 Bad Circulation: Symptoms, Root Causes, and Support Strategies
Bad Circulation: Symptoms, Root Causes, and Support Strategies
Your circulatory system is a system in your body that includes your heart and blood vessels. Good circulation is critical for heart health, immune health, brain function, wound healing, and other important functions. It supports your organs, tissues, and health, and helps your body to stay alive and thrive. Bad circulation may increase your risk of some serious health issues, including serious cardiovascular problems. Supporting good circulation is critical for your health and well-being.
In this article, you will learn about the importance of good circulation. I will go over the signs and symptoms of bad circulation. You will learn about the root causes of bad circulation. Finally, I will share my top support strategies to improve circulation.
Importance of Good Circulation
Let’s start with your circulatory system. What is it? Your circulatory system is a system in your body that includes your heart and blood vessels. You may also refer to this system as your cardiovascular system, cardio refers to the heart, and vascular refers to your blood vessels.
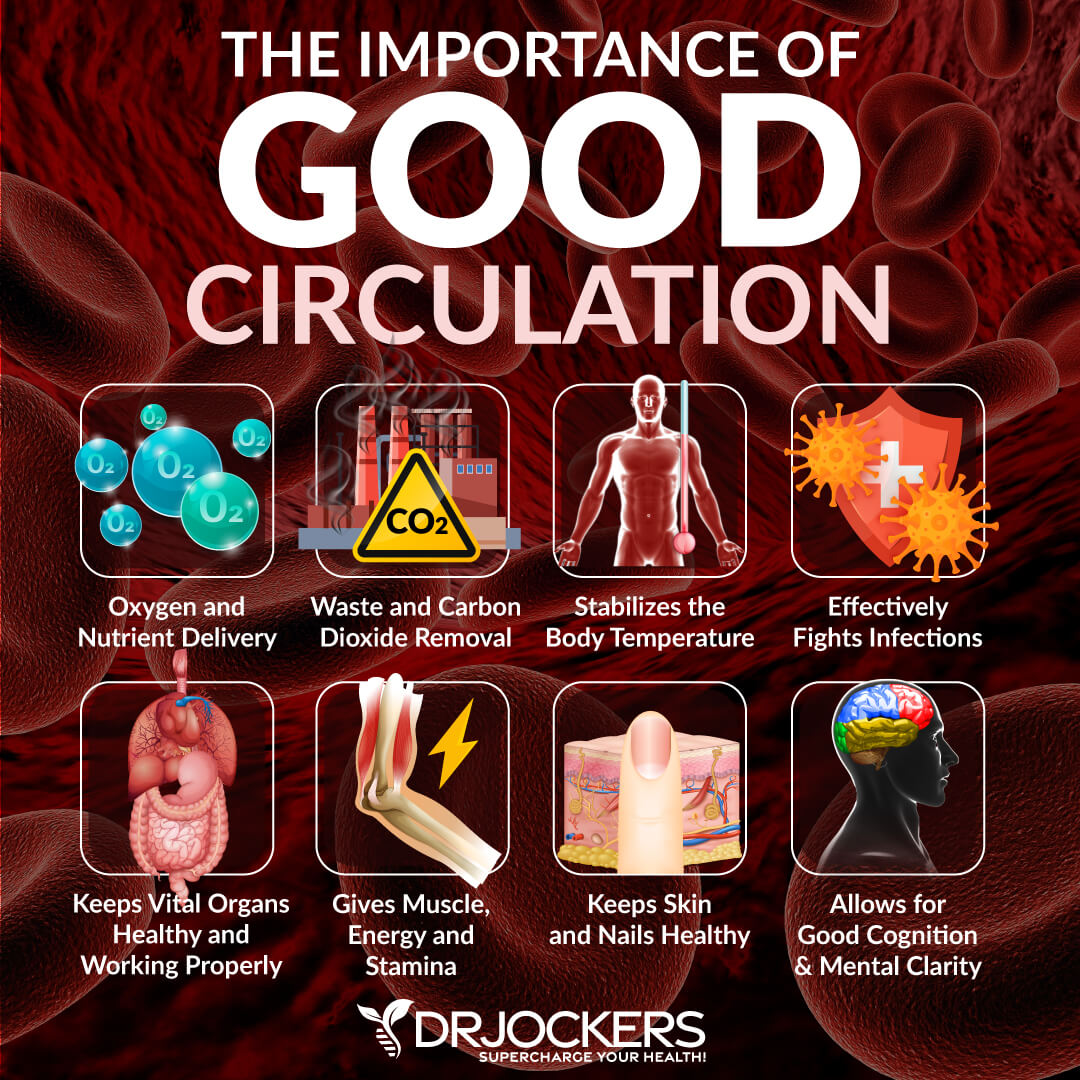
Your heart pumps blood through your blood vessels, including your veins and arteries, to ensure that blood, oxygen, and nutrients flow through your body and reach all your organs properly. Your circulatory system provides oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to your organs, tissues, and muscles.
It also helps to remove any waste and toxins from your cells, tissues, and organs. It keeps your heart healthy, supports your brain function, allows your immune system to fight infections, and aids faster wound healing.
Essentially, normal blood circulation keeps you alive and thriving and allows your organs, tissues, and muscles to stay healthy. Bad circulation obviously does the opposite.
