 8 Ways Intermittent Fasting Improves Heart Health
8 Ways Intermittent Fasting Improves Heart Health
Intermittent fasting is a powerful health strategy where you are fasting and not taking in food for a certain portion of your day, only non-caloric drinks, such as water or herbal tea. Depending on the specific intermittent fasting strategy, it may be practiced on certain days of the week or daily.
Intermittent fasting has many science-backed benefits, including immune regulation, cellular autophagy, genetic repair, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced risk of chronic diseases. One of the main benefits of intermittent fasting is that it improves heart health. Considering that that 610,000 people die from heart disease and is responsible for 1 in every 4 deaths each year in the United States, this is exciting news (1).
In this article, you will learn what intermittent fasting is and 8 ways it improves heart health. I will teach you how to get started with intermittent fasting and how to develop a lasting fasting lifestyle.
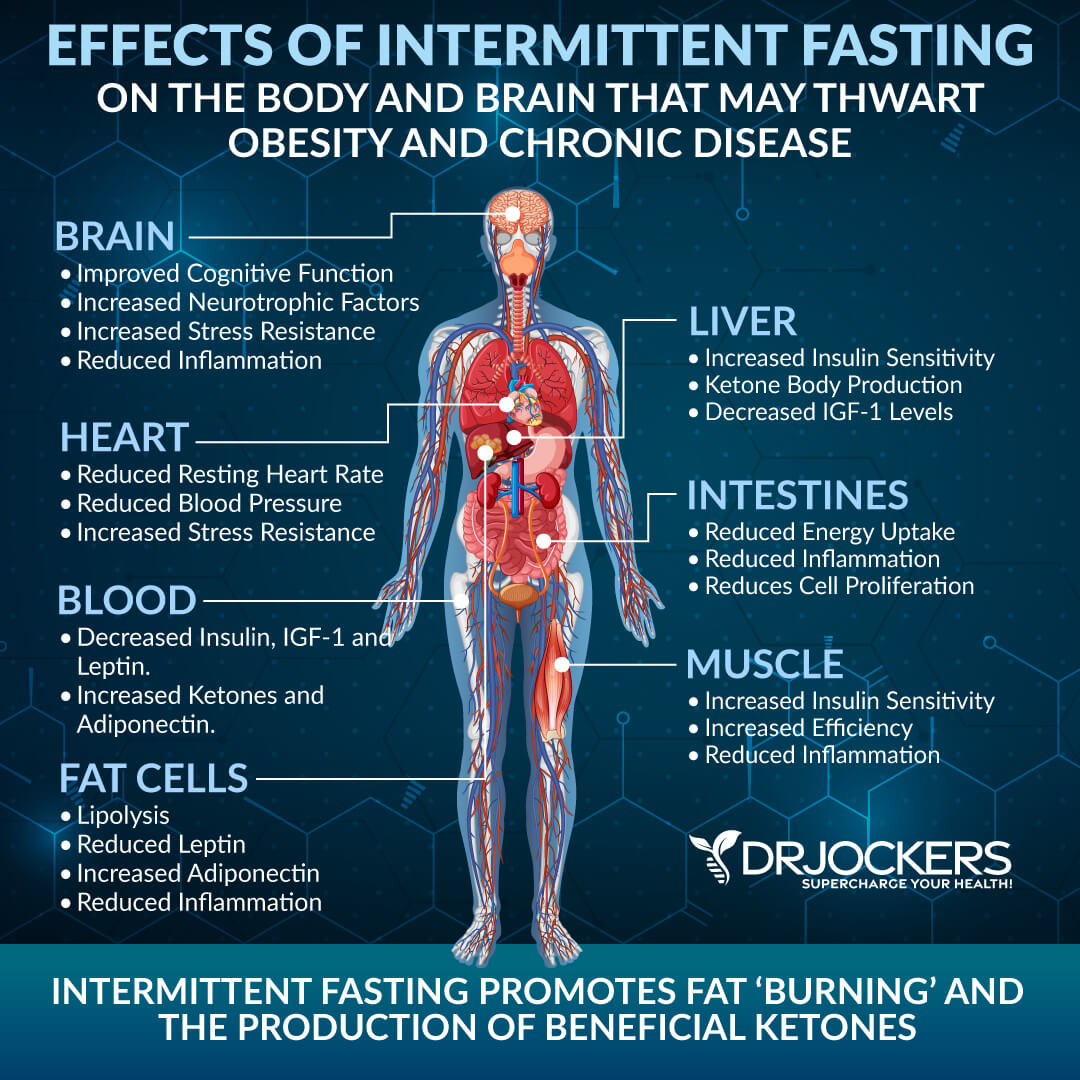
What Is Intermittent Fasting
Fasting is a powerful practice that has been used for thousands of years across cultures for religious, spiritual and health reasons. During the Biblical days, fasting was a normal part of spiritual life, for example, Jesus fasted for 40 days and encouraged his followers to do so. According to the Greek historian, Herodotus (484 – 425 BC) Egyptians were healthier than Greeks due to their fasting practice.
Another Greek philosopher, Plato said that fasting creates greater mental and physical efficiency. Hippocrates said that too much food can be harmful and at times it must be taken away. You can learn more about the history of fasting in this article.
Fasting, however, is not just a spiritual practice or an unproven remedy, but fasting actually has many science-backed benefits. Some of the benefits of intermittent fasting include immune regulation, cellular autophagy, genetic repair, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, as outlined in this article.

Intermittent Fasting
Fasting is a simple practice of not eating any food for a certain period of time. Instead during your fast, you are opting for non-caloric drinks, such as water or herbal tea, or in the case of dry fasting, not taking in any liquids either. There are a variety of fasting methods out there.
