2016 study found that healthy lifestyle factors can reduce the risk of heart disease by 46% regardless of genetic risk (3).
Smoking, eating an unhealthy diet, obesity, excessive alcohol use, and not exercising are all lifestyle factors that increase your risk for heart disease. These factors cause high blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, and elevated LDL cholesterol levels which raise your risk of developing heart disease.

The Anti-Inflammatory Healing Diet
Food provides biological information to our cells and DNA. It also provides critical building blocks for different physiological processes in the body. It is critical to focus on an anti-inflammatory nutrition plan to improve your health and overcome chronic health conditions. This nutrition plan is a plant-emphasized diet with healthy fats and clean protein.
An anti-inflammatory diet is a heart healthy diet. In fact, eating in a way that stabilizes blood sugar, provides and abundance of nutrition, and reduces exposure to toxins, will likely improve just about every aspect of your health. The foundational steps to an anti-inflammatory diet are as follows:

Eat Real Foods
The first step to a healing diet is to eat whole, unprocessed foods. You should remove refined sugars and grains that increase blood glucose levels, upregulate inflammation, and create extra acidity in the tissues. Instead, add a variety of low carbohydrate, low glycemic fruits and vegetables to your diet.
These fruits and vegetables contain powerful nutrients to improve energy, rid our bodies of excess weight, and overcome illness. This style of eating should have a heavy emphasis on non-starchy vegetables, herbs, spices, and sprouts of various types to load the body up with antioxidants.

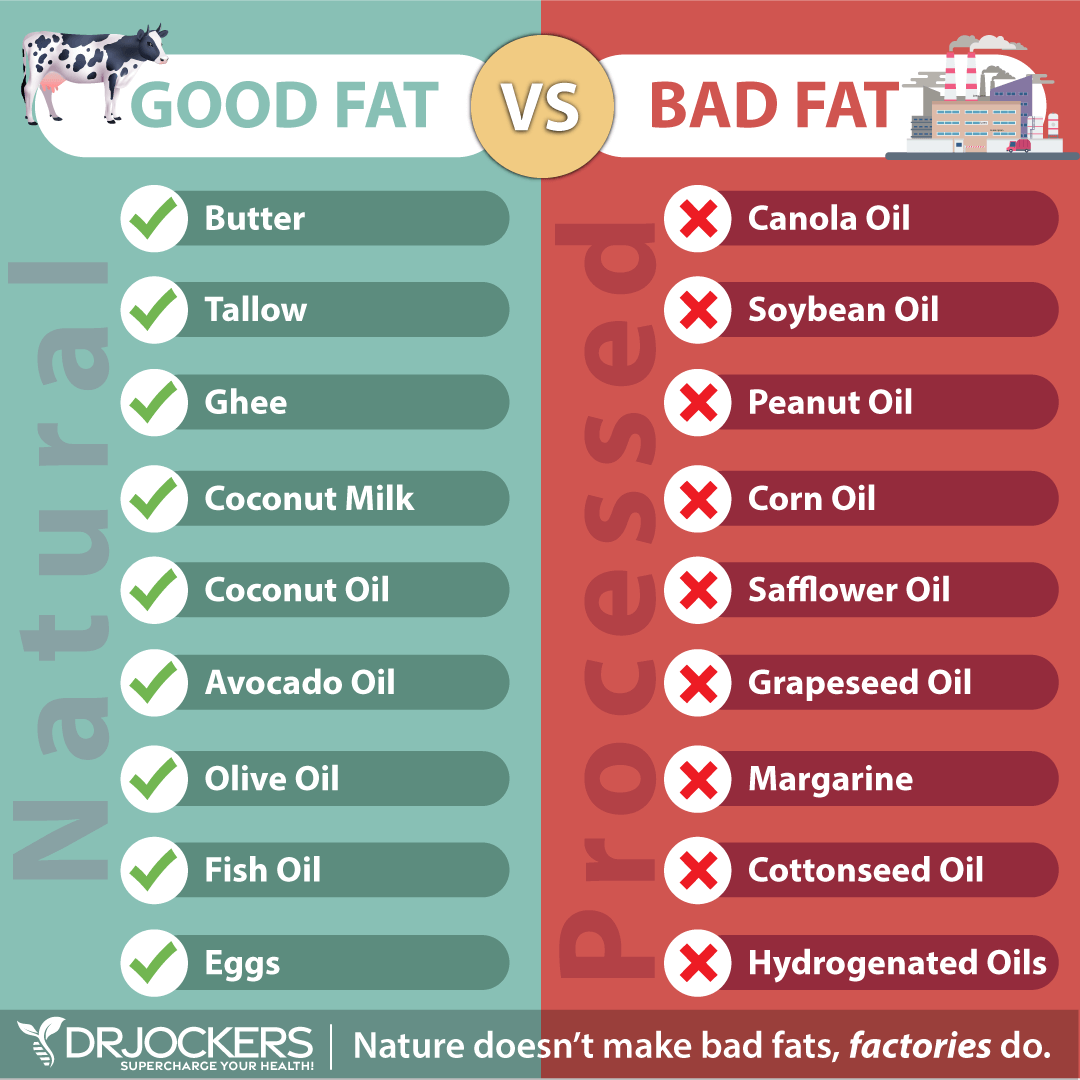
Eat Healthy Fats and Remove Harmful Fats
The second step to a healing diet is to eat more healthy fats and remove harmful fats from the diet. Healing fats are fats found in coconut, olives, avocados, and their oils. Omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) found in wild caught salmon and grass-fed beef and dairy are healing fats. These healthy fats are an efficient source of fuel for the body to combat inflammation and support brain function.
Unhealthy fats are man-made saturated fats, particularly trans fats, such as those found in margarine and partially hydrogenated oils. Highly processed oils, such as canola, peanut, and grapeseed oils, oxidize easily and should also be avoided.
