 Vitamin A: Benefits, Sources, and Signs of Deficiency
Vitamin A: Benefits, Sources, and Signs of Deficiency
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and potent antioxidant that can reduce inflammation, oxidative damage, and free radicals. It is critical for vision and eye health, immune health, healthy skin, neurological health, bone health, circulation, and fertility.
Vitamin A deficiency can lead to vision problems, immune system dysfunction, chronic inflammation, an increased risk of infections, illness, autoimmunity, neurodegeneration, and even cancer. Fortunately, meeting your needs can be simple through a nutrient-dense diet and, sometimes, some supplementation.
In this article, you will learn what vitamin A is and its main functions. I will discuss the signs and symptoms of a deficiency. You will learn about the main health benefits, and I will recommend the best lab testing for vitamin A levels.
I will discuss how vitamin A may play a role in supporting measles recovery. I will explain how topical treatment of vitamin A may help with skin warts. You will learn about the best food sources of this key nutrient to add to your diet. Finally, I will recommend the best supplements to improve your vitamin A levels.

What is Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin. It is a powerful antioxidant that’s needed for vision and eye health, healthy skin, neurological function, immune health, fertility, circulation, and other areas of your health. As an antioxidant, this key nutrient plays a critical role in fighting free radical damage and decreasing chronic inflammation in your body. (1, 2, 3).
Though we often refer to vitamin A as a singular nutrient, in reality, it is a group of fat-soluble compounds. These compounds include retinol, retinal, and retinol esters.
Retinol and retinol esters can be found in foods, more specifically in animal products, including dairy, fish, and liver. Carotenoids can be found in plant foods, including vegetables, fruits, and oils (1, 2, 3).
Once you consume these foods, your body needs to convert them into the active forms of vitamin A, which are retinal and retinoic acid. As a fat-soluble vitamin, vitamin A can be stored in your body to be used later.
Most of it is stored in your liver in the form of retinyl esters, which can be later broken down to all-trans-retinol to bind with retinol-binding protein and enter your bloodstream (1, 2, 3).

Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin A Deficiency