Intermittent fasting is a form of fasting when you are not taking in food, but only water, for a certain part of the day. One of the most popular intermittent fasting methods is the 16:8 approach, which means that you are fasting for 16 hours a day and can eat during the remaining 8 hours.
Intermittent fasting is something I recommend to my coaching clients and patients regularly. They use if for foundational healing and performance strategy.
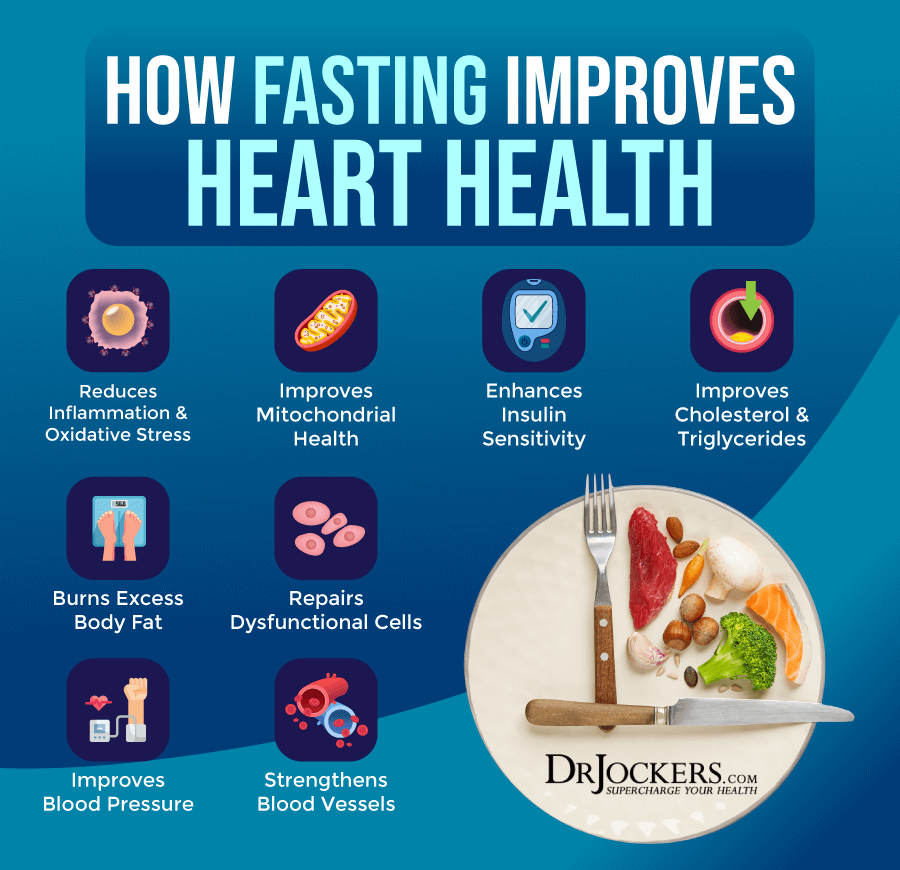
8 Ways Intermittent Fasting Improves Heart Health
Intermittent fasting may improve your heart health in many ways. It may help to decrease oxidative stress and inflammation, improve your mitochondria, cholesterol, triglycerides, insulin sensitivity, and blood pressure, repair dysfunctional cells, reduce excess body fat, and strengthen blood vessels. Let’s take a look at each of these intermittent fasting heart health benefits.
Decreases Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Researchers have found that your cells have a longer lifespan during times of famine or food scarcity. Intermittent fasting is one way to increase food scarcity for a period of time. During intermittent fasting, your body enhances cellular rejuvenation, learns how to use less energy, repair cells, and create cells.
During the fasting period, your body slows down cellular division. This may have many benefits on your body.
For one, cancer cells are driven by fast and out of control cellular division. Fasting may slow down this mechanism and cancer cells have less chance to grow or take control.
The human growth hormone (HGH) that governs your body’s cellular repair process is responsible for your metabolism, muscle tissue sparing, and fat burning. It helps to improve the function of your bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Researchers have found that men who fasted for 24 hours experienced a 2000 percent increase in HGH, while women had a 1300 percent increase. They also experienced lower cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood sugar levels (2).
Improves Mitochondrial Health
Your mitochondria are the powerhouse of your cells. They serve many important functions and their health is essential for your overall health. They are the batteries of your cells are responsible for generating 90 percent of cellular energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and for assisting metabolic functions. To learn more about mitochondrial health and how to improve it, read this article.
During intermittent fasting, old and damaged mitochondria become purged through the process of autophagy. Autophagy is essential for your mitochondrial health. It allows the mitochondria to remove damaged and unwanted debris and create health (3, 4).
According to research, calorie restriction and fasting can help to improve mitochondrial function, create better health, and increase longevity. One study on the anti-aging benefits of calorie restriction found that fasting may improve biogenesis and bioenergetic efficiency. Another study has found that calorie and protein restriction may lower oxidative damage in mitochondrial DNA (5, 6).