Make Healthy Meat Choices
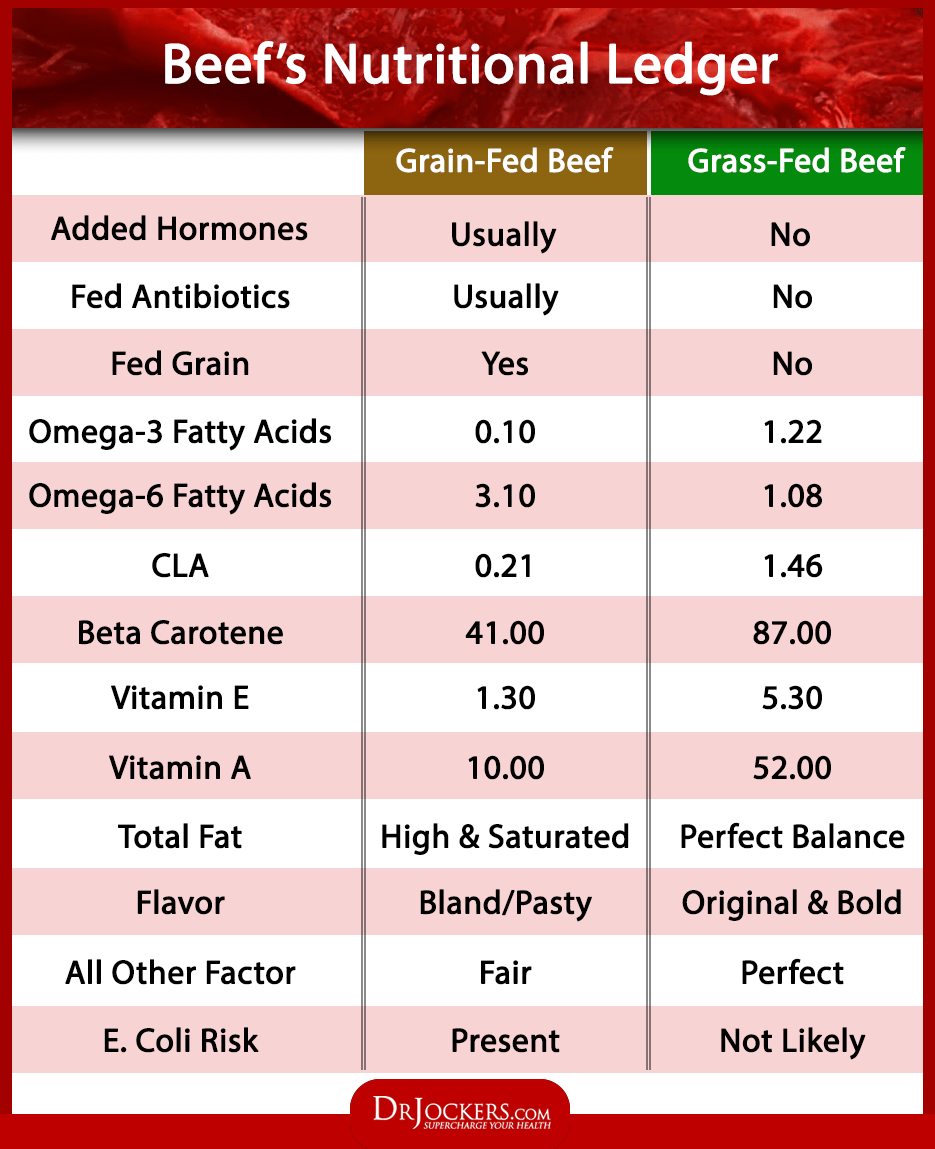
The third step to a healing diet is to choose grass-fed, pasture-raised, wild-caught meats and fish, rather than grain-fed, farmed, conventionally raised meats and fish. When choosing meat and fish, it is important to look at the food these animals and fish eat as well as the conditions in which they are raised. These factors directly influence the nutritional value of the meat and therefore what your body receives from consuming it.
To protect your heart from inflammation and heart disease, it is critical to incorporate this healing, anti-inflammatory diet into your life. By eating real foods, avoiding sugar and processed foods, eating healing fats rather than harmful fats, and choosing grass-fed, pasture-raised, wild-caught, organic meats and fish, you can go a long way in supporting a healing state in the body.
Now that we have covered the three steps to an anti-inflammatory, let’s look at the best heart healthy foods.
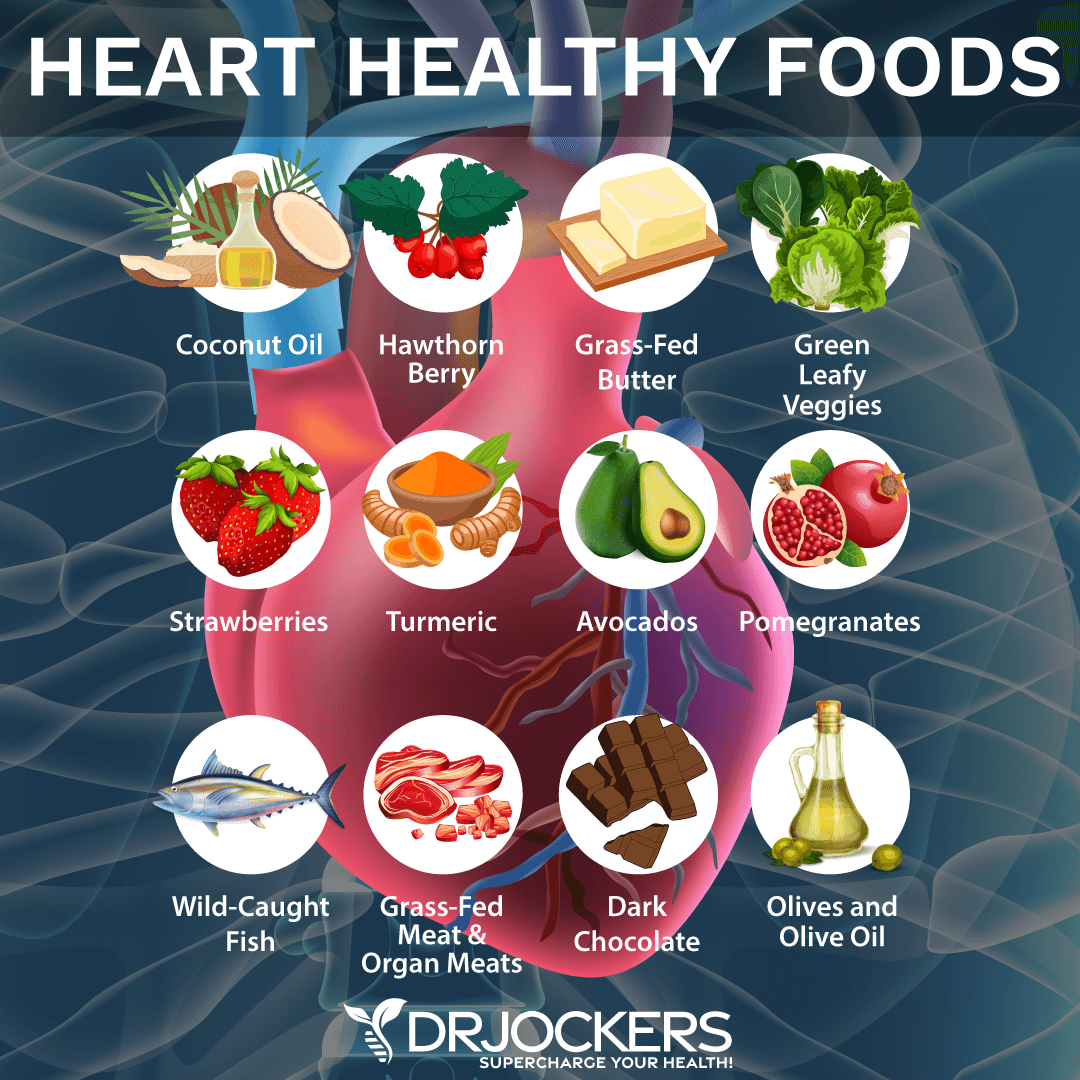
The Best Heart Healthy Foods
To prevent heart disease, it is important to eat anti-inflammatory foods rich in antioxidants, phytonutrients and essential fatty acids. This will lower oxidative stress and help fight free radical damage in your body. The following foods are my top picks for heart healthy foods.