Poor circulation may lead to a list of symptoms, including fatigue, cold fingers and toes, muscle pain, numbness, dizziness, and other symptoms that I will discuss in the next section. It may increase the risk of poor wound healing, heart issues, brain health issues, poor immune health, and other health issues.
Signs & Symptoms of Bad Circulation
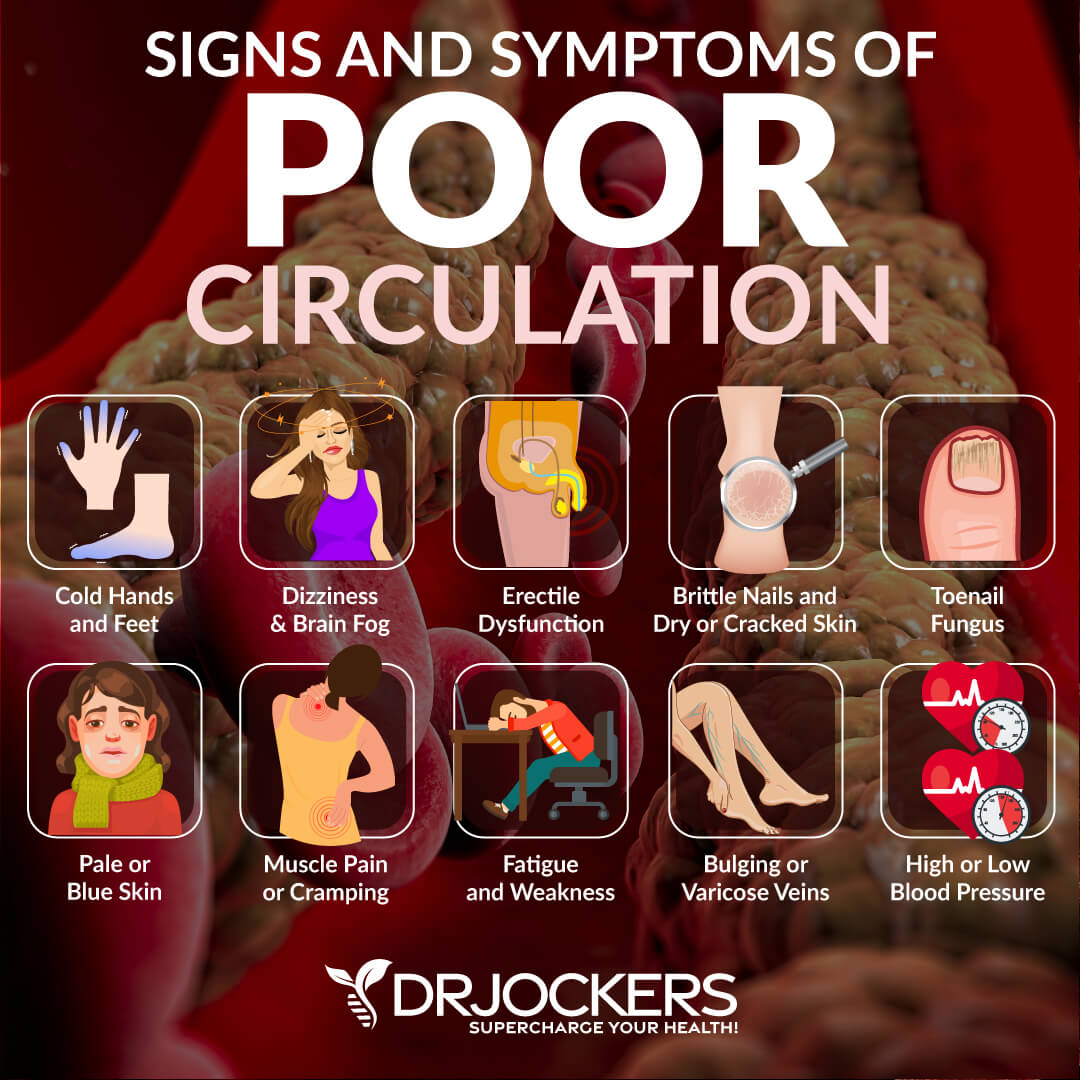
Signs and symptoms of bad circulation may include:
- Hurting or weak muscles when you walk.
- Cold fingers and toes may go numb.
- Pale or blue skin color
- Pins and needles feeling on your skin.
- Dizziness when standing up.