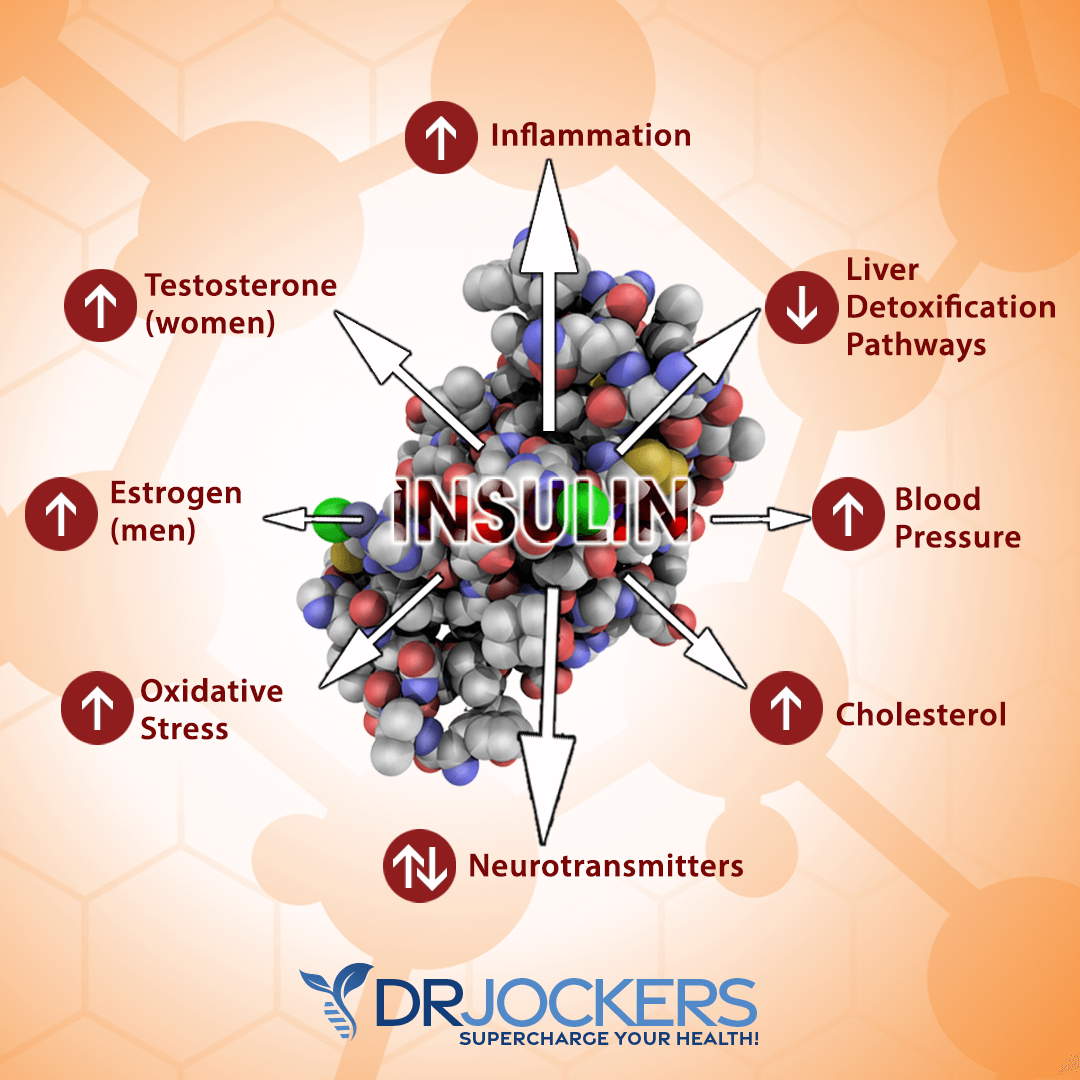
Enhances Insulin Sensitivity
The human body is amazing at adapting to different situations. Thousands of years of food scarcity allowed our body to develop a protective mechanism to adapt to altering phases of food scarcity and abundance due to any reason.
During times of food scarcity, such as fasting, your cell membranes become more sensitive to insulin, which allows your body to use the food you’ve eaten efficiently or store it for times when needed. During the phase of abundance, such as the feasting or eating period of your intermittent fasting protocol, your body desensitizes its cells to insulin in order to avoid the extra stress of calorie intake. This results in increased insulin levels, fats storage, oxidative stress, and potential inflammation.
The problem is that in today’s world we have an abundance of food. Unlike our ancestors, we can eat at any time we want to. While many health professionals recommend 5 to 6 small meals a day, this eating frequency sends the body the signal of surplus which interferes with key tissue repair hormones.
Human growth hormone (HGH) and insulin are endocrine opposites, which means that they influence your physiology in an opposite manner. HGH helps to improve tissue repair, lower inflammation, and enhance efficient fuel usage. Insulin, on the other hand, stimulates energy storage and increases inflammation and cellular division.
When you are eating and insulin releases, HGH is inhibited in your body. However, research has shown that fasting is a great way to lower insulin secretion and increase cellular insulin sensitivity. With the help of fasting, your body becomes more efficient, learns how to use insulin better, and needs less insulin when consuming food. The decreased demand for insulin results in lower inflammation and better HGH levels (7, 8).
