 Magnesium: Health Benefits, Sources, and Signs of Deficiency
Magnesium: Health Benefits, Sources, and Signs of Deficiency
Magnesium is one of the major essential minerals your body needs for healthy functioning. It is critical for various vital bodily functions, including your brain, mental, bone, muscle, and cardiovascular health.
Yet, magnesium deficiencies are common and may result in anxiety, depression, brain health symptoms, sleep issues, blood sugar imbalances, cardiovascular issues, and bone health problems, and other health issues. Optimizing your magnesium levels through diet and supplementation is critical for your health and well-being.
In this article, you will learn about the health benefits of magnesium. You will learn about the recommended daily intake and the signs and symptoms of a deficiency and the major causes.
I will go over the best food sources of magnesium. You will learn about the best forms of supplements, what to avoid, and how to select the right one. I will recommend my favorite magnesium supplement to improve your health.

Health Benefits
Magnesium is one of the major essential minerals your body needs for healthy functioning. It is critical for various vital bodily functions, including your brain, mental, bone, and cardiovascular health. This major mineral offers several major health benefits. Let’s look at them one by once.
Anxiety
Magnesium is important for your mental health. Anxiety is one of the most common mental health problems in our society today. A 2017 systematic review published in Nutrients has found that low magnesium levels may increase the risk of anxiety (1). Researchers found that magnesium may act on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. As a result, this key mineral may help to reduce stress and anxiety.
A 2020 review published in Nutrients has also found that magnesium deficiency may contribute to stress, creating a vicious cycle of stress and anxiety (2). Addressing magnesium deficiency may reduce stress response and lower stress and anxiety.

Brain Health
Magnesium may also benefit other aspects of your brain health, not just mental health. Magnesium plays a role in synaptic transmission, neuronal plasticity, and neural activity. Thus, this key mineral may affect your learning and memory.
A 2010 study published in Neuron has found that this mineral may help to improve learning and memory, including short-term memory, long-term memory, working memory, and learning functions (3). According to a 2018 review published in Nutrients, magnesium may play a protective role in neurological issues, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, migraines, stroke, and chronic pain (4).
Blood Sugar
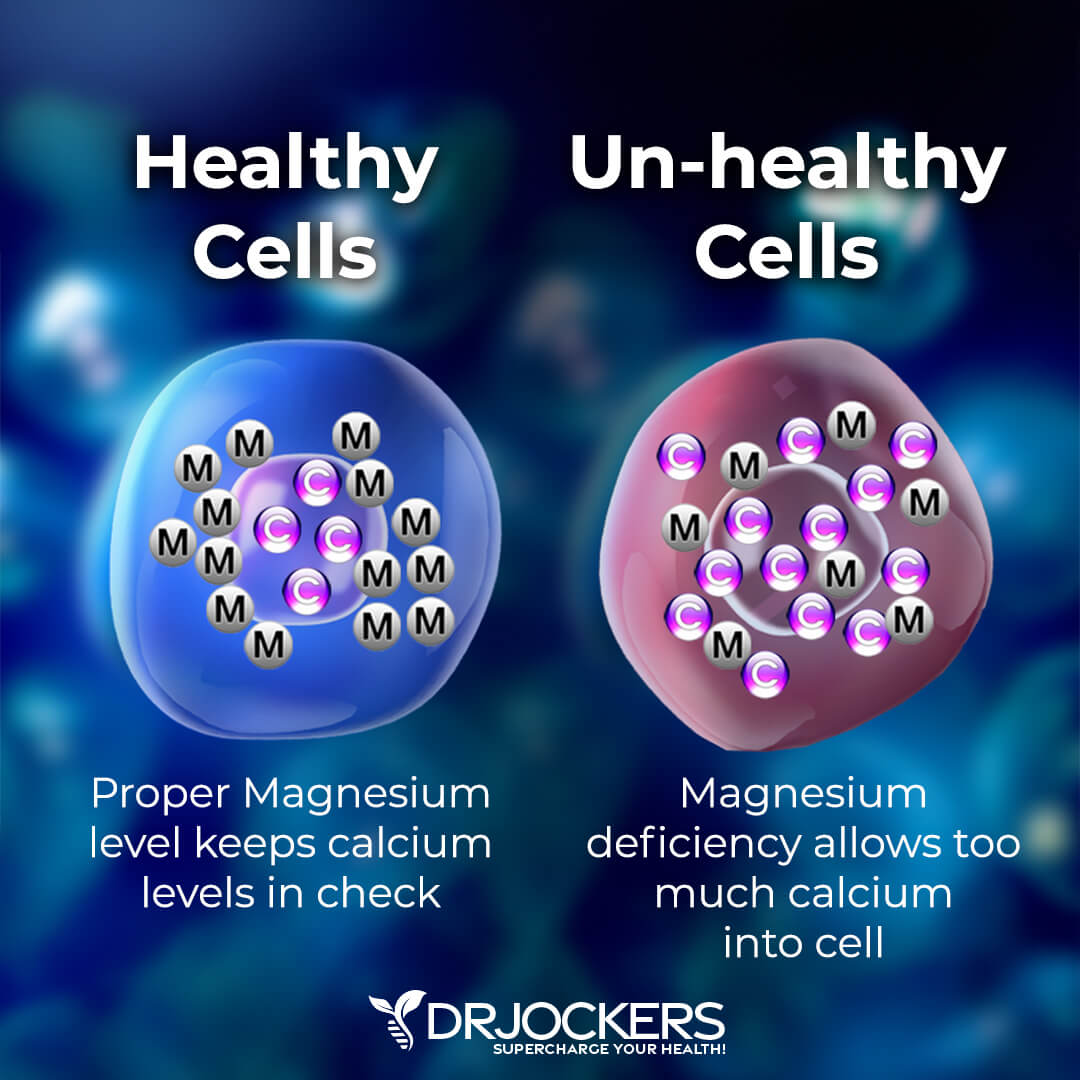
Magnesium is also good news if you want to improve your blood sugar (glucose) levels and reduce your risk of diabetes. It plays a part in glucose control and insulin metabolism thus may help to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
A 2015 review published in the World Journal of Diabetes has found that magnesium deficiency is common in people with diabetes (5). According to the researcher, supplementation may play a role in the management of diabetes. A 2017 systematic review published in Nutrition has found that magnesium may help to reduce insulin resistance and improve insulin sensitivity in those with a known deficiency (6).
