 Phytonutrients: What Are They, Benefits and Sources
Phytonutrients: What Are They, Benefits and Sources
Greens, vegetables, and low glycemic index fruits are an essential part of a healthy and balanced diet. They are not only rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants but are full of phytonutrients. Phytonutrients are health-boosting, nutrient-like compounds found in plant foods that are invaluable to your health.
In this article, you will learn what phytonutrients are. You will learn about the benefits of phytonutrients. You will understand how to add phytonutrients to your diet. I will go over the five major types of phytonutrients their benefits, and foods that contain them. I will discuss the importance of eating a rainbow, go over the major color groups of foods, and offer a delicious green mix to boost your phytonutrients for better health and well-being.

What Are Phytonutrients?
Phytonutrients can also be referred to as phytochemicals. They are natural, nutrient-like, and health-boosting substances that are found in plants. While you cannot develop a serious phytonutrient deficiency like you can with vitamins and minerals, phytochemicals are essential compounds for your overall health and well-being.
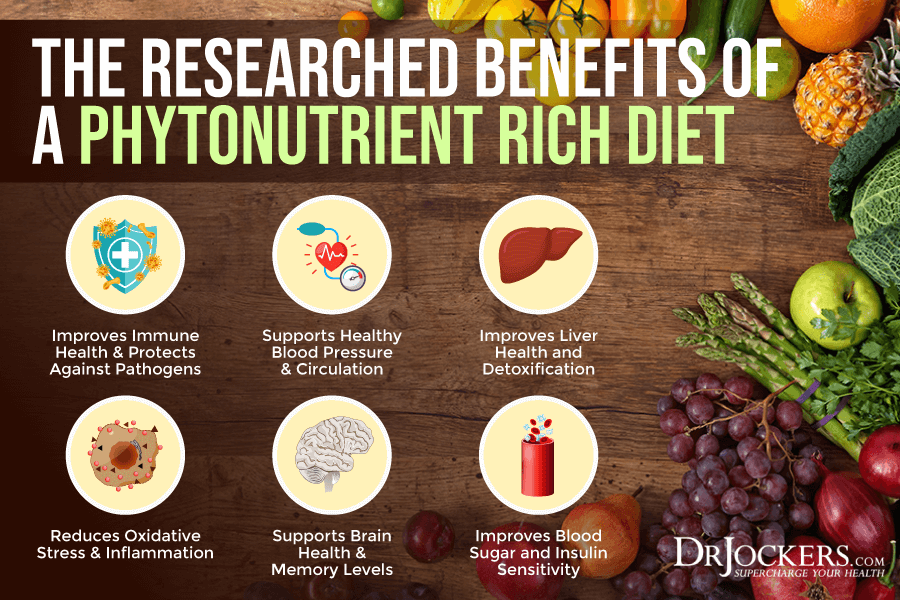
According to a 2014 review published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry and a 2017 review published in BMJ Open, phytonutrients offer a variety of health benefits, including improved immunity, detoxification, and a reduced risk of age-related health issues, such as osteoporosis, heart disease, and diabetes (1, 2).
Benefits of Phytonutrients
At this point, there have been over 5,000 phytonutrients identified, but there may be a lot more of them. According to a 2013 review published in Advanced Nutrition, phytonutrients are some of the main health-promoting components of vegetables and fruits (3). Let’s look at the benefits of phytonutrients.
The benefits of phytonutrients may include:
- Improved immunity: A 2014 study published in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine has found that phytochemicals may support your immune system (4).
- Lower blood pressure: A 2014 study published in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine has found that phytochemicals may reduce blood pressure (4).
- Reduced cholesterol: A 2014 study published in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine has found that phytochemicals may improve your cholesterol (4).
- Improved brain health: A 2014 study published in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine has found that phytochemicals may support your brain health (4).
- Improved liver health: A 2014 study published in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine has found that phytochemicals may support your liver health(4).
- Reduced risk of osteoporosis: A 2014 study published in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine has found that phytochemicals may reduce the risk of osteoporosis (4).