Vitamin A is critical for so many areas of your health, including vision, skin health, proper bone growth, immune health, respiratory health, urinary health, digestive health, and more. A deficiency in this key nutrient is a major health concern in lower-income countries, especially in Africa and Southeast Asia, and is particularly risky for pregnant women and young children.
However, you can develop a deficiency anywhere in the world. People with long-term malabsorption of fats, pancreatic disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, leaky gut syndrome, and autoimmune conditions are at higher risk of developing vitamin A deficiency.
Deficiency in this key nutrient can cause serious health issues, especially in children, including severe visual impairments, blindness, and a high risk of measles, infectious diarrhea, and other serious illnesses.
Common signs and symptoms of vitamin A deficiency may include:
- Dry lips
- Dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea (xerophthalmia)
- Night blindness
- Bitot’s spots are caused by keratin buildup on the conjunctiva
- Scaly skin
- Thick skin
- Poor immunity
- Stunted growth in children

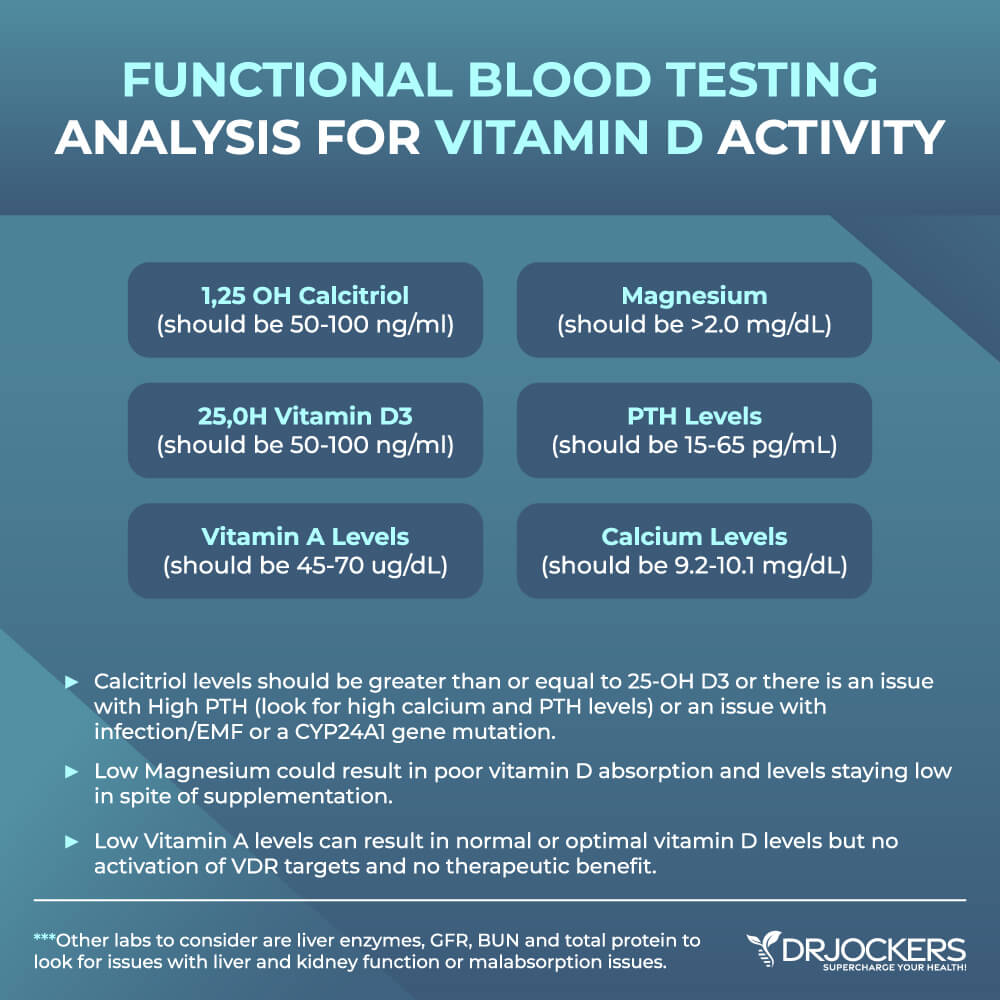
Lab Testing for Vitamin A
There are two main blood tests I recommend for testing for vitamin A deficiency.
Serum Vitamin A
The first lab test I recommend is looking at your serum vitamin A levels. This test measures retinol, the main form of vitamin A.
Poor vitamin D levels can indicate issues with the immune system, eyes, bones, skin health, healthy growth, and reproduction. Optimal vitamin A levels are between 45 and 70 μg/dl.
Vitamin D
The second lab test I recommend to check for a vitamin A deficiency is your vitamin D levels. Vitamin D and vitamin A (retinol) are connected and work together. Calcitriol binds to the VDR in the cell nucleus. Once this happens, the vitamin A receptor (RXRA and RXRB) helps the activation of the VDR targets.
According to a 2008 study published in the National Reviews in Immunology, vitamins D and A both play an important role in various immune processes and may help to prevent or treat inflammation and autoimmunity (4).
Since high or low vitamin A can also suppress vitamin D levels, so good to look at both 25-OH vitamin D and 1,25 OH vitamin D levels. Normal levels of vitamin D are over 50 ng/mL, while optimal levels are over 60 ng/mL.
Benefits of Vitamin A
Vitamin A has many functions and health benefits, including brain health, eye health and vision, skin health and tissue healing, skin health and reduce inflammation, better gut health, support for fertility, reproduction, and fetal development, improved bone health, and healthy circulation.
Let’s look at the benefits one by one.
