 Top 7 Foods to Burn Belly Fat
Top 7 Foods to Burn Belly Fat
Belly fat is not just about vanity. Visceral fat, or belly fat that wraps around and in between your organs inside your abdomen and causes a protruding belly, has some serious health risks. It may increase the risk of chronic inflammation, diabetes, heart disease, stroke, dementia, hormonal issues, gut health issues, and mental health problems. Reducing visceral fat and losing belly fat is critical for your overall health.
In this article, you will learn about the problem with belly fat. I will discuss the connection between belly fat and insulin resistance. You will understand the key nutritional principles of burning belly fat. Finally, I will share my top favorite foods to burn belly fat.
The Problem with Belly Fat
Carrying extra fat around your body and being overweight or obese have many health risks. But possibly one of the biggest risk factors with extra fat is if it’s fat in your abdominal area, commonly referred to as belly fat.
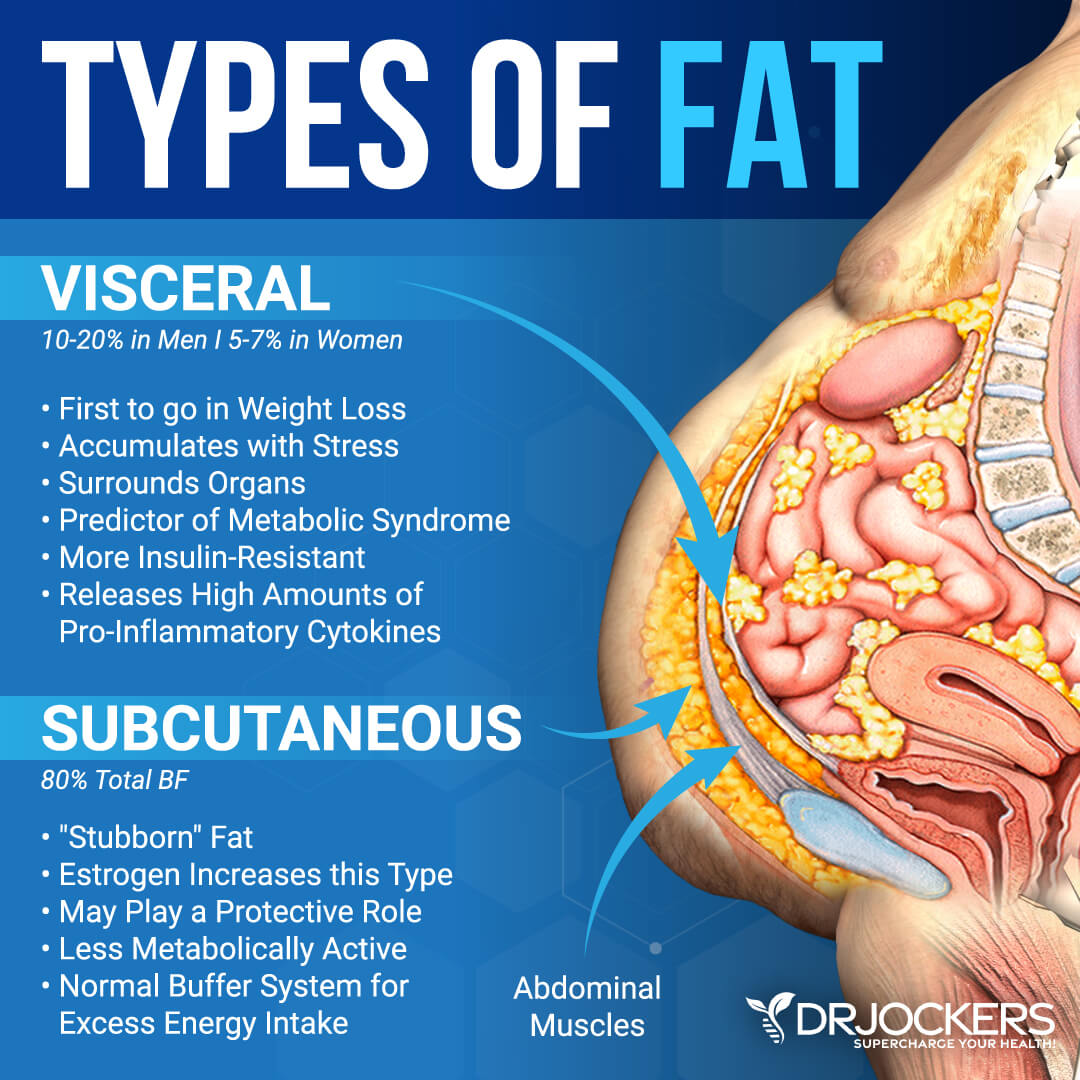
When we talk about belly fat, we have to differentiate between visceral fat and subcutaneous fat. Subcutaneous fat is the type of fat that you are able to see, touch, and pinch. Visceral fat is a type of fat that accumulates in your intra-abdominal adipose tissue. It is a gel-like fat that wraps around and in between the organs inside your abdomen, including around your pancreas, liver, and kidneys.
Having a large waist and protruding belly is usually a sign that you are having too much visceral fat. According to a 2016 study published in Nature Communications, visceral fat is a much more serious health issue than subcutaneous fat in the belly area (1).
Too much visceral fat may disrupt normal organ function. It may trigger inflammatory pathways, increase chronic inflammation, interrupt signaling between molecules, and affect normal hormonal functions. Visceral fat may increase hormone levels, cause weight gain, affect your brain function, and negatively affect your health in other ways.
