
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes and Natural Support Strategies
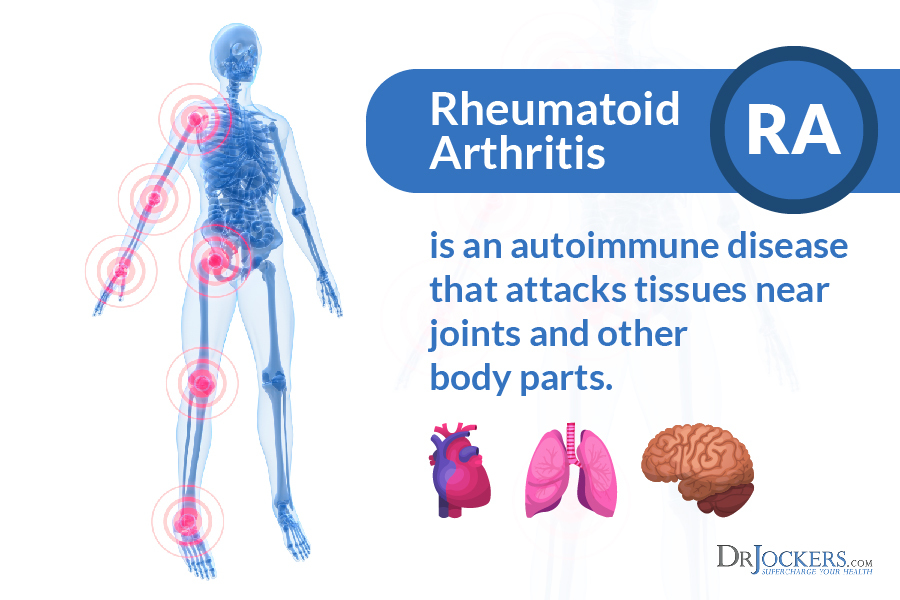
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that primarily attacks the synovial tissues around the joints. Autoimmune diseases cause the body’s immune system to mistake its own tissues for foreign invaders, such as bacteria or viruses. The confused immune system develops antibodies to seek out and destroy the “invaders” in the synovium.
RA is a systemic disease, in that has the ability to affect the whole body. It can attack many different organs, such as the heart, the lungs, or other tissues like muscles, cartilage and ligaments. RA causes chronic swelling and pain that is sometimes severe, and it can cause permanent disability.
Rheumatoid Demographics:
RA is a common chronic disease that affects about 1% of the world population. RA occurs at twice the rate in women compared with men, with a prevalence of 1.06% in women (as a percentage of the total population) compared with 0.61% in men (1).
The incidence (new cases per year) of RA increases with increasing age in most populations until about the eighth decade of life, when it declines (2). The prevalence of RA varies widely from population to population, with the lowest rates in Asian countries and higher rates among certain Native American populations (3).
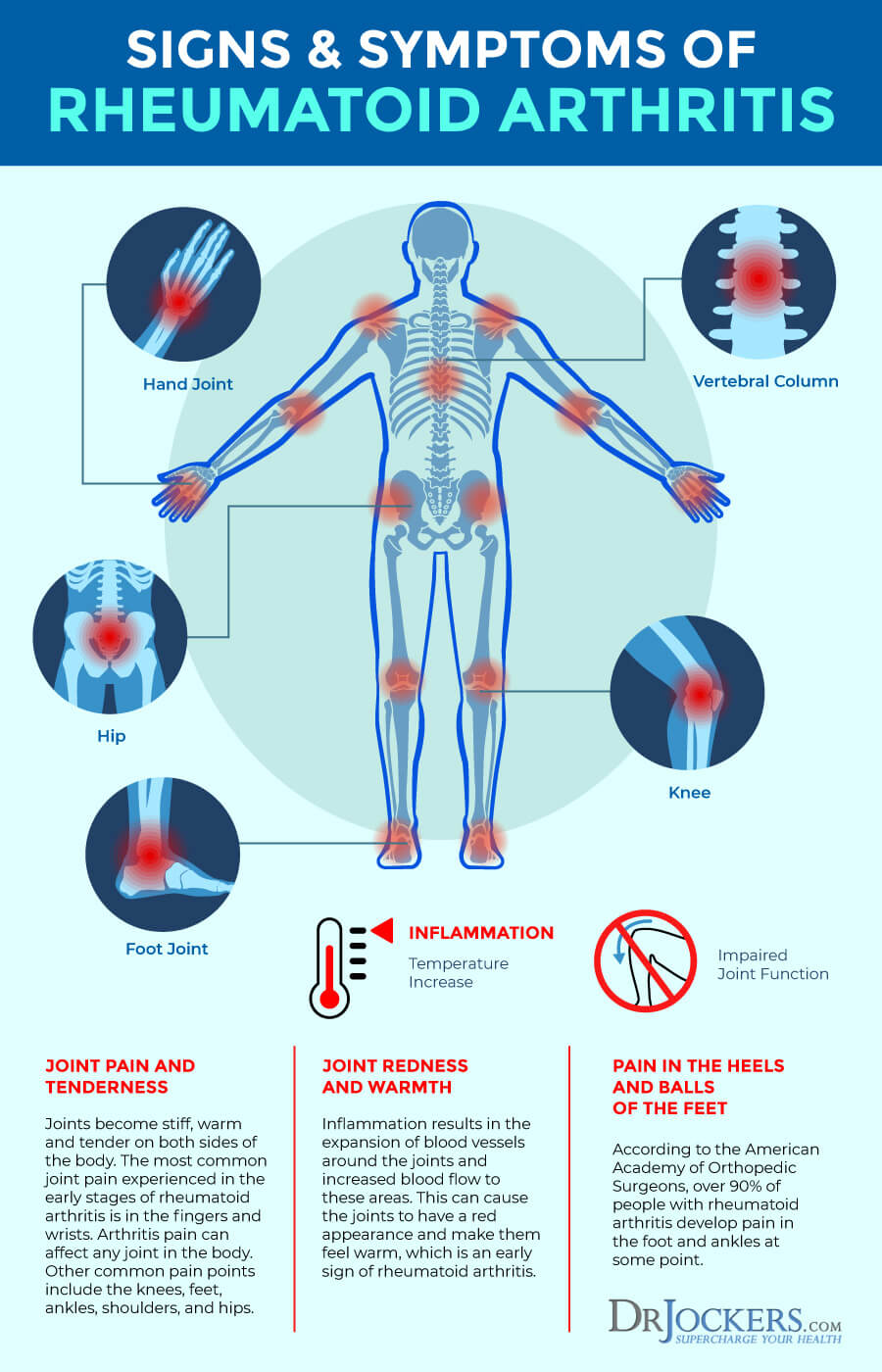
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
The early onset of RA typically effects the small joints such as the fingers and toes. Many just feel as though these areas are mildly warm, stiff or swollen. These symptoms are often intermittent, only flaring up for a few days at a time and most people ignore the issue for a while.
Over time, RA symptoms can get worse and cause deformity in the fingers and toes. The disease can also progress to larger joints such as the shoulders, knees and hips. RA may cause significant damage to the joints within 2 years of onset.
Other symptoms associated with RA include:
- Fatigue
- Low-grade fevers
- Pain and stiffness for longer than 30 minutes in the morning or after sitting
- Anemia
- Weight loss
RA also has been shown to significantly increase the risk of heart attack and stroke because it can damage the protective sheath around the heart called the pericardium (4).
Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
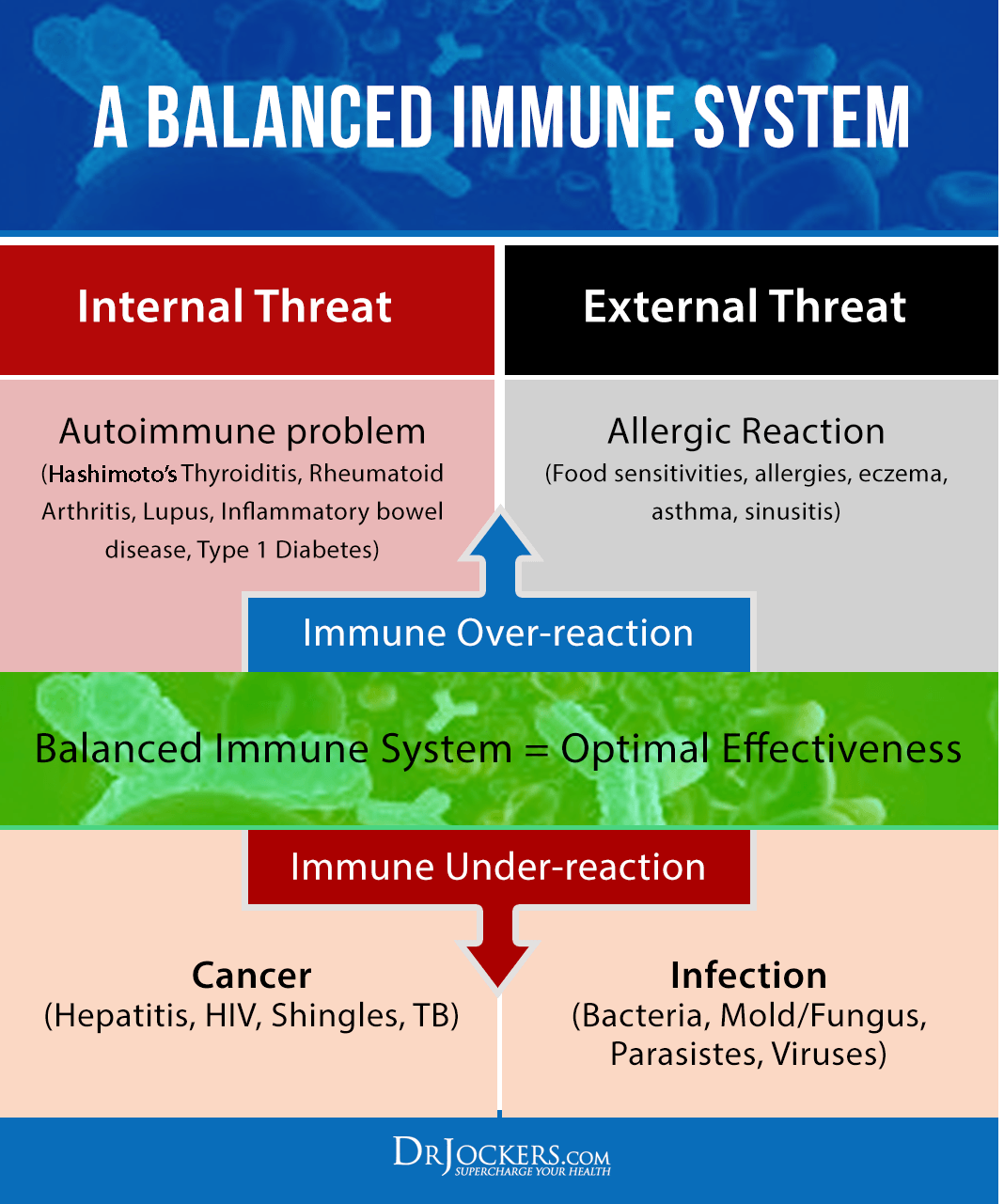
The development of RA is based around both genetic and environmental factors that effect the major histocompatability (MHC) genes and the bodies innate immunity. Environmental factors that increase the activation of the innate immune system can disrupt immune balance and cause chronic inflammatory activity in the body (5).
The process of developing RA can take many years. One key factor is the induction of the peptidyl arginine deiminase (PAD) enzymes, which convert arginine to citrulline. Increased citrullination is not specific to RA and occurs regularly with any environmental stress, including in lung alveolar macrophages in cigarette smokers (6).
What is unique to RA is the propensity for immune reactivity to the neoepitopes created by protein citrullination with the production of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) (7, 8). In “pre-RA,” ACPAs and autoantibodies like rheumatoid factors (RFs) can appear more than 10 years before clinical arthritis.
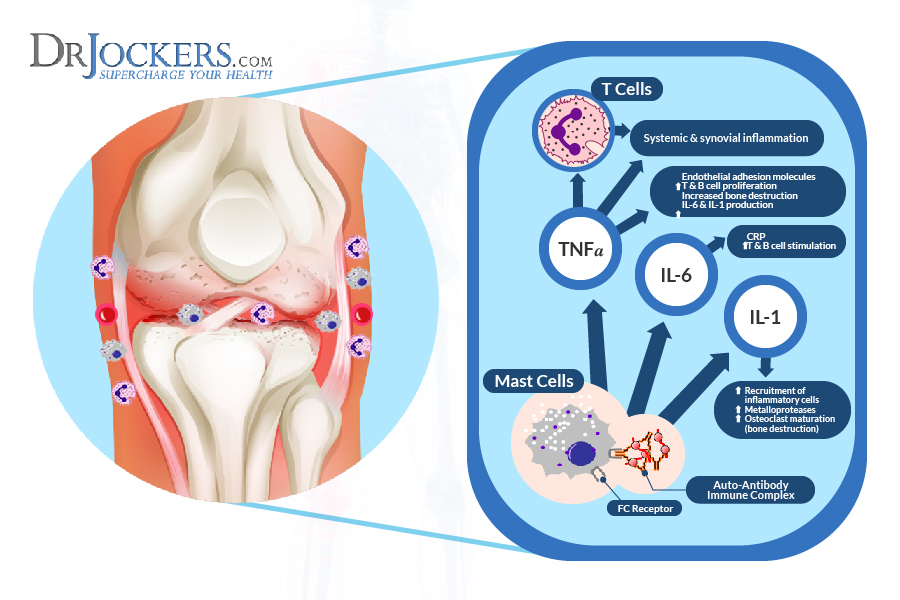
Additionally, inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-1 are active in individuals with pre-RA and this extends into RA where these cytokines only grow in number and accelerate the inflammatory storm in the joint and organs (9).
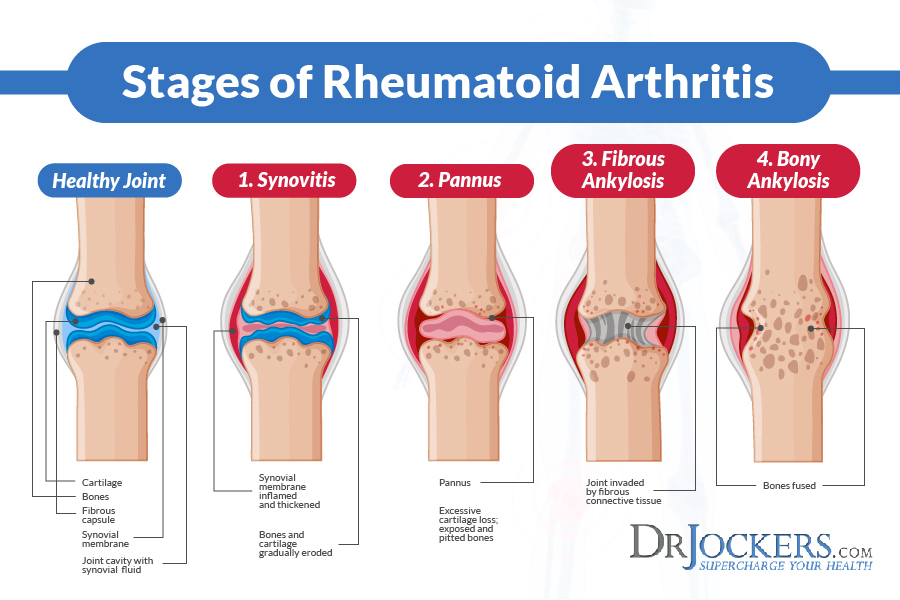
4 Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Stage I.
Early stage RA (stage I) is characterized by synovitis, or an inflammation of the synovial membrane, causing swelling of involved joints and pain upon motion. During this stage, there is a high cell count in synovial fluid as immune cells migrate to the site of inflammation. However, there is generally no x-ray evidence of joint destruction, with the exception of swelling of soft tissues and possibly evidence of some bone erosion.
Stage II.
In moderate RA, stage II, there is a spread of inflammation in synovial tissue, affecting joint cavity space across joint cartilage. This inflammation will gradually result in a destruction of cartilage, accompanied by a narrowing of the joint.
Stage III.
Severe RA, stage III, is marked by formation of pannus (vascular scar tissue that extends over the surface of an organ or joint) in the synovium. Loss of joint cartilage exposes bone beneath the cartilage. These changes will become evident on x-ray, along with erosions around the margins of the joint. Joint deformities may also become evident.
Stage IV.
Stage IV is called terminal or end stage RA. The inflammatory process has subsided and formation of fibrous tissue and/or fusing of bone results in ceased joint function. This stage may be associated with formation of subcutaneous nodules.
 Immune Modulation:
Immune Modulation:
Chronic inflammatory disorders are characterized by a hyper responsive immune system. There are several key factors that must be addressed to regulate and better coordinate the immune system.
1. Poor Blood Sugar Stability: Blood sugar imbalances cause immune dysfunction and malcoordination. Stable blood sugar is critical for a healthy immune response.
2. Low Vitamin D Levels: Individuals with low vitamin D3 levels (below 40 ng/ml) are at significant risk for developing chronic inflammation and autoimmunity (10).
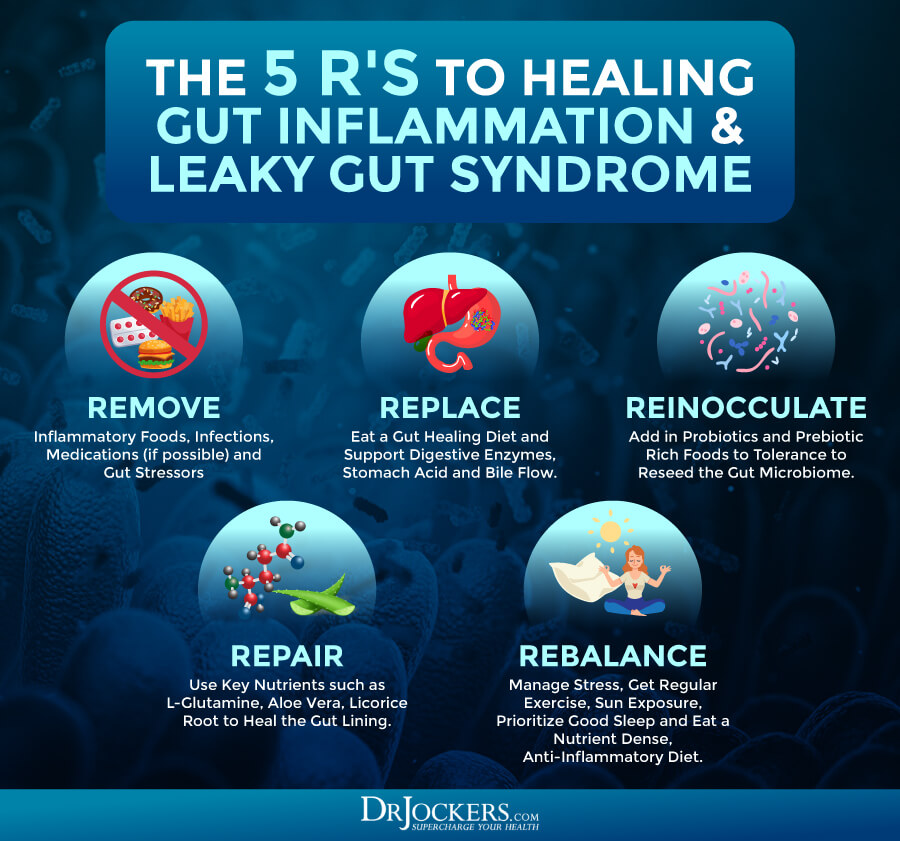
3. Gut Dysbiosis: Poor microbial balance in the gut microbiome leads to leaky gut syndrome and chronic inflammation (11). The gut must be addressed in order to get well.
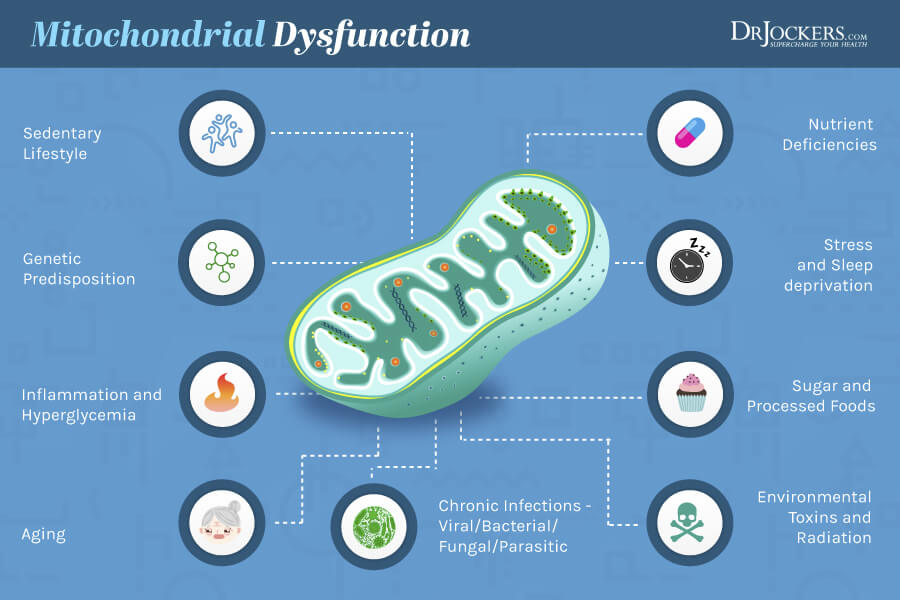
4. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: The mitochondria are the energy producing organelles in each cell of the body. They are extremely key in the bodies ability to handle oxidative stress. Dysfunction in the mitochondria leads to increased free radical and oxidative stress which creates immune alterations. Many researchers believe that other autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis are primarily a mitochondrial disease (12).
5. Low Glutathione Levels: Glutathione is the major anti-oxidant within every cell of the body. It is critical for white blood cell (WBC) function as the WBC’s encounter tremendous amounts of free radical and oxidative stress every second of the day. Low glutathione leads to chronic inflammation and often to autoimmunity (13).
6. Poor Omega 6:3 ratio: The average person has significantly more omega 6 fats than omega 3 fats. The increased omega 6 stimulate the release of pro-inflammatory mediating prostaglandin molecules. This is a key factor in the development of chronic inflammation and autoimmunity (14).
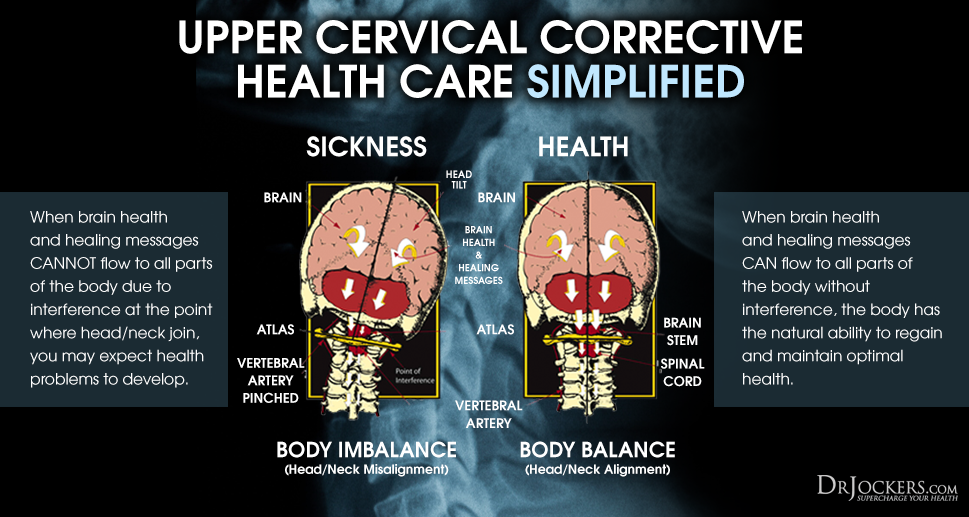
7. Upper Cervical Subluxation: The bottom of the skull (occiput) and the first bone (atlas) play a significant role in the coordination patterns of the brain and immune system. Dysfunction at this joint torques and compresses the top of the spinal cord and increases inflammatory activity in the body (15).
8. Environmental Toxins: Exposure to high levels of infectious microbes, environmental chemicals such as plasticizers, pesticides, herbicides, personal care products, heavy metals and biotoxins such as mold, viruses and bacteria wear down the bodies glutathione levels, alter the gut microflora and increase inflammatory activity in the body (16, 17, 18).
9. High Stress and Poor Breathing Habits: High mental and emotional stress increases stress hormone production which induces inflammatory activity within the body. Short and shallow breathing habits can simulate chronic mental and emotional stressors on the physiological level (19).
10. Lack of Sleep: Poor sleep promotes immune dysfunction and increased inflammation. Good sleeping habits and optimal melatonin secretion reduce inflammation and promote improved tissue healing (20).
11. Methylation: Methylation is a key process that protects DNA, turns on and off genetic traits and helps to detoxify environmental chemicals. Many individuals have certain genetic polymorphisms that limit their ability to appropriately methylate. Methylation plays a very important role in T cell function and poor methylation status is associated with the development of auto-immunity (21).
12. EMF Exposure: Electromagnetic frequency exposure has been shown to alter the function of the immune system and increase one’s susceptibility to developing an auto-immune condition (22)
I will touch on a few of these key areas and how they relate to Rheumatoid arthritis in this article.