- Reduced risk of chronic disease: A 2014 study published in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine has found that phytochemicals may reduce the risk of chronic disease (4). A 2015 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that phytonutrients may lower the risk of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, metabolic disease, insulin resistance, and cancer (5). A 2010 review published in Toxins (Basel) has found that phytochemicals may help to support cancer therapy (6).
- Reduced oxidative stress: A 2015 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that phytonutrients may help to combat oxidative stress and free radical damage (5).
- Reduced blood sugar levels: A 2015 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that phytonutrients may improve blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes (5). A 2008 study published in Metabolism has found that phytochemicals may help to improve blood sugar and support those with diabetes (7).
- Protection from pathogens: A 2015 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that phytonutrients may offer protection against pathogens (5). A 2017 review published in Microbiology Research has found that phytochemicals may offer antibacterial benefits (8). A 2009 review published in Current Medicinal Chemistry has found that phytonutrients may have antimicrobial and antiparasitic properties (9).
- Decreased inflammation: A 2015 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that phytonutrients may help to reduce inflammation (5). A 2016 review published in Current Pharmaceutical Design has found that phytonutrients may offer anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits (10). A 2018 review published in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition has also found that phytochemicals in vegetables and fruits may have anti-inflammatory effects (11).
- Improved detoxification: A 2015 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that phytonutrients may support detoxification (5). A 2012 study published in the Journal of Amino Acids has found that phytochemicals may help detoxification (12).
Foods Rich in Phytonutrients
Finding food that is rich in phytonutrients is not difficult. In fact, it’s pretty easy. Phytonutrient-rich foods are all around us. All plant-based foods are rich in phytochemicals, such as greens, vegetables, fruits, herbs, spices, nuts, and seeds.
However, a 2014 study has found that certain processing or cooking methods may reduce the phytochemical content of certain foods (15). If you are cooking, use steaming, sautéing, or baking with water or healthy oils, such as coconut oil or extra virgin avocado oil. Avoid deep-frying and refined vegetable oils. I also recommend eating plenty of raw greens, veggies, and low glycemic index fruits.
According to a 2017 review published in Nutrition Research, the color, flavor, and scent of food are determined by its phytochemical content (16). Berries, for example, get their purple, red, or blue colors from anthocyanins. Different colored fruits and veggies, such as green, red, yellow, and purple ones, offer different phytochemicals. This is one more reason to eat a rainbow.
However, foods that are not bright in color may also offer benefits from phytochemicals. A 2008 review published in the Asian Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition has found that nuts are rich in phytochemicals (17). A 2017 review published in the British Journal of Pharmacology has found that green tea and black tea also offer phytonutrient benefits (18). A 2017 review has found that cacao and dark chocolate are also rich in phytochemicals (19).
Moreover, essential oils are also rich in phytochemicals. A 2018 research published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, a 2018 study published in National Product Research, and another 2018 review published in Mental Health Clinician have found that essential oils, such as lavender, pine needles, and cedar, offer benefits from phytonutrients, such as reduced inflammation (20, 21, 22).
What Are the Main Types of Phytonutrients
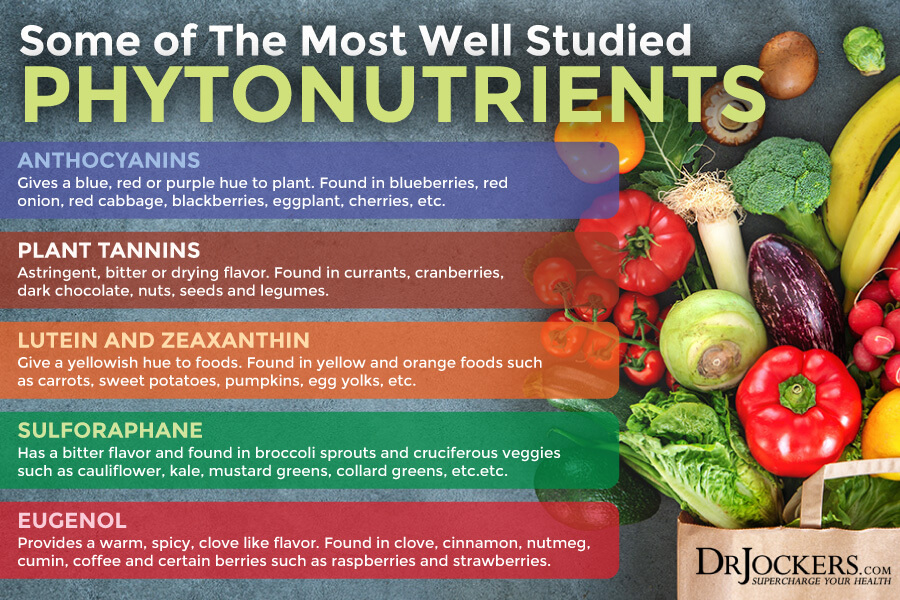
Since there are thousands of phytochemicals, it would be impossible to go over all of them. However, there are six major phytochemicals, including anthocyanins, tannins lutein and zeaxanthin, sulforaphane, and eugenol, that you should know about due to their incredible health benefits.
