 Top 7 Tips to Balance Blood Sugar and Burn Fat
Top 7 Tips to Balance Blood Sugar and Burn Fat
Healthy blood sugar levels are critical for your overall health and well-being. Unbalanced blood sugar may increase your risk of insulin resistance, prediabetes, diabetes, and other health issues, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, liver issues, vision loss, and other health issues. Balancing your blood sugar through a healthy diet, lifestyle, and supplementation is essential for reducing your health risks and improving your health.
In this article, you will learn about the importance of healthy blood sugar levels. I will discuss the connection between visceral fat and insulin resistance. You will learn about 7 great tips for balancing blood sugar. I will also share the best herbs and nutrients for balancing blood sugar and recommend some supplements for blood sugar support.
The Importance of Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is the main sugar in your blood and a source of energy for your body. Your body breaks down the food you eat into sugar. Then it is released into your bloodstream. Your pancreas makes a hormone called insulin. Insulin helps to regulate your blood sugar, and it also allows sugar to get into your cells for energy.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is critical for your overall health and well-being. It is also essential for reducing the risk of insulin resistance, prediabetes, diabetes, and other chronic health issues linked to unhealthy blood sugar levels. Unbalanced blood sugar levels, when not treated, insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes, which may increase your risk of heart disease, stroke, vision loss, liver issues, kidney failure, and other issues.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 100 million people in the United States are living with prediabetes or diabetes (1). Fortunately, it is possible to avoid prediabetes or diabetes.
Blood sugar issues, hypoglycemic episodes, and insulin resistance, or signs of these problems, can arise before developing prediabetes or diabetes. You will learn tips from this article on how to balance your blood sugar and reduce your risk of these health issues.

Insulin Resistance and Visceral Fat Formation
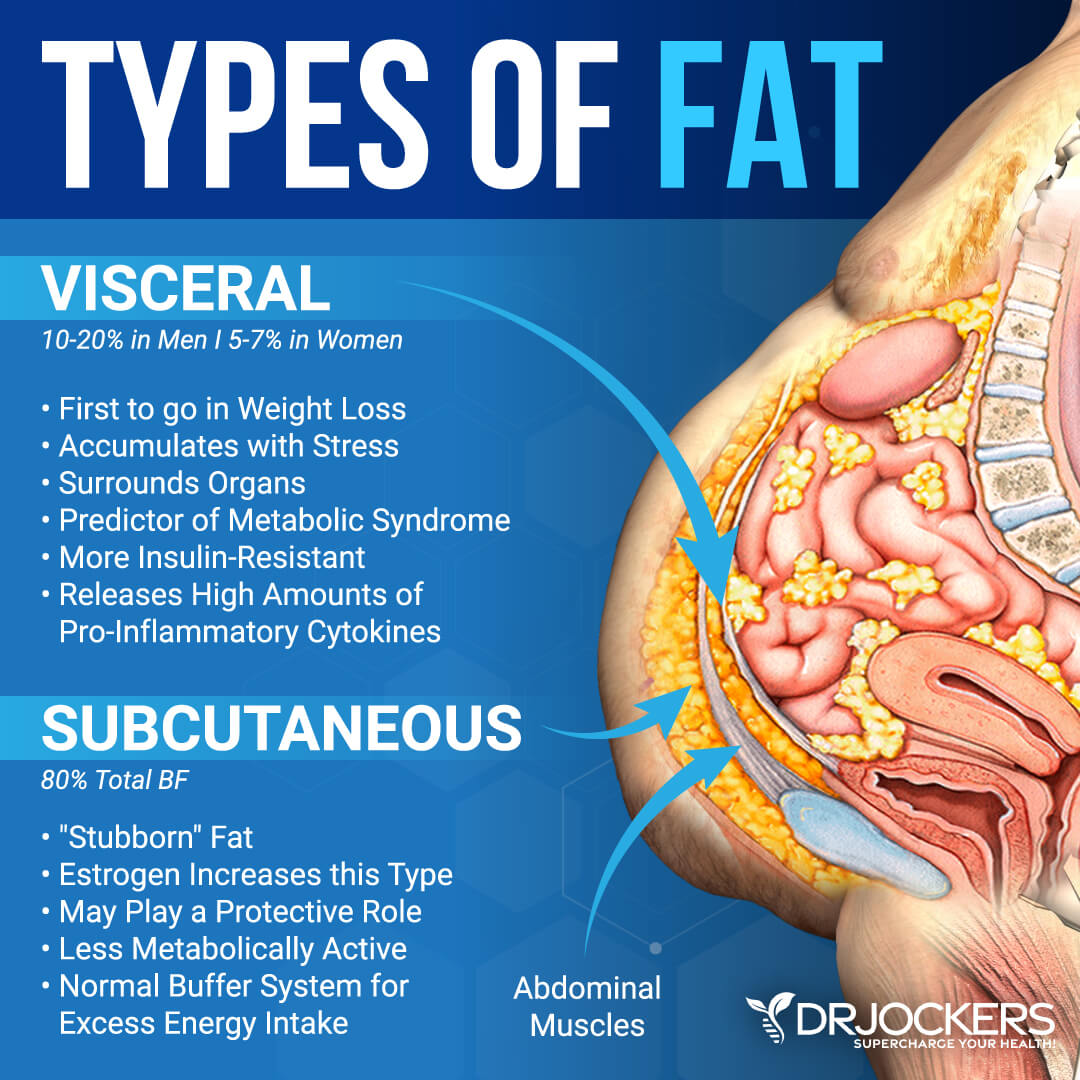
Visceral fat is a type of fat that accumulates in your intra-abdominal adipose tissue. It is a gel-like fat that wraps around and in between your organs inside your abdomen. It may be found around your liver, pancreas, and kidneys. It is different from subcutaneous fat, which is the pouch you can see and touch around your middle.
Having a protruding belly and a large waist is a sign of too much visceral fat in your midsection. This is a serious health risk. A 2016 study published in Nature Communications found that visceral fat is a much more serious problem than subcutaneous fat (2).