Belly Fat and Chronic Disease Risk
Visceral fat can increase the risk of many health problems, including:
- Obesity
- Coronary heart disease
- Stroke
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Dementia
- Arthritis
- Sleep disorders
- Sexual dysfunction
- Depression
- Hormonal health issues
Insulin Resistance and Belly Fat
When we talk about wanting to get rid of belly fat and achieve a flat belly, we often think about vanity first. But this is not just about vanity. Even if you don’t care about how a lean belly looks like, you should think about excess belly fat because of your health.
Excess belly fat, especially visceral fat, is an indicator of poor health. It may be a risk factor for insulin resistance and other health issues. A 2018 study published in Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorder has linked visceral fat to insulin resistance in both men and women (2).
A 2014 study published in Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome has found that visceral fat may be an indicator of insulin resistance (3). Findings of a 2023 study published in Frontiers in Endocrinology have also found that visceral fat levels may correlate with insulin resistance or insulin sensitivity (4). So how does this work?

Insulin, Belly Fat and Blood Glucose Levels
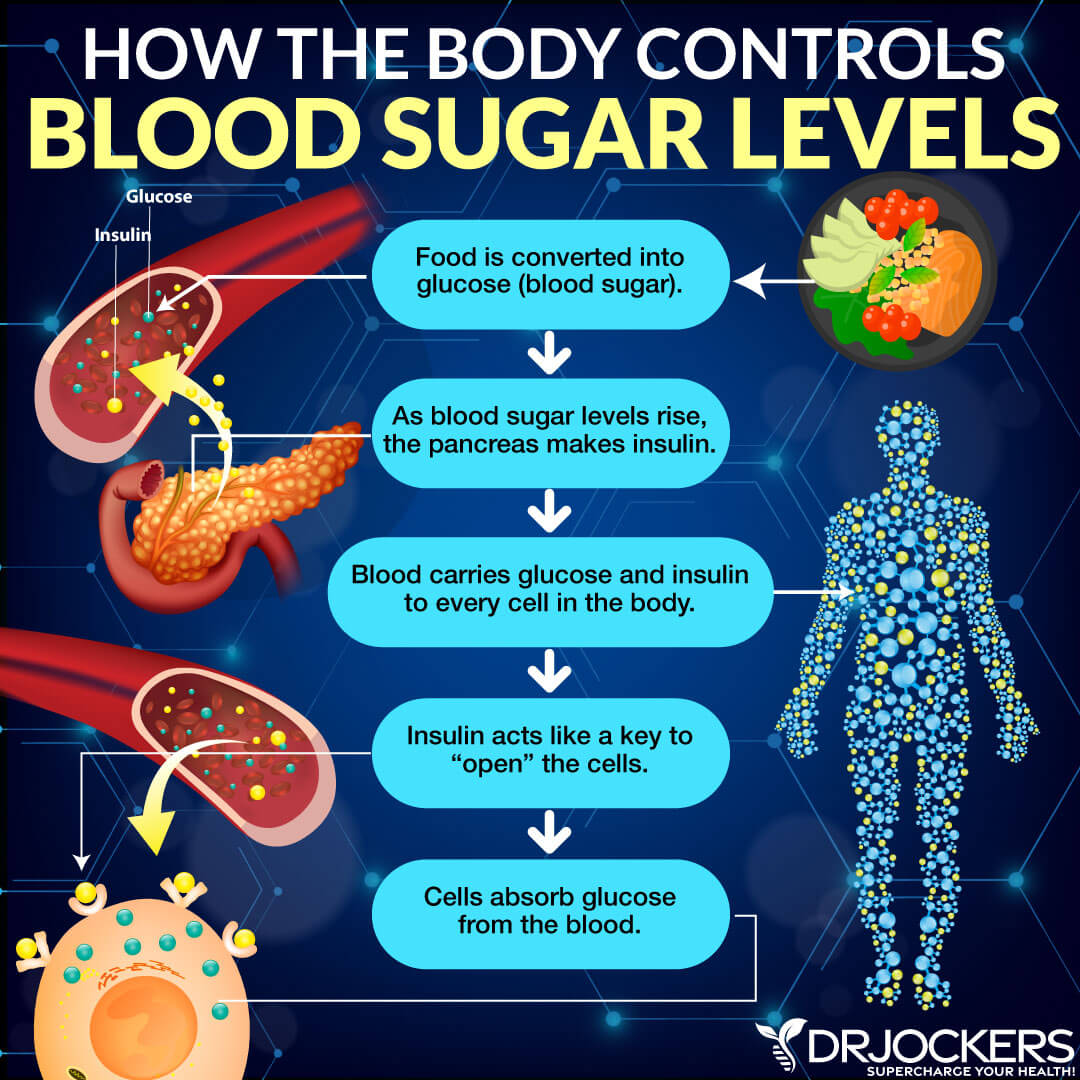
Keeping your blood glucose levels stable and encouraging insulin sensitivity is critical for your health and keeping visceral fat levels low. Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas. It helps to control your blood glucose (sugar) levels at a normal level. If you are eating something high in sugar or carbs, insulin comes to the rescue to decrease your blood sugar levels after meals and snacks.
As your body is digesting food, it will break down sugar and carby food into smaller units of glucose or fructose. Glucose and fructose will then enter your bloodstream. Your pancreas gets to work and pumps out insulin to move blood sugar into your cells. Blood sugar will then be stored in your body for energy to support brain, tissue, and muscle function.
Besides taking care of your blood glucose levels, insulin also communicates with your body’s fat store. This includes communication with your visceral fat. It’s no surprise some refer to insulin as a ‘fat-storage hormone’.
Belly Fat and Chronic Inflammation
Now, if your body has too much blood glucose, it will get stored as excess fat in your body. This tends to happen if you have a poor, inflammatory, high-carbohydrate, sugar-filled diet, for example, from eating lots of white bread, white pasta, white rice, cookies, cakes, candy, milk chocolate candy bars, and sugary soft drinks.