Gluten Sensitivity and Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Gluten is the common protein molecule found in wheat, barley, rye, kamut and spelt. Gluten is a sticky storage protein that binds to the small intestinal wall where it often causes digestive and immune system disorders. Gluten sensitivity is an epidemic that is a major factor in the development of autoimmunity.
Research has shown a high prevalence of gluten sensitivity in individuals with autoimmune connective tissue disorder such as RA, lupus, scleroderma and Sjogrens disease (23). Studies have shown that a gluten-free diet has improved antibody counts and symptoms in many individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (24).
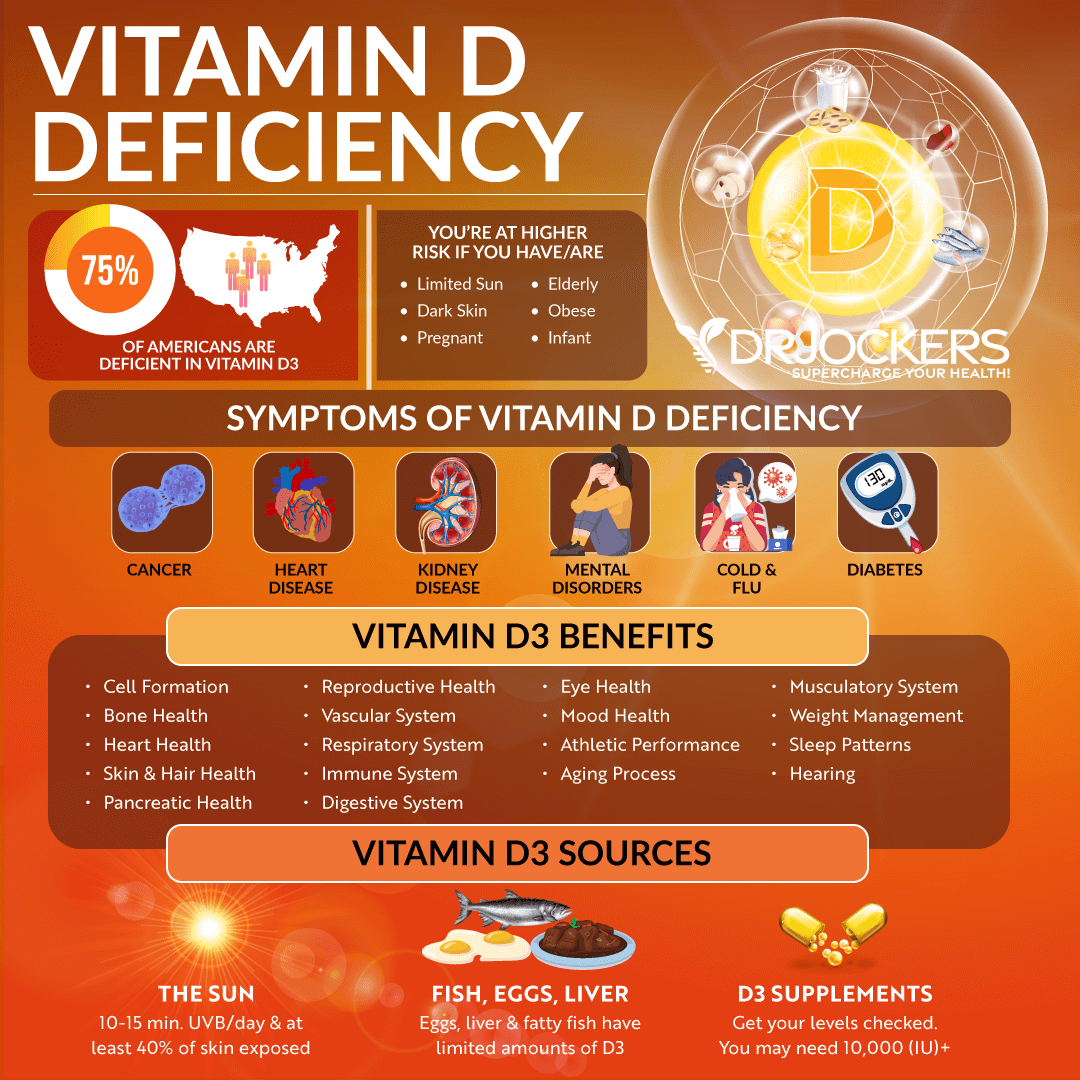
Vitamin D and Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Vitamin D is critical in the development and maturation of the immune system. It helps to enhance self-tolerance and reduce the risk of autoimmunity and chronic inflammation. Low vitamin D levels are a common finding in auto-immune diseases (25).
Reduced vitamin D intake has been linked to increased susceptibility to the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and vitamin D deficiency has been found to be associated with increased disease activity in patients with RA (26, 27).