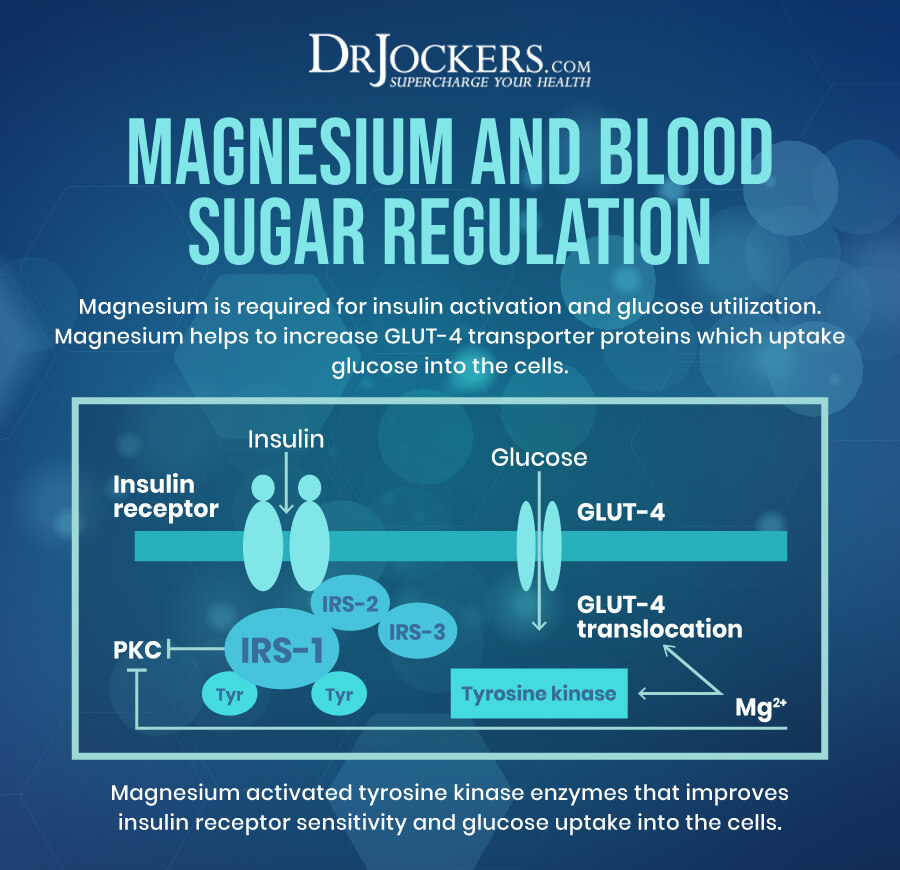
Bone Health
Though most people talk about the importance of calcium for bone health, there are many other nutrients that play a role in healthy bones. Magnesium is necessary for healthy bone formation and is important for your bone health.
A 2013 study published in Nutrients has found that getting enough magnesium may be linked to improving bone crystal formation, higher bone density, and a decreased risk of osteoporosis (7). It may be particularly important for women in perimenopause and menopause and older people as they are at a higher risk of osteoporosis. According to a 2022 systematic review published in Bone, magnesium may be beneficial for the bone health of older individuals (8).
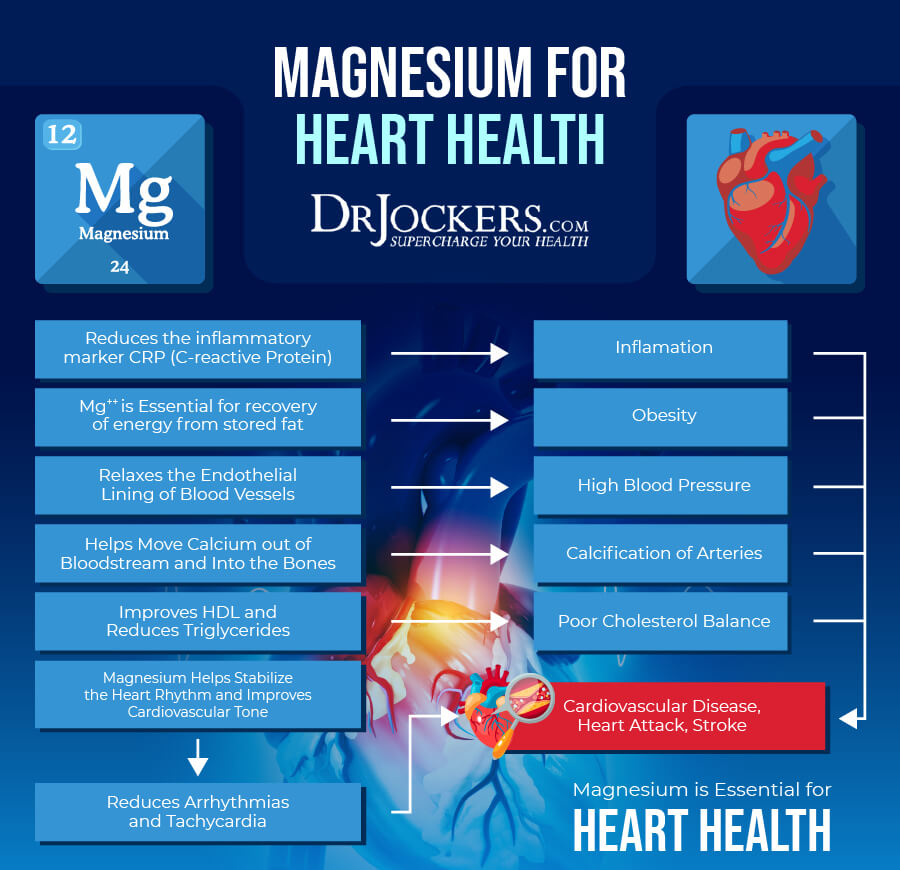
Cardiovascular Health
One of the major roles of magnesium is maintaining the health of your muscles. This is true for your health muscles as well. It is, thus, not surprising that magnesium plays an important role in your cardiovascular health.
According to a 2018 review published in BMJ, magnesium deficiency may increase the risk of cardiovascular issues (9). They found that low levels are common congestive heart failure and may compromise outcomes. According to a 2019 systematic review and meta-analysis published in Frontiers in Neurology, magnesium may reduce the risk of stroke (10).