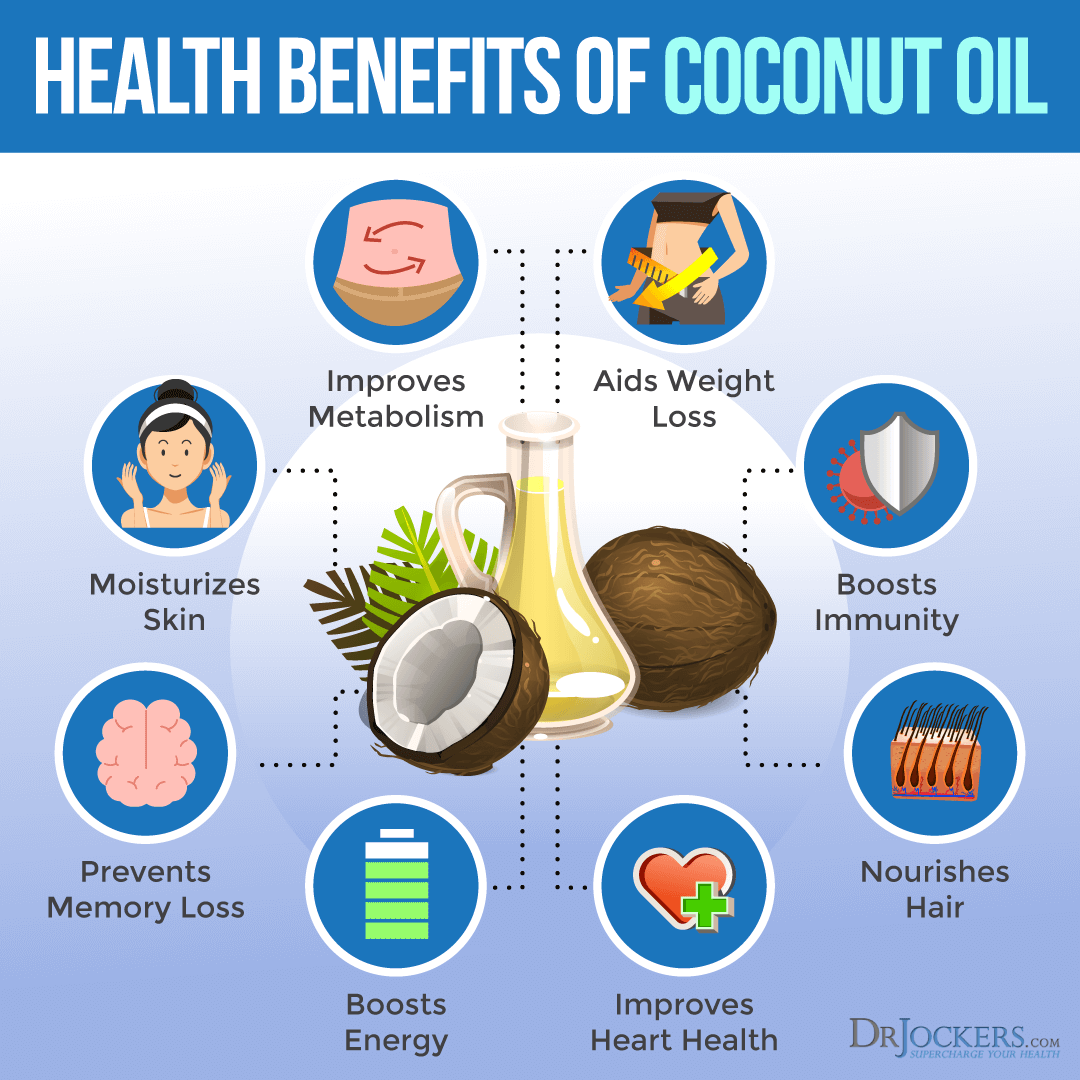
Coconut Oil
Despite years of misleading information, we now know that certain fats are heart healthy. Coconut oil is one of the best heart healthy fats. Studies have shown that coconut oil has cardio-protective effects through many mechanisms.
Coconut oil contains small to medium-chained saturated fats called medium chained triglycerides (MCTs). MCTs permeate cell membranes to provide energy without the need for carrier proteins or special enzymes. In other words, they are a good source of readily available energy for the body. These fatty acids also have an immune boosting effect through their antiviral, antimicrobial, and antibacterial properties.
Coconut oil is also rich in lauric acid which helps balance blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Coconut oil is the most stable source of fatty acids due to its high amount of saturated fats (92%). Coconut oil’s high saturated fat content actually supports healthy levels of HDL and LDL (4). By increasing the HDL in the body, coconut oil helps promote heart health and lowers the risk of heart disease (5). Coconut oil also helps lower high triglycerides providing additional heart healthy benefits.