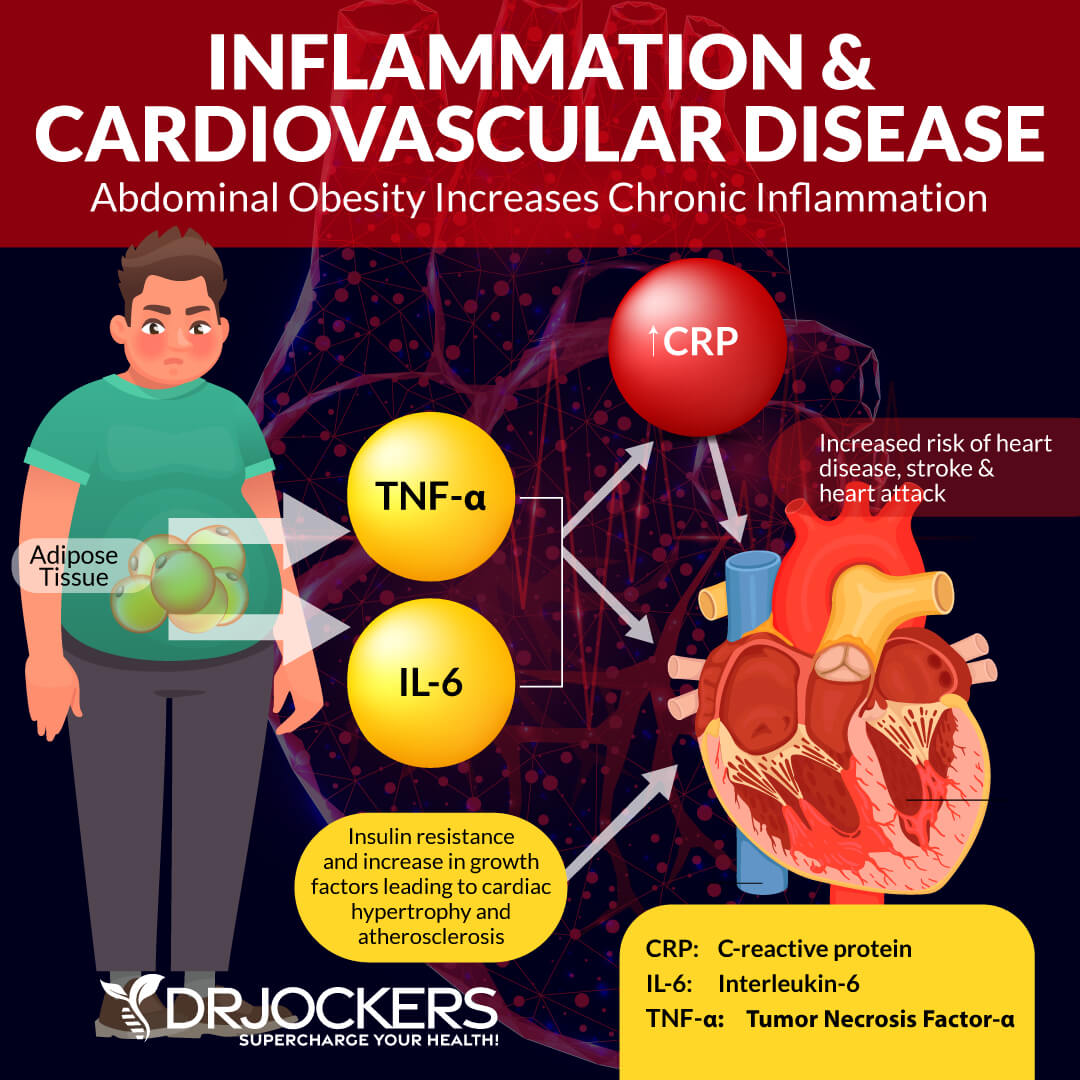
Visceral fat triggers inflammatory pathways, increases inflammation, interrupts signaling between molecules, and negatively affects hormonal functions. It also increases the risk of a number of health issues, including obesity, diabetes, coronary heart disease, stroke, cancer, sleep disorders, arthritis, hormonal issues, sexual dysfunction, and depression.
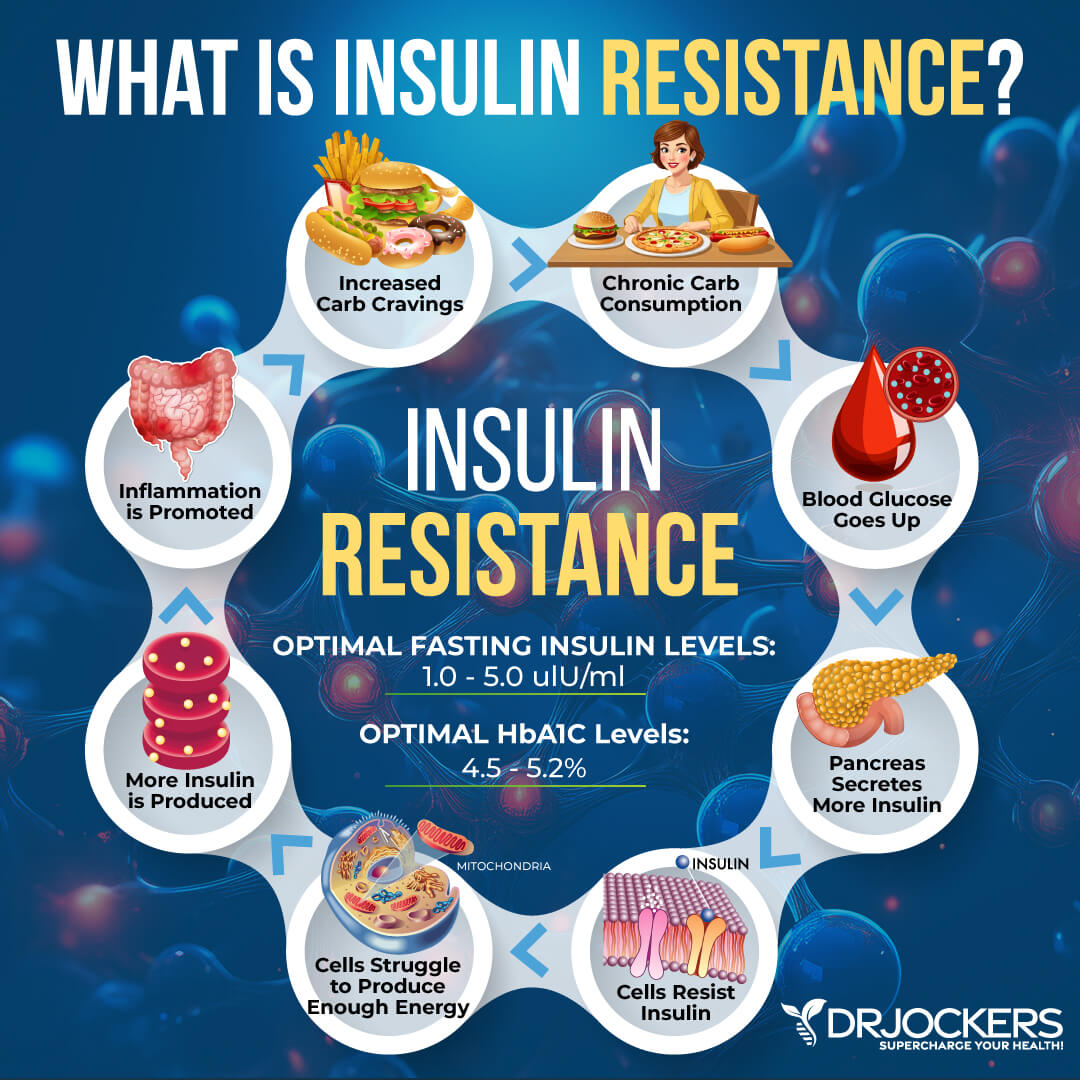
Among many of these health issues, visceral fat plays a role in the development of insulin resistance, which develops into prediabetes and diabetes. Insulin resistance means that your body is unable to respond to insulin well and cannot easily use all the sugar in your blood.