Depression
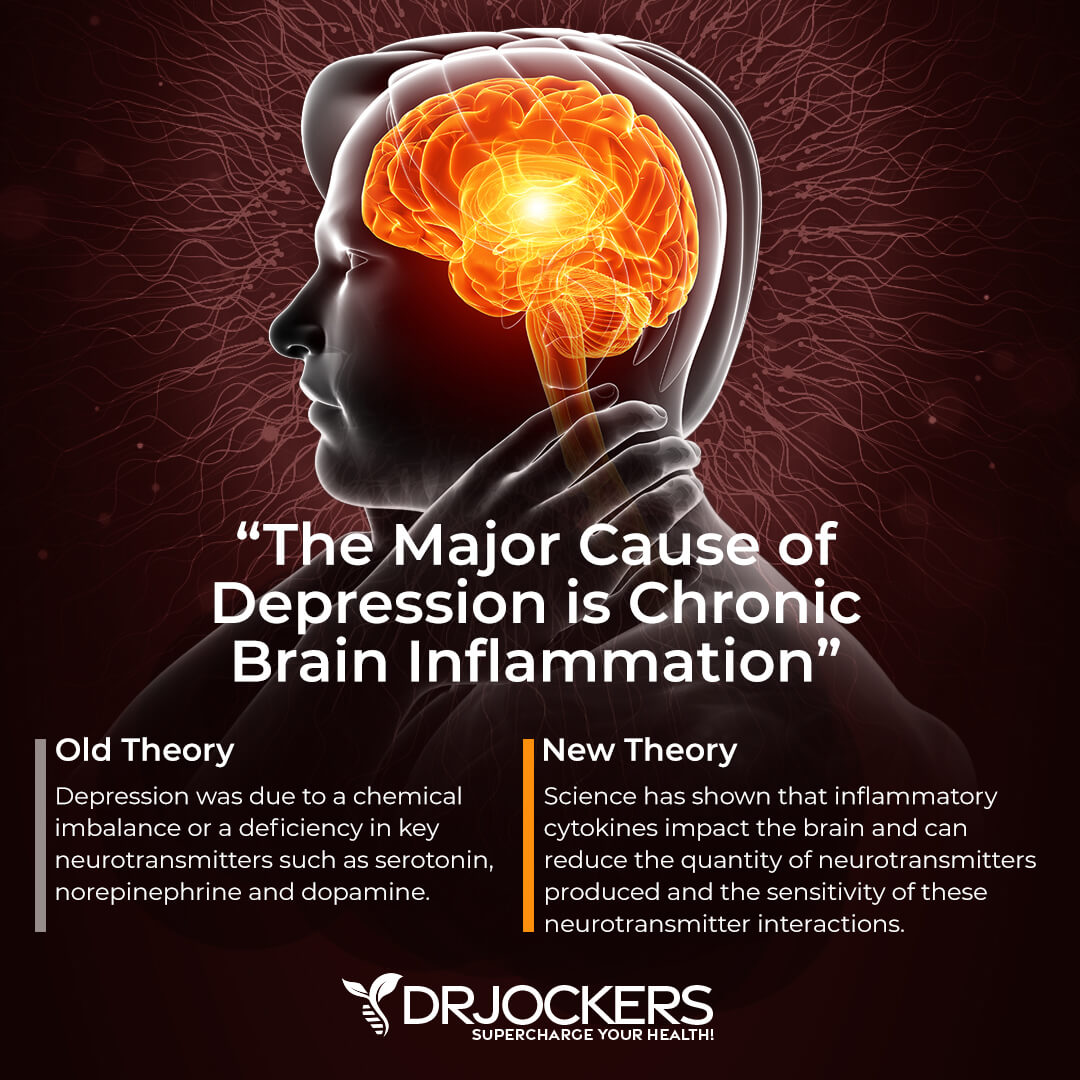
You already know that magnesium is important for mental health and brain health. It’s beneficial for reducing stress and anxiety, but it may also be helpful for depression.
According to a 2018 review published in Nutrients, magnesium may play a protective role for depression and anxiety (4). A 2006 case study published in Medical Hypotheses found that magnesium may support the treatment and recovery from major depression because it may help to correct intraneuronal magnesium deficiency and improve neuronal activity (11). A 2017 randomized clinical trial published in PLoS One has also found that supplementation may help to improve mild-to-moderate depression within 6 weeks (12).
Headaches
You may want to consider improving your magnesium levels if you have migraines or headaches. As we’ve discussed earlier, a deficiency may affect your neurotransmitter. It may also restrict normal blood vessel constrictions. Both of these factors can play a role in migraines and headaches.
Moreover, according to a 2022 study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditional Research, magnesium may help to relax your muscles and reduce muscle soreness (13). This may help with muscle pain and head pain associated with tension headaches.
According to a 2018 review published in Nutrients, magnesium may play a protective role in headaches and migraines (4). A 2017 review published in Headache has found that taking 600 mg of magnesium may help to reduce migraines (14). The American Migraine Foundation recommends about 400 to 500 mg of magnesium per day for migraineurs (15).
Sleep
Magnesium may help your body to relax (13). It can also calm your mind, reduce stress, and lower anxiety (1, 2). But easing your mind and body, magnesium may help you to fall asleep easier and faster. It may also help to improve your actual sleep.
A 2016 study published in the Journal of Research in Medicine Science has found that supplementation may help to reduce primary insomnia in older people (16). A 2021 study published in Current Developments in Nutrition has found an association between magnesium intake and better sleep quality and increased sleep duration (17). Participants with a higher magnesium intake slept better and longer.

Recommended Daily Intake
Recommended dietary allowance (RDA), or the recommended average daily intake of magnesium for healthy individuals for magnesium is as follows (18):
- Birth to 6 months: 30 mg for both female and male
- 7 to 12 months: 75 mg for both female and male
- 1 to 3 years: 80 mg for both female and male
- 4 to 8 years: 130 mg for both female and male
- 9 to 13 years: 240 mg for both female and male
- 14 to 18 years: 360 mg for females, 410 mg for males, 400 mg if pregnant, 360 mg if breastfeeding
- 19 to 30 years: 310 mg for females, 400 mg for males, 350 mg if pregnant, 310 mg if breastfeeding
- 31 to 50 years: 320 mg for females, 420 mg for male, 360 mg if pregnant, 320 mg if breastfeeding
- 51 + years: 320 mg for female, 420 mg for male

Best Food Sources
The best food sources of magnesium include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains. You may also find fortified cereals and other fortified foods on the market.
Unfortunately, some of these foods may not be right for you. Whole grains generally contain gluten, which may lead to inflammation, gut health issues, and other health problems. Legumes can be difficult for some people’s digestion, and they may not be ideal if you are on a low-carb diet. Fortified foods are often overly processed and contain artificial ingredients and additives.