It is best to use organic, unrefined coconut oil to reap the many benefits of coconut oil. Coconut oil is great for cooking because it has a higher smoke point than many other oils (like extra virgin olive oil). Rather than oxidizing, coconut oil remains stable and does not lose its antioxidant properties under high temperatures.
Hawthorn Berry
Hawthorn is called the “heart herb” for its ability to protect the heart. Hawthorn berry is a medicinal herb loaded with a wide array of powerful antioxidant nutrients, including numerous flavonoids. Flavonoids are polyphenolic compounds that have been shown to effectively decrease inflammation and boost immune function.
Hawthorn berry is widely used in Europe as a natural remedy to treat heart disease. There are numerous studies showing the ability of hawthorn to treat angina, high blood pressure, hardening of the arteries, irregular heartbeat, and congestive heart failure (6).
Look for the whole plant, leaves, flowers and berries, when purchasing hawthorn. The berries contain more proanthocyanins and the flowers and leaves contain more vitexin. Proanthocyanidins are powerful antioxidants that remove harmful free radicals from cells. Vitexin is an apigenin flavone glucoside with additional antioxidant properties.

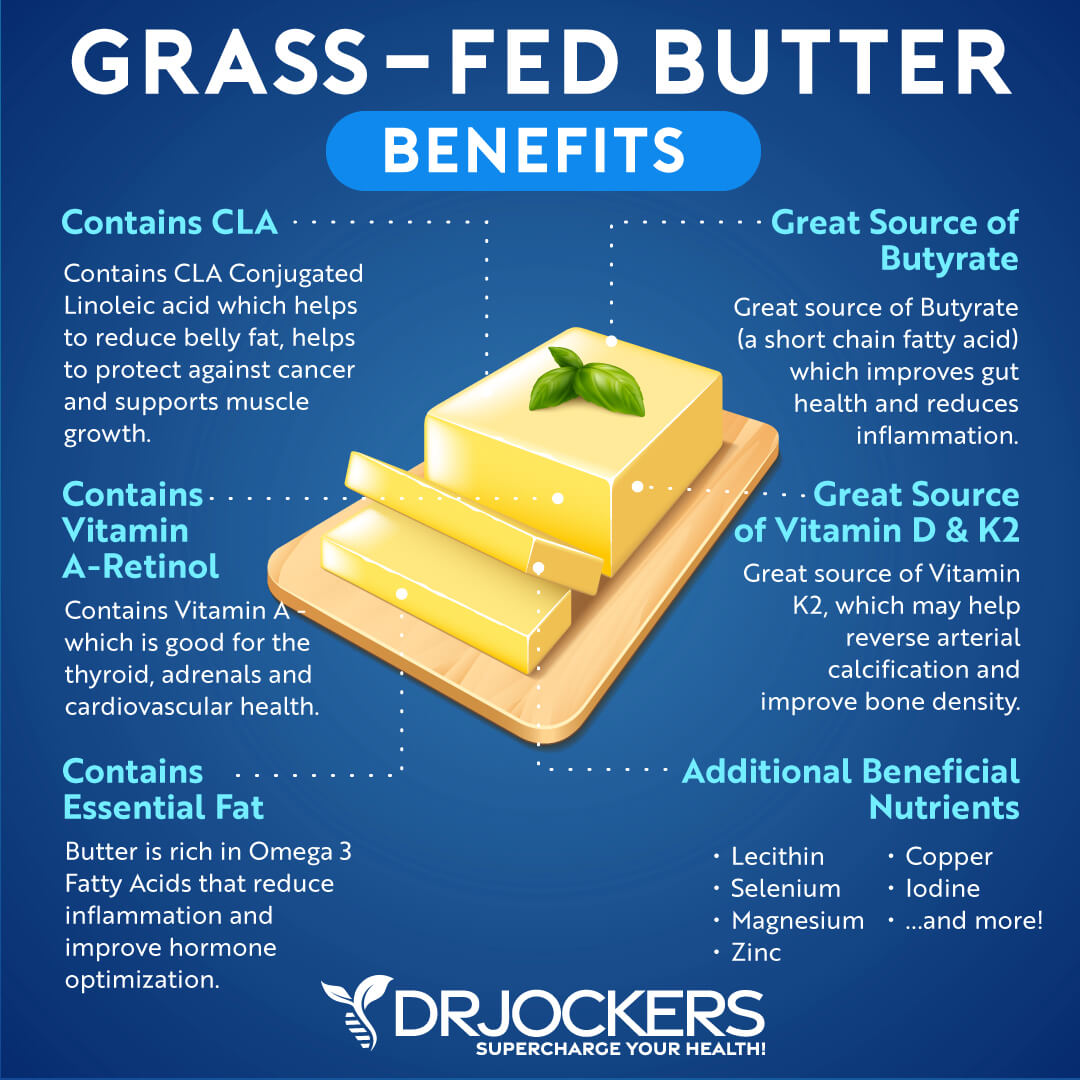
Grass-Fed Butter
Grass-fed butter is a nutritious, healthy fat with many healing properties. It contains short- and medium-chain triglycerides which support the immune system and boost metabolism. Grass-fed butter contains high levels of butyrate, arachidonic acid (ARA), and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). These acids have a myriad of health benefits.
Butyrate is a 4-carbon chain saturated fatty acid that is remarkably heart healthy in that it provides a direct source of energy for the heart. Butyrate also has anti-inflammatory effects on the entire body, promotes energy production, and benefits digestive health.
ARA and CLA are both important to overall immune system function. CLA is a type of polyunsaturated fat that helps reduce belly fat, improve immune function, and reverse atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). Studies have found that a higher percentage of CLA in the blood is associated with significantly reduced risk of heart failure (7).
Grass-fed butter is also a rich source of vitamin A which is good for the thyroid, adrenal glands, and cardiovascular health. It is also an excellent source of vitamins D and K2. Vitamin K2 may reverse arterial calcification. Grass-fed butter contains beneficial vitamin E tocopherols and other carotenoid antioxidants which help reduce oxidative stress in the arterioles.
Many Americans choose margarine rather than butter under the false belief that margarine is healthier for your heart. The reverse is actually true. Studies show that margarine consumption increases your risk of heart disease, while consuming butter is not associated with heart disease (8).