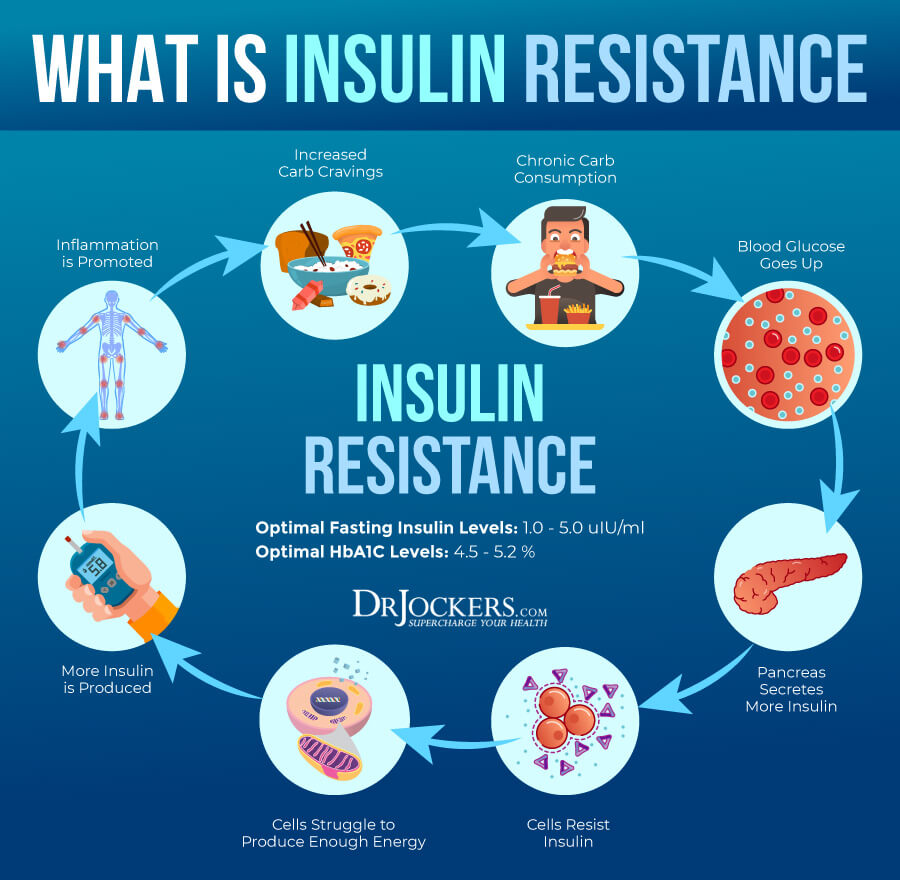
This high-sugar, low-nutrient foods and drinks get converted into simple sugars and enter your bloodstream quickly. As a result, your body will release lots of insulin. Unfortunately, this will only lead to a cycle of hunger, sugar cravings, and overeating, as well as weight gain and excess visceral fat.
If this cycle continues for a while, your body will have a hard time pumping out insulin at all times. Your pancreas will be overworking yet won’t be able to pump out enough insulin to keep up with the excess sugar. This will lead to insulin resistance, which means that your body cannot handle the glucose entering your body properly. It will also increase visceral fat gain and cause an ongoing battle with weight gain, belly fat, and related health issues.
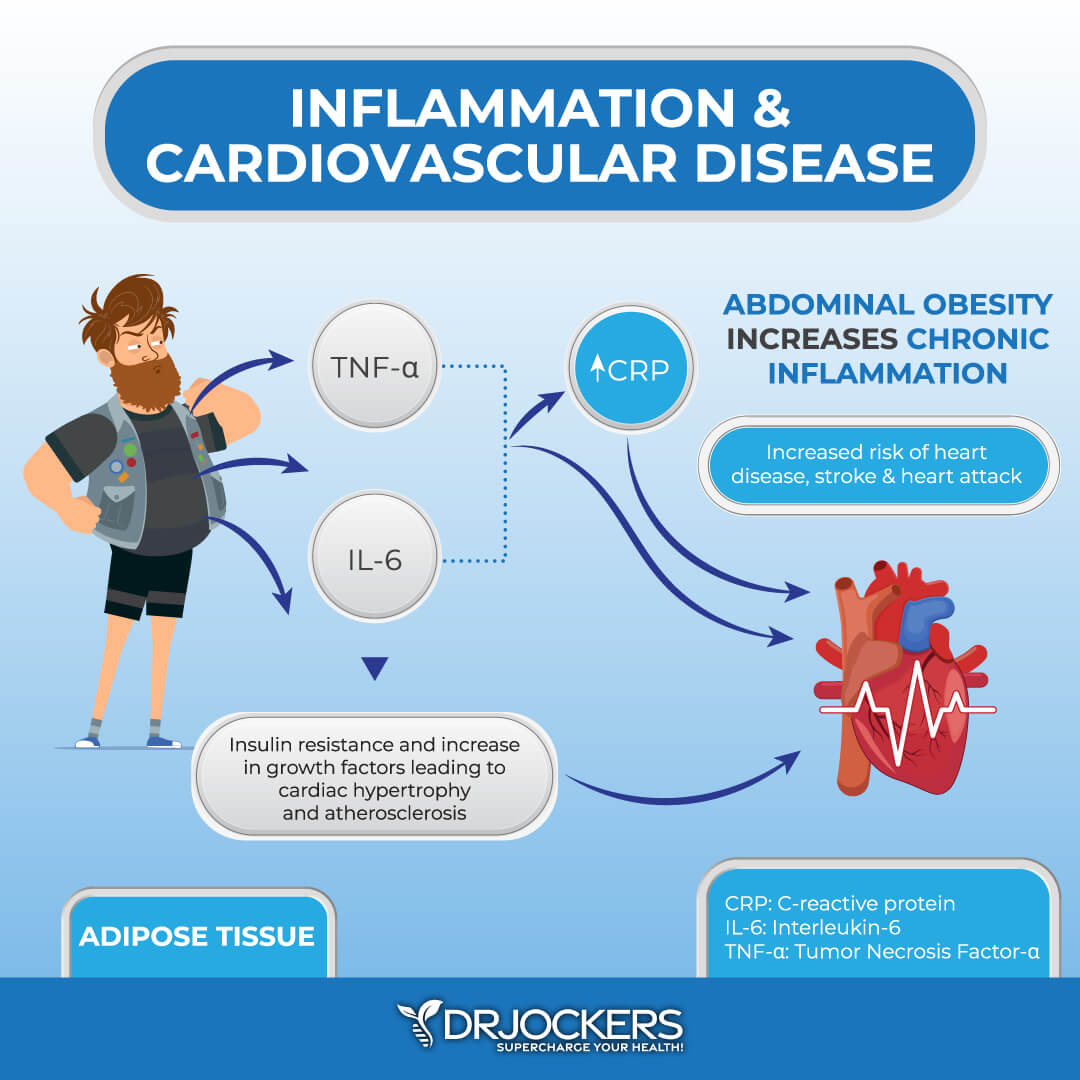
On top of all this, researchers have found that visceral may increase insulin resistance. Visceral fat actually releases retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4), which is a protein that may increase resistance to insulin (5). So visceral fat gain may increase insulin resistance, and insulin resistance may increase visceral fat gain — unless you do something about it, this can turn into a serious health issue.