Don’t worry, there are still plenty of food sources of magnesium you may enjoy. The best food sources I recommend (18):
- Pumpkin seeds, roaster: 156 mg per 1 ounce, 37 percent of the daily value
- Chia seeds: 111 mg per 1 ounce, 26 percent of the daily value
- Almonds: 80 mg per 1 ounce, 20 percent of the daily value
- Spinach, boiled: 78 mg per half a cup, 19 percent of the daily value
- Potato, baked with skin: 43 mg in 3.5 ounces, 10 percent of the daily value
- Salmon: 26 mg per 6 ounces, 6 percent of the daily value
- Halibut: 24 mg per 3 ounces, 5 percent of the daily value
- Avocado: 22 mg per ½ cup cubed, 5 percent of the daily value
- Chicken breast: 22 mg per 3 ounces, 5 percent of the daily value
- Ground beef, 90 percent lean, pan-broiled: 20 mg per 3 ounces, 5 percent of the daily value
- Broccoli, cooked: 12 ounces per ½ cup chopped, 3 percent of the daily value
- Apple: 9 mg per 1 medium apple, 2 percent of the daily value
- Carrot, raw: 7 mg per 1 medium carrot, 2 percent of the daily value
As you can see, despite there being some great food sources of magnesium, meeting your needs and correcting deficiencies through diet alone can still be challenging. Since our soils are depleted, these foods don’t always contain as much magnesium as they should. You may still benefit from supplementation along with consuming these foods.

Signs & Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Signs and symptoms of magnesium deficiency may include:
- Fatigue and sleepiness
- Weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Pins and needles feeling
- Tingling
- Numbness
- Muscle spasm
- Cramps
- Muscle contractions
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- High blood pressure
- Hyperexcitability
- Shaking
- Seizures
- Personality changes
- Mood changes
- Coronary spasms
- Low potassium and/or calcium levels

Reasons for Magnesium Deficiency
You may develop magnesium deficiency for a number of reasons. Of course, poor dietary intake may be one of the reasons.
But you will be surprised what other non-dietary factors may increase your risk or contribute to magnesium deficiency. Let’s look at the potential reasons for magnesium deficiency.

Diet High in Sugar and Processed Foods
A diet high in sugar and overly processed foods is generally not good for your health. Such a diet is low in nutrients, including magnesium. It may also cause chronic inflammation and related health issues. However, too much sugar and too many overly processed and refined foods may directly lead to magnesium deficiency.
According to a 2018 review published in Open Heart, a Western diet high in refined sugar, refined flours, processed foods, and refined fats it’s low in magnesium and is associated with magnesium deficiency (19). Furthermore, high blood sugar levels from increased sugar consumption may lead to impaired absorption and increased excretion leading to a vicious cycle. In the next section, I will discuss the connection between high blood sugar and magnesium deficiency.

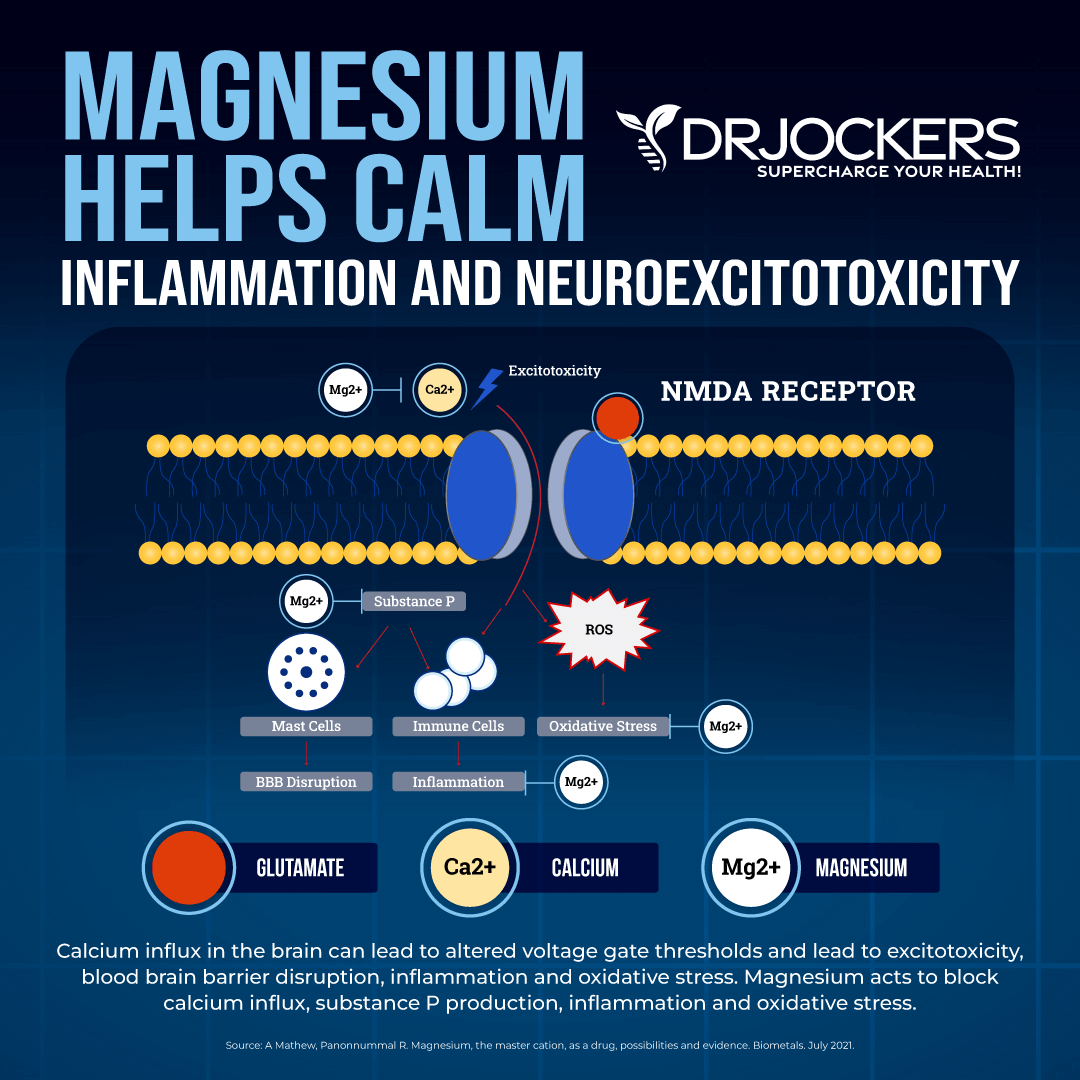
Insulin Resistance
Magnesium plays an important role in sugar control and insulin metabolism. Insulin resistance, elevated insulin levels, and high blood sugar are all linked to reduced magnesium absorption. It may also make your kidneys excrete magnesium at a faster speed.