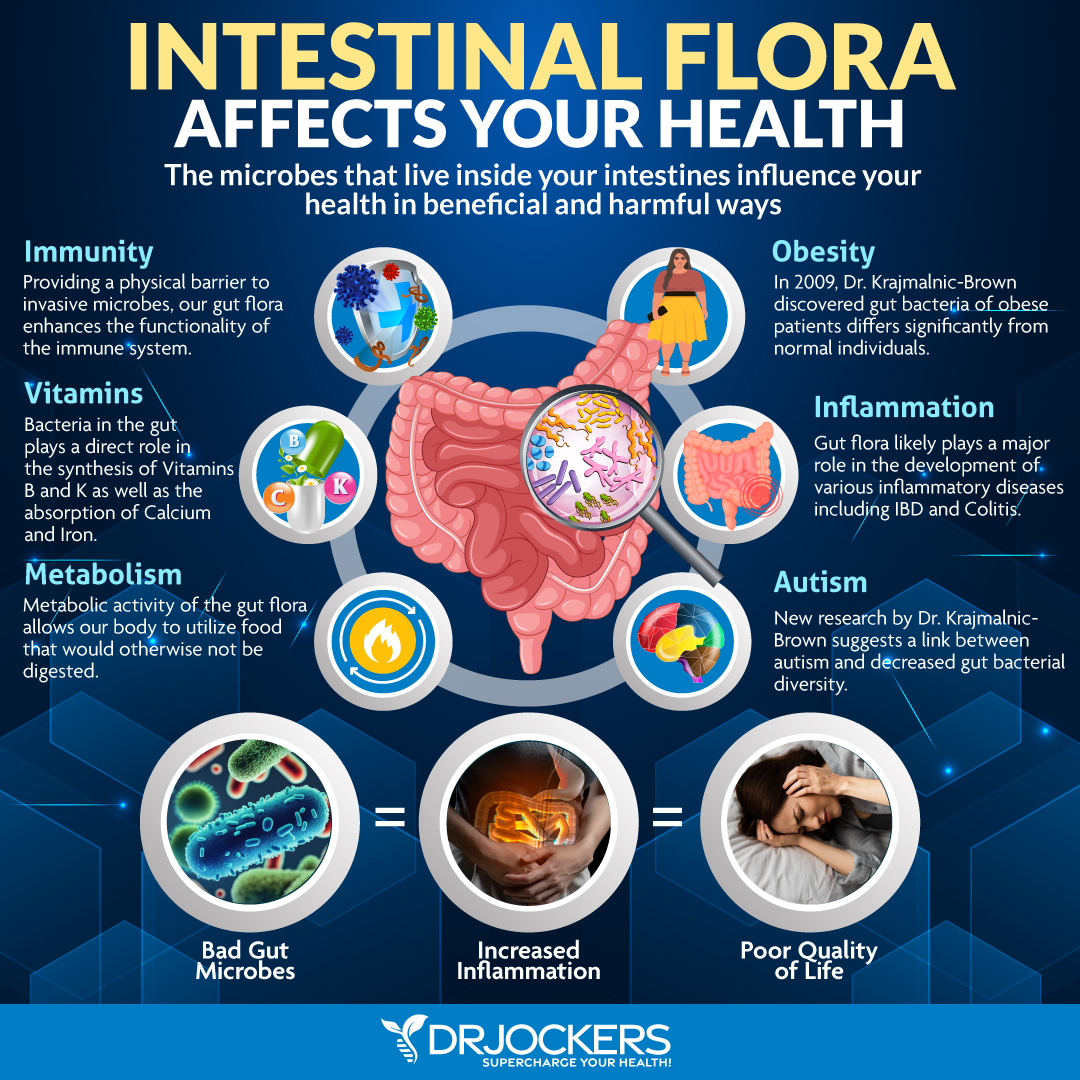
The MicroBiome and Rheumatoid Arthritis:
The gut microbiome is made up of over 1000 different species of microbes and it plays a huge role in nutrient absorption, detoxification and the development and maturation of the immune system. Certain bacteria of the gram negative classification are known to release a potent inflammatory mediator called lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Researchers have found that individuals with RA have high levels of the gram-negative bacterium Prevotella copri, which is correlated with an increase in LPS and inflammation. Additionally, these individuals had an overall loss of beneficial anti-inflammatory microbes. Additionally, the P Copri drove up the inflammatory cytokine Th-17, which promoted inflammation through another mechanism (28, 29).
SIBO and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Individuals with RA have a much higher tendency to have small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) than the normal population (30). We should normally have the majority of our bacteria in the large intestine and not in the small intestine.
SIBO develops when the normal homeostatic mechanisms that control intestinal bacterial populations are disrupted. The two processes that most commonly predispose to bacterial overgrowth are diminished stomach acid secretion and lack of small intestine motility (31). SIBO can lead to key nutritional deficiencies and chronic inflammation.
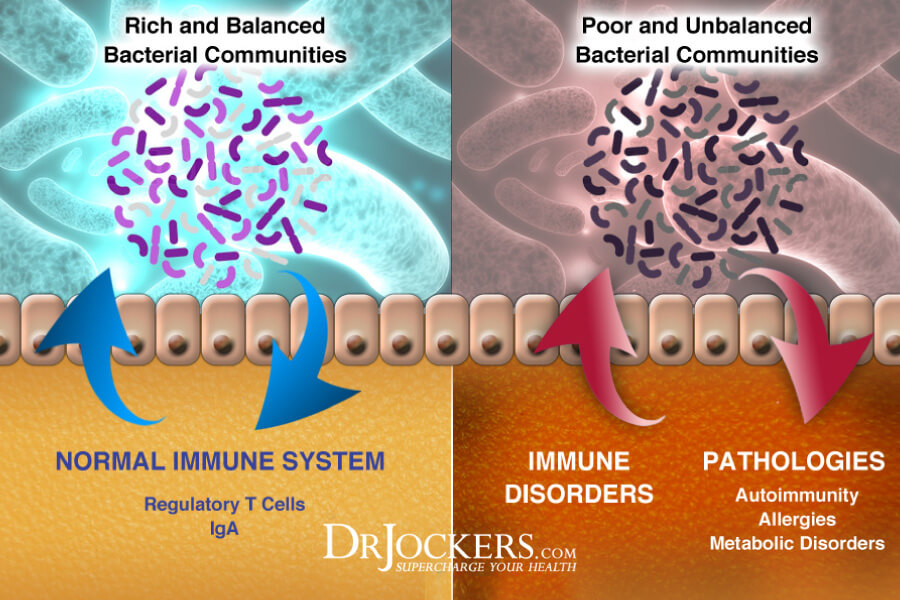
Leaky Gut Syndrome and Autoimmunity:
When the microbiome is dysregulated it often leads to a damaged gut lining and intestinal permeability. This is found in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and other auto-immune diseases (32, 33).
This “leaky gut” causes undigested food particles to pass into the bloodstream where they are tagged by the immune system and attacked with massive inflammatory processes that have the ability to affect nearly every system in the body. This creates a food allergy or sensitivity that the body reacts to whenever it is exposed.
The most common food based culprits include all processed foods, artificial sweeteners/preservatives and gluten containing products. Soy, peanuts, pasteurized dairy, corn and eggs are often not tolerated well. The nightshade family of eggplant, potatoes and tomatoes are often challenging on the system as well.
The most common medications given to individuals with RA, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, have been shown to increase intestinal permeability (34). So these medications may reduce inflammation and pain by suppressing key inflammatory prostaglandins, but they also promote further development of the disorder.