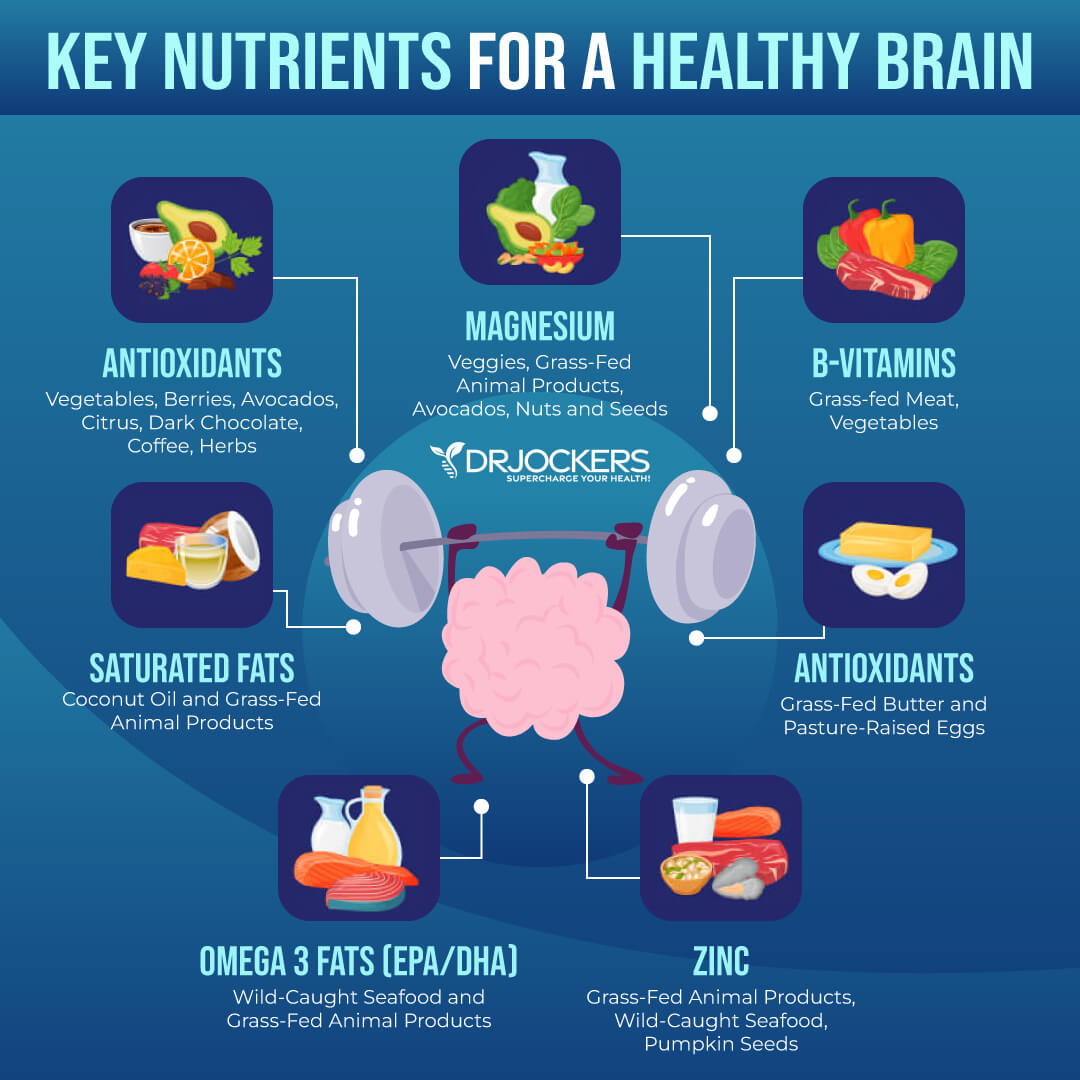
Supports Brain Health
Vitamin A plays an important role in supporting your brain health. According to a 2025 animal study published in Science of Food, vitamin A may help to improve cognition and reduce the progression of Alzheimer’s disease in older individuals (5). It also supports your brain by impacting various key neurological processes.
Influencing synaptic plasticity is one of the benefits of this nutrient. Synaptic plasticity refers to your brain’s ability to form and reorganize connections between neurons to allow memory and learning. Though its active metabolite, retinoic acid, it can support gene expressions that strengthen their synaptic connection.
Vitamin A may also support neuronal survival, which can protect your brain from oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. It may also support neurogenesis in the hippocampus, which is the part of your brain that is essential for both memory and emotional regulation. Thus, this key vitamin may help to support cognition and also allow you to respond to stress better.
Important for Eye Health and Vision
Vitamin A is critical for your eye health and vision. This is potentially the most well-known benefit of this vitamin. It helps your eyes and vision because this nutrient is a component of the rhodopsin molecule.
This molecule gets activated anytime light shines on your retina. It sends a message to your brain to activate vision.
Beta-carotene, which is converted in the body to vitamin A, plays a critical role in reducing the risk of macular degeneration, which is among the leading causes of age-related blindness.