A 2015 review published in the World Journal of Diabetes has found that low magnesium intake, increased magnesium loss through urine, and magnesium deficiency are common issues in people with type 2 diabetes (20). A 2019 study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences has also found that magnesium deficiency may play a role in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (21).
Researchers found that magnesium supplementation may help the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance. According to a 2004 study published in Diabetes & Metabolism, oral supplementation for 3 months may increase insulin sensitivity (22). A 2015 review published in the World Journal of Diabetes has also found that supplementation may play a role in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes (20).
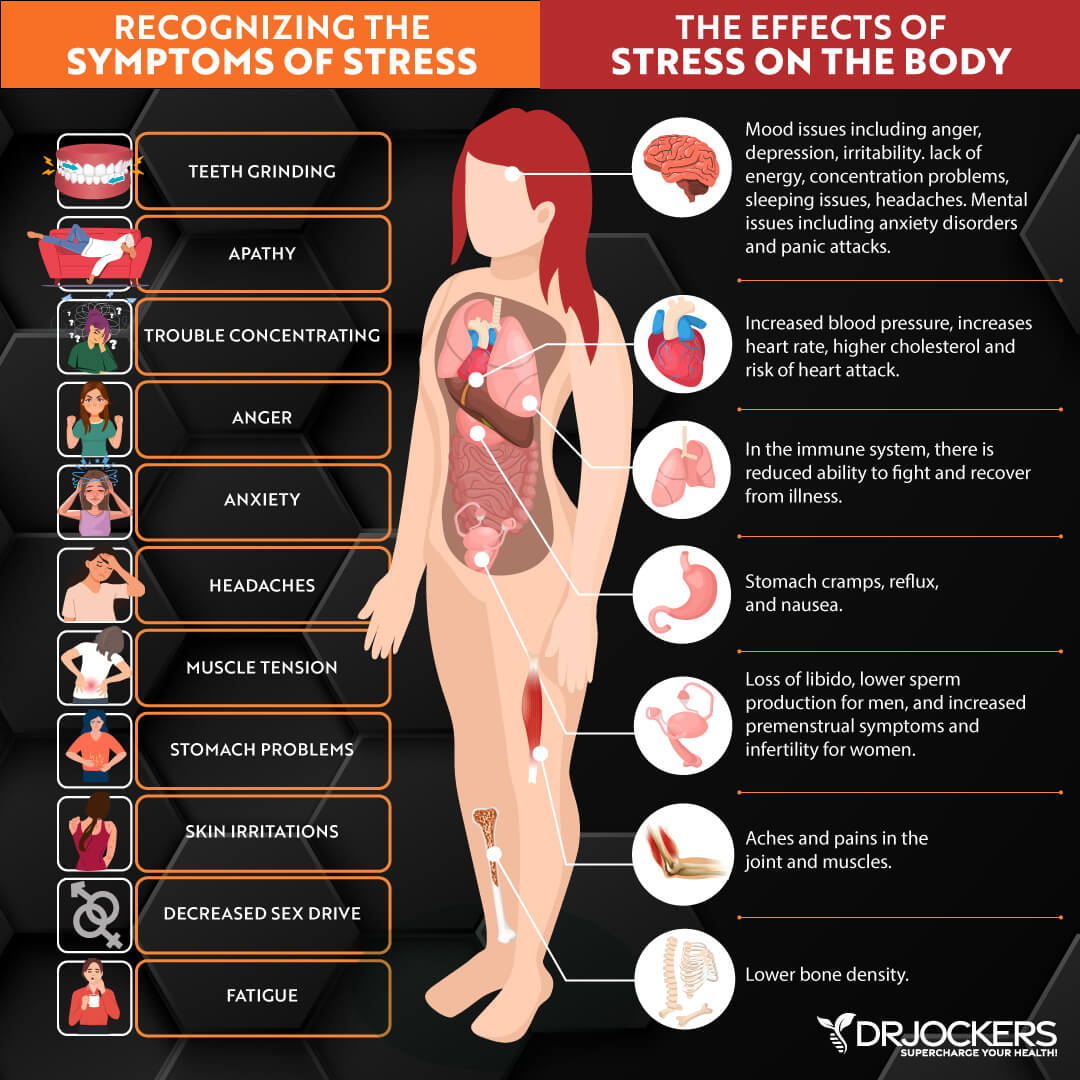
High Stress
We’ve already talked about how magnesium deficiency can contribute to stress and anxiety (1, 2). But chronic stress and high stress can also lead to magnesium depletion and deficiency. This can lead to a vicious cycle of stress and magnesium deficit.
A 2011 book, Magnesium in the Central Nervous System, published by the University of Adelaide Press, discussed how magnesium interacts with your stress pathways and how magnesium deficiency may be connected to stress-related health issues (23).
According to a 2020 review published in Nutrients, magnesium plays a key role in stress response and stress regulation (24). Researchers found that stress can lead to less magnesium and consequent deficiency, but a deficiency can make you more susceptible to stress feeding the cycle.
Diet High in Phytic Acids
Phytic acid, also known as inositol hexaphosphate or IP6, is a natural substance found in plant seeds. It’s found in all edible seeds, nuts, legumes, and grains in varying quantities. It is commonly used as a preservative because of its antioxidant effects. Even within the same food, the amount of phytic acid can differ.
Phytic acid is often called an anti-nutrient because it may reduce the absorption of zinc, calcium, magnesium, iron, and other minerals. According to a 1998 animal study published in Nutrition Research, phytic acid may reduce the bioavailability of magnesium (25). A 2004 study published in the American Journal of Nutrition found that phytic acid may inhibit magnesium absorption in humans (26). A 2021 review published in Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety has found that phytic acid can contribute to nutrient deficiencies (27).