- Numbness
- High or Low Blood Pressure
- Bulging veins
- Swelling
- Chest pain
- Dry or cracked skin
- Erectile dysfunction
- Brittle nails
- Slow-healing wounds
- Fatigue
- Brain Fog and Trouble Thinking
- Poor immune health
Root Causes of Bad Circulation
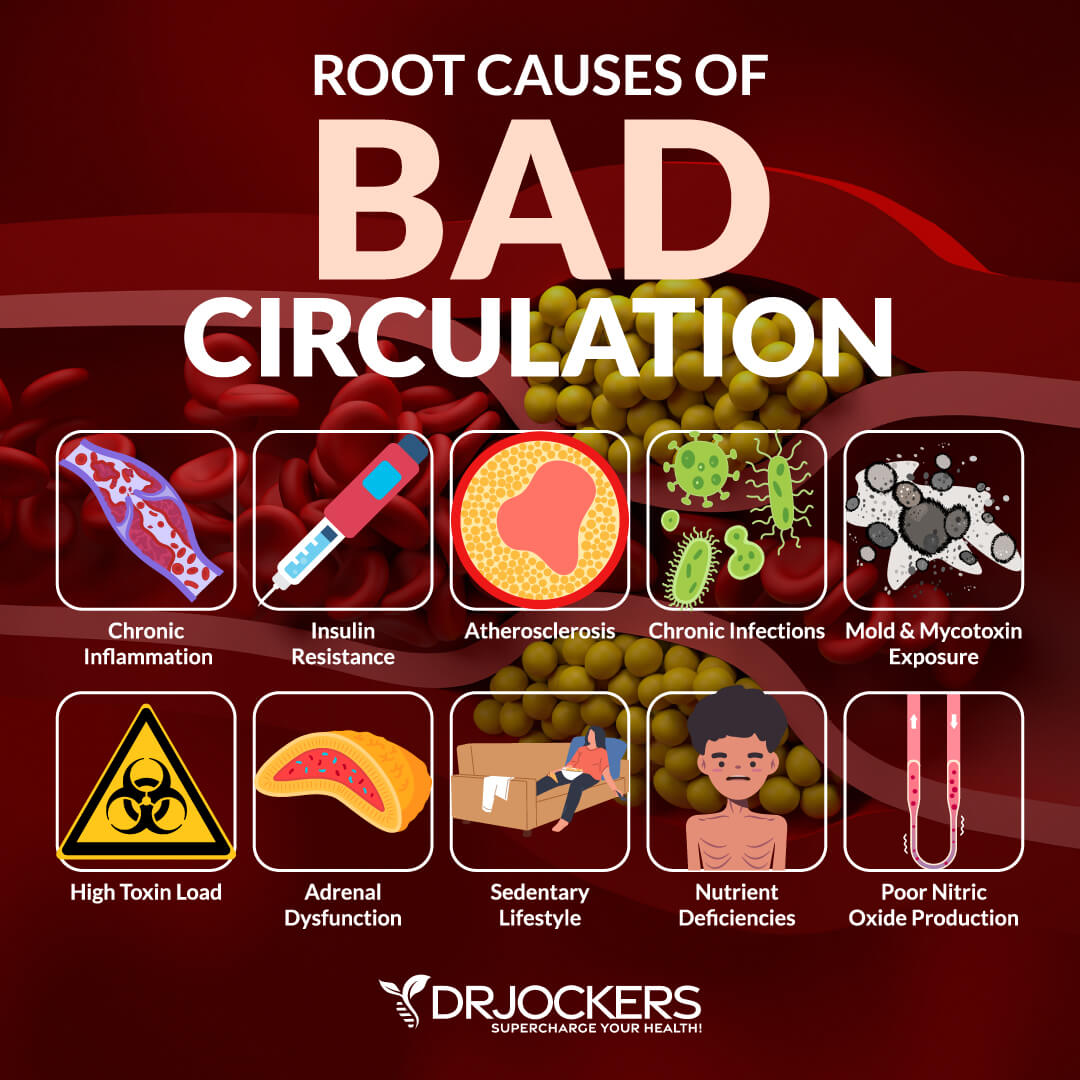
Let’s talk about the root causes of bad circulation.
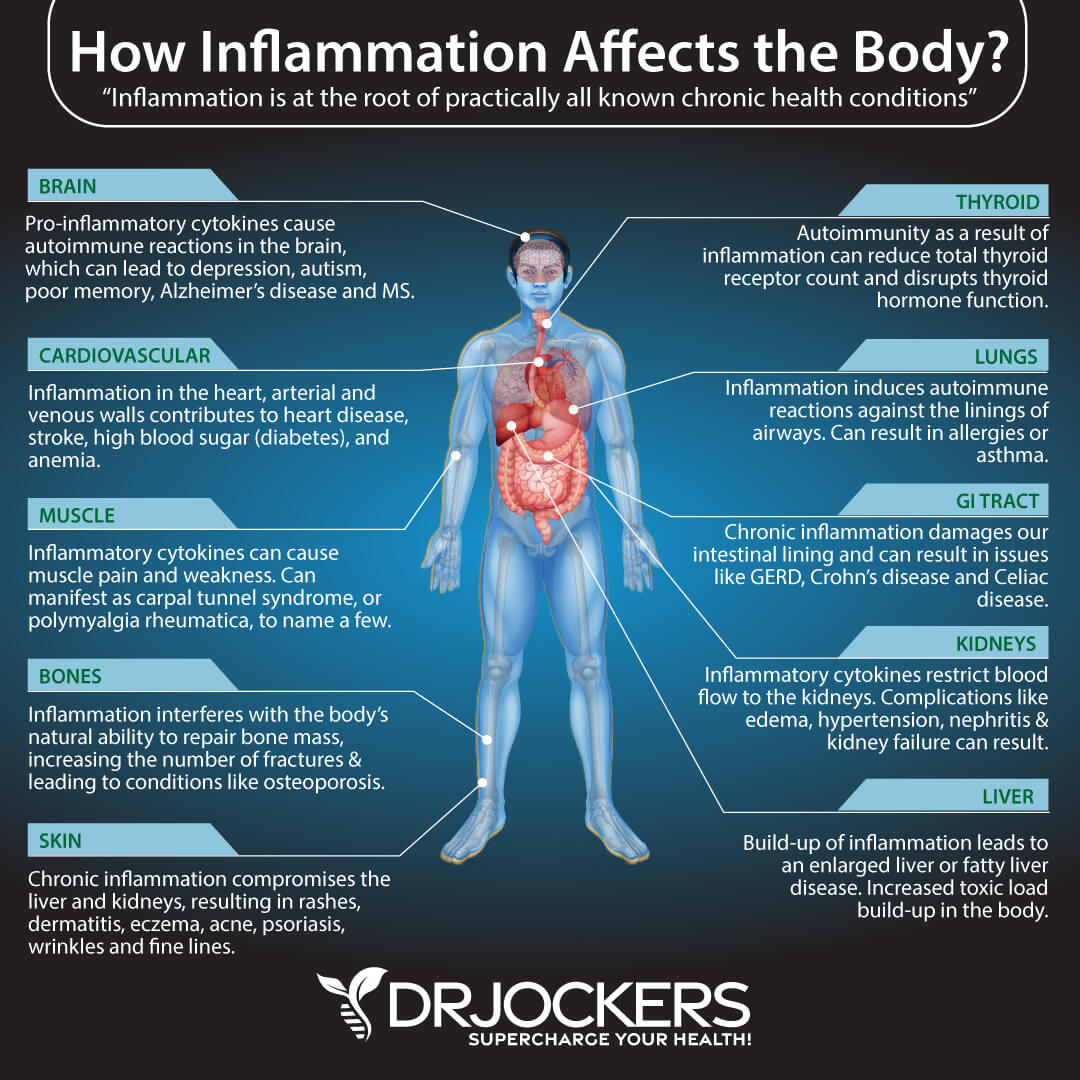
Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is part of your normal immune response to injury, infection, or illness. Acute inflammation helps your body recover from these issues. However, inflammation is unhealthy when it becomes chronic. You may develop chronic inflammation from an unhealthy diet, unhealthy lifestyle, environmental stressors, and chronic stress.
Chronic inflammation may increase your risk of various health issues, including bad circulation and cardiovascular issues, including atherosclerosis, stroke, and heart attack. According to 2020 research published in the Journal of Hypertension, there may be a connection between chronic inflammation and circulatory and vascular issues (1).
Researchers found that inflammation may increase the risk of vascular dysfunction, including atherosclerosis and arterial stiffening. Findings suggest that people with inflammatory conditions may have an increased risk of cardiovascular issues.
Insulin Resistance
You may develop insulin resistance when your body is unable to respond and use insulin at the rate it is being produced. Your pancreas ends up working overtime and making more insulin than a healthy body normally needs to help glucose enter your cells.