According to 2024 research published in Nutrients, vitamin A is among the nutrients important to reduce the risk of macular degeneration, along with vitamin C, zinc, copper, lutein, and zeaxanthin (6). According to a 2025 study published in the European Journal of Medical Research, it may also be beneficial for reducing the risk of glaucoma (7).

Supports Skin Health and Tissue Healing
Vitamin A may also be beneficial for skin health and tissue healing. Dermatologists commonly recommend it for acne, fine lines, and wrinkles. According to a 2024 study published in Skin Health and Disease, retinol can help to reduce wrinkles and fine lines (8).
Retinol is also the most common form of vitamin A used topically for wrinkles. Additionally, due to the anti-inflammatory benefits of retinaldehyde, it may help to improve eczema, psoriasis, and other skin conditions.
However, according to a 2025 study published in Food Science and Nutrition, vitamin A and other antioxidants in the diet can also reduce signs of aging (9). So, it’s not only topical use that benefits your skin, but also when eaten in food and used internally.
Moreover, vitamin A may also be effective for tissue repair and cellular regeneration, which may help to improve wound healing and tissue healing. According to 2019 research published in Nutrition in Clinical Practice, it can help to improve epithelial growth, fibroblasts, angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, granulation tissue, epithelialization, and fibroplasia, which supports wound healing (10).

Improves Immune Health and Calms Inflammation
One of the major roles of vitamin A is related to supporting the immune system. It can help to reduce the risk of infections and illness. According to a 2022 review published in Nutrition Clinique et Metabolisme, a deficiency can lead to poor immune cell function, weaker immunity, and related increased risk of health issues, including allergic issues, infectious diseases, inflammatory conditions, and cancer (11).
According to a 2022 study published in Science Reports, beta-carotene is a powerful antioxidant that can help reduce free radicals and oxidative damage, and chronic inflammation in the body. As a result, it may help to lower the risk of inflammatory conditions and chronic inflammation-related diseases, including autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative issues, and cancer (12).
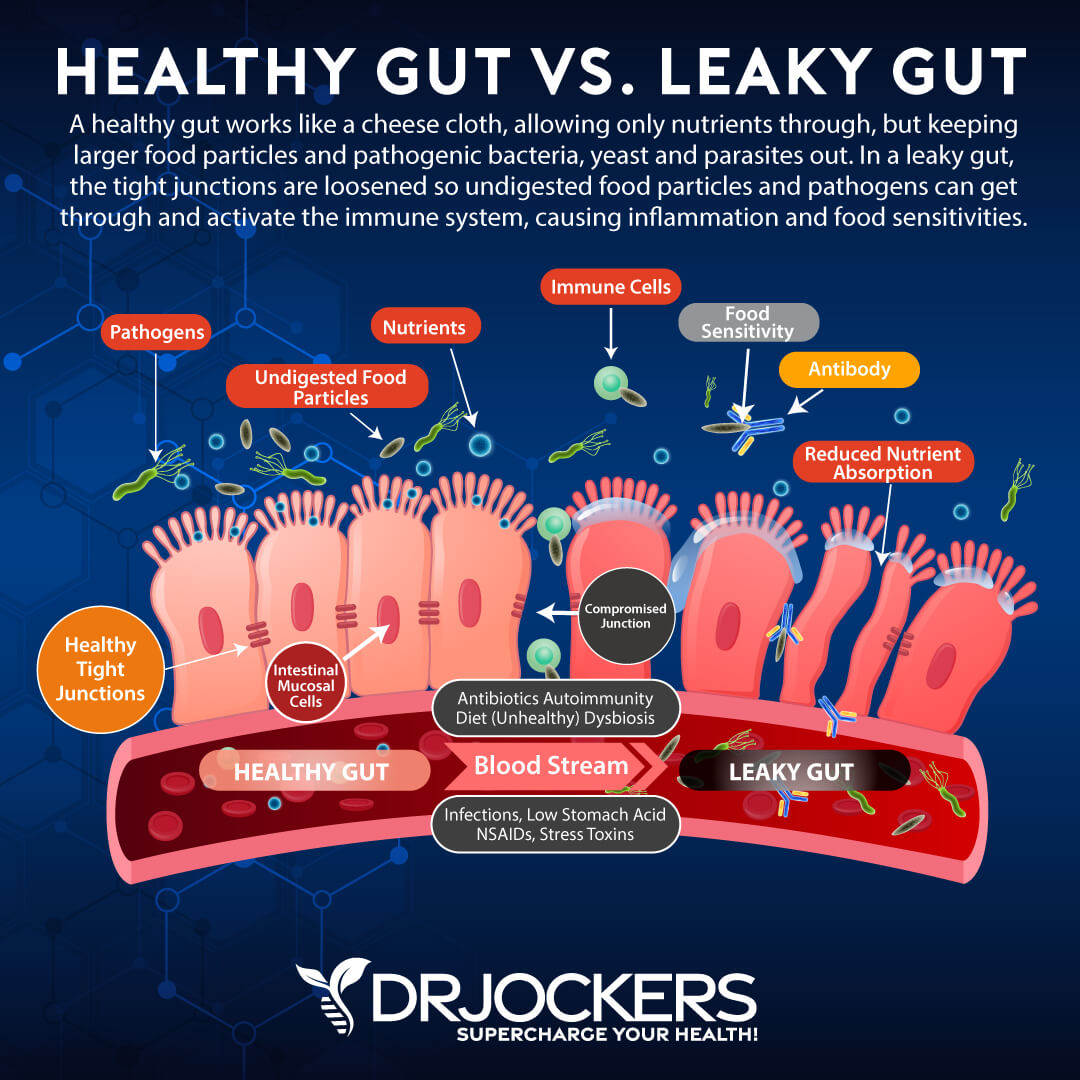
Helps to Heal Leaky Gut
Vitamin A may also play an important role in maintaining a healthy gut and gut lining. It may help to reduce the risk of developing leaky gut. A healthy gut lining has small openings to allow nutrients to enter the bloodstream, but not toxins, pathogens, or undigested food particles.