Since insulin is in contact with other hormones, insulin resistance may increase the risk of other hormonal imbalances, such as high cortisol levels, adrenal issues, and low energy. Insulin resistance and visceral fat may contribute to poor energy, cravings, mood imbalances, sleep issues, chronic inflammation, chronic symptoms, and the increased risk of chronic disease.
Key Nutritional Principles to Burn Belly Fat
So how do you fight belly fat? You won’t be surprised to hear me say this: diet is key! There are some key nutritional principles that may help you to burn belly fat and improve your health naturally. Here is what I recommend:
Blood Sugar Stability
Since blood sugar imbalance and insulin resistance are major risk factors when it comes to belly fat and visceral fat, achieving blood sugar stability should be your main goal when it comes to diet. First and foremost, you want to keep your carb intake low.
Absolutely avoid refined sugar and carbs in overly processed and junk foods. This means avoiding bread, sugary baked goods, candy, cakes, and sugar drinks.
Any carbs you eat should come from natural, fiber-rich, whole foods, such as vegetables and fruits. Fiber helps digestion and absorption, and soluble fiber in these foods may help to improve blood sugar control. According to a 2018 study published in the Journal of Chiropractic Medicine, fiber may help to improve blood sugar stability and reduce the risk of diabetes (6).
Still, don’t overeat from these high-carb whole foods either, but keep your overall carbohydrate intake low. When it comes to fruits, focus on low-glycemic index fruits, such as berries. Higher-carb, starchy vegetables, such as beets, carrots, or sweet potatoes, should be an addition, not the main part of your meal.
Focus on protein and healthy fats. They should take up the majority of your diet and should be part of every meal. According to a 2003 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, a higher intake of dietary protein may improve blood glucose response in type 2 diabetes (7). According to a 2000 review published in Atherosclerosis, following a diet higher in unsaturated fats may improve glucose metabolism compared to a high-carb diet (8).
Clean protein sources include grass-fed beef, organ meats, pasture-raised poultry and eggs, wild-caught fish and seafood, and wild game. Healthy fats include avocados, olives, extra virgin olive oil, coconut oil, coconut meat, coconut milk, MCT oil, grass-fed butter, ghee, and lard, and fat from wild-caught fatty fish.
 Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is a dietary strategy using a period of fasting every day, reserving specific times for meals. It is not about caloric or nutrient restrictions. If you are intermittent fasting, the idea is to meet your nutrient needs during the reserved eating window.
Intermittent fasting has many health benefits, including better insulin sensitivity, increased autophagy, and reduced risk of disease. You may learn about the top benefits of intermittent fasting here. Losing belly fat is one of the potential perks.
A 2023 study published in Obesity (Silver Spring) has found that intermittent fasting may be beneficial for visceral fat loss (9). The study compared intermittent fasting combined with protein pacing to regular caloric restriction.
Protein pacing refers to spacing out the amount of protein you are eating throughout the day, instead of eating protein only at breakfast, lunch, and dinner. People using protein pacing generally recommend eating 0.12 to 0.2 grams of protein per pound of body weight every four hours or so. They found that intermittent fasting combined with protein pacing may have superior benefits for weight and visceral fat loss and cardiometabolic health.

If you are new to intermittent fasting, start easy. Stop eating after dinner and avoid eating for the next 12 hours until breakfast. Gradually extend your fasting window until you find what works for you.
Most people feel their best with a 16-hour fasting and 8-hour eating window. During your eating window, focus on anti-inflammatory, nutrient-dense foods, and a diet high in healthy fats, moderate in clean protein, and low in carbs.
You may try to combine it with protein pacing by eating a bit of protein by evenly spacing out your meat and consuming protein evenly and regularly throughout your eating window.
Minimize Toxins
Reducing toxin exposure is critical for all areas of life — including your diet. Conventional produce is treated with pesticides and herbicides and may be exposed to other environmental toxins. Conventional meat and animal products are usually treated with antibiotics and hormones and fed on pesticide- and herbicide-treated low-nutrient feed. Moreover, packaged and processed foods are generally filled with additives, unnatural ingredients, and harmful materials. Plastic packaging may also contribute to toxin exposure.