This forces your pancreas to overwork and make more and more insulin to keep up and try to keep your blood sugar levels at a normal range. Insulin resistance increases your risk of prediabetes and diabetes. Prediabetes means that your blood sugar levels are too high but not high enough to meet the criteria of having type 2 diabetes.
Simply being overweight and having extra abdominal fat on your body increases your risk of insulin resistance, diabetes, and other health issues. Abdominal fat has a higher risk than fat on your thighs or hips. However, excess visceral fat has even more risk than excess subcutaneous fat.
According to a 2013 study published in Nutrients, body fat distribution plays a large role in developing insulin resistance (3). Researchers found that visceral abdominal fat may increase your risk of insulin resistance more than other types of fat. Improving adipose tissue function and reducing visceral fat may play a critical part in decreasing insulin resistance.
Visceral fat can contribute to insulin resistance even if you don’t have diabetes or didn’t have prior issues with blood sugar imbalance. According to a 2010 study published in the Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology (Tokyo), we may use visceral fat as a predictor of insulin resistance even in non-diabetic people (4).
According to a 2016 study published in the Yonsei Medical Journal, there may be a strong connection between visceral fat and the risk of developing prediabetes and diabetes (5). This link was stronger than any other anthropometric obesity indicators measured.
Of course, your diet may play a role in this connection as well. Eating too many calories and too many foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates may increase the visceral fat in your body.
Visceral fat itself may also contribute to your cravings for sugar and carbs. According to a 2018 study published in the International Journal of Obesity (London), visceral fat may disrupt your brain’s sensitivity to interoceptive feedback (6). This may impact your eating behavior, appetite, and cravings.
Having excess visceral fat may increase the risk of obesity. This may further increase insulin resistance and the risk of diabetes, which may only feed your cravings for unhealthy foods. Cravings can lead to the increased consumption of sugar and inflammatory foods, which will increase visceral fat, further feeding obesity and the risk of insulin resistance. As you see, this can turn into a vicious cycle.

Measuring Visceral Fat Levels
The only way to measure your visceral fat levels exactly is by using an MRI or CT scan. However, these procedures are not only expensive but also unnecessary. You can take some easy measurements at home or with the help of your doctor that can indicate your risk for visceral fat.
Calculating your waist to hip ratio and waist to height ratio is the best way to figure out your risk factors. It’s simple and completely free. Here is how to do it.
Waist to Hip Ratio
Calculating your waist to hip ratio (WHR) at home is simple. However, if you need help, you can always ask for assistance from your healthcare provider. Here is how to do it:
- Stand up straight. Don’t slouch.
- Find the smallest part of your waist. It is generally located right above your belly button. Measure your waist circumference with a tape measure.
- Find the widest part of your hips or buttocks. Measure your hip circumference here with a tape measure.
- TO calculate your waist to hip ratio, divide your waist circumference by your hip circumference.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and a 2001 study published by the International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, a waist to hip ratio of .85 for women and .90 for men may indicate abdominal obesity and increases the risk of diabetes and other metabolic issues (7, 8).

Top 7 Tips to Balance Blood Sugar Levels
So how can you balance your blood sugar levels naturally? Here are many tips on how to balance your blood sugar and burn fat with a healthy diet and herbal support.