A leaky gut occurs when the openings become too large and pathogens, toxins, and large food particles can pass through, increasing the risk of chronic inflammation, gut health issues, and autoimmunity.
According to a 2019 review published in Critical Reviews of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, vitamins A and D both play a role in intestinal epithelium and mucosal immune system regulation and gut homeostasis (13). Deficiencies may increase the risk of leaky gut syndrome.
Vitamin A helps to regulate the growth and differentiation of epithelial cells, which form your gut lining. It also allows the production of mucin, a protective layer that strengthens the gut barriers and allows better digestion. It can also support the immune system, reduce the risk of chronic inflammation, and support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Supports Fertility, Pregnancy, and Fetal Development
According to a 2011 review published in Nutrients, vitamin A is a great vitamin for supporting reproductive health, fertility, pregnancy, and fetal development (14). It plays a role in hormone regulation and reproductive organ function in both men and women. It helps ovulation and also prepares the uterine lining for implantation in women.
It helps with normal sperm production in men. During pregnancy, it is important for placental development, maternal tissue growth, and the formation of the fetus’s organs, including the eyes, lungs, heart, and immune system.
Adequate vitamin A can reduce the risk of developmental delay, impaired growth, and other complications for the child, while deficiencies can increase such problems. According to a 2023 review published in Cureus, deficiencies may contribute to the development of night blindness, bone anomalies, or epithelial cell problems, but excessive levels can result in fetal central nervous system deformities (15).

Improves Bone Health
Vitamin A is critical for bone growth and bone health. It is essential for the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, which are the cells necessary for making and remodeling bone tissue and creating strong and resilient bones (16).
In children, vitamin A is critical for skeletal development and bone elongation. In adults, it is necessary for bone density. According to a 2025 study published in Science Reports, it is also essential for the bone mineral density of adolescents (17). It also helps bone repair processes.
Low levels of vitamin A may increase the risk of fragile, brittle bones, osteoporosis, and fractures. On the other hand, too much can also negatively affect bone health and result in bone loss. You need normal levels of vitamin A, not too low, not too high, for bone health.