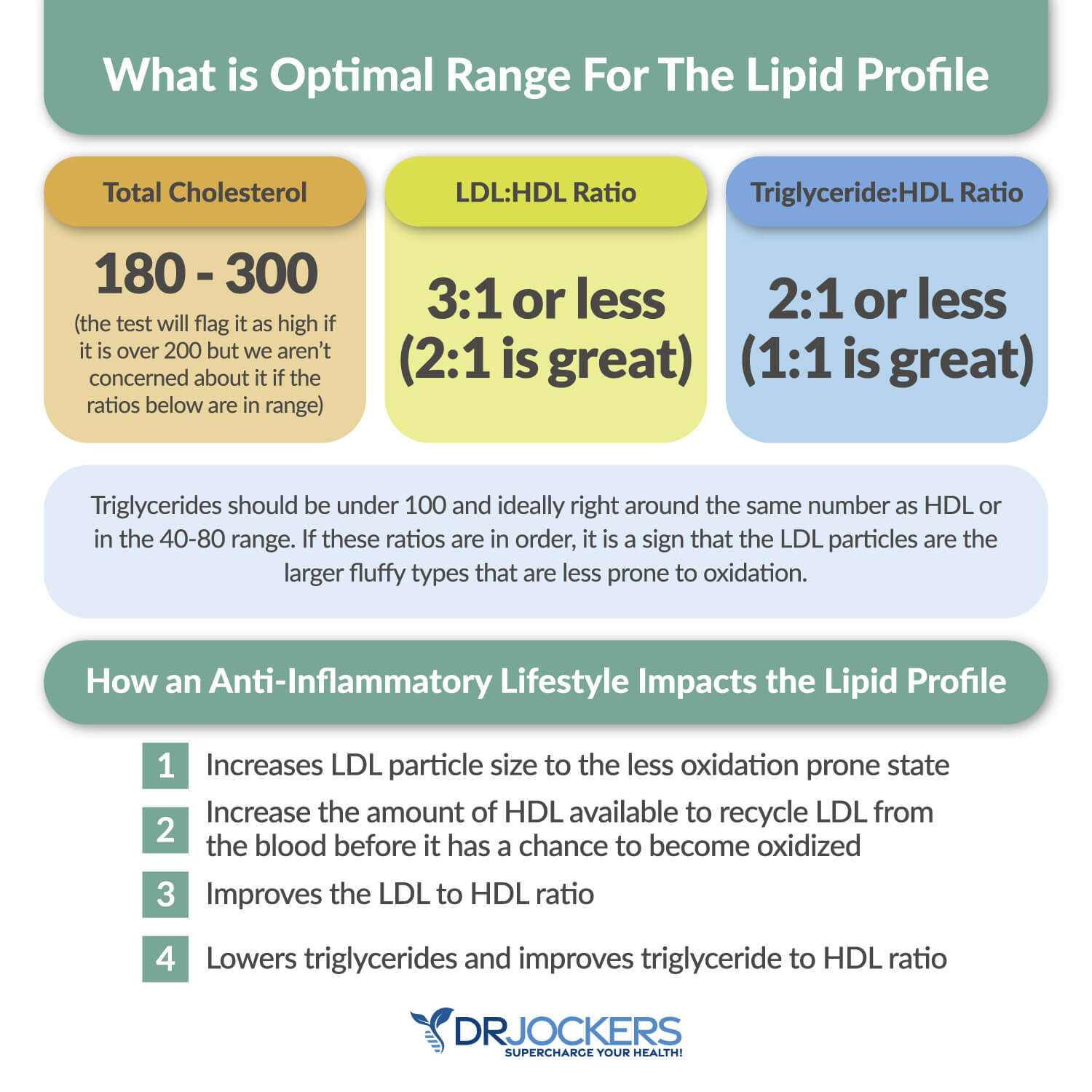
Improves Cholesterol & Triglycerides
Cholesterol and triglycerides are two different kinds of lipids that circulate in your blood. Cholesterol is an organic molecule and compound found in your body. They help to build cells and certain hormones. Triglycerides are ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids and serve as the main components of body fat in humans. They store unused calories in your body and fuel you with energy.
Healthy cholesterol and triglycerides are both crucial for your heart health. Too much cholesterol may increase your risk of heart disease. High triglycerides may lead to hardening of the arteries or arteriosclerosis or thickening of the artery walls. This may increase your risk of heart disease, stroke, heart attack, and heart disease.
Intermittent fasting may be beneficial for both your cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Regular fasting may your low-density lipoprotein, which is your bad cholesterol. Researchers have found that men who fasted for 24 hours experienced lower cholesterol, and triglyceride levels.
Another study on intermittent fasting and its benefits on lipid profile and the bodyweight loss have found that intermittent fasting may help to improve the lipid profile in healthy, obese and dyslipidemic men and women by resulting in lower total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides, and higher HDL levels (2, 9, 10).
Burns Excess Body Fat
Having excess body fat, especially around your belly, may result in serious health consequences. Carrying too much weight around your middle may increase your risk of heart disease. Research has shown that excess belly fat may increase your risk of heart disease and heart issues even in those who have a healthy body mass index (BMI) (11, 12).
Research has shown that intermittent fasting has many health benefits. One of them includes burning excess body fat and improved body fat percentage which may lower your risk of heart disease and other health issues.
One study has found that time controlled fasting may prevent mitochondrial damage and aging due to excess fat. Further research has shown that intermittent fasting may increase HGH in the body, improve blood glucose, improve insulin sensitivity, and enhance fat loss. Lower insulin levels may help your body to burn fat more efficiently. Intermittent fasting may also boost your metabolism and aids weight loss and fat loss as a result along with heart and other health benefits (13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20).