Anthocyanins
According to a 2010 review published in the Annual Reviews in Food Science Technology has found that there are over 635 types of anthocyanins (23). The word anthocyanin comes from the Greek language and means blue or flower. It usually gives a blue, red, or purple hue to anthocyanin-rich vegetables and fruits.
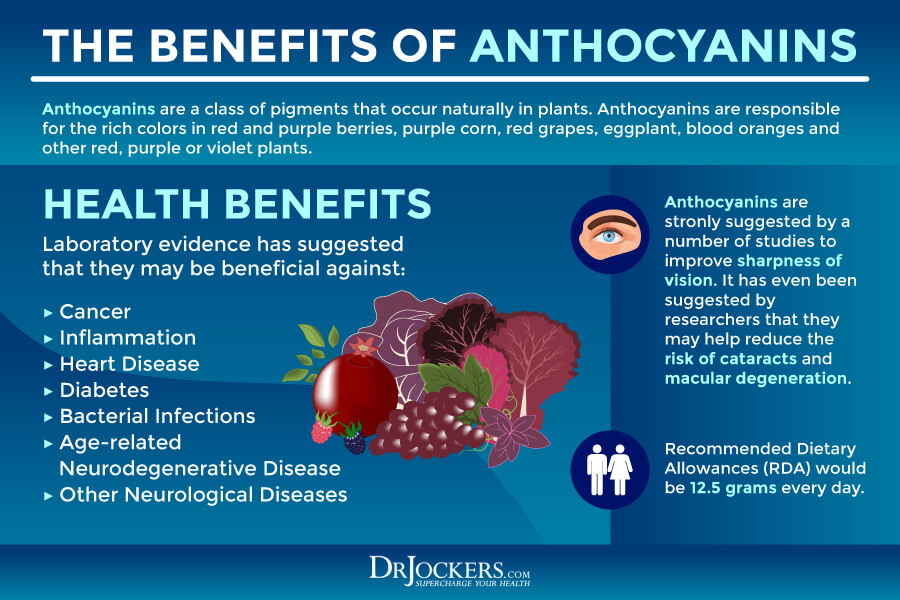
Benefits of Anthocyanins
The benefits of anthocyanins may include:
- Reduced risk of disease: A 2010 review published in the Annual Reviews in Food Science and Technology has found that anthocyanins may reduce inflammation and the risk of disease (24).
- Lower inflammation: A 2010 review published in the Annual Reviews in Food Science and Technology has found that anthocyanins may reduce inflammation (24).
- Weight loss of weight maintenance: A 2010 review published in the Annual Reviews in Food Science and Technology has found that anthocyanins may help with weight control (24).
- Reduced risk of heart disease: A 2010 review published in the Annual Reviews in Food Science and Technology has found that anthocyanins may lower the risk of heart disease (24).
- Reduce insulin sensitivity and diabetes: A 2018 review published in the Current Medicinal Chemistry has found that anthocyanins may reduce the risk of diabetes (25).
- Lower free radicals and oxidative stress: A 2019 review published in Food Chemistry has found that anthocyanins offer antioxidant benefits and may reduce oxidative stress and free radical damage (26).
- Protect DNA: A 2019 review published in Free Radical Research has found that anthocyanin may offer antioxidant benefits and may help to protect the health of the DNA (27).