Dark Leafy Green Vegetables
Dark Leafy green vegetables are packed with an array of vitamins, minerals (including trace minerals), and fiber. Some of the most nutrient-dense leafy greens are spinach, kale, chard, arugula, bok choy, and collards.
Spinach, kale, chard and other dark leafy green vegetables are true superfoods. They contain almost 400% of the recommended daily value of vitamin A in just one cup. They also contain vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin K, and folic acid. Vitamin K has been shown to positively affect heart structure and functioning (9). The abundant antioxidants in leafy greens protect cells from damaging free radicals.
Many leafy green vegetables are in the cruciferous family. Kale, swiss chard, collard greens, arugula, spinach, bok choy, and mustard greens are cruciferous vegetables. They have a characteristic bitter taste and pungent aroma. Leafy greens in the cruciferous family are full of phytonutrients, carotenoids, and flavonoids that help combat free radical damage and neutralize toxins in the body.
Cruciferous vegetables also contain glucosinolates, sulfur-containing compounds that are broken down into metabolites that trigger specific enzymatic reactions. These reactions help detoxify the body by increasing its ability to remove carcinogens and heavy metals from the blood.
There are a variety of ways to prepare and consume leafy green vegetables. Leafy green vegetables are delicious roasted or sautéed in coconut or avocado oil or steamed and topped with grass-fed butter or extra virgin olive oil or used raw in salads.
It is important to combine leafy greens with healthy fats for better absorption of the fat-soluble vitamins. You can also consume a high-quality greens powder for a convenient option to absorb the nutrients in leafy greens.

Strawberries
Strawberries are one of the most popular fruits for many reasons. Even with their delicious, sweet taste, strawberries are a low-glycemic fruit and do not cause blood sugar spikes for most people. They also contain dietary fiber and numerous vitamins and minerals.
Strawberries are an excellent heart healthy food because they contain bioactive compounds with antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, and anti-inflammatory effects. The most abundant of these are ellagic acid and certain flavonoids, including anthocyanin, catechin, quercetin, and kaempferol (10).
Antioxidants help lower the risk of cardiovascular disease by inhibiting LDL cholesterol oxidation, promoting plaque stability, improving vascular endothelial function, and decreasing the tendency for thrombosis (blood clotting) (10).
Strawberries are delicious added to shakes or as a healthy snack or dessert. It is very important to buy organic strawberries due to high pesticide levels in conventionally grown strawberries. Frozen organic strawberries have the same health benefits and are a convenient option.

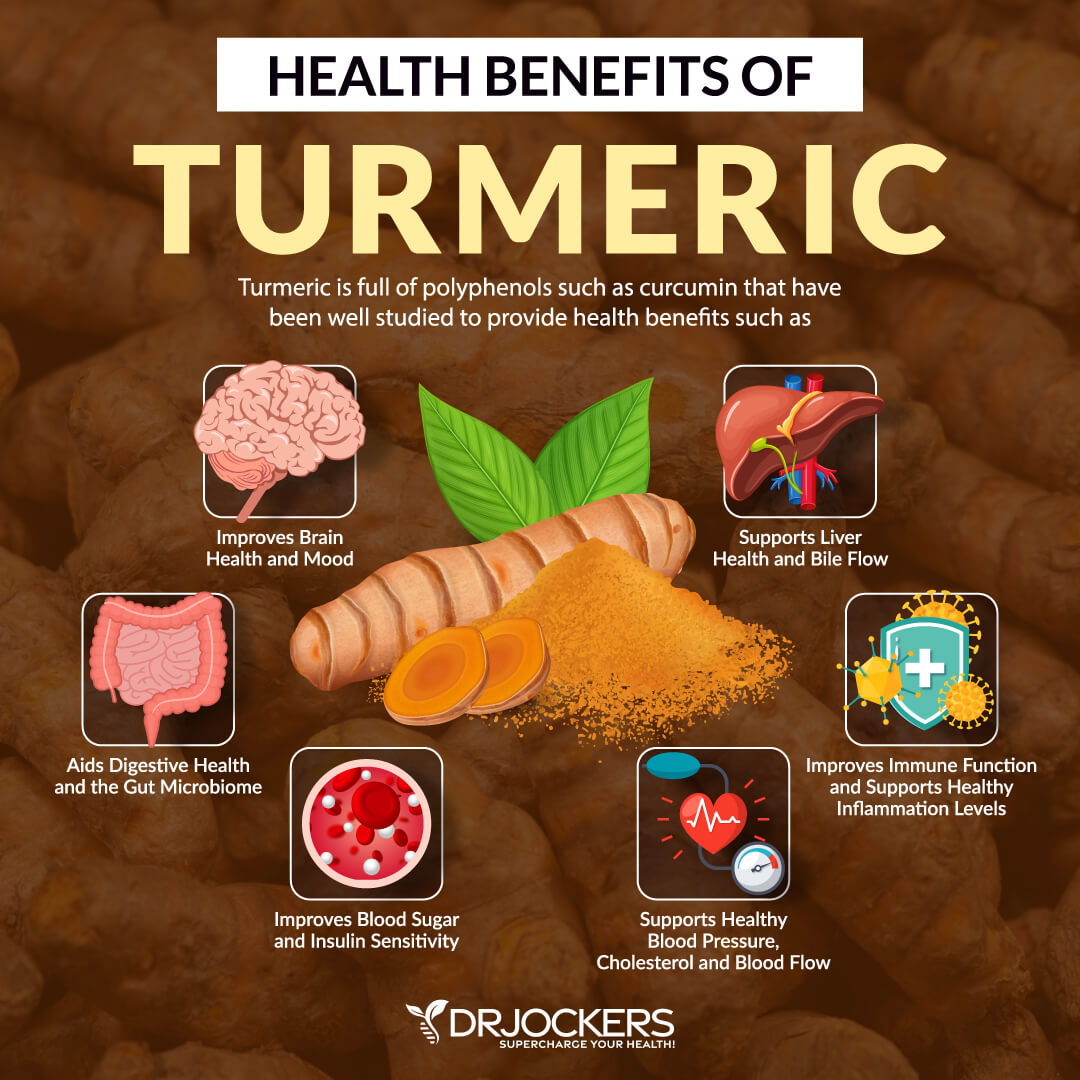
Turmeric
Turmeric is a powerful herb with abundant cardiovascular protective effects. Turmeric is good for the heart due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-thrombotic, and antimicrobial properties. Many of these benefits are attributed to a compound called curcumin.