Mitochondrial Dysfunction and RA:
Every cell of the body has mitochondria within it that produce energy for the cell. The mitochondria are the battery packs of the cell and they are extremely important. High levels of oxidative stress wear down the mitochondria and cause a dysfunctional state.
Mitochondria are one of the main cellular sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and play a pivotal role in many autoimmune and chronic inflammatory conditions. Mitochondrial dysfunction leading to excessive production of ROS and RNS plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of RA (35, 36).
In rheumatoid arthritis, the cells are under so much stress that their main protective shield, glutathione (GSH) gets worn down and oxidative stress damages the mitochondria and the DNA leading to cell death. Poor blood sugar control and high environmental toxin exposure are known to deplete glutathione levels and impair mitochondrial function (37, 38).
Anti-Inflammatory Diet & Lifestyle
Anti-inflammatory foods help to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammatory activity in the body. Great anti-inflammatory foods include healthy fats from coconut products, avocados, olive oil, berries & phytonutrient rich vegetables. Healthy meat sources such as grass-fed beef, wild game, wild salmon, organic poultry and organic eggs are great if the gut can tolerate them.
It is advisable for anyone with chronic inflammation to include organic vegetable juices, fermented foods and herbal teas in their diet. Homemade sauerkraut, apple cider vinegar, coconut water kefir, and kimchi are great. Begin with small doses of all of these and add more if you tolerate them well.
Organ meats such as grass-fed liver, heart, etc. are rich in mitochondrial support nutrients. Powerful herbs such as turmeric, ginger, garlic, onion, rosemary, thyme, cinnamon, & oregano among others should be used as much as possible to improve immune coordination.
Consuming lots of sulfur based onions, garlic, cruciferous veggies on a daily basis and getting high quality seaweed in the form of kelp can be extremely helpful. Using purified fish oils to boost up omega 3 levels is also very important.