According to a 2023 study published in Environmental Pollution, pesticide exposure may increase insulin resistance (10). According to a 2021 study published in Endocrine Connections, toxins and endocrine disruptors may increase the risk of obesity (11).
Pesticides, herbicides, antibiotics, hormones, and other toxins in food may increase insulin resistance, inflammation, and visceral fat formation. Instead of conventional toxin-filled options, choose organic produce, grass-fed meat, and pasture-raised poultry and eggs to avoid pesticide, herbicide, antibiotic, hormone, and GMO exposure. Avoid overly processed food and minimize the use of plastic packaging.

Maximize Nutrients
Maximizing the nutrient content in your meals is critical because nutrient deficiencies can lead to visceral fat formation and insulin resistance. According to a 2022 study published in Nutrients, vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of visceral obesity (12). According to a 2016 study published in Acta Endocrinology (Bucharest), vitamin D, vitamin B12, and folate levels may play a role in insulin resistance (13).
According to 2009 research published in Metabolism and a 2015 review published in Medical Principles and Practice, antioxidants are also important for reducing insulin resistance and obesity (14, 15). I recommend following an anti-inflammatory, nutrient-dense, antioxidant-rich whole foods diet with lots of greens, vegetables, herbs, spices, low glycemic index fruits, nuts, seeds, grass-fed meat, pasture-raised poultry and eggs, wild-caught fish, and wild game.

Top Foods to Burn Belly Fat
Now that you understand my general dietary recommendations for burning belly fat, I want to go over some specific foods that help to burn belly fat naturally. Here is what I recommend (you may also learn about these by watching this video):
Grass-Fed Red Meat
The number one food I recommend is grass-fed red meat. Why grass-fed? Conventionally raised cows are raised on corn and grain. This is not only unnatural for the cows but may also be treated with pesticides and herbicides. These cows are generally also treated with antibiotics and hormones.
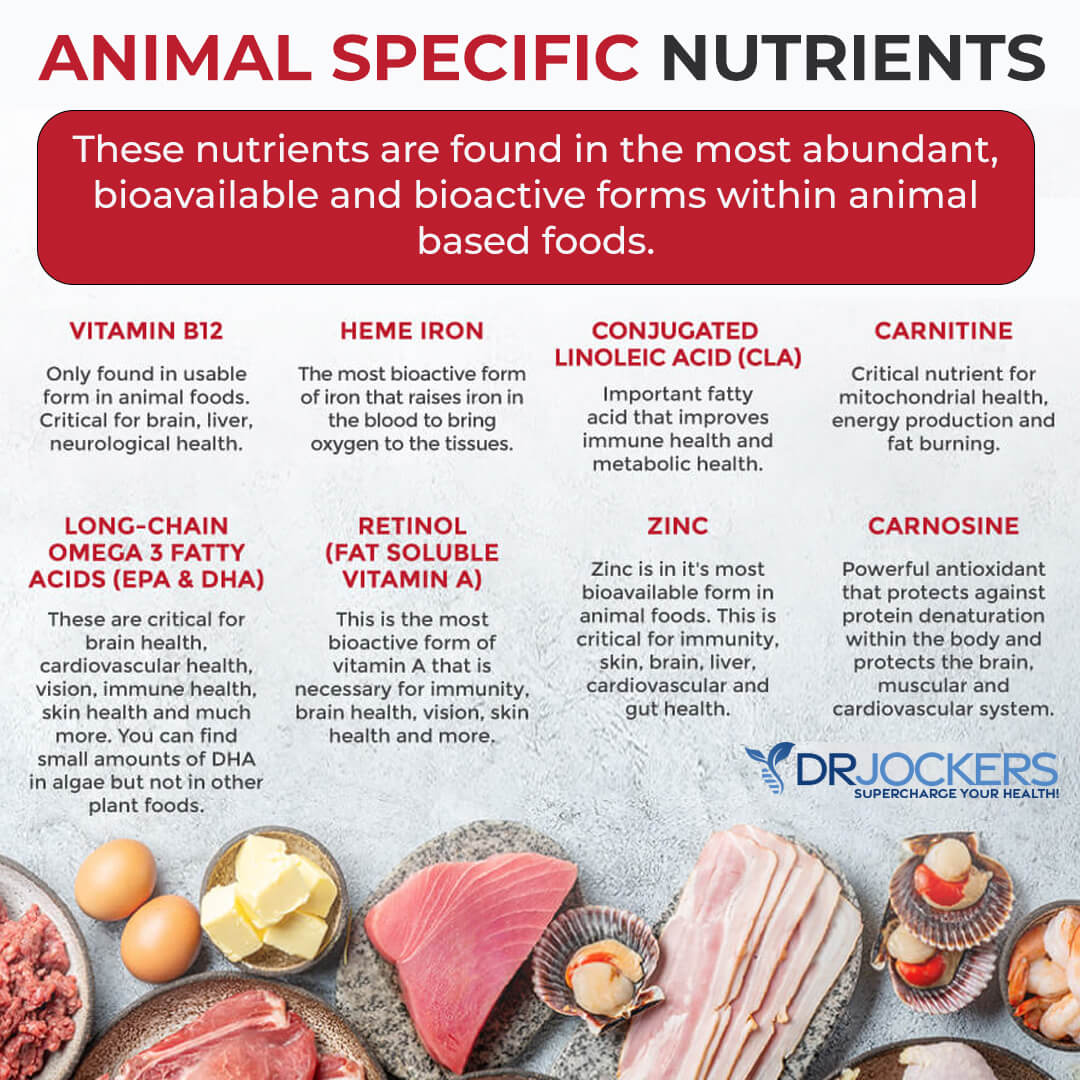
When cows eat grass, they get their natural food, and they provide healthy meat. They accumulate omega-3 fatty acids, which support low inflammation levels and cellular health. Grass-fed red meat is also high in CLA, carnitine, and carnosine.