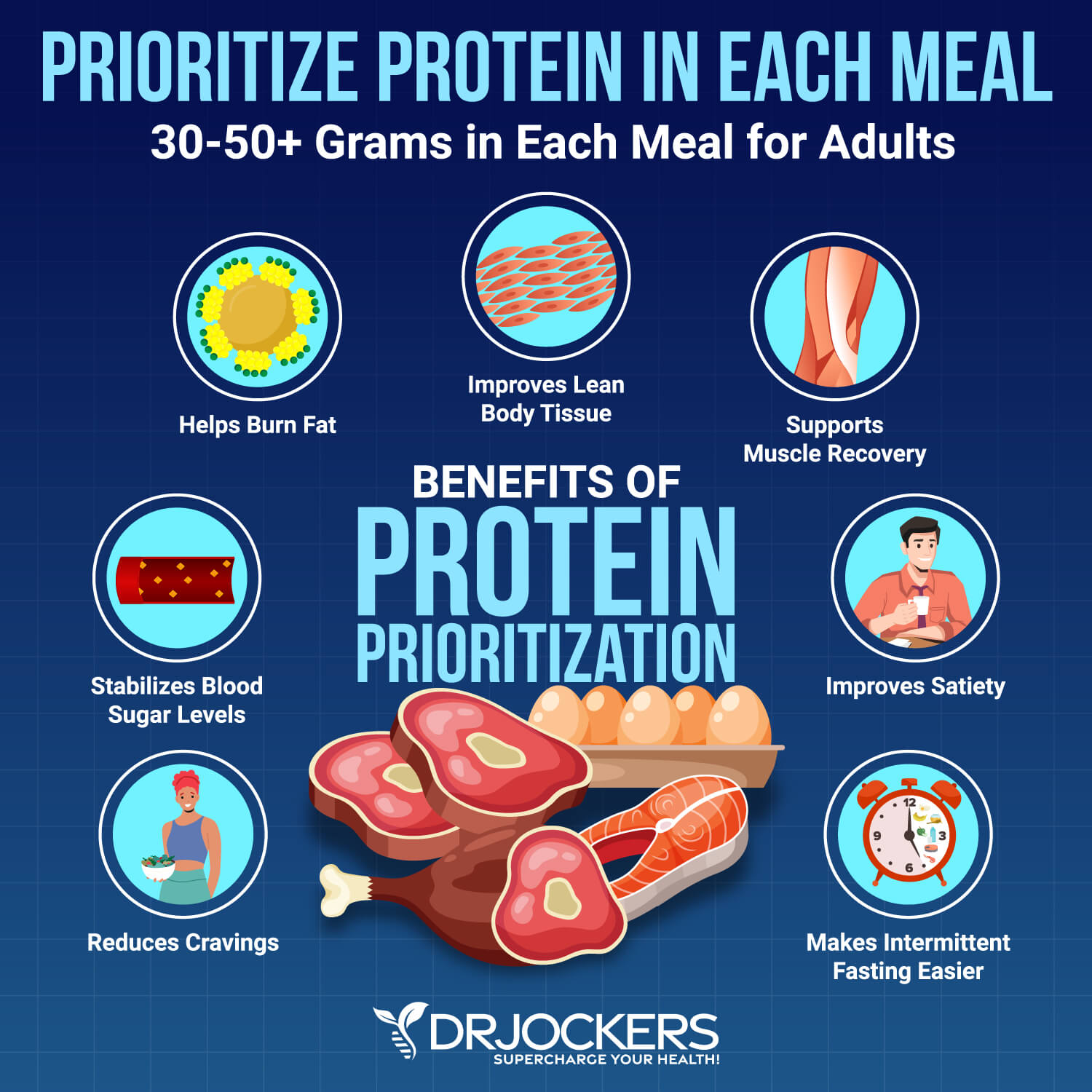
Eat 30 – 50+ Grams of Protein in Each Meal
Eating a healthy diet of nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods, including greens, vegetables, herbs, spices, grass-fed meat, pasture-raised poultry and eggs, wild-caught fish, and wild game, is, of course, critical for balanced blood sugar levels. However, you need to be conscious about your macronutrient ratios as well.
I recommend getting 30 to 50 grams of protein or more each meal. According to a 2021 study published in the Iranian Journal of Public Health, eating protein with your meals may help to balance your blood sugar levels (9).
They found that participants with type 2 diabetes who were given a meal containing both carbs and protein had lower blood sugar levels after their meals than those given a meal of carbohydrates. A 2022 study published in Women’s Health Reports (New Rochelle) found that a higher protein and lower carbohydrate diet was more beneficial for the blood sugar levels of women with gestational diabetes (10).
Enough protein in your meals may also help to decrease cravings for unhealthy foods and help you feel mentally alert and energized. Healthy sources of protein may include grass-fed beef, pasture-raised poultry and eggs, wild-caught fish, organ meats, wild game, seeds, and nuts.
Eat at Least 15-20 Grams of Healthy Fats in Each Meal
As I already mentioned, research has shown that a diet lower in carbs and higher in protein is better for your blood sugar levels (9, 10). You can’t forget about healthy fats, either. A 2020 meta-analysis published in Cureus has found that a high-fat, low-carb ketogenic diet may help to improve fasting blood sugar levels, improve fasting insulin levels, support weight loss, improve cholesterol levels, and improve diabetes (11).
I recommend eating at least 15 to 20 grams of healthy fats with each of your meals. Healthy fats include avocados, avocado oil, olives, extra-virgin olive oil, extra-virgin coconut oil, coconut milk, MCT oil, wild-caught fish and seafood, flax seeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds.
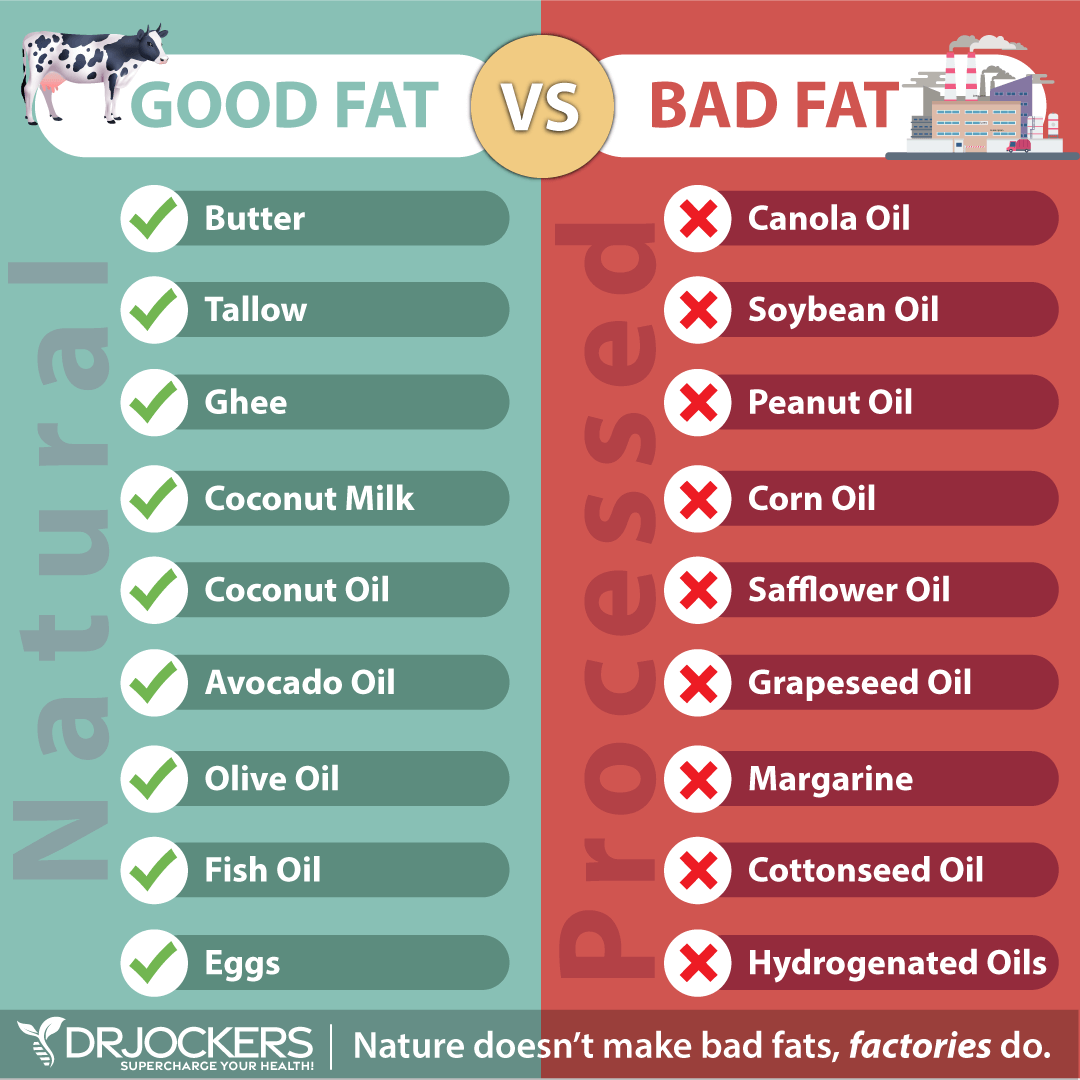
Avoid Processed Carbs and Naked Carbs
Even a high-fat, protein-rich diet contains some carbs. To balance your blood sugar, I recommend keeping your sugar and carbohydrate intake low. Any carb intake should be from healthy sources and shouldn’t be eaten alone.