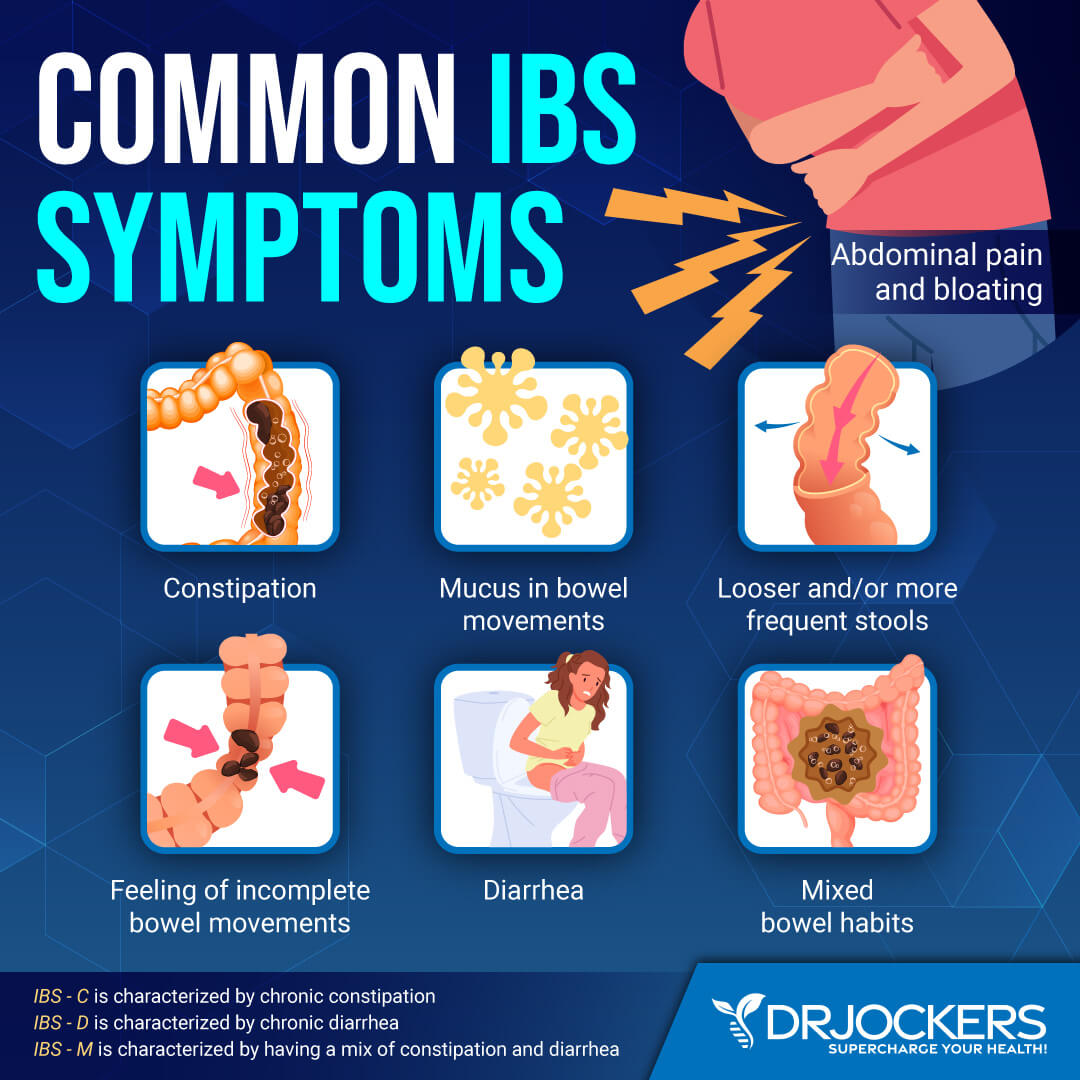
IBS – Malabsorption
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) refers to a group of digestive symptoms that occur together without a detectable sign of damage or other digestive diseases. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, cramps, gas, constipation, and diarrhea. IBS can also lead to the malabsorption of nutrients and nutrient deficiencies.
According to a 2014 review published in PLoS One, IBS may lead to malabsorption of nutrients (28). Taking magnesium may not only help to correct deficiencies but may also reduce your symptoms of IBS. According to a 2016 study published in Forsch Komplementmedizin, magnesium may help to reduce constipation and improve IBS symptoms (29).
Heavy Alcohol Intake
Heavy alcohol intake may also lead to magnesium deficiencies. For one, certain alcohols, such as beer, wine, and cocktails, may be particularly high in sugar. Too much sugar may increase the risk of magnesium deficiency (19). Furthermore, alcohol may lower the bioavailability of magnesium and lead to the increased excretion by your kidneys.
According to a 2008 study published in Substance Abuse Treatment, Prevention, and Policy, magnesium deficiency is common among people with alcoholism, and improving mag levels may reduce the risk of death from alcohol abuse (30). A 2021 meta-analysis and systematic review published in Nutrients has found that poor magnesium metabolism, depletion, and deficiency are serious problems in chronic alcohol-use disorders (31).

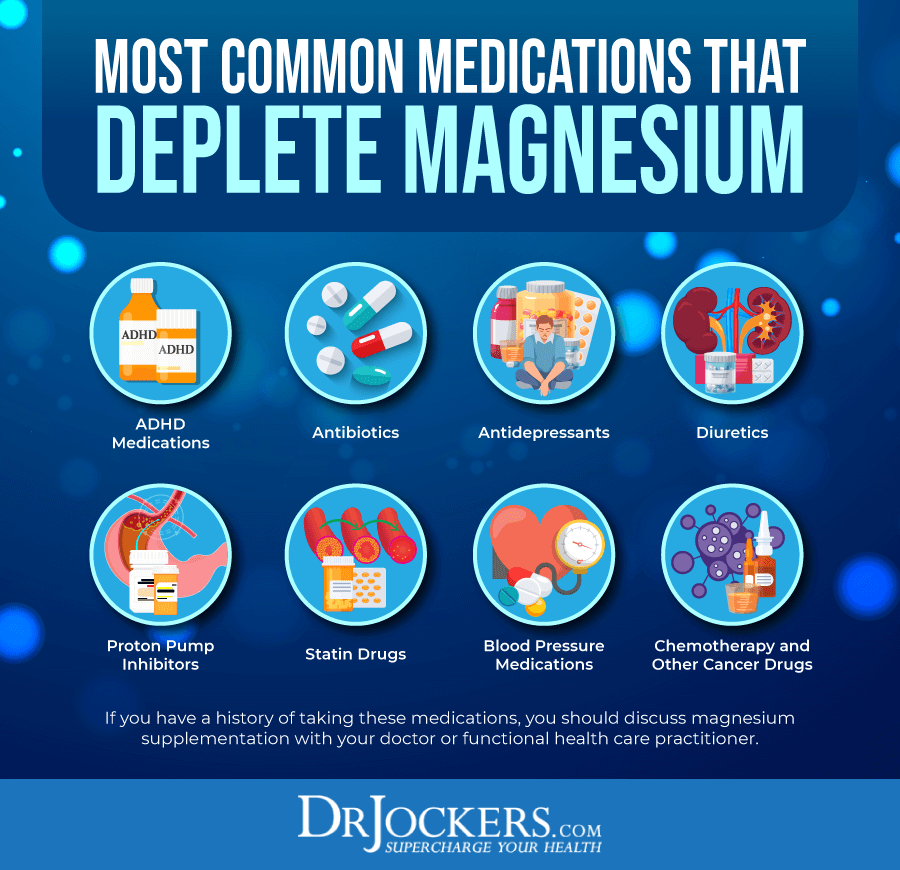
Certain Medications
Last but not least, certain medications may also contribute to magnesium deficiency. According to a 2021 research published in Pharmacology Research and Perspectives, certain antibiotics, diuretics, proton pump inhibitors, anti-depressants, adhd medications, antineoplastic drugs, and calcineurin inhibitors may cause magnesium deficiency (32).