Insulin not only affects your muscles, liver, and fat, but it may also impact your vascular cells. Thus, it may not be surprising that insulin resistance may increase your risk of bad circulation, blood vessel issues, and circulatory problems. A 2010 study published in Cell Metabolism has found that insulin resistance may affect your arteries (2).
If you have insulin resistance, your blood vessels may not be able to open up well, which may increase your risk of clogged arteries and circulatory issues. A 2018 study published in Cardiovascular Diabetology found that insulin resistance may result in several metabolic alterations that may increase the likelihood of the development of cardiovascular disease (3). Researchers found that addressing insulin resistance may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and atherosclerotic plaque formation.

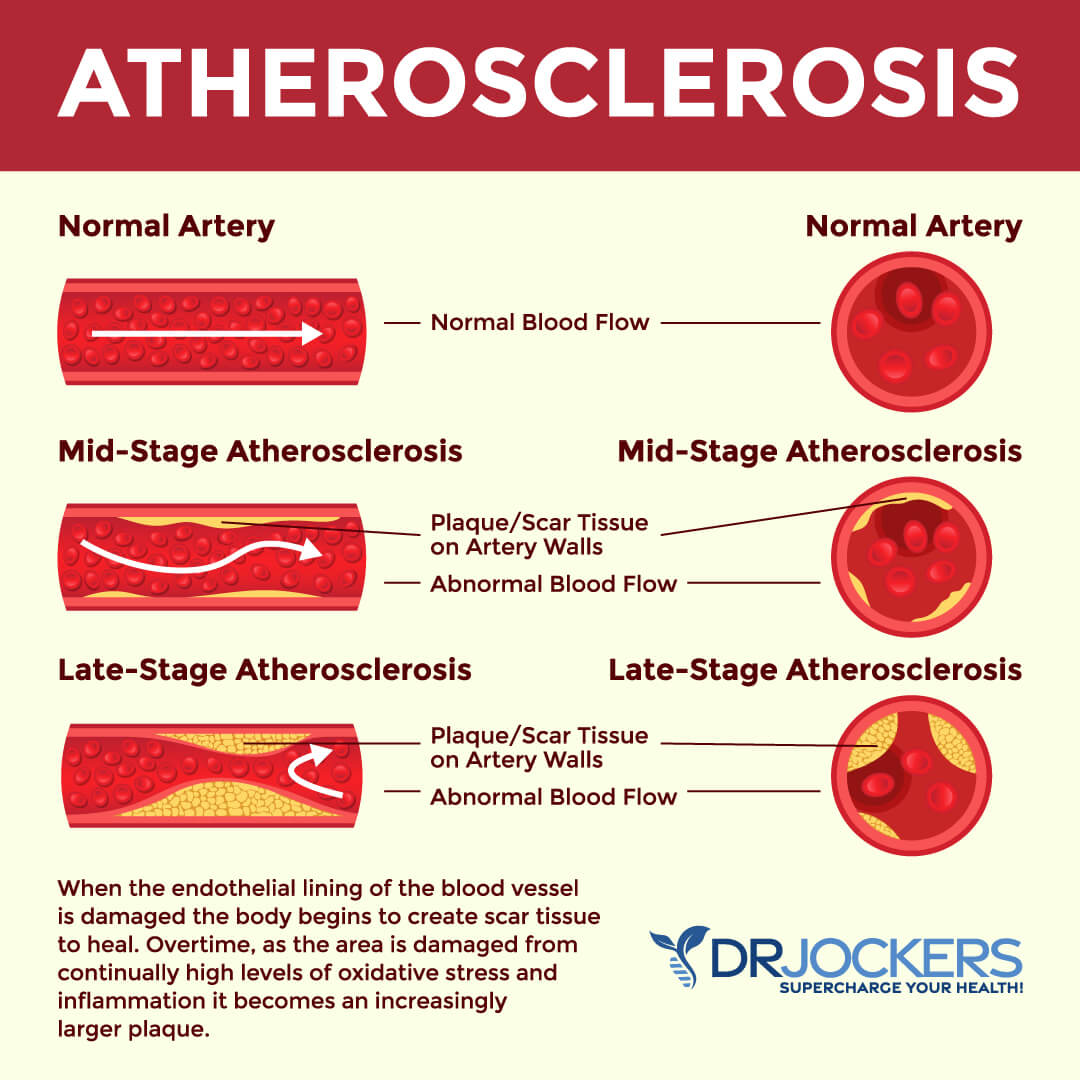
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis refers to a condition that develops when plaques build up inside your arteries. Plaques are sticky substances that clog up your arteries. You may develop atherosclerosis from chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, gut dysbiosis, a poor diet, chronic stress, poor sleep, chronic infections, and other issues.
Atherosclerosis may cause your arteries to narrow, which can lead to poor circulation, hypertension, and an increased risk of blood clots. It may increase your risk of cardiovascular issues, including heart disease, stroke, and heart attacks. A 2021 study published in Hypertension has looked at 2580 people (mean age 52 years, 49% women) looking at their markers for cardiovascular disease (3).