- Protect the brain: A 2016 review published in Phytotherapy Research has found that anthocyanins may be protective to your brain (28).
- Increase the benefits other phytonutrients: A 2016 review published in Phytotherapy Research has found that anthocyanins may help to boost the benefits of other phytochemicals (28).
Foods Rich in Anthocyanins
Red, blue, and purple plant foods are usually rich in anthocyanins. Some great examples include berries, currants, grapes, cherries, plums, red cabbage, and purple potatoes (23).

Tannins
Tannins provide an astringent, drying, and mouth-puckering flavor and affect the foods they are in. Despite their bitter taste, they actually offer many health benefits. Though some people believe that tannins may interfere with iron absorption, a 2017 review in Current Developments in Nutrition has found that your body will adapt to tannins over time and won’t affect your iron levels (29).
Of course, consuming plenty of iron-rich foods, such as beef, liver, poultry, seafood, egg yolks, pumpkin seeds, broccoli, chard, spinach, and kale, is a great way to ensure that you have optimal iron levels.
Benefits of Tannins
The benefits of tannins may include:
- Increased antioxidants: A 2018 review published in Animal Nutrition has found that tannins are rich in antioxidants (30).
- Reduced inflammation: A 2018 review published in Animal Nutrition has found that tannins may help to lower inflammation (30).
- Reduced microbes, parasites, and other pathogens: A 2018 review published in Animal Nutrition has found that tannins may help fight microbes, parasites, and other pathogens (30).
- Improved blood pressure: A 2017 review published in the British Journal of Pharmacology has found that tannins may offer cardioprotective benefits, such as reduced blood pressure (31).
- Decreased risk of health issues: A 2017 review published in the British Journal of Pharmacology has found that tannins may reduce the development of disease (31).
- Improved immune system: A 2017 review published in the British Journal of Pharmacology has found that tannins may support the immune system (31).
Foods Rich in Tannins
Tart foods, including pomegranates, currants, cranberries, and blackberries, are usually rich in tannins. Almonds, pecans, pistachios, walnuts, hazelnuts, and other nuts are also high in tannins. Beans, lentils, rice, and barley are also good sources of tannin. Lastly, dark chocolate, coffee and tea are rich sources of tannins (30).

Lutein and Zeaxanthin
Lutein and zeaxanthin tend to give food a rich orange or yellow hue although they are also very high in green vegetables but the chlorophyll content of the greens overpowers the yellow/orange. They are powerful phytochemicals. As a 2016 review published in the Annual Reviews in Nutrition explained, they are the most beneficial for your eye health (32).
Not surprisingly, your retina has the highest concentration of lutein and zeaxanthin. These two phytonutrients help to absorb about 40 to 90 percent of blue light and also help to reduce oxidative damage due to their antioxidant content. This helps to protect your retina and eye health.
Benefits of Lutein and Zeaxanthin
The benefits of zeaxanthin may include:
- Improved eye function: A 2016 review published in the Annual Reviews in Nutrition has found that lutein and zeaxanthin support your eye health (32). A 2017 review published in Molecules has found that lutein and zeaxanthin may help to reduce the risk of various eye disorders (33).
- Better cognition, memory, and brain function: A 2017 review published in Molecules has found that lutein and zeaxanthin may help to reduce the risk of cognitive disorders (33). A 2017 study published in Nutrients has found that lutein and zeaxanthin may help to improve cognitive function (34).
- Improved insulin sensitivity: A 2015 review published in Food and Nutrition Research has found that lutein and zeaxanthin may help to improve insulin sensitivity (35).
- Reduced inflammation: A 2015 review published in Food and Nutrition Research has found that lutein and zeaxanthin may help to lower inflammation (35).
- Lower blood pressure: A 2015 review published in Food and Nutrition Research has found that lutein and zeaxanthin may help to decrease your blood pressure (35).
- Better heart health: A 2015 review published in Food and Nutrition Research has found that lutein and zeaxanthin may help to improve your heart health (35).
- Improved skin health: A 2009 review published in Clinical Dermatology has found that lutein and zeaxanthin may be beneficial for your skin health (36).