Avoid eating processed carbohydrates, such as cakes, pastry, bread, pasta, candy, or ice cream. Avoid eating naked carbs. Naked carbs mean eating carbs without protein and fat on the sides, for example, eating potatoes or bread without much or any fats or protein.
When you eat carbs, make sure your plate is balanced, with mostly healthy fats and protein, with a little carbs on the side. Healthy carbohydrate sources include sweet potatoes, carrots, beets, and other sweet vegetables and fruits. Ideally, choose low glycemic index fruits, such as berries.

Go For a Walk After Meals
You may be surprised to hear that going for a walk after your meals may help to balance your blood sugar levels. According to a 2022 systematic review and meta-analysis, even 2 to 5 minutes of walking after a meal may help to improve your blood sugar and cardiometabolic markers (12).
Since your blood sugar levels tend to spike about 60 to 90 minutes after eating, according to 2017 research published in Frontiers in Endocrinology, it’s best to go for a walk within an hour of your meal (13).
It doesn’t have to be a long walk; even 2 to 5 minutes does the trick, though if you can, I recommend a bit more. It can turn into a great family activity or activity with your colleagues at work to take a short stroll after lunch or dinner. I also recommend moving around throughout the day to support healthy blood sugar levels.

Eat Protein & Fiber Before Carbs
Eating your protein and fiber before carbs may also help to balance your blood sugar levels. Eating protein along with carbs may be better for your blood sugar than carbohydrates alone (7, 8). Eating protein first may also help with satiety, reducing carb cravings, and overeating.
According to a 2014 study published in the Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, eating vegetables before carbohydrates may help with blood sugar levels and long-term glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes (14).
According to a 2020 study published in Nutrients, eating fiber along with your meals, before carbs, may help to balance blood sugar levels and manage or reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes (15). Not to mention that vegetables are full of micronutrients that nourish your body and reduce cravings.
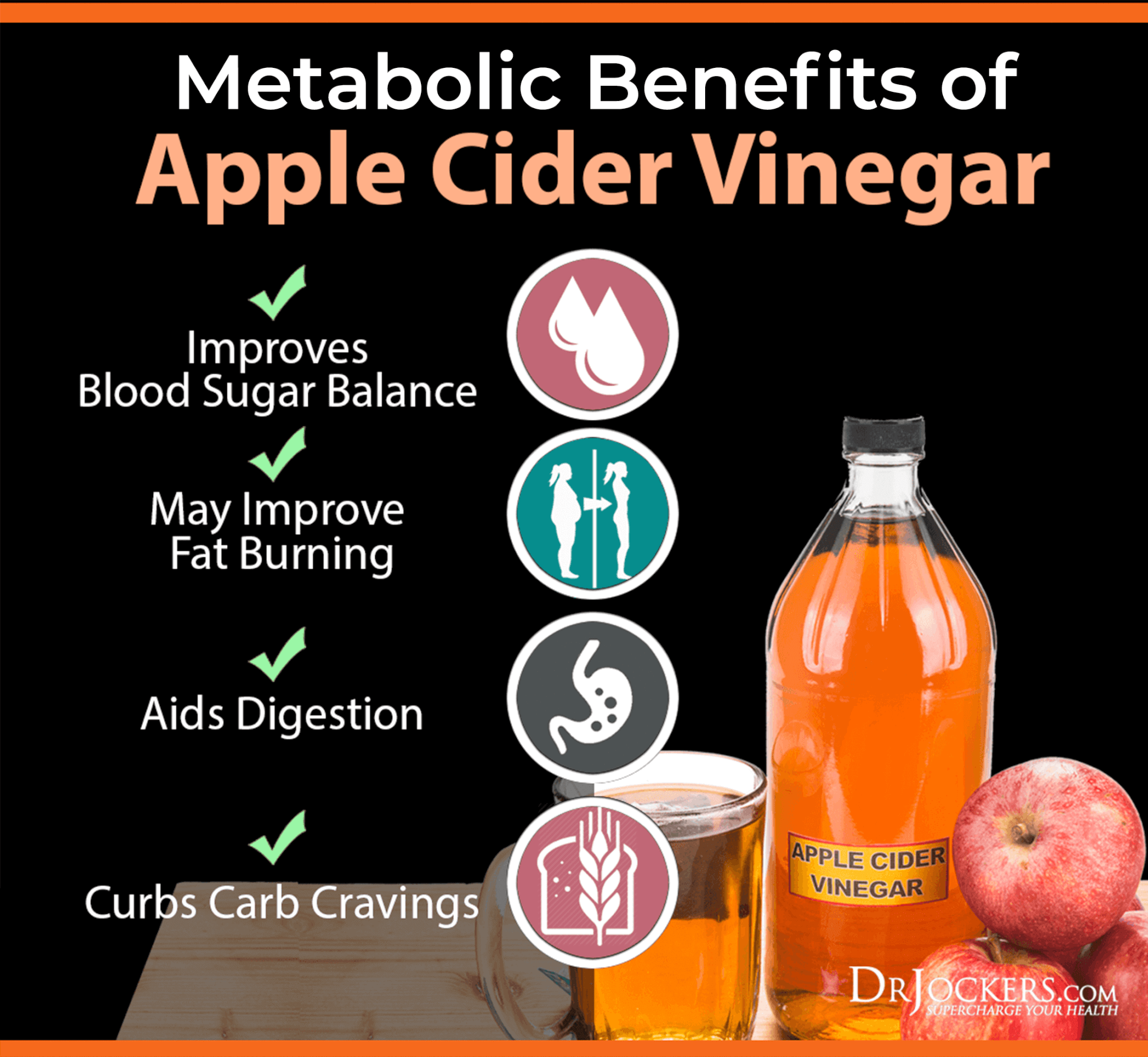
Use ACV or Lemon Juice with Meals
Using apple cider vinegar or lemon juice with your meals may help to balance your blood sugar levels. A 2019 review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Advanced Nursing found that apple cider vinegar may have beneficial effects on blood sugar and glycemic control in those with type 2 diabetes (16).