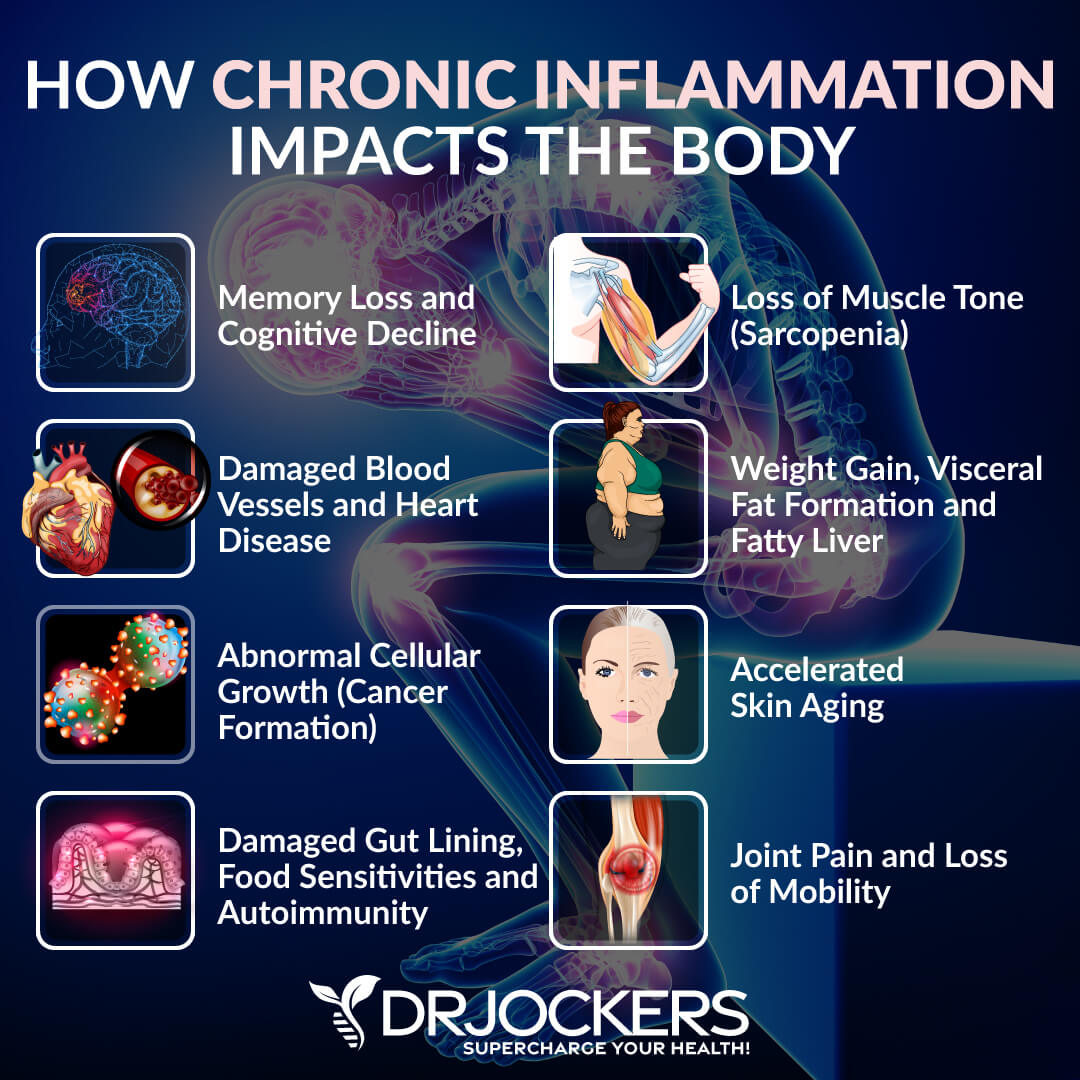
Repairs Dysfunctional Cells
Repairing dysfunctional cells is incredibly important for your heart health and overall health. New and healthy cells are ready to protect your body and function well as they are supposed to, whereas old, dysfunctional, or impaired cells may only lead to problems.
As you’ve just learned, HGH helps to improve tissue repair, lower inflammation, and enhance efficient fuel usage. During times of eating, insulin increases and HGH is inhibited in your body. However, during fasting, your body learns how to work more efficiently, use insulin better, and need less insulin when consuming food. This decreased demand for insulin results increased HGH levels, lower inflammation, and improved cellular repair (8).
One study on cell signaling has found that intermittent fasting increases autophagy and helps the removal of dysfunctional cells. It has also found that intermittent fasting may help to reduce cardiomyopathy, a disease of the heart muscle that makes it more difficult for your heart to pump blood.
It may also help to improve various cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension and aging‐induced cardiac hypertrophy. It may be a beneficial part of cardiomyopathy and heart failure treatment (21).
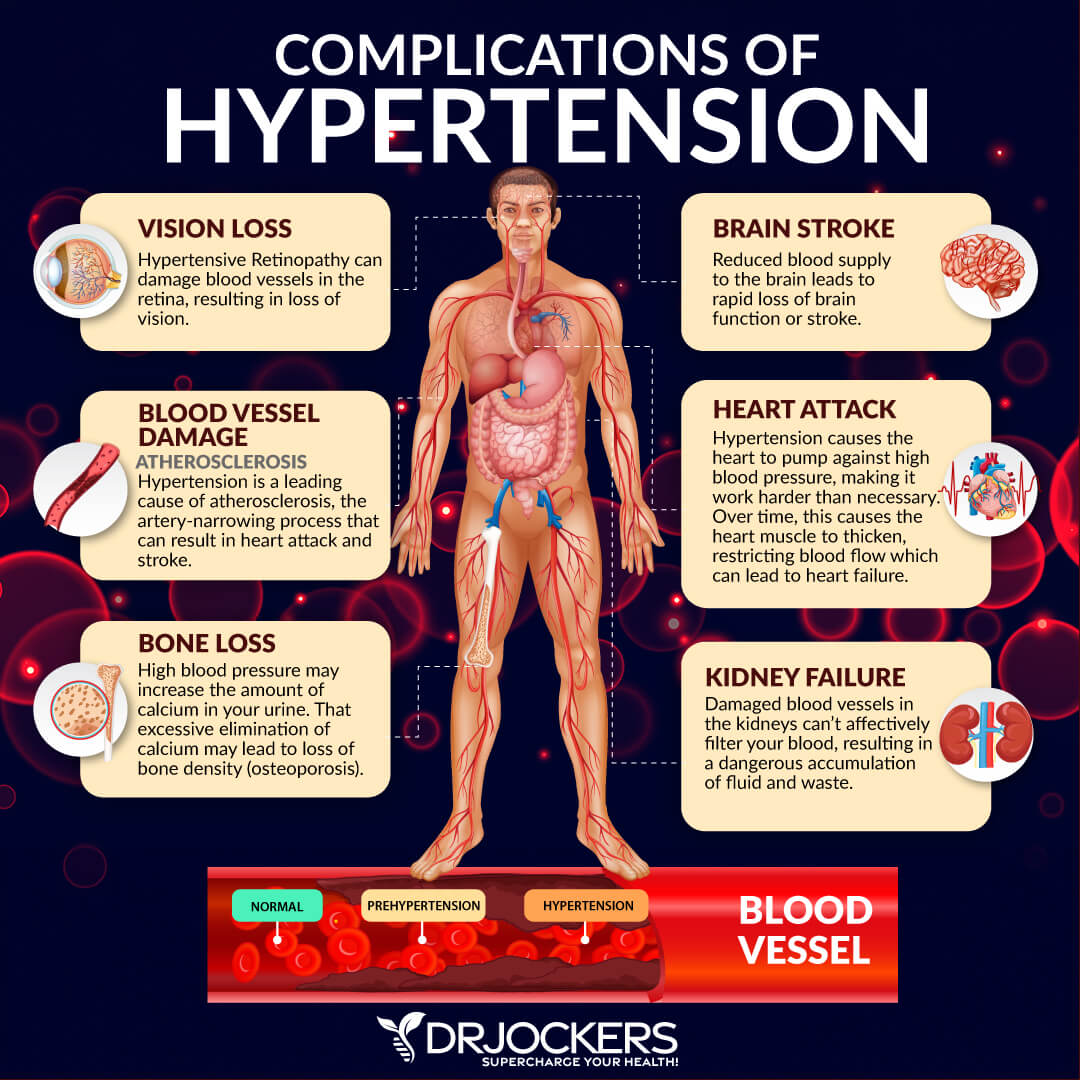
Improves Blood Pressure
Your blood pressure is the pressure of the circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. Keeping is your blood pressure healthy is crucial for your entire health. The higher your blood pressure is, the higher your risk of developing heart and other health problems. Having a high blood pressure puts an enormous strain on your arteries and your heart.
One study on fasting blood pressure involving 60 participants noted that blood pressure volume was higher when individuals ate after waking up and in those who rose before sunrise. Intermittent fasting also resulted in lower blood pressure on office and ABPM measurements.
In another study, researchers have found that men who fasted for 24 hours experienced a 2000 percent increase in HGH, while women had a 1300 percent increase. They also experienced lower cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood sugar levels (2, 22).
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a protein. It is encoded by the BDNF gene. BDNF is a part of the neurotrophin family of growth factors and connected to the canonical nerve growth factor.
One study has found that intermittent fasting helps to increase the BDNF factor in your body, which helps to lower both your systolic and diastolic blood pressure by activation of the body’ s parasympathetic system. BDNF allows the release of acetylcholine by the vagus nerve, which helps to lower the frequency of heart contractions, better your blood pressure, and protect your heart (23).