Foods Rich in Lutein and Zeaxanthin
Yellow and orange foods, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, butternut squash, oranges, egg yolks, orange peppers, yellow corn, and pumpkins, are generally high in lutein and zeaxanthin. Pistachios are also rich in phytonutrients, including lutein and zeaxanthin. However, eating greens, such as kale, parsley, spinach, and romaine lettuce, is another great way to boost your lutein, zeaxanthin, and other phytonutrients intake (32).

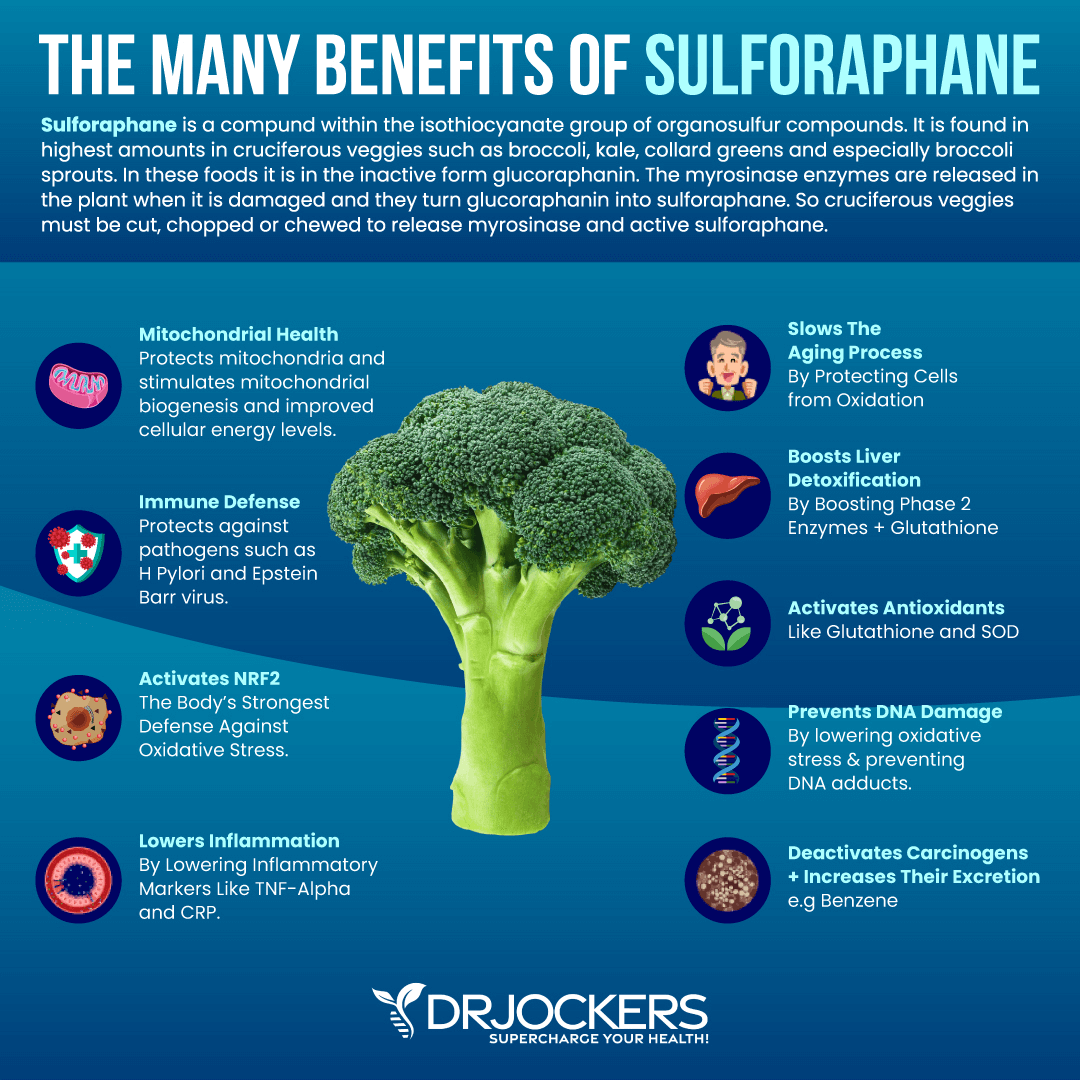
Sulforaphane
Sulforaphane is a powerful antioxidant that may help to reduce inflammation and reduce the risk of disease. A 2018 review published in the Journal of Cellular Communication and Signaling and another 2018 study published in PLoS One have both found that sulforaphane may play a role in cancer prevention and treatment (37, 38).