According to a 2021 study published in the European Journal of Nutrition, lemon juice may also help reduce the glycemic response after carbohydrate-heavy foods (17). You may benefit from adding 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar to 8 oz of water or squeezing some lemon juice into your water and drinking that with your meals for better blood sugar control.
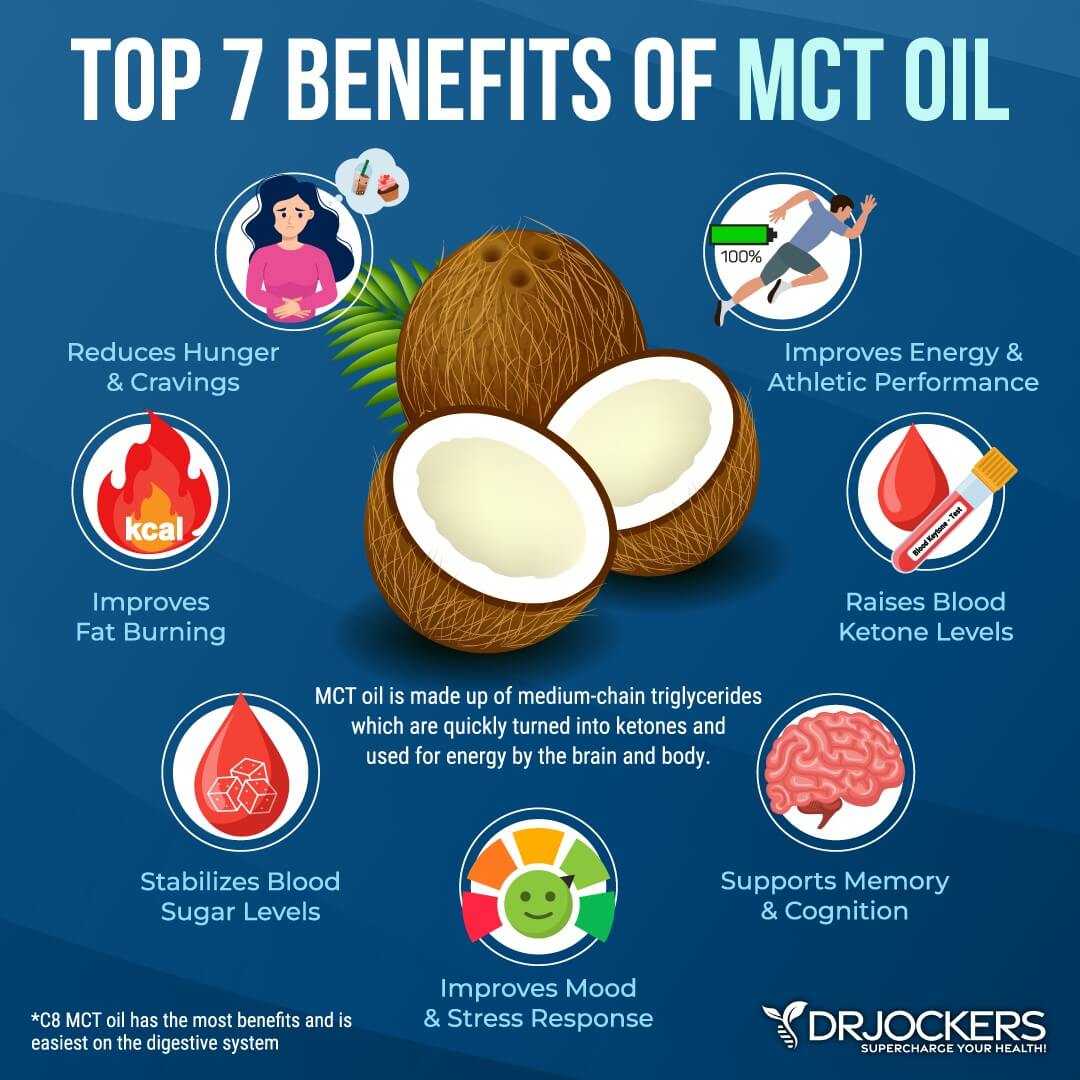
Have MCT Oil with Meals
As I already mentioned, a higher-fat diet may help to improve your blood sugar balance, and consuming healthy fats with your meals is critical (11). MCT oil is one source of healthy fats that may help to balance your blood sugar.
According to a 2019 study published in PLoS One, using MCT oil may help improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar (18). I recommend using MCT oil with your meals for better blood sugar balance. At the end of this article, I will recommend a great MCT oil product.
Best Herbs and Nutrients for Blood Sugar
You may also benefit from some specific herbs and nutrients for better blood sugar levels. You may use these herbs in your diet and also as a supplement.