Rebuild the Intestinal Wall:
The best way to rebuild the intestinal wall is to incorporate a daily lifestyle of intermittent fasting. This should be a 16-20 hour liquid diet each day in which only cleansing beverages such as fermented drinks and lemon water are consumed.
Consume high quality shakes with berries, coconut or hemp milk and a hypoallergenic protein powder. No more than one solid food meal a day should be consumed for at least a 3 month period of time to ensure proper healing. One could also incorporate a six week liquid diet to take the stress off the digestive tract and speed up the process of healing the gut lining.
Vegetable juices can and should be consumed throughout the fasting period. Some of the best vegetable juices include wheatgrass & cabbage juice among others. Wheatgrass is known for its incredible chlorophyll content and ability to purify the bloodstream. Cabbage is loaded with the amino acid L-glutamine which is the primary amino acid in the gut wall.
Digestive enzymes and fermented foods should be used before or during the solid food meal to enhance digestion. Heavy duty probiotic supplementation should be used in the evening after the solid food meal to reduce inflammation that would be caused by the solid food of the meal.
Subluxation and Neurological Distortion:
Chronic inflammatory disease processes are influenced by the nervous system which controls the coordination of the immune system. Nerve stimulation is essential for the growth, function and control of inflammatory cells. Researchers have found that abnormal neurological control results in the development of auto-immune based inflammatory conditions such as RA (39, 40).
Subluxation is the term for misalignments of the spine that cause compression and irritation of nerve pathways affecting organ systems of the body. Subluxations are an example of physical nerve stress that affects neuronal control. According to researchers, such stressful conditions lead to altered measures of immune function & increased susceptibility to a variety of diseases (41).
Upper Cervical Spine is the Most Important:
The upper cervical spine is the most important region for immune coordination. Various wellness chiropractors specialize in stabilizing the upper cervical spine which allows the nervous system to control and coordinate the body with greater efficiency.
Many individuals with autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis have ligament laxity at the upper cervical spine. It is essential to see a well-trained wellness based chiropractor that specializes in upper cervical care and corrective care and has much experience working with individuals with advanced conditions such as RA (42).
These chiropractors will use a regiment of specific adjustments and corrective exercises to minimize subluxation, restore proper neurological tone and maximize the bodies healing potential.
Natural Support Strategies For Healthy Inflammation
Here are the best action steps to get started with on your journey to improve your inflammatory response. These strategies are not at this time FDA approved to prevent, mitigate, treat or cure rheumatoid arthritis and should not be confused as such. You should always consult with your physician before stopping or changing medications or taking on new health strategies.
Additionally, you should be working with a functional health practitioner to help guide you through these strategies. This is not an exhaustive list and there are other natural therapeutic strategies that I and functional health practitioners will utilize to help individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
Change Your Diet:
Eating an anti-inflammatory diet rich in nutrient-dense foods is the first best thing you can do to prevent autoimmunity and chronic inflammation. First, eliminate all inflammatory foods, including refined sugar, gluten, refined oils, deep-fried and processed foods, conventional dairy, grain-fed meat and eggs, soda and sugary drinks, and foods that you are sensitive to.
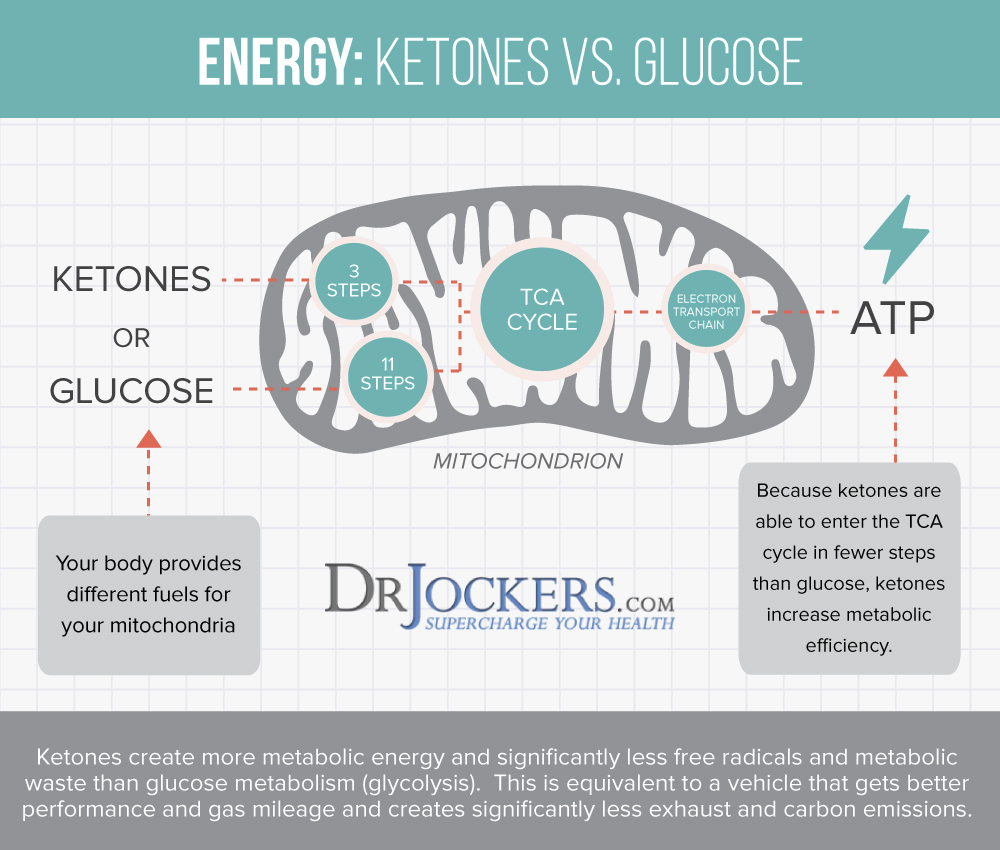
Instead, it is important to eat an anti-inflammatory diet that is rich in nutrient dense vegetables, low glycemic index fruits, herbs, spices, healthy fats, grass-fed meat, and wild-caught fish. I also recommend a ketogenic approach for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis conditions. Getting into ketosis will enhance mitochondrial function and significantly reduce inflammation in the body.
Test For Food Sensitivities:
Most people with autoimmune conditions have leaky gut and food sensitivities. These sensitivities can be hard to pinpoint as they result in delayed symptoms that are not life threatening.
The most common food sensitivities include gluten, corn, dairy, soy, peanuts and sugar. Some other potential food sensitivities to consider include all grains, eggs, nuts, seeds and nightshade vegetables (tomatoes, potatoes, peppers and eggplant).
It can be helpful to do a 28 day elimination diet where you remove all of these and then slowly add these back in one at a time. You can also do both biofeedback and blood testing to determine what foods are causing stress in your system and an elimination diet to test how you are responding to eliminating certain foods for periods of time. You can also