Sulforaphane may not only reduce inflammation but may also lower the risk of cancer cells or other diseases spreading throughout your body. It may also trigger unhealthy cells to die. Sulforaphane gives plants that contain it a bitter flavor.
Benefits of Sulforaphane
Sulforaphane may offer a variety of health benefits, including:
- Improved ability to fight pathogens: A 2016 study published in PLoS One has found that sulforaphane may help to reduce viral infections (39). A 2008 research published in Planta Medica has found that sulforaphane may help to fight bacteria and fungal pathogens (40).
- Improved detoxification: A 2014 study published in Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, PA) and a 2005 study published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers, & Prevention have both found that sulforaphane may help to support detoxification (41, 42).
- Improved liver function: A 2015 study published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology has found that sulforaphane may help to improve liver health (43).
- Reduced symptoms of autism: A 2014 study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America has found that sulforaphane may help to reduce symptoms of autism (44).
- Improved eye health: A 2016 research published in Neurochemistry International has found that sulforaphane may help to protect your eye health and reduce photoreceptor degeneration thanks to its antioxidant benefits (45).
- Improved mood and mental health: A 2015 study published in Behavioral Brain Research has found that sulforaphane may have antidepressant and anxiolytic benefits (46). A 2021 study published in The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry has found that sulforaphane may help to reduce depression (47).
- Added antioxidant benefits: A 2016 research published in Neurochemistry International has found that sulforaphane may offer antioxidant benefits (45).
Foods Rich in Sulforaphane
Greens and cruciferous vegetables are rich in sulforaphane and other phytonutrients. For example, kale, cabbage, broccoli, mustard greens, and kohlrabi are great options. A 2018 study published in Molecular Nutrition and Food Research has found that mustard seeds may improve the bioavailability and support the absorption of sulforaphane (46).
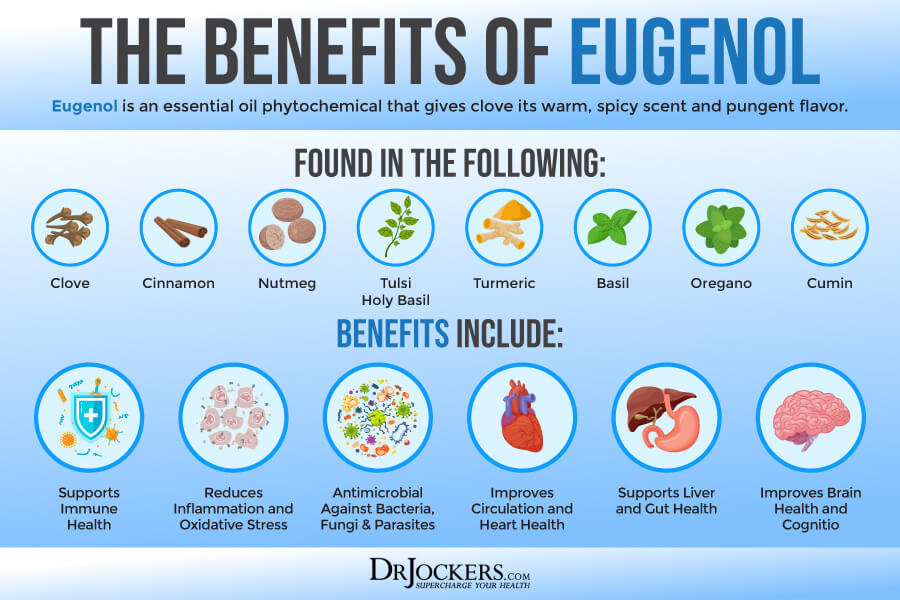
Eugenol
Eugenol is a powerful phytochemical with a long list of benefits to your health. A 2018 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that eugenol offers anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits (47). A 2018 study published in Science Reports has found that eugenol may fight parasitic infections (48).