They found that atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis (a vascular disease affecting the arteries), and poor cardiovascular health may occur together, and this conjoint presence may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. You may learn more about atherosclerosis by reading this article.
Chronic Infections
Chronic infections may increase the risk of chronic inflammation and other health issues that may increase your risk of poor circulation and cardiovascular issues. According to a 2003 review published in Cardiology Clinics, chronic infections may trigger pre-existing plaques through T-cell activation and inflammatory response (4).
A chronic inflammatory response may increase the risk of chronic inflammation, which, as you already know, may increase the risk of poor circulation (1). According to researchers, infections that you may need to be aware of include but are not limited to Lyme disease, EBV, herpes, influenza, C pneumoniae, cytomegalovirus, bacterial infections, and oral infections, including ones that lead to root canals (4).
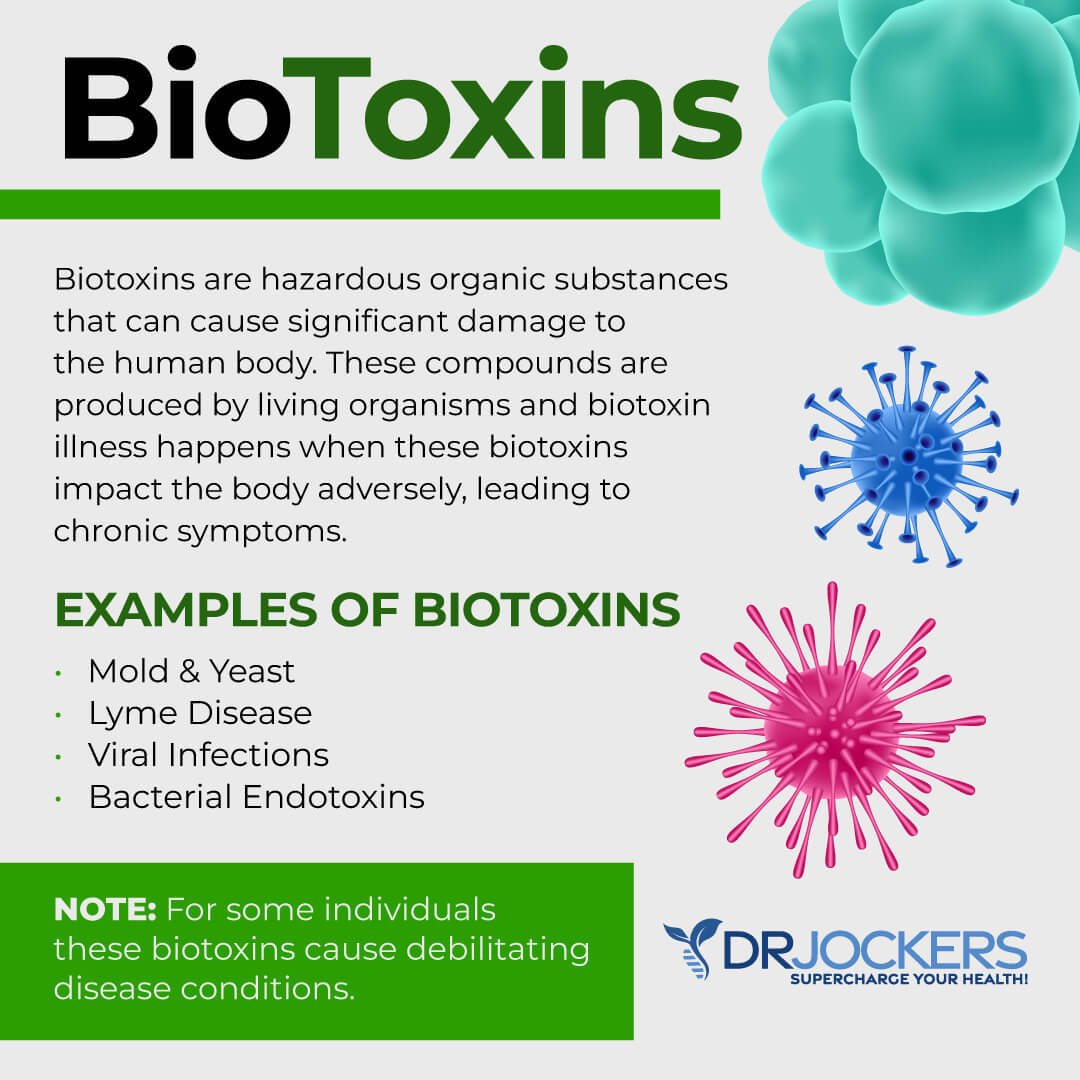
Mold & Mycotoxin Exposure
Mold is a fungus that can grow on almost anything, with the ability to thrive in many conditions but most specifically in warm temperatures and high moisture environments. Mold has the ability to spread far and wide, as tiny, microscopic spores, called mycotoxins, are released from the source in an effort to allow additional mold to grow.
Mold toxicity occurs when mycotoxins are produced by micro-fungi such as mold. Mold and mycotoxin exposure may increase the risk of chronic inflammation and the risk of an array of chronic health issues, including poor circulation.
According to 2015 research published in PLoS One, mold and mycotoxin exposure may increase inflammatory cytokine and chemokine response in the body (5). As you already know, inflammation may increase the risk of poor circulation (1).