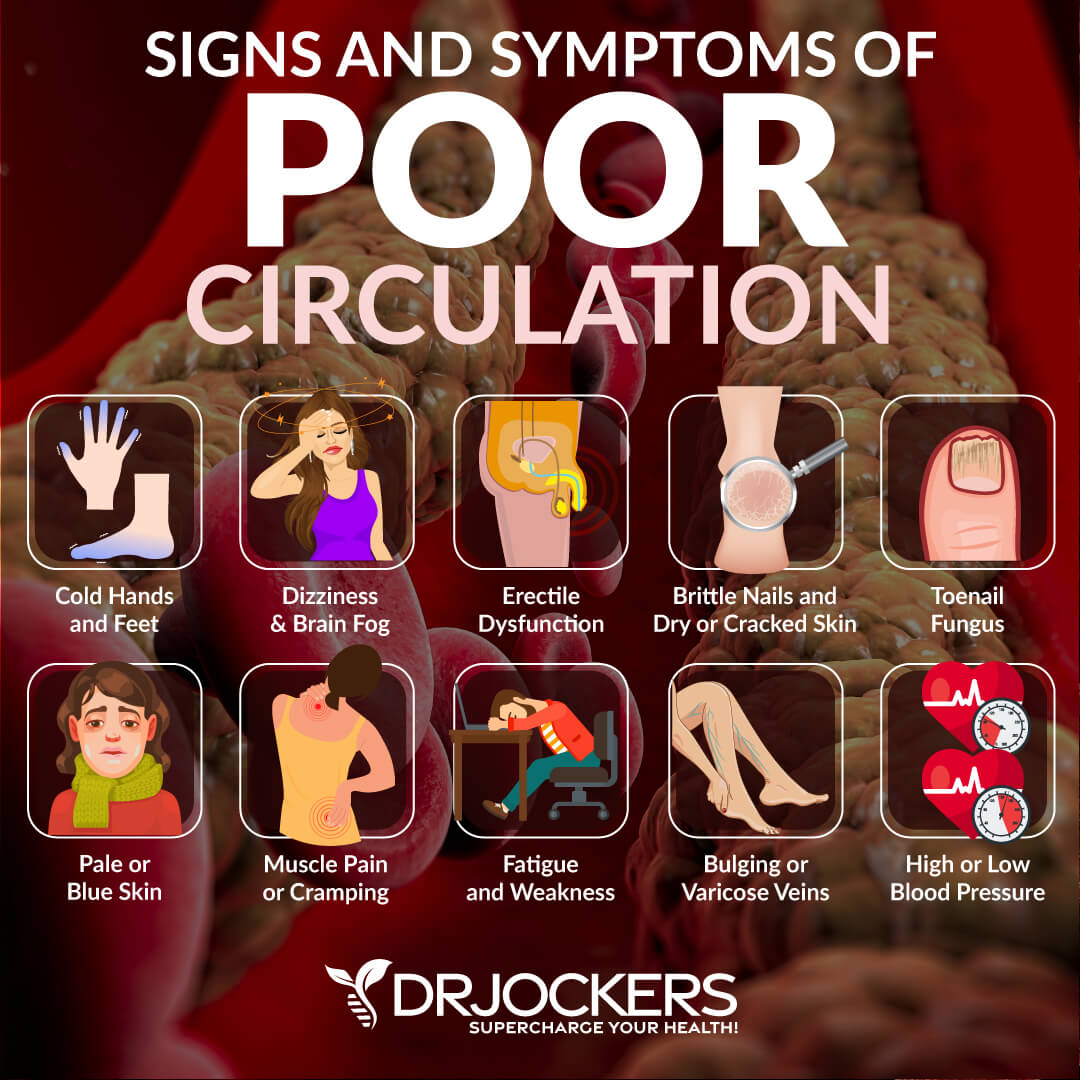
Supports Healthy Circulation
Finally, vitamin A may also support healthy circulation and overall cardiovascular function. It is important for the growth and repair of endothelial cells, which keep your blood vessels flexible and strong.
Adequate vitamin A levels are critical for proper blood flow to tissues and organs, supporting energy, endurance, and healing. Deficiencies can increase the risk of weakened vessel integrity, impaired oxygen delivery, and greater susceptibility to circulatory problems.
According to a 2020 study published in Hearts, it is a regulator of cardiac formation and may also serve a role as a regulator of cardiac regeneration, postnatal cardiac function, and cardiovascular disease progression (18). It may also help to reduce oxidative stress and chronic inflammation.