If you are taking any of these medications, watching out for signs of magnesium deficiency and eating a healthy diet and key supplementation may be particularly important.
Magnesium Supplements
You may benefit from magnesium supplementation if you are deficient, want to prevent deficiency, or want to improve your health. The problem is that there are so many different types of magnesium supplements out there. Unfortunately, some forms are not absorbable by your digestive tract, and some of them don’t have many health benefits.
You want to buy a magnesium supplement that absorbs and works and the type of magnesium that works for your particular health issues and goals. Below is a list of some of my favorite forms and the ones that are most likely to benefit your health.

Malate
Magnesium malate is a form of magnesium bonded to malic acid. It naturally occurs in many foods, especially in fruits. Malic acid is a key component of the Krebs Cycle, which is the biological process responsible for making ATP energy.
Thus mag malate is a great option for improving energy-related disorders, including chronic fatigue syndrome and depression. According to a 2011 study published in Orvosi Hetilap, mag malate may help to improve your blood sugar and support a healthy magnesium-calcium balance (33).

Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate or chelated magnesium is made up of magnesium and amino acid glycine. According to a 2017 review published in Nutrients, magnesium glycinate is one of the most bioavailable forms of magnesium (34).
Even better, it is also gut-friendly, making it a perfect choice if you have diarrhea when taking magnesium. It is the most commonly recommended option for hypomagnesemia or clinically diagnosed mag deficiency.
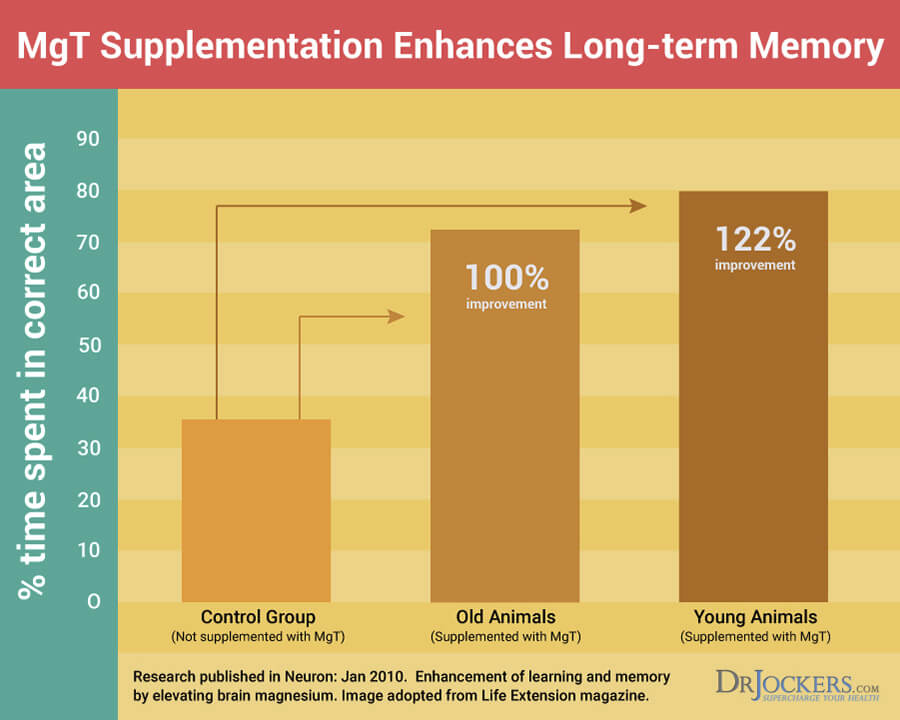
L-Threonate
Magnesium L-threonate (MgT) is a newer form of magnesium that’s commonly used for brain and mental health. According to a 2014 study published in Molecular Brain, mag threonate may offer neuroprotective and cognitive-boosting benefits that may be protective against Alzheimer’s disease (35).
It may be beneficial for long-term memory, learning, and cognitive performance. It may help to improve brain fog, depression, and anxiety.
Citrate
Magnesium citrate is one of the most commonly used forms of magnesium because it generally has the lowest cost. According to a 2017 review published in Nutrients, mag citrate is a reasonably bioavailable form of magnesium (34).
It is one of the only naturally acidic forms of magnesium because it bonds to citric acid, a common food additive in citrus fruit. Mag citrate is the best for aiding bowel movements and supporting oxalate metabolism. It may also be helpful for kidney stones which develop due to high levels of dietary oxalates.
Chloride
Magnesium chloride brings you the benefit of both magnesium and chloride. According to a 2017 review published in Nutrients, mag chloride is a reasonably bioavailable form of magnesium (34). Mag chloride may be particularly beneficial for detoxification and healthy kidney function.
Since chloride is an electrolyte, it may support the nervous system, and along with sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium, and phosphate, it may be beneficial for proper muscle contractions, blood pressure control, and brain health. Chloride may also support stomach acid production and proper digestion.
Inferior Magnesium Supplement Forms
There are also some forms of magnesium that I recommend that you avoid. These are low in bioavailability and don’t absorb well. I don’t recommend magnesium oxide, dihydroxide (milk of magnesia, sulfate, aspartate, and carbonate forms.