Intermittent Fasting:
Intermittent fasting is a form of fasting cycles between not eating (fasting) and eating (feasting) over a period of time. The benefits of intermittent fasting benefits include cellular repair, autophagy, immune regulation, inflammation levels, and insulin sensitivity.
It also helps to lower the risk of developing autoimmune and chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Going 16–18 hours between dinner and breakfast is one of the best ways to improve mitochondrial production. Your body improves energy efficiency by increasing and strengthening the mitochondria during periods of fasting. Consume your meals in a 6-8 hour window such as 11am–7pm or 12–6pm.
When you do this you enhance cellular healing and joint cell regeneration. Intermittent fasting helps to reduce pain, swelling and damage to the joints in individuals with RA (43, 44). To learn more about the benefits of intermittent fasting and best intermittent fasting practices, I recommend this article.

Reduce Stress:
Reducing stress is a critical for reducing inflammation and improving immune health. I recommend that you reduce stressors from your life as much as possible. Turn off the news, and only look at it once a day or a few times a week for a specific period. Reduce your social media use and time on the internet.
Avoid people and situations that bring you down. Surround yourself with loving and uplifting people. Engage in uplifting and relaxation-promoting activities. Read, try some arts and crafts, play cards or board games, sing, and dance.
Spend time in nature and do some grounding walking barefoot on grass. Practice daily gratitude and try positive affirmations. Practice self-love and laugh with friends and family. Meditate, pray, journal, and try daily breathing exercises. Be grateful and smile more.

Improve Your Sleep:
Prioritizing good sleep is just as important as reducing your stress levels. Develop a regular schedule going to bed and getting up at the same time every day to support your circadian rhythms.
Avoid electronics, sugar, caffeine, heavy foods, and stress close to the bed. Engage in relaxing activities, including stretching, relaxing baths, meditation, and prayer. Make sure that you have a supporting bed, pillow, and bedding, and sleep in a dark calming room.

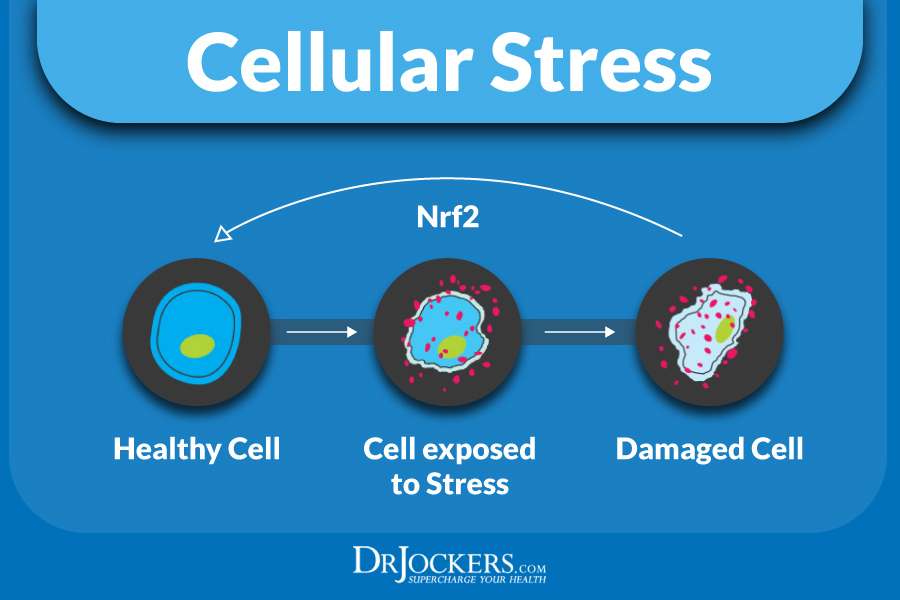
Power Up Your Nrf2 Pathway:
Nrf2 (NF-E2-related factor 2) is a transcription factor in humans encoded by a specific gene that regulates the expression of a set of antioxidant and detoxifying genes. This pathway is activated under times of oxidative stress to enhance the expression of a multitude of antioxidant and phase II liver detoxification enzymes that restore homeostasis to the ox/redox cycles in the body (45, 46, 47).
The Nrf2 pathway has been researched to be a key player in the development or prevention of chronic inflammation and autoimmune activity. Adding in clinical dosages of resveratrol, curcumin, quercetin, sulfuraphane and green tea (EGCG) can be extraordinarily beneficial for driving up the Nrf2 Pathway.
Include Magnesium & B Vitamin Rich Foods:
Magnesium helps to improve blood sugar signaling patterns and improves mitochondrial health. The best magnesium and B vitamin rich foods include dark green leafy veggies, avocados, grass-fed animal products, raw cacao and pumpkin seeds.
You can also do Epsom salt baths to support your magnesium levels. It would also be wise to supplement with a good magnesium and B complex supplement. Look for magnesium L-threonate which is the best form of magnesium for crossing the blood brain barrier.
When it comes to B vitamins, it is best to look for one with pre-activated forms such as methyl-folate, methyl-cobalamin (B12), Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate form of B6, and Riboflavin-5-phosphate form of vitamin B2. The methyl groups are in the active form and will be better utilized by the body.

Focus on Deep Breathing:
Improving your posture, seeing a high quality chiropractor and optimizing your breathing patterns is highly recommended. Taking time to slow down your breathing and take long-deep breaths for a few minutes every hour will help reduce the sympathetic, fight or flight part of the nervous system.
The better we breathe, the better we will heal and the more blood flow we will get and the better our immune and inflammatory health will be. Follow these tips here to improve your breathing patterns.

Use Antioxidant Rich Herbs:
Carminatives are herbs that help to improve digestive health by reducing pathogens in the gut, stimulating the production of stomach acid, bile and pancreatic enzymes and modulating the gut microbiome.
Examples of these herbs include turmeric, ginger, oregano, garlic, basil, thyme and rosemary. These herbs are help to improve digestion, reduce inflammation and support a healthy brain. There are a number of ways to use these that I discuss in the following image. I like putting the herbs on foods, using herbal teas, fermented foods and essential oils.

Ground Your Body:
In our society we are surrounded by toxic electromagnetic frequency’s (EMF’s). These EMF’s increase stress and inflammation within the body and can be a trigger for autoimmune activity for some individuals.
By going outside daily and walking barefoot on grass, dirt or sand you absorb natural EMFs from the ground that balance your electrical rhythms. Follow the steps in this article here.