These are underlying risk factors for poor circulation, atherosclerosis, or cardiovascular disease. Thus, adequate levels may reduce the risk of these issues. Moreover, vitamin A may also help the production of red blood cells, allowing oxygen to be efficiently transported throughout the body.
Vitamin A and Measles
Vitamin A is also a critical nutrient when it comes to the management and recovery from measles. Measles can significantly deplete the body’s vitamin A stores. This can critically weaken the immune system and increase the risk of severe complications of the disease, including diarrhea, vision problems, blindness, and pneumonia.
According to 2020 research published in Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice, supplementing with vitamin A during measles infection may reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, lower the risk of complications, and may decrease child mortality rates (19).
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends high-dose vitamin A supplementation for children diagnosed with measles to support immune function, protect vision, and promote faster recovery (20). The recommended oral dosage is 200,000 IU (60,000 mcg) for children or 100,000 IU in infants (30,000 mcg) in Vitamin A per day for 2 days.

Vitamin A Topical Treatment of Skin Warts
Topical vitamin A treatment may be used for treating skin warts, including those from human papillomavirus (HPV) infections, which can result in abnormal skin cell growth. According to a 2012 study published in Virology Journal, topical vitamin A may be beneficial for addressing verruca vulgaris, common warts from HPV, and other benign and cancerous warts from HPV (21).
According to a case study of a female patient with serious skin warts that resisted salicylic acid, apple cider vinegar, and over-the-counter essential oils, topical vitamin A turned out to be an effective solution.
They used a daily topical application of 25,000 IU of vitamin A derived from fish liver oil. Her smaller warts disappeared within 70 days, while one larger (9 millimeters) wart took 6 months to heal.
If you are dealing with a serious and stubborn case of skin warts, topical vitamin A may be your best bet. Make sure to buy a high-quality, hypoallergenic, and highly concentrated vitamin A brand for optimal results and safety (21).
These benefits come from its ability to increase healthy cell turnover and normalize keratinization, which can make it more difficult for the virus to thrive. Vitamin A topicals, especially with retinoids, may help to lower viral activity and reduce the size of the warts. However, topical treatments may cause problems in sensitive individuals, so it’s important to start slow and use them with care.

Best Food Sources of Vitamin A
The RDA for vitamin A is 900 mcg for adults and 300-600 mcg for children, and an extra 500-600 mcg for pregnancy and nursing. Most functional nutrition experts recommend at least 1500-2000 mcg of vitamin A daily from food. An upper limit for vitamin A would be at 3000 mcg daily, although many have consumed more than that from foods without reaching toxicity levels.
The best way to improve your vitamin A levels is through a nutrient-dense diet high in vitamin A-rich foods. Let’s look at some of the best foods:
- Beef liver: 3 ounces of cooked, boiled beef liver has about 17,800 mcg, which is 1977% of your Daily Value or DV of Vitamin A
- Cod liver oil: 1 tablespoon of cod liver oil has about 4,080 mcg, which is 453% DV of Vitamin A
- Liver sausage (liverwurst): 0.25 cup of liverwurst spread has 2,250 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 250% DV
- Sweet potato: 1 medium, cooked, boiled sweet potato without skin has 1,190 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 132% DV
- Butternut squash: 1 cup of baked, cooked butternut squash or winter squash, without salt, cubed, has 1,140 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 126% DV
- Spinach: 1 cup of cooked, boiled, drained spinach, without salt, has about 943 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 105% DV.
- Bluefin tuna: 3 ounces of cooked bluefin tuna has 643 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 71% DV
- Carrot: 1 medium raw carrot has about 509 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 56% DV
- Cantaloupe: 1 cup of raw cantaloupe cubes has about 270 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 30% DV
- Mackerel: 1 cup canned jack mackerel, drained, has 247 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 27% DV
- Red peppers: 1 cup of chopped raw, red peppers has about 234 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 26% DV
- Kale: 1 cup of cooked, boiled, drained kale without salt has 172 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 19% DV
- Lettuce: 1 cup of shredded green leaf lettuce has 133 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 15% D.V.