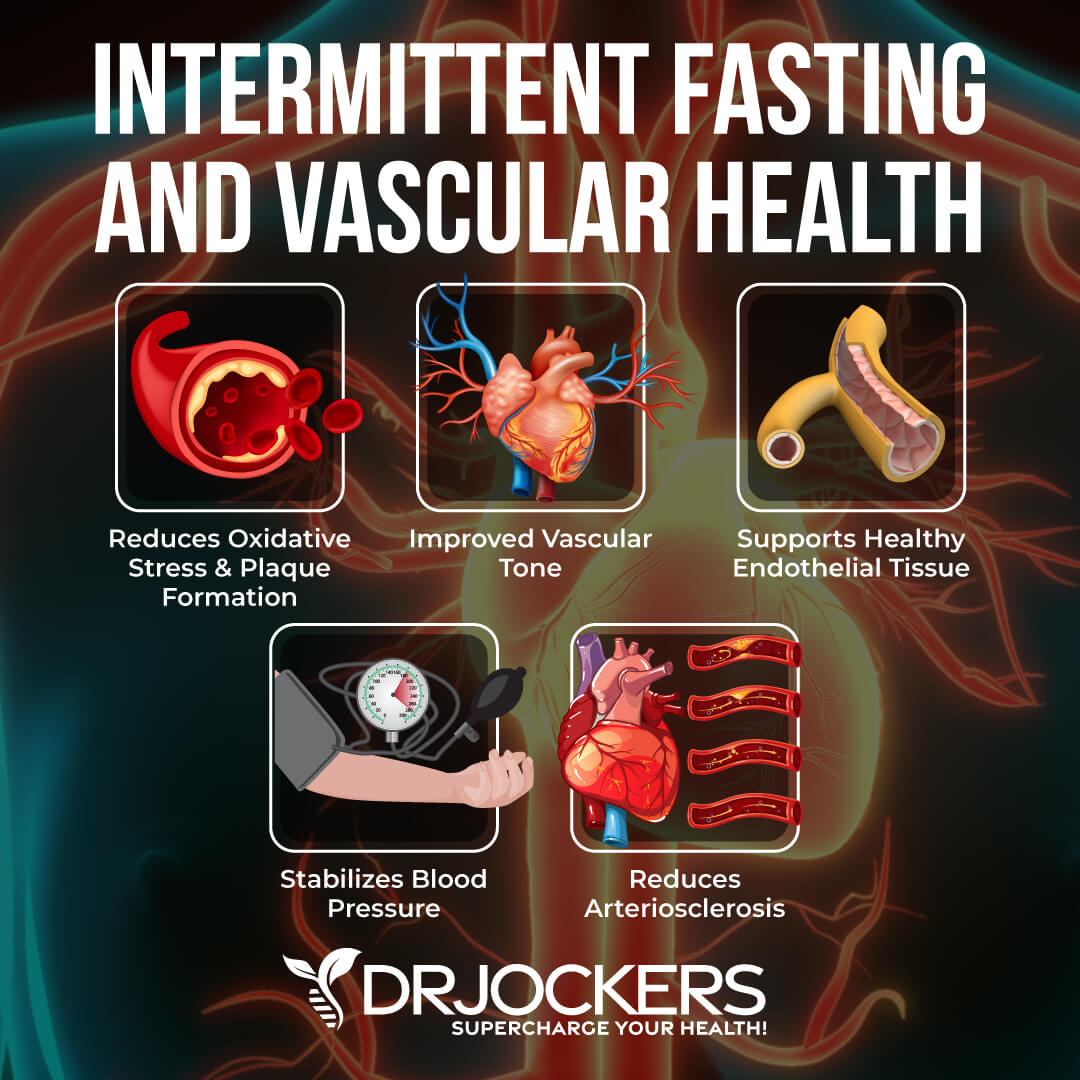
Strengthens Blood Vessels
Your blood vessels are a crucial part of the circulatory system. They carry blood throughout your body. Your arteries and veins are particularly important as they are the blood vessels that carry blood away from or towards the heart. Your blood vessels carry blood, oxygen, and nutrients, and also take away waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. You entire body and all your tissues rely on your blood vessels healthy functionality.
The health of your blood vessels is an important factor in developing cardiovascular disease. Intermittent fasting may help to reduce your risk of heart problems by creating stronger blood vessels.
Researchers have found that intermittent fasting allows the blood vessels to become stronger and expand and improve your blood pressure as a result. Intermittent fasting may reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. This is important because lower oxidative stress helps to make nitric oxide levels rise.
Nitric oxide is a naturally produced compound that helps blood vessels to expand and dilate, so it is crucial when it comes to the health of your blood vessels. Higher nitric oxide levels are also associated with better blood pressure, cardiovascular health and improved libido due to the improvements in blood flow (24, 25).
Getting Started with Intermittent Fasting
As I explained in this article, intermittent fasting and a fasting lifestyle have many benefits. Today, you’ve learned that intermittent fasting may improve your heart health. But if you are new to fasting, getting started with intermittent fasting can be intimidating to you.
Don’t worry, getting started with intermittent fasting is not that scary. I recommend starting with a shorter form of intermittent fasting method, such as the simple fast, for 1 to 2 weeks or as needed. See how your body responds and build your way up to longer fasting periods.

Simple Fast
The Simple Fast is the shortest duration of intermittent fasting strategy. It is also the best and easiest for beginners.
During the Simple Fast, you are fasting for 12 hours and have a 12-hour eating window. Since the fasting period includes your overnight sleep, it is not difficult to follow. Practicing the simple fast will open up your drainage pathways, allow cleansing of your bloodstream, reduce stress on your gut, and help to burn fast, allowing you to experience the benefits of fasting with such a short fasting period.
Keeping the 12-hour fasting window is simple. If you finish dinner at 6 pm, you can eat again at 6 am. With a 7 pm dinner, you are ready for your first meal at 7 am.