High Toxic Load
Environmental toxins are all around us. Air pollutants, toxins in tap water, chemicals in conventional cleaning, personal hygiene, and body products, pesticides in our foods, and so on may contribute to the development of poor circulation and cardiovascular issues, including clogged arteries, heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
A 2021 study published in Frontiers in Pharmacology has found that environmental toxins may increase cardiotoxicity (6). Smoking is one of the issues that may particularly increase your risk of poor circulation.
According to 2011 research at Uppsala University, smoking cigarettes may increase the risk of developing fatty deposits, which may result in the growth of plaques and atherosclerosis (7). Atherosclerosis may increase the risk of poor circulation, blood clots, and cardiovascular issues (3).

Adrenal Dysfunction
The adrenal glands are small, but critically important, endocrine glands that sit on top of the kidneys. They produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress, and other essential functions.
Adrenal dysfunction may increase the risk of all kinds of health issues, including poor circulation and cardiovascular issues. A 2017 review published in BioMed Research International has found a potential link between adrenal insufficiency and cardiovascular disease (8).
Researchers found that “imbalances in blood cortisol may lead to a higher prevalence of coronary heart disease, major adverse coronary events, and increased mortality”. They noted that physicians should be aware of these risks and address adrenal issues to reduce cardiovascular risks.