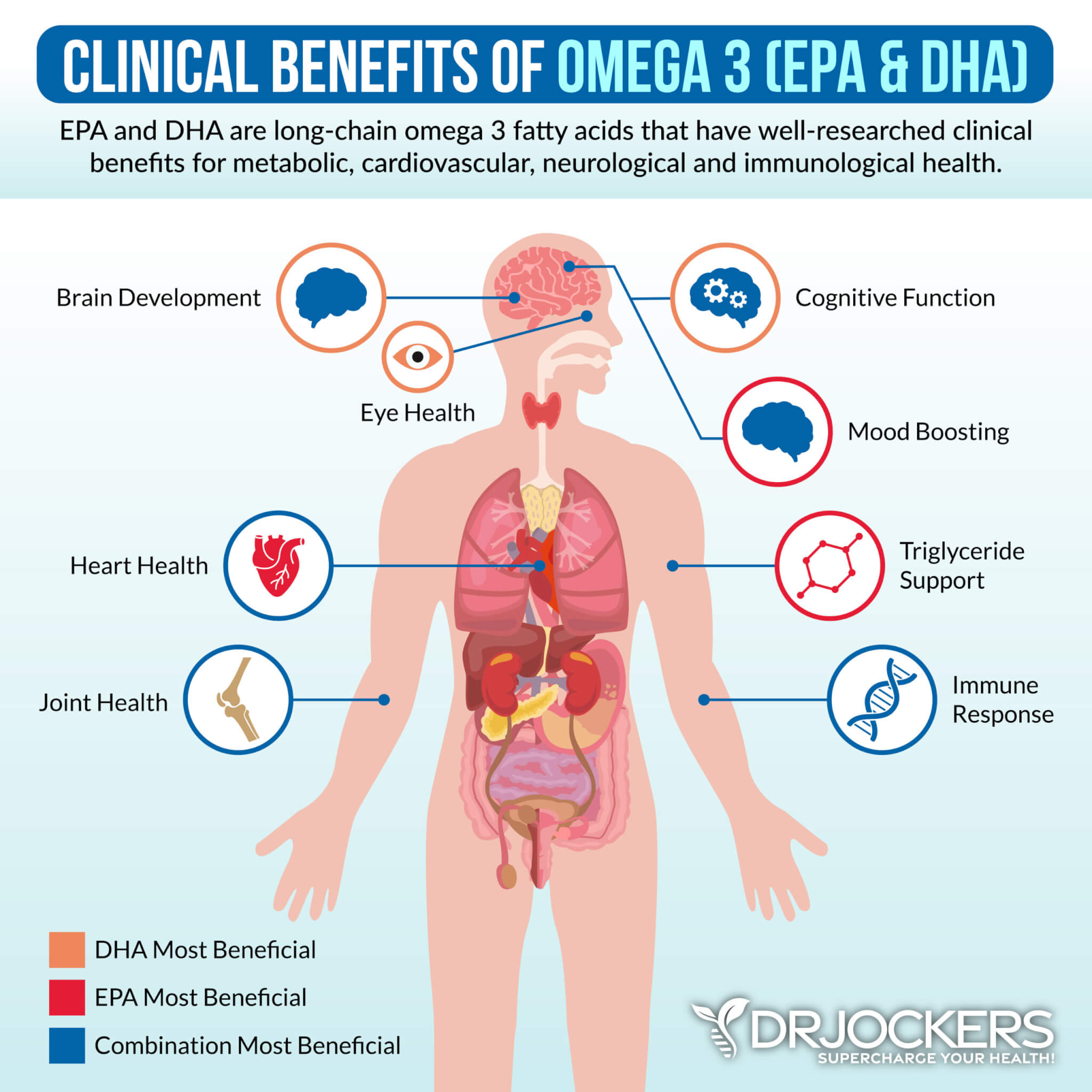
Supplement With Omega 3’s:
Omega 3 fatty acids and in particular the long chain variety EPA and DHA are critical for stabilizing blood sugar, reducing inflammation and autoimmunity improving joint health. Consume grass-fed meat, grass-fed butter, wild-caught fish, seafood and spirulina to get it in your diet.
Plant based omega 3’s such as flax oil only contain the small chain omega 3 called ALA and do not have any DHA. It is very hard for our body to convert ALA into DHA so it is best to get a high quality fish or krill oil that is rich in EPA and DHA. You want to find a brand that is molecularly distilled to take out any heavy metals and other unwanted contaminants.
Be sure to discuss with your physician before using as fish oils have a blood thinning affect and can be contraindicated if you are on blood thinning medications.
Improve Your Mitochondria:
The mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of every cell. When someone has an autoimmune disorder it is a clinical sign that they have dysfunctional activity going on in the mitochondria.
Support your mitochondria with clinical doses of CoQ10, L-carnitine, N-acetyl cysteine, creatine monohydrate, B vitamins, magnesium, alpha lipoic acid and D-ribose. You can find mitochondrial support supplements that have most if not all of these key nutrients.

Optimize Your Vitamin D:
Low vitamin D3 is associated with chronic inflammation and autoimmune conditions. Vitamin D is arguably one of the most powerful nutrients responsible for modulating and coordinating the immune system.
In autoimmune disease, the immune system has a hard time differentiating self from non-self (foreign invaders). Vitamin D helps the immune system make this important distinction, which reduces autoimmune disease formation (48). Vitamin D also helps to modulate the immune system to reduce inflammation throughout the body (49).

Support Gut Health
In order to reduce inflammation and autoimmunity, you have to repair and heal your intestinal lining. I recommend eating a gut friendly diet that works best for your body type. For some individuals with RA, a low oxalate diet is very helpful.
Consuming liquid nutrition for is great for stimulating the digestive process, increasing nutrient absorption, and improving gut health. Liquid nutrition does not require as much energy to digest, so your body can focus on healing and repair. You can combine liquid nutrition with fasting strategies for quicker healing.
Using a good quality bone broth collagen in a shake or smoothie is a great way to include liquid nutrition in your diet. Collagen contains amino acids, including glycine and glutamine, which are essential for healing leaky gut. These amino acids seal the holes in the gut by healing damaged cells and building new tissue. Collagen also makes up the villi, small finger-like structures on the intestinal wall and assists with water absorption in the intestines.
Additionally, I recommend taking a daily probiotic supplement. Probiotics helps to optimize your gut health and improve your nutrient absorption while reducing gut related inflammation. When gut inflammation goes down it also reduces inflammatory mediators that impact joint health.

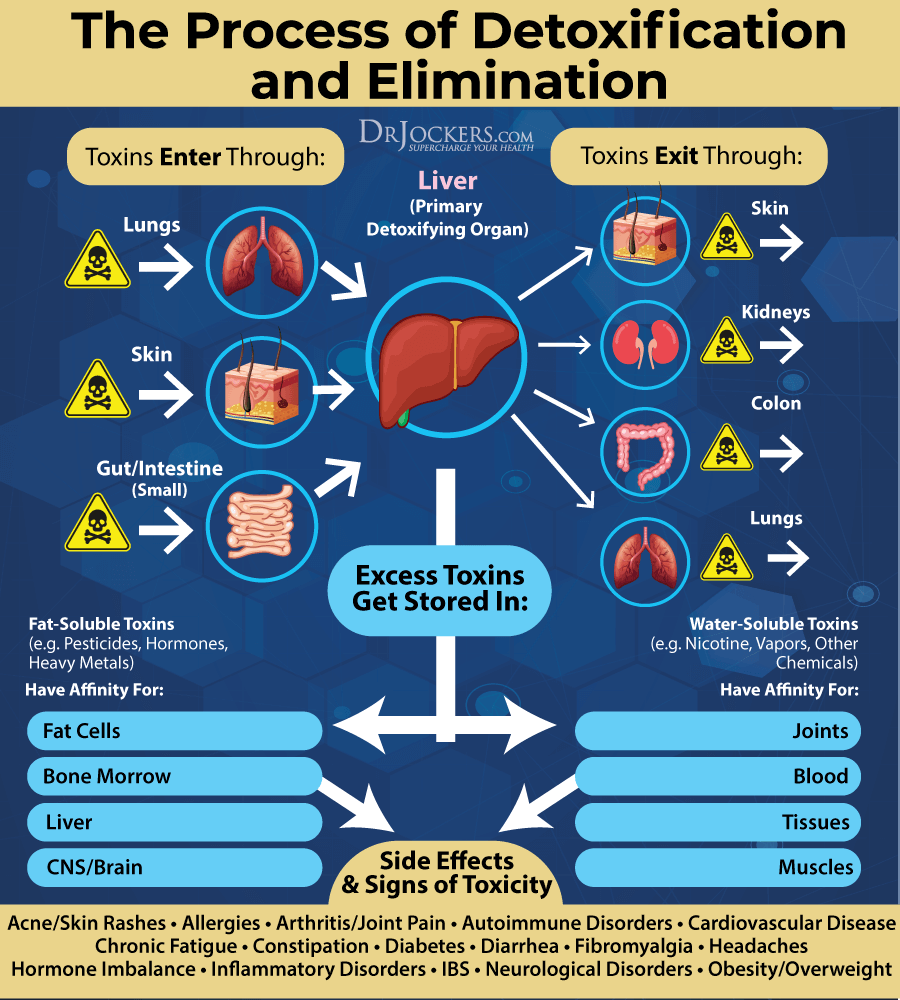
Reduce Toxin Exposure
Reducing your toxic exposure is critical for improving liver function and reducing inflammation. Buy organic food as much as possible. Stop using conventional beauty, body, and household products, and replace them with organic, natural, or homemade alternatives.
Use glass, stainless steel, wood, and bamboo products instead of plastic. Spend time in nature and breathe in the fresh air. Use a good indoor air filtration system. Make sure that you drink clean, toxin-free water by using a high-quality reverse osmosis system. Add a slice of lime for some extra flavor.