CLA or conjugated linoleic acid, is great for turning up your metabolic rate, reducing inflammation, improving immune health, and burning visceral fat. According to a 2019 review published in Nutrients, CLA may support fat burning and fat loss, reduce obesity, and decrease the risk of atherosclerosis and cancer (16).
Carnitine and carnosine help metabolic function and fat burning. According to a 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis published in Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, l-carnitine may support fat loss, weight loss, and healthy body composition (17). According to a 2021 study published in Biology (Basel), carnitine and carnosine may support a lean body composition (18).
And, of course, protein from red meat is an important macronutrient that helps to reduce hunger and cravings and supports fat-burning and muscle-building. Great sources of grass-fed red meat include beef and wild game, such as deer or antelope.
Pasture-Raised Eggs
Chickens and poultry that provide pasture-raised eggs are not kept in confined spaces but are raised more naturally and fed on high-nutrient food natural to them instead of toxin-filled, genetically modified grain feed given to conventionally raised poultry. As a result, their eggs are full of choline, CLA, retinol, K2, and phospholipids. These are great nutrients that help to reduce inflammation and improve fat burning.
According to a 2014 study published in the Journal of Human Kinetics, choline may be effective for weight loss in athletes (19). However, choline is not only critical for burning fat but also for liver health and brain health.
According to a 2011 study published in Diabetes Care, vitamin K2 may help to improve insulin resistance. (20) Vitamin K2 is essential for vitamin D and calcium metabolism and bone health. It is also essential for cardiovascular health and reducing atherosclerosis.
Vitamin A in pasture-raised eggs is also important for metabolic function, immune health, and skin health. A 2022 study published in Nutrients has found that vitamin A may help to reduce metabolic risk factors, including obesity (21). Of course, pasture-raised eggs are also a great source of protein that may help to improve fullness, reduce cravings, and support weight loss.

Extra Virgin Olive Oil
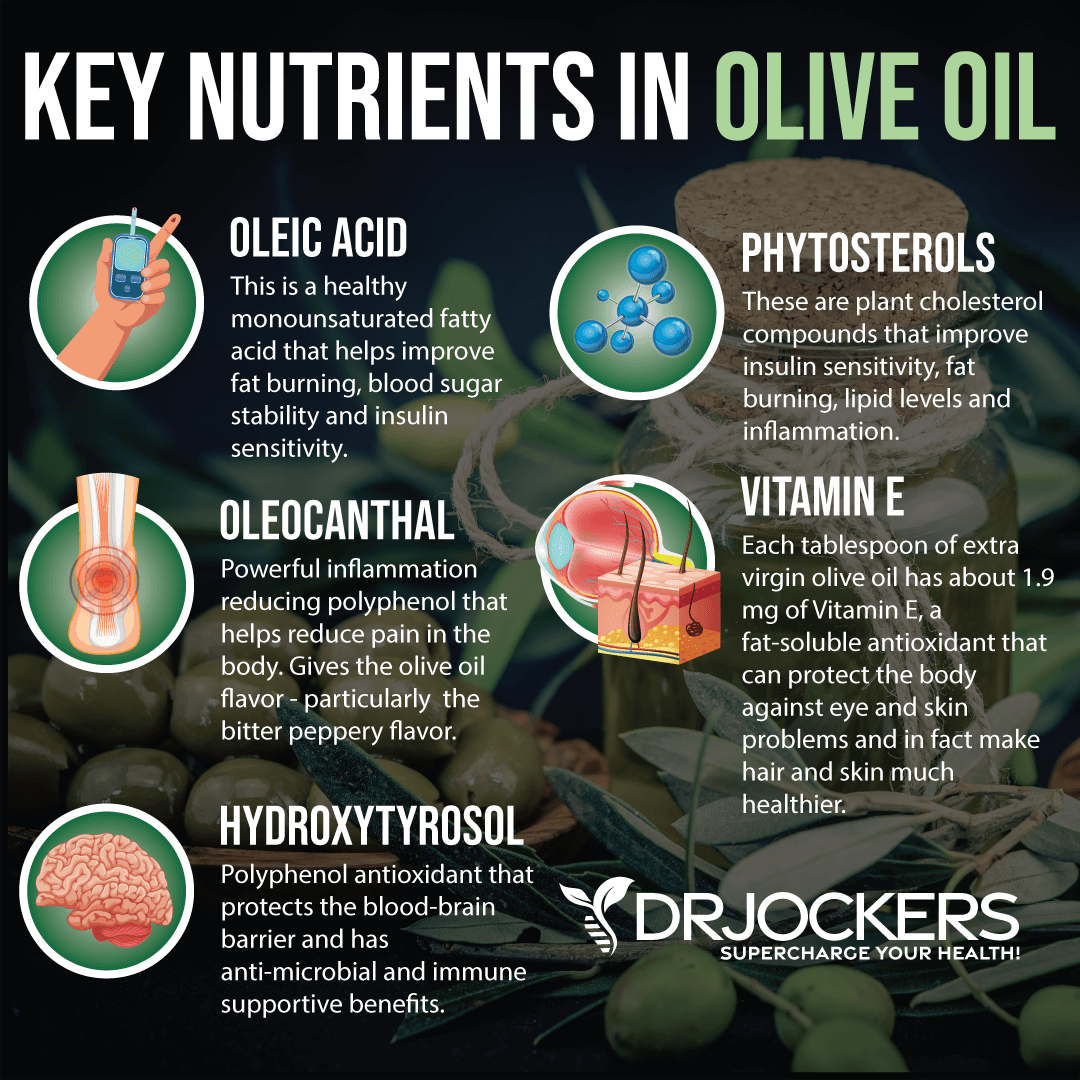
Extra virgin olive oil is a fantastic source of healthy fat. You can add it to your meat dishes and buffer any oxidative stress that may occur while cooking meat. You may also add olive oil to your salads and vegetable dishes. Extra virgin olive oil is a rich source of oleic acid, oleocanthal, and vitamin E, which help to reduce inflammation and improve fat burning.