Benefits of Eugenol
Eugenol may offer a number of health benefits, including:
- Reduced fungal infections: A 2011 study published in the Brazilian Journal of Microbiology has found that euganol may offer antifungal benefits (49).
- Decreased bacterial infections: A 2017 study published in Microbial Pathogenesis has found that eugenol may reduced bacterial infections (50).
- Reduced parasetic infections: A 2018 study published in Science Reports has found that eugenol may fight parasitic infections (48).
- Improved dental health: A 2017 study published in Microbial Pathogenesis has found that eugenol may reduce gingivitis and oral bacterial infections and biofilm (50).
- Better gut health: A 2010 study published in Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Archives in Pharmacology has found that eugenol may offer gastroprotective benefits (51).
- Reduced inflammation: A 2018 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that eugenol offers anti-inflammatory benefits (47).
- Reduced oxidative stress: A 2018 review published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity has found that eugenol offers antioxidant benefits which may reduce oxidative stress (47).
- Improved brain health: A 2016 study published in Neurochemistry International has found that eugenol may have neurorestroative effects and protect brain health (52).
- Improved heart health: A 2016 study published in Cardiovascular Toxicology has found tha eugenol may reduce inflammation and cardiovascular health issues (53).
- Reduced risk of thrombosis: A 2016 study published in Cardiovascular Toxicology has found tha eugenol may have antithrombotic effects (53).
- Better liver health: A 2014 research published in the Journal of Cancer Prevention has found that eugenol may protect liver health (54).
- Reduced risk of disease: A 2017 review published in Nutrients has found that eugenol may reduce the risk of oxidative stress, age-related diseases, and chronic diseases thanks to its antioxidant activity (55).
Food Rich in Eugenol
Many herbs and spices, including cinnamon, nutmeg, clove, tulsi/holy basil, allspice, basil, turmeric, oregano, marjoram, bay leaf, basil and cumin are rich in eugenol which has a characteristic warm, clove like flavor. Coffee, soy beans, and mung beans also offer a small amount of eugenol and phytochemical activity. Certain fruits, including raspberries, strawberries, tomatoes, and melons are a good source of eugenol as well (55, 56, 57).
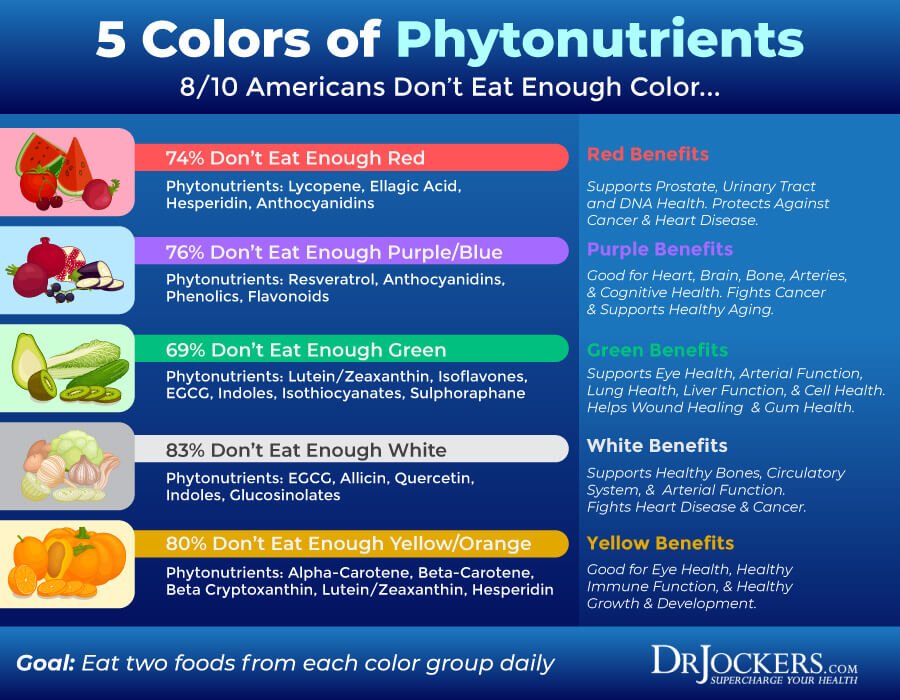
Eat the Rainbow for Unique Phytonutrients
I can’t emphasize the importance of eating the rainbow enough to meet your phytonutrient and other nutrient needs. Eating a variety of whole foods with lots of greens, vegetables, low-glycemic index fruits, herbs, spices, nuts, and seeds will help you meet your needs.