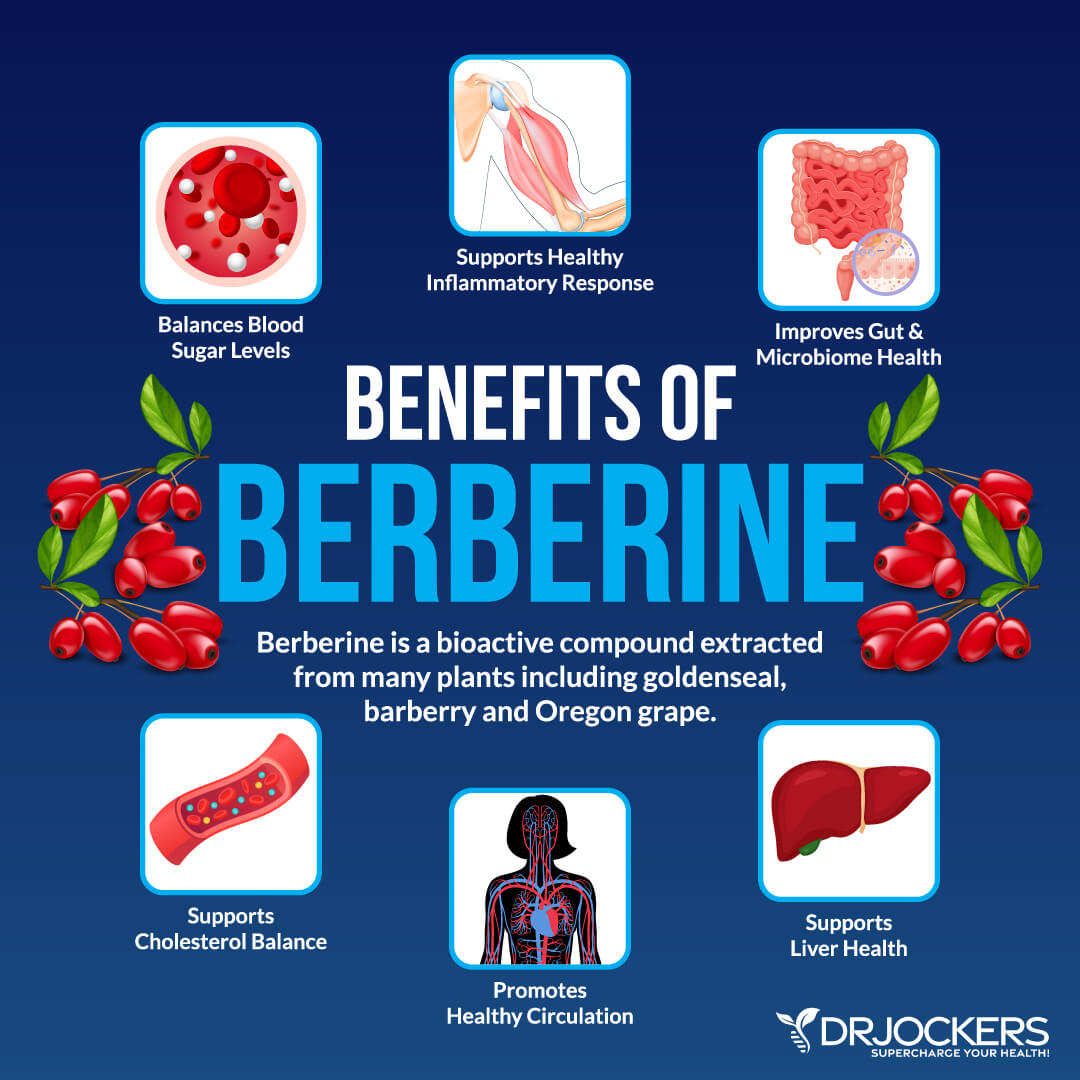
Berberine
Berberine is a nutrient found in European barberry, Oregon grape, goldenseal, tree turmeric, and some other plants. It is yellow in color and bitter in taste.
It has been used as herbal support to balance blood sugar, aid diabetes treatment, support weight loss, support heart health, decrease blood pressure, reduce cholesterol, improve liver health, improve burns, and for other uses.
According to a 2008 study published in Metabolism, berberine may help reduce HbA1c levels in diabetes (19). You may benefit from supplementing with berberine for balancing your blood sugar.
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice found in most households. It is known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. However, it may also help balance blood sugar. According to a 2019 study published in the International Journal of Food Science, 3 to 6 grams of cinnamon may help to improve blood sugar levels in healthy individuals (21).
You may use cinnamon in your cooking, including your meat dishes, sweet potatoes, apple dishes (raw or baked), and coffee. You may also use some blood sugar-supporting supplements with cinnamon.

Gymnema
Gymnema is a plant native to India and Africa. It’s commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine for various benefits, including blood sugar control.
According to a 2010 study published in the Journal of Dietary Supplements, Gymnema may be beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes (22). You may benefit from supplementing with Gymnema.