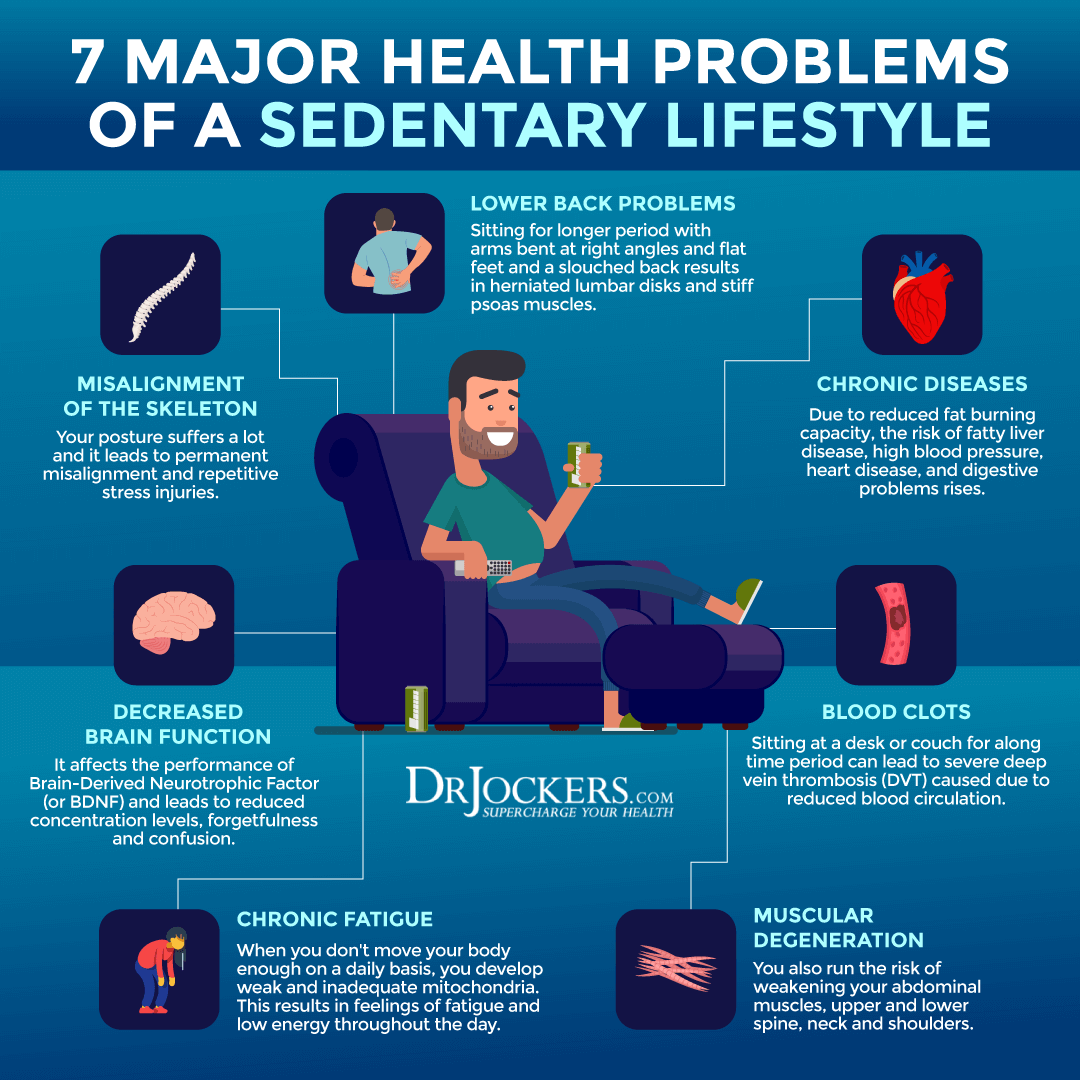
Sedentary Lifestyle
Moving your body and exercising regularly is important for a multitude of health issues, including maintaining a healthy weight, healthy immune function, brain health, mental health, metabolic health, and cardiovascular health. 2019 research published in Circulation Research has found a link between a sedentary lifestyle and poor circulatory health (9). Researchers found that exercise may improve cardiorespiratory fitness and cardiovascular health.
A 2020 study published in the Korean Journal of Family Medicine has found that a sedentary lifestyle may increase the risk of a list of health issues, including cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular mortality, hypertension, dyslipidemia, metabolic disorders, and so on (10). A sedentary lifestyle may also increase the risk of being overweight, obesity, insulin resistance, and other factors that may contribute to bad circulation and circulatory issues.
Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium is an important mineral. It serves as a cofactor for over 300 enzyme systems that play a role in many biochemical reactions inside your body. For example, it’s important for blood pressure regulation, blood glucose control, muscle function, nerve function, and protein synthesis.
It plays a role in circulation and cardiovascular health. According to a 2018 review published in Open Heart, magnesium deficiency may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (11). Researchers called for action as magnesium deficiency is a public health crisis.

Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D is an important vitamin for bone, muscle, immune, brain, and mental health. It is also critical for circulatory health. Deficiencies in vitamin D may increase the risk of a long list of issues, including poor circulation.
A 2018 review published in Clinical Hypertension vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of cardiovascular issues (12). They found that it may increase the risk of peripheral vascular disease, congestive heart failure, impaired systolic and diastolic function, hypertension, nonvalvular AF, myocardial infarction, and abdominal aortic aneurysm in older men.