In the fight against inflammation, turmeric can be a powerful weapon. Turmeric’s anti-thrombotic, anti-proliferative, and anti-inflammatory effects protect against changes occurring with atherosclerosis. Curcumin also effectively balances serum cholesterol levels by eliminating excess LDL cholesterol from the arteries and blood vessels. This can also help prevent atherosclerosis.
The curcuminoids in turmeric have antioxidant properties. The antioxidant effects of turmeric have been shown to reduce cardiotoxicity and prevent cardiac complications (11). Turmeric has even been shown to boost the body’s natural antioxidant capacity which fights damaging free radicals.
Turmeric powder should be added to foods after cooking to maintain its potency as an anti-inflammatory. Add a dash of black pepper and eat with healthy fats to allow for better absorption of the beneficial compounds.
Avocados
Avocados are nutrient and phytochemical dense superfoods for the heart. Numerous studies have found that avocado consumption is a heart healthy choice (12).
Avocados have numerous antioxidant phytochemicals, including beta-sitosterol, glutathione, and lutein. Glutathione is the body’s most powerful antioxidant and is critical for lowering inflammation. Beta-sitosterol helps lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. These antioxidants phytochemicals prevent free radical damage.
Avocados are also rich sources of vitamins B and C, important trace minerals, healthy fats, and antioxidant compounds carotene and lutein. They also contain a compound called oleic acid which may help the body absorb carotenoids for further anti-inflammatory benefits.
Avocados are loaded with healthy monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and contain healthy cholesterols, or high-density lipoprotein (HDL), which the body needs for proper function. Studies have shown that dietary MUFAs are protective against metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease risk factors (13).
There are many ways to incorporate avocados into your diet. You can add them to smoothies or puddings for creaminess. Consuming guacamole made from avocados, cilantro, lime juice, and shallots would be great for the liver. Avocado oil is a fantastic choice for a heart healthy oil.

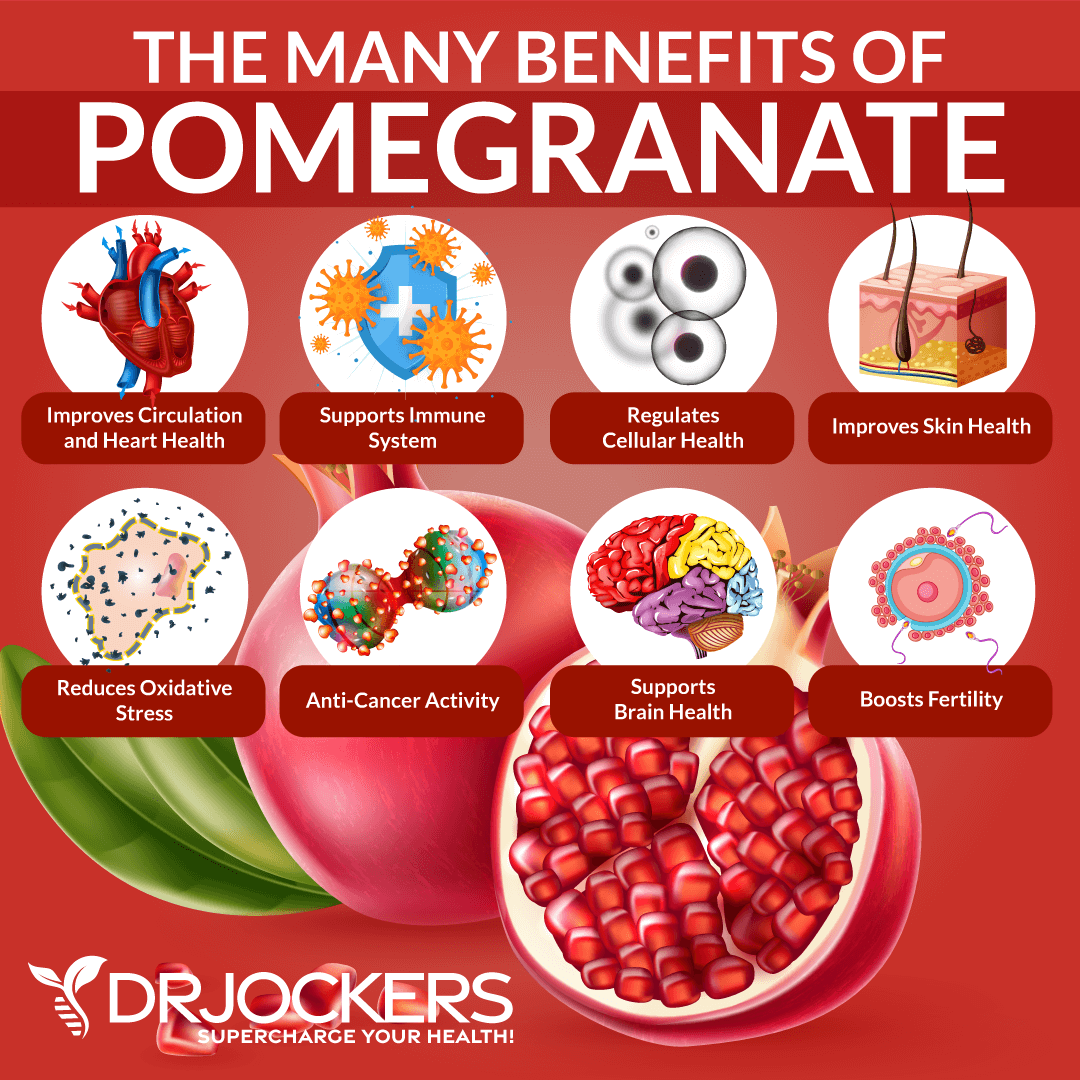
Pomegranates
Pomegranates are fruits with a high fiber content and filled with many small seeds. They are nutritional powerhouses, full of vitamin C, potassium, pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), and antioxidant phytonutrient polyphenols. The anthocyanins in pomegranates protect cells from oxidative and environmental stress and damage. Pomegranates have been shown to protect against heart disease, boost immunity, lower cholesterol, lower blood pressure (14).
It is best to consume pomegranates in their fresh, whole form due to the high sugar content in pomegranate fruit juices. If you do consume the juice, limit it to a 2-ounce shot. Even a small amount is beneficial because of the potent antioxidants in pomegranates.