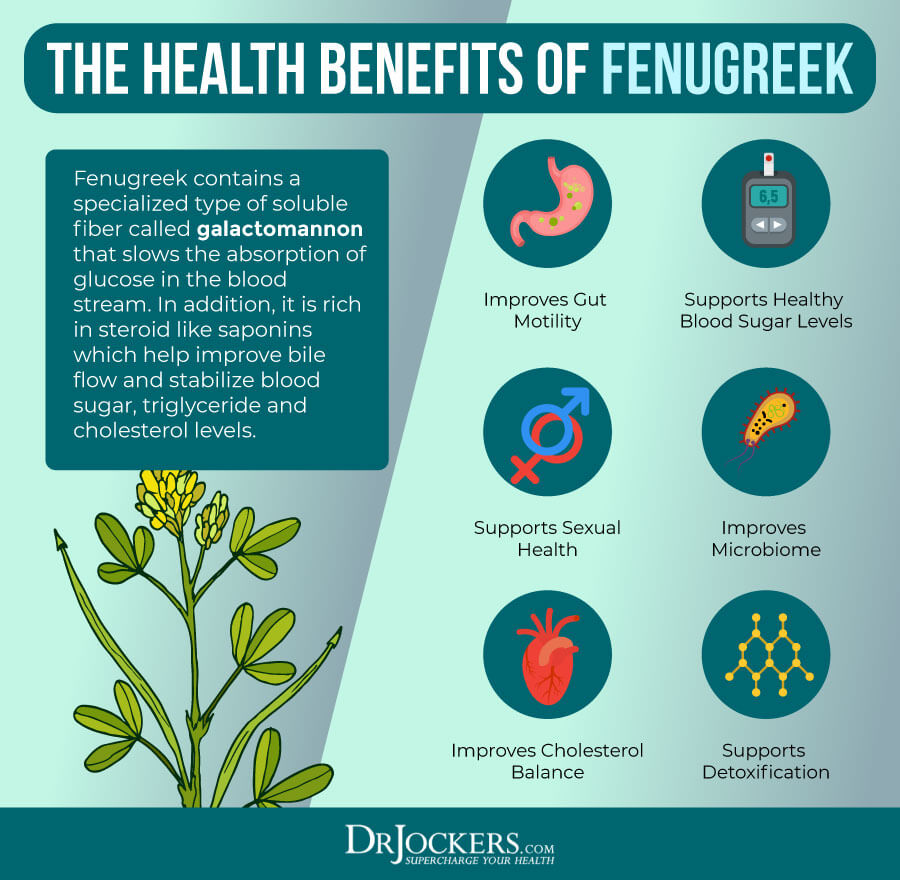
Fenugreek
Fenugreek is a powerful herb similar to clover with natural medicinal properties. It may be beneficial for healthy blood sugar.
According to a 2015 study published in the Journal of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders, fenugreek may help to lower blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes (23). You may use fenugreek in sauces, as a seasoning, in vegetable dishes, and as a supplement.
Chromium & Vanadium
Chromium and vanadium may also be great for blood sugar balance. Chromium is an essential trace mineral. According to a 2004 scientific review published in Diabetes Education, chromium may help to improve insulin resistance (24).
Vanadium is another chemical element with potential benefits for blood sugar. According to 2016 research published in Food and Chemical Toxicology, vanadium may be beneficial for supporting people with diabetes (25).
You may benefit from supplementing with chromium and vanadium. I recommend Insulin Manager. This is an extraordinary combination of herbal and nutrient support for healthy glucose metabolism.
It features concentrates of fenugreek, Gymnema, and bitter gourd, the addition of high levels of vanadium along with select B vitamins, and the mineral chromium. This formula provides nutritional support for glucose and insulin metabolism and supports healthy blood lipid levels already within the normal range. From my clinical experience, Insulin Manager works quickly and powerfully to stabilize blood sugar and reduce inflammation.
Sugar Support
I recommend trying Sugar Support for blood sugar balance. This supplement is ideal for supporting healthy insulin and glucose levels. This unique, synergistic formula combines standardized herbs and other botanicals that are shown to support healthy blood sugar through various mechanisms, including cinnamon, corosolic acid from banaba, isoflavones from kudzu, and ginsenosides from ginseng.
It also contains berberine (Berberis aristata), a compound highly regarded for its efficacy in supporting healthy blood glucose regulation and insulin sensitivity. As a dietary supplement, take four capsules per day with meals, or as directed by your health care practitioner (divided dosing recommended).
Due to its effects on blood sugar, consult with your health care provider before taking this product, along with medication for blood sugar or diabetes.
Keto Brain
I also recommend Keto Brain C8 MCT Oil. This C8 MCT Oil is extracted from natural sources using a three-stage steam-based filtering process without the addition of any chemicals. The result is a pure and ketogenic C8 (caprylic acid triglyceride) formulation.
Unlike long-chain fatty acids, medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are quickly converted into ketones and are less likely to be stored as body fat. The result is improved mental performance and energy. Although C12 (lauric acid) is considered a medium-chain triglyceride, it behaves in the body like a long-chain fatty acid.
Some brands include up to 50% lauric acid in their MCT oil. Choosing an MCT oil with only caprylic acid will provide the greatest health benefits. MCT oil is very versatile and also heat stable up to 320 o F. Use it as a salad dressing or a thickening agent for coffee and teas. Add it to smoothies to help curb hunger and keep you satisfied longer.
Final Thoughts
Healthy blood sugar levels are critical for your overall health and well-being. Unbalanced blood sugar may increase your risk of insulin resistance, prediabetes, diabetes, and other health issues, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, liver issues, vision loss, and other health issues.
Balancing your blood sugar through a healthy diet, lifestyle, and supplementation is critical for reducing your health risks and improving your health. I recommend trying my 7 tips, herbs, nutrients, and supplements for balancing blood sugar.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. Our website offers long-distance functional health coaching programs with our world-class team of health coaches. For further support with your health and other goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!







My husband take memformin pill for type 2 .i take your oroduct both medic.recently diagnostic dec 2022
Yes I would work with a functional health practitioner to help him use herbs and lifestyle to improve his blood sugar. Here is a helpful article: https://drjockers.com/balance-blood-sugar/
Protein and being vegetarian?
Best source’s?
Best to use high quality pea, chia and hemp seed protein powders. https://drjockers.com/8-best-protein-powders-and-how-to-properly-use-them/
Diane, I think your understanding from Forks over Knives is correct. It is important, however, to reduce your fat intake if increasing healthy carbohydrates in order to keep your blood sugar stable. Mastering Diabetes also takes this same approach.
I did not see any reference to snacking during the day. I am convinced that my A1C is high cuz I snack, on good things: nuts, fruit, beef sticks (paleovalley!) but my A1C is 5.9. What are your thoughts on snacking vs 3 meals a day??
I am so stumped. I eat low carb, low calorie, low added sugar. I am below 100 grams of carbs per day- often in the 50 range. I have been working on getting added sguars as close to 0 as possible. so, my a1c last year was 6.2. Today it is 7.1. Triglerides went from 99 to 67. No idea what I am doing wrong. I exercise every day, have added weight lifiting. I do have a hard time getting over 1200 calories a day, but have been trying to get to 1500. I am 5’4… was 222 this morning- lost 5 pounds in 4 weeks. I do have a very stressful and toxic job situation- no raises, no vacation time-been there 15 years. Sole accounting employee- no vacation since 2011. Could it be stress doing this?
Does ACV an hour after dinner still have the same effect?