As I discussed earlier, different phytochemicals provide different colors and tastes to different foods. The color of your food can help you understand what kind of phytonutrients and benefits you may be getting.
Let’s break down the general food colors to help you navigate your produce aisle:

Red Foods
Red foods anthocyanins, tannins, eugenol, hesperidin, ellagic acid, lycopene, and quercetin. They may protect your urinary tract, prostate, heart, and DNA health.
They may reduce the risk of serious health issues. Red foods include strawberries, cherries, cranberries, tomatoes, watermelon, kidney beans, and red beans.

White Foods
White foods offer benefits from various phytochemicals, such as EGCG, indoles, tannins, allicin, and quercetin. They may help to support your arteries, circulation, heart, and bones. They may help to reduce the risk of serious health issues. White foods include mushrooms, onions, cauliflower, apples, and great northern beans.
Green Foods
Green foods may contain various phytochemicals, including EGCG, indoles, lutein, zeaxanthin, sulforaphane, glucosinolates, and isoflavones. They may support your blood cells, liver, lungs, eyes, arteries, and gums, and help wound healing. Green foods include cucumbers, avocadoes, green peppers, kale, celery, asparagus, spinach, zucchini, and kiwi.

Purple Foods
Purple foods offer benefits from various phytochemicals, such as flavonoids, phenols, tannins, anthocyanins, and resveratrol. They may protect your bones, brains, arteries, and heart. They may support healthy aging and reduce the risk of serious health issues. Purple foods include blackberries, plums, purple grapes, raisins, elderberries, eggplants, and purple cabbage.
Yellow Foods
Yellow foods offer benefits from various phytochemicals, such as beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, lutein, zeaxanthin, beta-cryptoxanthin, and hesperidin. They may support your vision, heart, and immune health. Yellow foods include carrots, apricots, grapefruits, yellow pear, cantaloupe, yellow peppers, and yellow winter squash.

Boost Your Phytonutrient Intake with Organic Greens Powder
If you aren’t consuming enough phytonutrients or want to increase your phytonutrient levels you can supplement with Organic Greens Powder. This delicious green juice mix is rich in chlorophyll, antioxidants, and trace mineral.
It includes an organic green juice blend with oat grass and alfalfa grass juice, an organic alkalizer and detoxifying blend with cracked-wall chlorella, ginger, spinach, kale, turmeric, spirulina, beet, and carrot. It also has an organic fermented botanical blend with fermented astragalus, fermented ashwagandha, fermented ginger, fermented holy basil, fermented turmeric, fermented chia seed sprout, fermented hemp seed sprout, fermented pumpkin seed sprout, fermented broccoli seed sprout, fermented milk thistle seed sprouts, fermented mung bean sprouts, fermented pea sprout, and ground flaxseed.
The Organic Greens Powder also contains a custom organic fruit, veggie and antioxidant blend with noni juice, pomegranate, wild blueberry, acai, elderberry and goji. To support gut health and digestion there is also a raw probiotic & enzyme blend with bacillus clausii, bacillus subtilis, cellulase complex, xylanase, hemicellulase, pectinase, phytase, beta-glucanase. This blend will help to maximize your nutrition, alkalize your body, detoxify your system, support your digestive system, boost your energy, and improve your mental clarity.
Final Thoughts
Following a diet rich in phytochemicals is critical for thriving in life. As you’ve learned, they may help to reduce inflammation, promote detoxification, offer antioxidant benefits, fight pathogens, and protect you from various health issues. Eating the rainbow is the best way to support your body with plenty of phytochemicals. I recommend that you add plenty of colorful greens, vegetables, low-glycemic index fruits, herbs, spices, nuts, and seeds to your diet to improve your health and well-being.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. If you want further help with your health, we offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out and our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!