Magnesium sulfate, also known as Epsom salt, absorbs well through the skin and may be helpful for Epsom salt baths. However, Magnesium Chloride Salt is even better for soaking.

Topical Magnesium Supplement Options
If you have digestive issues that make taking magnesium supplements difficult, you may want to consider using a topical magnesium option. You may reduce your supplements and add some topicals or rely only on topicals if required. Topical magnesium is also fantastic for tense muscles, aches, and pains, fibromyalgia pain, and other chronic pain issues.
For this purpose, I have found that the Ancient Minerals brand works the best. The topical magnesium with MSM is the best for applying to problem areas or as a general magnesium supplement. The combination of magnesium and MSM is powerful for controlling inflammation and strengthening damaged tissues. This form is also very suitable for athletes!
For those who have trouble sleeping at night, Ancient Minerals also carries a topical magnesium with melatonin. For this one, I will typically recommend applying one pump to the bottoms of the feet or abdomen 30 minutes to 1 hour before going to bed.
Before You Buy a Magnesium Supplement
You will find many different forms and brands of magnesium on the market. It can feel confusing. Make sure to read this guide and consider your health goals before selecting the right one. As with all supplements, it is important to ensure you are getting yours from a source that tests every batch to ensure you are getting what is on the label and nothing else. This includes things like unwanted toxins, allergens, and heavy metals.
All of my personal line products are pharmaceutical grade, GMP compliant. This means they are produced in strictly monitored facilities that also send batches of their product to third parties for analysis before selling to consumers. In the next section, you will learn about my favorite magnesium supplement, Brain Calm Magnesium.
The Magnesium Supplement I Use
I recommend Brain Calm Magnesium. We developed Brain Calm Magnesium in order to provide the best form of magnesium to improve brain function and neuronal health. This product helps you to focus, concentrate and perform at a significantly higher level. In addition, it is fantastic for reducing anxiety while improving mood, memory, and sleep.
Brain Calm Magnesium features key Albion forms of Magnesium (malate, lysinate & glycinate chelate) as well as mag L-threonate the only form of magnesium proven in animal studies to cross the blood-brain barrier. Boosting the brain’s magnesium level is vital to healthy cognition, which includes long- and short-term memory, learning, stress management, and sleep.
Because many forms of magnesium have low bioavailability, we carefully selected magnesium compounds backed by research and studies to formulate Brain Calm Magnesium. This product features a unique combination of highly absorbable, organic Albion minerals—di-magnesium malate and magnesium lysinate glycinate chelate—and Magtein.
Magtein is a groundbreaking organic magnesium compound that was developed by MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) researchers to support “brain power.”
Magtein is the result of 10 years of research at MIT. This novel form of magnesium is changing the way we support brain health. Unlike other brain products on the market that work via brain stimulation (often overstimulation), Magtein works via a completely different mechanism.
When brain magnesium levels are not optimal, synapse function deteriorates. By delivering magnesium into synapses, Magtein helps brain cells stay healthy without being overactivated; consequently, brain cells respond to signals with clarity and robustness.
Brain Calm Magnesium supports healthy brain magnesium levels, healthy synapse number, and function, supports memory and cognitive acceleration, supports stress management, helps sleep quality, supports healthy mood, and ensures optimal magnesium intake.
I use Brain Calm Magnesium on a daily basis myself during the daytime in order to improve my concentration and productivity. I also take some at night and have noticed much deeper and more restorative sleeping patterns. I use this product with clients that are struggling with neurodegenerative issues, mental clarity, sleep, and mood issues.
Final Thoughts
Magnesium is an important mineral for your brain, mental, bone, cardiovascular, bone, and muscle health, energy, and sleep. Deficiencies are common. I recommend supplementing with magnesium to improve your health and well-being.
I recommend following my guide to magnesium supplements to select the best one to optimize your levels. You may notice improvements not only in your cognition, mental sharpness, mood, and energy but also in your overall health.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!









Thank you from heart for all these valuable information. What about the Magnesium Bisglycinate ?
Now i understand why my friend has often headaches, He eat very badly n doesn’t accept to take Mg, Hopefully after reading your excellent report he will be convinced !! God bless you
Jacquelina De Los Rios
Yes the bisglycinate is in the glycinate family! Very good form!
THANKYOU!
Can you take both the CalMag support and Brain Calm Magnesium daily, like one am and one pm?
Yes you can, but if you have loose stools, than back off of the Calmag a bit. You can take either at any time. The BC Mag will help with focus and concentration during the day so I prefer that and Calmag can help with sleep at night.
Thanks for another very informative article!
The richest natural source of magnesium are hulled hemp seeds, far beyond any of the other high magnesium foods, gram per gram. They are also rich in zinc, iron, omega-3’s and GLA. Hemp seeds are a true superfood, more so than any other seed or nut. For me, they should definitely be at the top of the magnesium list.
Thanks for sharing!
So you sell magnesium tablets ? I want to make sure that I take the correct amount .I have severe feet leg & hand cramps stage 3 kidney disease pre diabetic fatigue tendinitis I’m a female & 74 .
Do you sell magnesium tablets ? If you don’t what is a good brand name . I am a 74 woman who has severe leg foot & hand cramps my primary care Dr told me 9/15/22 to start taking magnesium that it can be purchased anywhere . I also have pre diabetics stage 3 kidney disease & almost everything the pill is good good for
The above article states both the Brain Calm Magnesium powder and capsules contain several forms of magnesium however your store shows the nutrition info label for the powder only has 1 form, L-Threonate. I’ve contacted customer service. 1 rep said there’s an error on the powder and would get it fixed but another said it was correct.
Please clarify!
Yes this is because our Brain Calm Magnesium powder contains a combination of Mag L-threonate, magnesium malate and magnesum lysinate glycinate chelate. Meanwhile, our Brain Calm Magnesium capsules only contain Mag L-threonate. Hope that helps!
Does the Brain Calm Mag powder have a taste?
Yes you can get it in Mixed Berry, Lemon Lime, Unsweetened or in capsule form.
Which is the best form to take
That is discussed in the article.
Thank you so the very informative article!
One of the graphics you shared shows mag chloride is 0 for stability constant and totally ionized, what do these factors mean? I currently take this form of magnesium.
Thank you!
Brilliant read.very helpful
Thank you!
When did you first researched on Magnesium Chloride? It’s very good..
Great article thanks. You also cannot replete potassium without magnesium. It is so important to our health.