Wild-Caught Fish
Wild-caught fish, especially salmon, are fantastic for heart health. They contain the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA which have been shown to help reduce risk factors for heart disease. Fatty acids found in fish help to reduce high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and high triglycerides (fats in the blood) (15).
Fish consumption is associated with lower risk of death, subsequent heart attack, stroke, and abnormal heart rhythms in people who have already had a heart attack. The oils in wild-caught fatty fish also help prevent and treat atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) by slowing the development of plaque and blood clots, which can clog arteries. They may also have antioxidant properties that improve endothelial function and contribute to heart health.
The omega-3 fatty acids in wild-caught fish help reduce inflammation in the body. It is critical to have the optimal ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. While omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation, most omega-6 fatty acids increase inflammation in the body. Studies show that higher dietary omega-6 to omega-3 ratios are associated with worsening inflammation over time (15). The ideal ratio is between 4:1 and 1:1.

Pecans
Pecans are nutritionally-dense, consisting of a unique blend of fatty acids, bioactive compounds, and essential nutrients. Nuts are concentrated with powerful heart healthy plant compounds that fight inflammation in the body. Frequent consumption of nuts is associated with decreased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Pecans are rich in monounsaturated fats. In studies, the frequent consumption of pecans has been shown to decrease total and LDL cholesterol levels, reduce triglyceride levels, and increase HDL cholesterol levels (16).
Pecans contain different forms of the antioxidant vitamin E, known as tocopherols, plus numerous phenolic substances with antioxidant abilities. Eating pecans increases the number of healthy antioxidants in the body which has the protective benefit of preventing development of heart disease (16).
Dark Chocolate
Many people are surprised to find that the right kind of chocolate is actually very heart healthy. Dark chocolate contains many nutrients including fiber, magnesium, iron, copper, calcium, protein, and manganese.
Dark chocolate is high in antioxidant flavonoids and polyphenols that combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Flavanols are the main type of flavonoid found in dark chocolate. Flavanols have been shown to have numerous heart healthy benefits including lowering blood pressure and improving blood flow to the heart (17).
The darker and less processed the chocolate, the higher the amount of catechins are in the chocolate. Catechins are super antioxidant flavanols with beneficial effect on cardiovascular health. Catechins can effectively lower blood pressure, prevent oxidation of LDL (bad) cholesterol, and increase nitric oxide release.
Dark chocolate also contains oleic acid which a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid with many health benefits. Oleic acid has been shown to reduce blood pressure and increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Oleic acid has also been shown to protect cell membranes from free radicals and other oxidative stressors. Oleic acid is also one of the most common fats in myelin which is a protective sheath around nerves.
When purchasing dark chocolate, look for minimally processed dark chocolate with at least 70 percent cocoa content or higher. This will have the most powerful antioxidants and the least amount of sugar.

Olives and Olive Oil
Consuming olives and olive oil have numerous heart healthy benefits. Olives contain fiber, vitamin E, vitamin, copper and calcium. The healthy fats in olives and olive oils benefit the heart. Studies have shown that both polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats are inversely associated with the risk of heart disease (18).
Olive oil contains biologically active phenolic compounds (polyphenols) that have been shown to benefit atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (19). Phenolic compounds have positive effects on plasma lipoproteins, oxidative damage, inflammatory markers, platelet and cellular function, and antimicrobial activity.
Studies also show that olive oil can increase adiponectin levels (20). Adiponectin is a protein hormone which is involved in regulating glucose levels as well as fatty acid breakdown. Low levels of adiponectin are associated with numerous health conditions, including inflammation, lipid abnormalities
Extra virgin olive oil is the healthiest form of olive oil and has the richest flavor. It is made without any heat or chemicals and has a low smoke point. Because of its low smoke point, extra virgin olive oil is best used drizzled over cooked or raw foods, or as a heart healthy salad dressing.
The Worst Foods for the Heart
There are several foods that are detrimental to the heart. The three least heart healthy foods are sugar, processed vegetable oils and trans fats, and grain-fed meats. This is because they provide very little nutrition and are highly inflammatory to the body.

Refined Sugar
Studies have associated intake of added sugars with the development of hypertension, high blood pressure, increased triglyceride levels, obesity, and inflammation. All of these conditions increase the risk of heart disease. Added sugar intake is even associated with a significantly increased risk of death from cardiovascular disease (21).
A high-sugar diet can stimulate the liver to dump harmful fats into the bloodstream and cause insulin resistance. Both of these factors are known to boost your risk of heart disease.
Insulin resistance is the decreased ability to respond to the effects of insulin. As a result, the body produces additional amounts of insulin which increases inflammatory processes within the body. Over time, surges of insulin can cause chronic health complications including heart disease.
Chronically elevated blood sugar also reacts with enzymes and other protein molecules to create Advanced Glycolytic End Products (AGEs) (22). AGEs are highly inflammatory and damage tissue throughout the body. The result is neurological and cardiovascular complications. Removing sugar and grains from the diet is a powerful heart healthy move.

Trans Fats
Hydrogenated and partially-hydrogenated (trans) fats top the list of fats that kill. Hydrogenation is a process that turns polyunsaturates, which are normally liquid at room temperature, into fats that are solid at room temperature and the opposite of heart healthy. Common hydrogenated fats include hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated cottonseed, palm, soy, and corn oils.
Margarine and shortening are two hydrogenated fats. Manufacturers use cheap oils, such as soy, corn and canola to create margarine and shortening. The new soft margarines or tub spreads, while lower in hydrogenated fats, are still produced from rancid vegetable oils and contain many additives.
Consumption of hydrogenated and partially-hydrogenated fats is associated with cancer, atherosclerosis, diabetes, obesity, immune system dysfunction, birth defects, decreased visual acuity, sterility, difficulty in lactation and problems with bones and tendons (23). Trans fats from partially hydrogenated vegetable oils are most strongly related to increased risk of heart disease. It is essential to eliminate trans fats from your diet to avoid the myriad of health issues associated with these toxic fats.

Grain-Fed Meats
Grain-fed meats are far from heart healthy. Animals that are conventionally raised are fed genetically modified grains that are laden with pesticides, herbicides and other toxins. These animals are given antibiotics and other pharmaceuticals to keep them from getting diseases and to treat illnesses. They are also given hormones to make them larger. These drugs and hormones make their way into the meat, eggs, and dairy products from these animals.