According to a 2020 study published in Metabolites, extra virgin olive oil may help to reduce inflammation, waist circumference, and body weight (22). Moreover, according to a 2020 review published in Advanced Nutrition, oleic acid in olive oil may help to reduce obesity and support healthy body weight (23).
According to a 2009 review published in Progress in Lipid Research, olive oil may help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes (24). However, not all olive oil is made equal.
Many olive oils on the market are of lower quality with fewer health benefits. Some of the olive oil bottles you see are falsely advertised and are not even olive oil.
My Favorite Olive Oil
My favorite olive oil is this Fresh-Pressed Olive Oil. It is the most flavorful artisan olive oil you can find out there. It comes from award-winning artisan farms with a harvest-fresh taste to your table. These oils are independently lab-certified to be 100 percent extra virgin olive oil — so you can trust the quality. My family swears by it. We use it daily on our salads and meals. Our kids love it. I am sure your family will too.
I am excited to share a special offer with you. You can get this $39.00 bottle of Fresh-Pressed Olive Oil for only $1.00 to help with shipping if you click on the link here
Apple Cider Vinegar
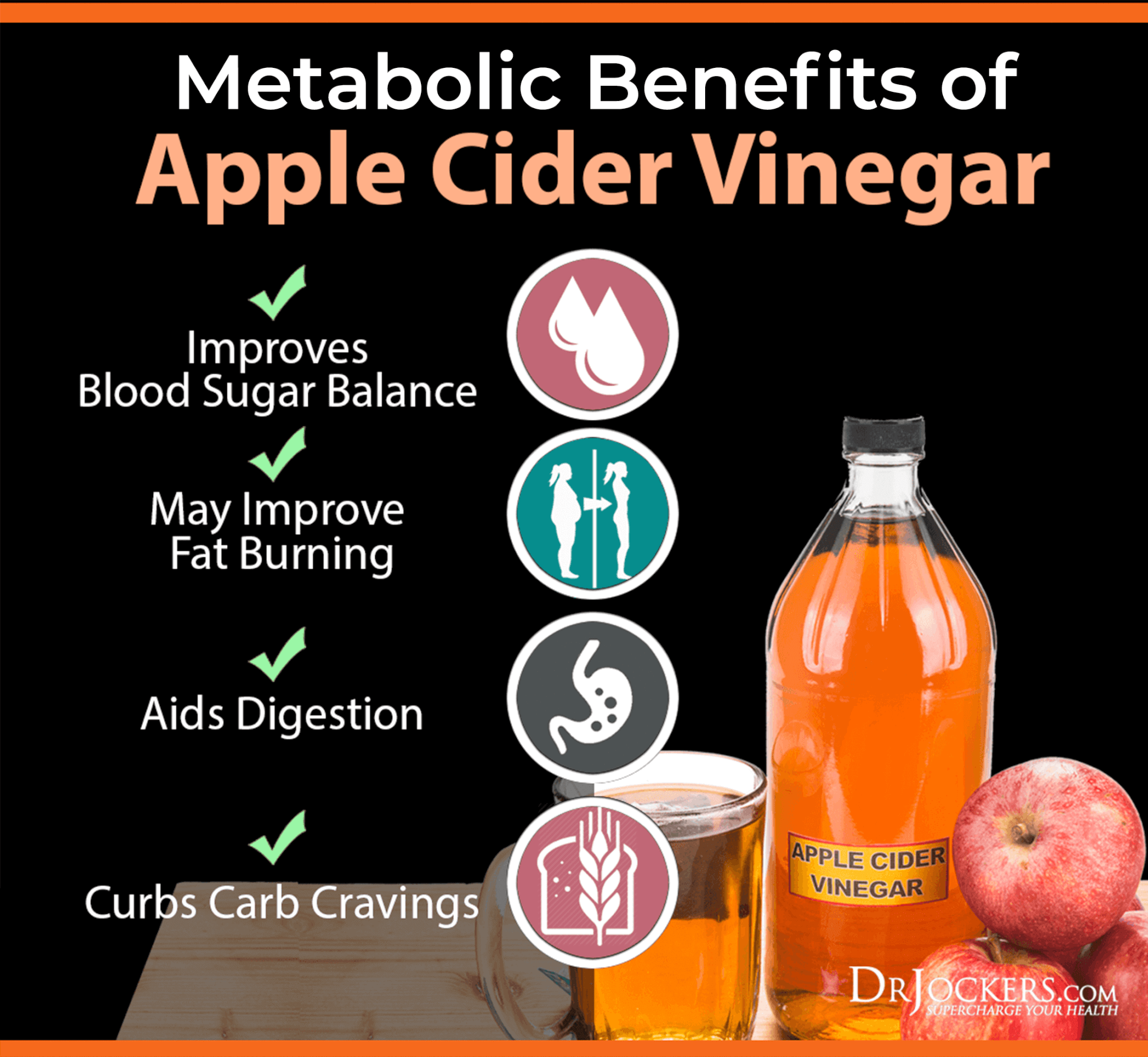
Apple cider vinegar is rich in acetic acid, which is a postbiotic formed from bacterial fermentation. As a rich source of postbiotics and enzymes, it may help to reduce the glycemic impact of meals. This is important since insulin resistance is one of the root causes of visceral fat.
It also helps to nourish the enterocytes and create a healthier gut lining and microbiome. This may also help to activate the vagus nerve for parasympathetic tone and improve the production of digestive juices, including stomach acid, bile, and pancreatic enzymes for better digestion.