- Broccoli: 1 medium stalk of cooked, boiled, drained broccoli without salt has about 139 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 15% DV
- Whole milk: 1 cup of whole milk with 3.25% milkfat, with added vitamin D, has about 112 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 12% D.V
- Papaya: 1 cup of mashed raw papaya has 108 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 12% DV
- Eggs: Two scrambled large, whole eggs have around 98 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 11% DV
- Butter: 1 tablespoon of unsalted butter has 97 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 11% DV.
- Mango: 1 cup of raw mango pieces has about 89 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 10% DV
- Goat cheese: 1 ounce of soft goat cheese has 82 mcg of Vitamin A, which is 9% D.V
Other foods that are also good sources include cod liver oil, green peas, basil, paprika, other herbs, tomatoes, and oatmeal. Additionally, fat-soluble retinol is favored over water-soluble beta carotene, but both are good to have in the diet.

Best Vitamin A Supplements
A nutrient-dense diet rich in high vitamin A foods is often enough to achieve optimal levels. In addition to a food source, some supplements may help.
Please note that too much vitamin A can also turn into a problem. I detail this under the Vitamin A Drops section. Use enough supplements to meet your needs, but don’t overdo it.
Cod Liver Oil
Cod liver oil is a rich source of fat-soluble vitamin A, which supports the health of the brain, thyroid, skin, and eyes. Nordic Naturals Arctic-D Cod Liver Oil is one of my favorites.
Cod Liver oil is one of the world’s best sources of the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve both brain and cardiovascular health.
In addition, cod liver oil is a rich source of fat-soluble vitamin A, retinol, which supports the health of the brain, thyroid, skin, and eyes. In addition to all the benefits of Nordic Naturals Arctic Cod Liver Oil™, each serving of this fruit-flavored liquid also provides 1000 I.U. of vitamin D3. This is the perfect dosage for young children. It is great for the immune, cardiovascular, brain, thyroid, skin, and eye health.
Grass-Fed Beef Organ Complex
Another supplement I highly recommend for improving your vitamin A levels is this Grass-Fed Beef Organ Complex. This supplement is a unique combination of freeze-dried bovine organs sourced from 100% grass-fed and finished New Zealand cattle. This product is formulated with a targeted blend of five different bovine organs, including the liver, heart, pancreas, kidney, and spleen, which may help support nutrient status in the body.
Edible offal and organ meats are one of the most nutrient-dense food groups. Compared to skeletal muscle meat, organ meats are known to store and contain higher amounts of proteins and other key nutrients. These vital nutrients include important energy-producing compounds, enzymes, beneficial fats, and amino acids. Bovine liver contains a variety of micronutrients that support various biological processes in the body.
Many people do not like the taste of this sharply flavored food. Beef liver has a very strong taste, while that of chicken is generally considered to be much milder. There are also excellent options provided by companies like US Wellness Meats that combine organs with ground beef in a sausage form called Braunschweiger. You can also turn liver into an excellent dish called a Pâté that involves all kinds of herbs, spices, and unique flavors.
Now, I already know that most people will not introduce liver to their diet regularly, so my team and I researched and found the very best pasture-raised beef liver and full organ complex on the market, and we recommend it for people looking to support and improve their liver health.
ImmunoCharge
Finally, I also recommend using ImmunoCharge. This supplement contains quercetin, zinc, vitamin D3, N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC), vitamin C, selenium, resveratrol, magnesium, vitamin K2, and vitamin A.
These ingredients support the body’s natural immune mechanism to help maintain good health. This blend is specifically designed to provide you with optimal dosages of these key immune-modulating nutrients and compounds.
The synergy of these key nutrients and compounds strengthens immune function and improves the process of inflammation. Rather than taking multiple different supplements to get these key nutrients, you can get the clinical dosages within four capsules daily of ImmunoCharge.
Final Thoughts
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and potent antioxidant that can reduce inflammation, oxidative damage, and free radicals. It is critical for vision and eye health, immune health, healthy skin, neurological health, bone health, circulation, and fertility.
Vitamin A deficiency can lead to vision problems, immune system dysfunction, chronic inflammation, an increased risk of infections, illness, autoimmunity, neurodegeneration, and even cancer. Recommend that you follow my tips in this article and incorporate the foods and supplements I listed to improve your levels and increase your health and vitality.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. On our website, we offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.

Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!