Conventionally-raised animals live in unsanitary, crowded conditions with little to no access to clean air. They are fed a high-carbohydrate corn and soy feed to cause to become unnaturally large in a short time. Their digestive systems are not designed to eat these foods.
Feeding cattle high starch food like corn and soy makes their intestinal tracts acidic which can lead to ulcers, infection, and the growth of bacteria like E. coli. Grain-fed animals can also have antibiotic resistant bacterial like MRSA and superbugs (24).
Conventionally raised meats and fish are not as nutritious as grass-fed beef. Grain feeding significantly reduces the omega-3 and CLA content and the vitamins A and E amounts in the meat, eggs, and dairy products. You should always choose grass-fed meats such as grass-fed beef, bison, lamb, and wild game, rather than conventionally raised, grain-fed meats.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!
Conclusion
The heart is an incredible organ with the vital job of keeping blood flowing throughout the body. When the heart becomes weakened through lifestyle factors, it can lead to heart disease.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Smoking, eating an unhealthy diet, obesity, excessive alcohol use, and not exercising increase your risk for heart disease. It is critical to eat an anti-inflammatory, healing diet to reduce your risk of developing heart disease. This diet includes low-glycemic fruits and vegetables, clean protein sources, and healthy fats.
The top heart healthy foods you can eat are listed above. You should incorporate these foods into your diet on a regular basis to prevent heart disease.
Additionally, you should avoid the three worst foods for your heart; sugar, processed vegetable oils and trans fats, and grain-fed meats. These foods promote inflammation which leads to heart disease. These foods should be eliminated or minimized to keep the heart healthy.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. Our website offers long-distance functional health coaching programs with our world-class team of health coaches. For further support with your health and other goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.




This is a wonderful list. Thank you, Dr. Jockers, for going to all the trouble of putting all theses important pieces of information together. Jutta
Thanks so much Jutta!!!
Hi Dr. Jockers,
I appreciate your articles because they always are well thought out. Your list of oils helped me make better choices when I tried to go on a ketogenic diet a couple of years ago. However, I noticed that in your list of bad fats you left out the worst one of them all–rapeseed oil. Rapeseed was believed to be a major cause of mad cow disease. The oil is now commonly used in lesser quality peanut butters. (I personally have never seen it used anywhere else. Maybe you did not include it because common people never use it.) When I tell people about oils, I have only rapeseed oil on my list of bad oils. All the ones you listed as “bad,” I tell people that they are “not good, or with some, like Canola oil, “very not good.” I tell them to avoid all the “not good” oils and throw away anything that has rapeseed in it, just as you would throw away any oil that is strongly rancid. Elman
Hey Elman,
Yes rapeseed oil is canola oil…so that was included. Be Blessed!
Hi Dr. Jockers,
I love the knowledge you share with us Thank you very much! I have heard that a type 1 diabetic can not safely eat a keto diet is this true? I see my Endo in 2 months and want to talk to him about it but don’t feel I should if it is not safe.
Andrew Koutnik has a Ted-X talk on managing type 1 diabetes w/keto. There may be other similar voices as well. All the best to you.
Yes absolutely type I diabetics can do very well on keto. But it is important to work with a keto literate doctor or functional health coach!
I see so many “keto” recipes with tons of cheese. I don’t see a whole lot of cheese up there, on either the good or bad foods side of the equation. Common sense tells me that organic cheese from grass-fed animals is probably ok in moderation on a sensible keto diet, but based on the number of recipes I see centered around cheese, I think we are being led to think otherwise. What’s the story on cheese with respect to keto?
Yes Andrew, organic grass-fed cheese can be very healthy for some. However, many people have immune sensitivities to dairy protein, so you have to be careful!
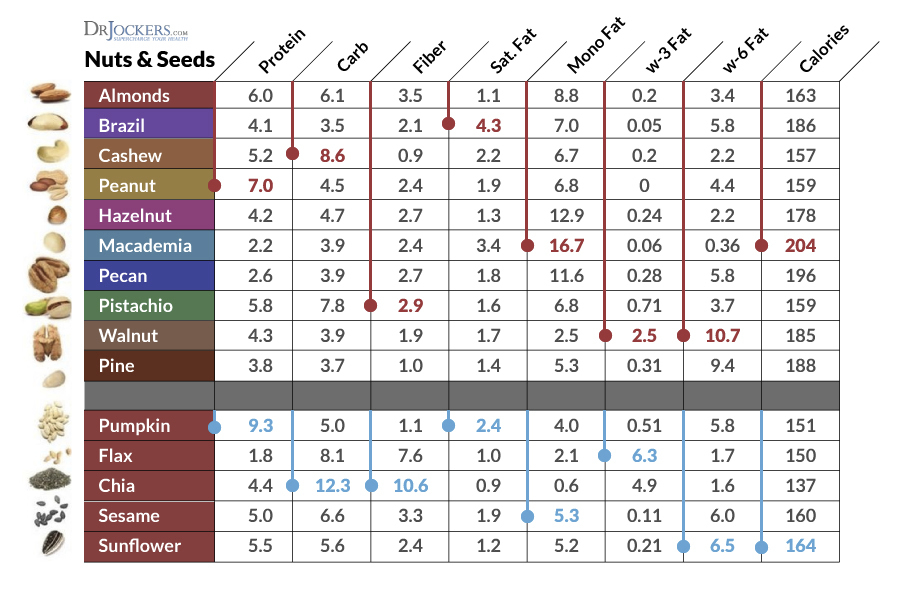
Great article. I was especially interested in your chart for the nuts and seeds. Can you PLEASE specify how to read it ! What do the numbers represent? What are the units? Is it for a standard serving? Is it for some referent quantity grams or ounces)? Do the numbers represent percentages? If percentages, of what?
As it stands, with just a table of a bunch of anonymous numbers, the only value I could get out of it was the ratio of Omega 6 to Omega 3, which is of use even without units.
Please clarify.
Yes all those numbers are in grams
Can blockage of circulatory system be reversed?? Can a person nutritionally
Clean out his arteries?
Yes, you can significantly reduce inflammation in the blood vessels. Read this article: https://drjockers.com/clogged-arteries/