Apple cider vinegar has actually been shown to help balance this blood sugar response when strategically utilized around mealtime. According to a 1998 study published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, apple cider vinegar was able to reduce the glycemic index of carbohydrate-rich meal (white bread) from 100 to 64 (25).
According to a 2015 study published in Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, apple cider vinegar may actually have a modest boosting effect on fat oxidation in the body and support fat burning (26).
Ginger and Bitter Herbs
Ginger and bitter herbs, such as arugula, artichokes, parsley, cilantro, dandelion, radishes, and any herbs with a pungent, bitter taste. Bitter herbs may be great for liver health, which is great for your gut health and for reducing inflammation. This may help to reduce visceral fat formation. Ginger and bitter herbs are also great for vagal activation, which can also reduce inflammation and related issues.
A 2018 systematic review published in Phytotherapy Research has found that ginger may have anti-obesity, fat burning, and weight lowering effects (27). According to a 2021 review published in Nutrients, bitter herbs may help improve glycemic control and reduce the risk of obesity (28). You can use these herbs in salads, meals, and teas, depending on the actual herb.

Wild-Caught Salmon
Wild-caught salmon is one of my favorite sources of healthy fats and protein. They are rich in Omega 3’s, which helps to reduce inflammation, improve insulin sensitivity, and fat burning. They are rich in an antioxidant called astaxanthin, which gives them a pinkish color.
Conventionally raised salmon doesn’t have this quality and color, not naturally, at least. According to a 2020 study published in Molecules, astaxanthin may help to reduce fat accumulation and reduce the risk of obesity (29). According to a 2010 study published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, salmon may be the most beneficial for reducing inflammation and supporting weight loss compared to other seafood studies (30).

Avocados
Last but not least, I love avocados. They are a great source of healthy fats, lutein, and zeaxanthin that help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity and fat burning. They are also rich in prebiotics that support metabolic health and support fat burning.
According to a 2021 study published in The Journal of Nutrition, avocados may help to improve glucose tolerance and reduce abdominal fat in people who are obese or overweight (31). According to a 2019 study published in Nutrients, avocados may reduce the risk of weight gain (32). Avocados are a great addition to salads, vegetable dishes, and wraps, and make excellent guacamole and dips.

Bonus: MCT Oil
And finally, my bonus tip is using medium chain triglycerides (MCT) in the form of MCT oil. Pasture-raised eggs and grass-fed butter are rich in short-chain fatty acids, which are great for metabolic health.
But medium-chain triglycerides are even better for metabolic health. Unlike long-chain fatty acids, medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are quickly converted into ketones and are less likely to be reserved as body fat. The result is improved mental performance and energy! You can get this by consuming grass-fed dairy, such as grass-fed yogurt, as well as coconut oil and coconut oil products.
In MCT oil, you are particularly getting C8 or eight-carbon length medium chain triglyceride and a 10-carbon chain medium triglyceride called capric or caprylic acid. These are the ones that have been studied the most for mitochondrial health. They may help to keep inflammation levels low, insulin sensitivity high, and fat-burning ideals. They may help to reduce cravings and sugar consumption. They are not only great for metabolism and burning belly fat, but also for brain health and overall health.
According to a 2007 study published in Metabolism, MCT oil may help to improve insulin resistance and weight loss in moderately overweight people with type 2 diabetes (33). According to a 2020 study published in Frontiers in Nutrition, caprylic acid and coconut oil may help to achieve ketosis (34).
I recommend using Keto Brain. KetoBrain C8 MCT Oil is extracted from natural sources using a three-stage steam-based filtering process without the addition of any chemicals. The result is a pure and ketogenic C8 (caprylic acid triglyceride) formulation. MCT oil is very versatile and also heat stable up to 320 o F. Use it as a salad dressing or a thickening agent for coffee and teas. Add it to smoothies to help curb hunger and keep you satisfied longer. Try it in one of my favorite coffee and dessert recipes!
Final Thoughts
Belly fat is not just about vanity. Visceral fat, a belly fat that wraps around and in between your organs inside your abdomen and causes a protruding belly, has some serious health risks. It may increase the risk of chronic inflammation, diabetes, heart disease, stroke, dementia, hormonal issues, gut health issues, and mental health problems.
I recommend that you follow the nutritional principles and try the top fat-burning foods to reduce belly fat and improve your health. If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. On our website, we offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!






Thank you! I think I have been eating the way I should according to what you said in your article.
When protein pacing combined with 18:6 fasting I would have lunch with protein around 1:00, 20 ounces protein around 4;00 and dinner at 7:00 with protein. Is that correct?
I weigh 156 and need to lose 16 pounds. What would be a good total amount of protein for day?
Thank you. Can Visceral fat be too low? Evolt 360 body scan says 1.7%. Subcutaneous 17.6.
I am 5 8 126 lbs 68 yr female. I used to be “buff” until mycotoxin poisoning (down to 114) and have struggled to regain muscle and weight. Other parameters are optimal: muscle, water etc. Friends say I look good even though I am not as strong as before. (135 and 11.2% body fat by calipers). I eat Br and lunch 100 g protein and more Optimal aminos for another 30 -60gs. Weight train 6x/wk. Eat as you suggest. What more should I do?
While I had consumed all the 7 foods you mentioned, it wasn’t until I cut out the avocado, salmon, olive oil, completely and beef to only once a week that I finally started losing weight. I stick to chicken and white fish like flounder & haddock, only having salmon once a week (found out salmon does a number on your pancreas!) also, I’ve switched to macadamia oil as it is healthier than olive oil.
For some reason I can’t seem to get the right images in the Capcha because the images are so fussy even with my glasses and me magnifier.