If your body takes the Simple Fast well, after a week or two, you can increase your fasting window to 14 hours. With a 6 pm dinner, you can start your new eating window at 8 am with a 14-hour fast.

Creating a Fasting Lifestyle
I bet that learning about the benefits of intermittent fasting for your heart health and overall health makes you interested in creating a fasting lifestyle. While the Simple Fast may be your first step to a fasting lifestyle, soon you will be ready to advance, try longer fasting periods, and learn more about other fasting-enhancing lifestyle strategies.
Cycle Fast
After the Simple Fast, you are ready for the Cycle Fast. It is just a step up from the Simple Fast with a 16-hour fasting window. The main difference is that due to the long fasting period, the Cycle Fast is only performed 3 times per week.
If you finish dinner at 6 pm, you can eat again at 10 am the next day. You can have your fasting days on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday, or Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday, or any other 3 days that feel convenient. While the Cycle Fast requires a bit more planning if you have mastered the Simple Fast, it won’t be difficult.
As you get more comfortable with fasting, you can move up to more advanced intermittent fasting strategies with longer or more varied fasting periods.
Strong Fast
The Strong Fast is a step up from the cycle fast with a 16 to 18-hour fasting window practiced daily. If you finish dinner at 6 pm, you are ready for your eating window on the next day by noon.
The 16:8 strong fast is the one method that most people find the highest level of benefits in terms of health and performance.

Warrior Fast
The Warrior Fast is one of the most advanced intermittent fasting strategies with a 19 to 21-hour fasting window. If you eat dinner at 6 pm, you are ready for your next meal between 1 and 3 pm with a 3 to 5-hour window.
While this provides high fat-burning and ketosis benefits, it is for more advanced people only. You may learn about the Simple Fast, Cycle Fast, Strong Fast, and Warrior Fast from this article.
One Meal a Day Diet (OMAD)
OMAD is a very advanced intermittent fasting strategy. It involves 23 hours of fasting and only 1 hour for an eating window. It is only for the more advanced individuals, who are used to intermittent fasting. You may learn more about OMAD here.
Crescendo Diet
Women have to be more careful with intermittent fasting so they receive the benefits of intermittent fasting without disrupting their hormones. It is a strategic mixing of different fasting windows. You may learn more about Crescendo Fasting in this article.