Support Detoxification Pathways
It is not enough to put good things into your body, you have to make sure that the bad things come out as well. Drink plenty of water to support detoxification through sweating and urine. Support your detoxification pathways to protect your body from brain inflammation.
I recommend using infrared saunas to promote detoxification through sweating. Try rebounding and dry-skin brushing to support your lymphatic pathways. Support two major detoxifying organs, your kidneys and liver with herbs like milk thistle, parsley, dandelion and bioactive carbons which can penetrate and remove toxins from deep within the tissues and cells.
Final Thoughts
Rheumatoid arthritis is a serious issue that affects millions of people around the world. The symptoms of RA include joint pain, impaired joint function, fever, weight loss, anemia and fatigue. To protect yourself from chronic inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, follow the recommendations in this article. You may notice improvements in your pain, energy and overall health.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. On our website, we offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out and our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!




I thought this was an excellent article. Im going to be taking on board alot of your advice, Thankyou
Glad you got a lot out of the article Beth!
The article is very informative. I’ve had RA for 19 years, Celiac Disease for over 3 and have been on a gluten free diet for 2 or so years, I’m also IgA difient so getting a true test result on the Celiac was very complicated. I have problems with my Vitamin D3 for 12 years but now have it at normal levels, I still don’t sleep well, I have fibromyalgia, 2 broke hips with one replaced, also have GERD, asthma and COPD. Much of what i read in your article I’ve rad in other books or articles. It’s so overwhelming. Where to start when there are so many issues. I feel sick most of the time from one or more issues. Very depressing sometimes. Thank you for what you do. Information is key to helping people like me.
So sorry to hear about all of this Kathy! So glad you are taking many great action steps like the gluten free diet and boosting D3. Be sure to follow the other strategies in the article to get better results and overcome these health challenges!
Is dextrose suitable?
It is made by corn and can be immune reactive, so I don’t recommend it.
And what red beet? Is for RA OK?
Hi. I see that RA is not the only disfunction if this relates autoimmune state of health. There is the whole complex of metabolic og digestive dysfunctions. I have some similar symptoms, but not so much on RA. I am just thinking all the time on what is a real cause of this state. Taking into account literature which I have read, I believe that the cause is in lymphatic system, intestinal inflammation lymphatic nodder og wrong circulation of lymphe. What do you think about that?
Nathalie,
It is definitely a complex issue. It depends on the situation but some common culprits are the digestive system problems and blood sugar that cause chronic inflammation. I have an article about it here https://drjockers.com/5-steps-to-heal-autoimmune-disease/
I have a chronic RA pain, it is really painful. Please let me know more about the disease. Your article is so informative and has cleared some issues I falsely believed in the past.
Hey Ronaldo, everything in the article above is geared towards helping you solve your pains. If you would like to work with a functional nutrition practitioner to build a customized health plan, reach out to michael@drjockers.com to get started!
Hello Dr. Jockers,
I have gluten intolerance but because of stress at work had been cheating with some gluten tainted foods. In January, I started getting joint pain in my right thumb now swollen and painful. Now the left thumb is starting to get joint pain as well as the ball of my left foot. A month ago, my neck began to ache making it difficult to turn my head side to side. Recently, I had a horrible flew virus with vomiting and diarrhea which completely depleted me. The next day or so, as I recovered, all of my pain and swelling symptoms disappeared, but once I began eating regular foods, it all came back. I have been very careful to keep gluten out of my diet since then but the pain and swelling has returned. I also have had hypothyroidism and have been on medication for 25 years. I plan to get blood work done in the next few weeks to confirm what this swelling and pain could possibly be. My symptoms appear to be caused by RA. Why would it all disappear after my flu? Is it possible all caused by a leaky gut?
I am not sure why it might go away after a flu. Were you fasting during that time? I will say it is very common for people that have RA to also have a lot of gut issues. It is an important stressor to address to help the body heal!
I want to study causes of ra .i want to help my wife to fight her deses. I need a natural food treatment helping her to control ra semptoms. I need some body care of us.
Sorry to hear about this!! Here is a helpful article: https://drjockers.com/heal-autoimmune-disease/
About to resign from work, today both lower limbs are painful and sometimes swollen,tomorrow upper limbs next day the neck any remedy that will work a little bit faster for me so that I won’t loose my job am stressed
So sorry to hear that! Praying for you!
I am on methotrexate and sulfasalazine tablets for my RA, both of which are to be taken with or after food – if I were to attempt the 6 week liquid diet will that negatively affect how my medication is absorbed? Basically can I take my medication without food?
You will need to discuss this with your prescribing physician!
After my Rheumatoid Arthritis diagnosis in 2009. I was put on Naprosyn and after some time i didn’t feel any different, so i started on a Natural RA Formula treatment protocol from RICH HERBS FOUNDATION (ww w. richherbsfoundation. com), the treatment effectively treated my Rheumatoid Arthritis condition. The swellings, stiffness, fatigue and joint/muscle/body pains has subsided, I feel better overall than i have felt in years. Six months after the treatment, I made an appointment with a rheumatologist in Houston, after examining me, she looked at me and told me I did not have Rheumatoid Arthritis because all the usual Rheumatoid Arthritis symptoms had stopped. Its almost like a miracle!
That is wonderful to hear Monica! Thank you for sharing.
4stage rhymatalogy so much bady pains but local recment taken because money problem sir.iam p.e.t.teacher in school level. I have baby aslo please any pain reduce solution Dr.sir
Hey Megan, It sounds like there is a lot going on. It is important for you to work with a functional health practitioner that will get to the root cause of the problem and customize a specific plan for you while you are pregnant. This article offers the importance of good hydration and other techniques to reduce pain.
I am wondering what you would do if a microbiome DNA sequencing test discovered extremely high levels of Prevotella copri in an otherwise healthy young male? Are there herbs which could combat it? Thanks for your advice
Yes I would use a powerful full-spectrum anti-microbial such as our GI Clear or our Para 2 product
GI Clear: https://bit.ly/39qoP0Y
Para 2: https://bit.ly/2sC5t8r
Are the symptoms listed in the article inherent only to RA?
No there is crossover with other issues. However, the combination of all of these would be very suspicious of RA.
Thank you Dr. Jockers!
You are very welcome!
I am interested in the Three most important nutrients in healing autoimmunity ebook however there was no link provided even though the opt in page said that it was at the bottom of the page.
So??
Yes you can register for that here: https://drjockers.com/autoimmune-elimination-opt/
Thanks so much, Dr Jockers. You´re great. (Greetings from the Netherlands!) I had had RA for about 18 years, with painful wrists. I never took medicines. After a week of leaving out the nightshades (in 2019), the pain disappeared completely and has never come back . I don´t seem to react negatively to gluten or dairy (not even to sugar or other unhealthy things). So on the whole I could say I´m “cured”. The strange thing, though, is that I do react heavily against very healthy foods such as olive oil, collagen peptides, chlorella, pomegranate juice, raw garlic, etc. (they cause me a lot of pain in my joints and/or my groins). Of course I can opt for not eating these things and I´m very well, but I realize it means that there still is something (very) wrong with my system.
Wspaniały wywód profesjonalisty ,pomocny w zrozumieniu problemu z którym boryka się wielu ludzi na świecie .Cywilizacja niesie ze sobą niestety i nieprzyjemne zjawiska i tu jest szczególna uwaga by pamiętać czym odżywiali się Nasi przodkowie ,nie niszczmy przekazanych w genach odporności a wręcz starajmy się o powrót do zdrowego i smacznego jedzenia. Poruszona kwestia nieszczelności jelit ma również swoje podłoże w paskudnej przypadłości candida i z tym też trzeba walczyć. Ponadto trzeba pamiętać o odpowiednim dostarczeniu żelaza.Wspaniała praca pozdrawiam z pięnej Kotliny Kłodzkiej na Dolnym Śląsku w Polsce Wojtek