Dry Fasting
Dry fasting means that you are not consuming any liquids during your fasting window. While it may have some benefits, it is not for everyone.
If you are experienced with intermittent fasting, you may try if dry fasting is right for you. You may learn more about it in this article (26, 27, 28, 29, 30).

Important Things to Pay Attention to While Intermittent Fasting
While practicing intermittent fasting, it is important to pay attention to more factors that simply keeping a fasting eating schedule.
Unless, you are dry fasting, hydrate well. Add a pinch of salt to replace electrolytes.
Make sure to eat plenty during your eating window to meet your calorie and nutrient requirements. To boost ketosis and the benefits of fasting, you may combine it with the ketogenic diet. You may learn more about the keto diet here.
Make sure to get plenty of good quality sleep. Exercise regularly. Go outside, get some sunlight, and do grounding.
Reduce your stress levels. Add a spiritual addition to your routine. Meditate, try some breathwork, journal, practice gratitude, or say a prayer.
Looking at intermittent fasting more than just a diet but as a holistic lifestyle choice will benefit your physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health and well-being greatly.

Final Thoughts
Intermittent fasting is a powerful way of fasting that when you are fasting when you are not taking in food for a certain portion of your day. One of the main benefits of intermittent fasting is that it improves heart health. Heart disease is rampant in our modern world, and protecting your heart is incredibly important.
Follow my tips on how to get started with intermittent fasting and how to develop a sustainable fasting lifestyle, to set yourself up for success, improve your heart health, and enhance your overall health. Soon you will realize that intermittent fasting is a fantastic lifestyle that can enhance your life in many ways.
If you want to improve your metabolic health and burn fat, improve your brain and overall energy levels…intermittent and extended fasting are incredibly powerful strategies.
That is why I want to introduce you to my best-selling book, The Fasting Transformation. It goes into the most recent scientific research and strategies for implementing intermittent and extended fasting into your life.
This book is the best book on fasting the world has ever seen and I have read them all! It is now, my great honor to present this to you and I am deeply appreciative of your support!
Metabolic Autophagy & Cellular Healing Masterclass
Autophagy is the body’s innate mechanism for deep cellular healing and repair and it helps us reduce the effects of aging, inflammation and cellular damage.
The Nobel Prize in 2016 was awarded to the Japanese researcher Yoshinori Ohsumi for his breakthrough work in helping us understand the process of autophagy and how it works. If you are struggling with your health or desire to optimize your health, activating the appropriate amount of autophagy is a critical component.
This masterclass will give you in-depth video trainings along with image-rich, research-based guides to help you understand the tools and strategies to unlock your body’s dormant healing potential. You will also learn my signature 6-week Metabolic Reset Cycle that will show you how to utilize advanced nutrition strategies for deep cellular healing!
Check out the masterclass here where you will learn my best action steps for optimal healing!





It’s hard to say because each person is different, medical issues, etc., but I think 7 to 8 pm is pretty late to eat. I eat between 5 and 6 and go to bed by 10 or 11 and don’t eat anything until 8am or so. That’s just one thought for you.
a wise person once said: a saint eats once a day, a normal person eats twice a day and a cattle human eats constantly!
Guys. You have to do a 40 day fast and drink only distilled water. I did at the age of 50. And lost 25 kilos in the 6 weeks . In the first 2 weeks I lost the most and the it gradually tapper down. Also fasting start where you have the most fat not diet that starts where you have the least amounts of fat
Thanks for sharing Nyllin. So good to hear you had a great experience with this!
I I have struggled with excruciating back spasms for the past 8 to 10 years. Are use chiropractic care consistently. I did a mineral analysis about six months ago and I followed their protocol with supplementation including magnesium and potassium as well as many other supplements. I have slight herniated disc‘s in my thoracic area and also herniated disc’s in my neck. I’ve had that this since I was 10 years old.I do intermittent fasting every day and sometimes 24 to 48 hours once or twice a month. The back spasms are generally in the thoracic area on either side of the spine, but most recently for the last couple months it’s been the left lateral dorsi muscle. I know this is lengthy I’ll get to the point. Can you suggest anything that would be the reason for these spasms that truly are debilitating?
Really sorry to hear that. Here is our fasting pain relief protocol: https://drjockers.com/fasting-protocol-pain-relief/
In January I did a 5-day water fast, while monitoring my blood glucose. From the second day on, my blood sugar was decreasing until the end of the fast, when I did a one-day mostly liquid re-feeding. So everything went well.
At the end of February, I wanted to repeat it, but some curious things happened.
On the second, third and fourth day, my blood glucose remained the same, 5.7 mmol/L.
I terminated the 5-day fast and switched on to intermittent fasting. Next day at noon my blood glucose was quite high, 6.3, which I have not experienced before. I also became fairly tired and skipped my daily exercise.
Note that I have lost 1 kg in the past three years while doing intermittent fasting,
so I am not overweight, my body mass index is 20. I have very little subcutaneous and no visceral fat around my waist.
My private reasoning is that my blood glucose did not go down, because there was no fat from which to generate ketones thus my body desperately wanted to maintain glucose to continue to supply my brain. I became tired because I was suddenly glucose-bound instead of fat -bound.
Anyway, what do you think?
Please I made a big mistake before. I actually lost twelve kg not 1 kg in teh past threee years of having done intermittent fasting.
Hello Ian, you may have done this second fast without enough recovery from the first fast. If you are not overweight, I recommend not doing more than one extended fast every 3-4 months.
Can you take nutritional supplements during the fasting period or would that negate the whole process?