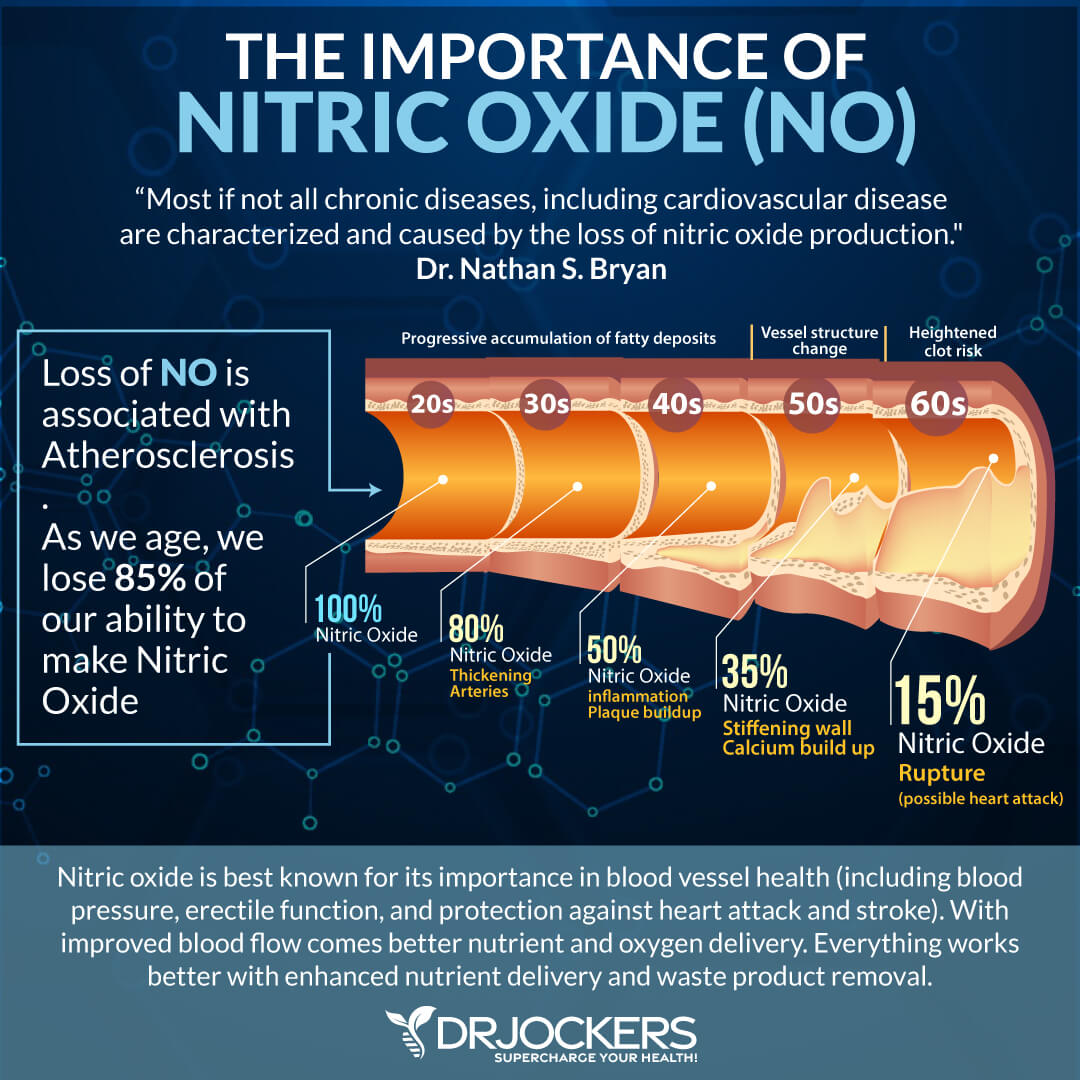
Poor Nitric Oxide Production
Exercise helps to increase your body’s ability to make nitric oxide and keep your endothelial cells and blood vessels to stay healthy. Nitric oxide may be beneficial for cardiovascular health, healthy blood pressure levels, erectile dysfunction, exercise performance, and respiratory response.
Poor nitric oxide production may increase the risk of endothelium dysfunction. They may increase the risk of atherosclerosis, poor circulation, high blood pressure, and other risk factors for developing heart disease.
According to a 2005 review published in Vascular Health and Risk Management, endothelial dysfunction and poor nitric oxide levels may increase the risk of circulatory health issues and poor outcomes (13).
Natural Support Strategies
You may support your circulatory health with the help of some natural support strategies. Here are the natural support strategies I recommend for poor circulation.
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition Plan
Since a poor, inflammatory diet is one of the common potential causes of chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, and some of the other underlying issues behind bad circulation, I recommend following an anti-inflammatory nutrition plan (1). Remove inflammatory foods, such as refined sugar, refined oil, artificial ingredients, additives, and overly processed food products.
Eat lots of anti-inflammatory, nutrient-dense food. Focus on greens, vegetables, herbs, spices, low-glycemic index fruits, seeds, fermented foods, grass-fed beef, pasture-raised poultry and eggs, wild-caught fish, and wild game.
Eat lots of healthy fats, including avocados, grass-fed butter and ghee, coconut oil, MCT oil, extra-virgin olive oil, and olives. Keep your carb intake low, coming from vegetable sources and low-glycemic index fruits. Eat enough clean protein. You may also incorporate intermittent fasting. You may find information on intermittent fasting in this article.

Consume Dietary Polyphenols
Polyphenols are micronutrients that come from plants, including tea, fruits, vegetables, and spices. There are over 8,000 types of polyphenols. Quercetin, resveratrol, and catechins are some of the most common ones. The most commonly known ones are quercetin and catechins. According to a 2021 review published in Dove Press, polyphenols may help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (14).
I recommend consuming foods rich in polyphenols for healthy circulation. Quercetin is found in olive oil, red leaf lettuce, romaine lettuce, red onions, pepper, kale, chicory greens, sprouts, snap peas, asparagus, cabbage, cruciferous vegetables, many herbs, apples, grapes, cranberries, black currants, blueberries, raspberries, chokeberries, cherries, and black plums.
Resveratrol is found in the skin of red grapes, raspberries, mulberries, and blueberries. Catechins are found in cacao, green tea, apples, blueberries, gooseberries, grape seeds, kiwi, and strawberries.

Regular Exercise & Movement
A sedentary lifestyle may cause health issues, including cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular mortality, hypertension, dyslipidemia, metabolic disorders, and so on (10). It may also reduce nitric oxide levels, which may increase the risk of poor circulation (13). Thus, exercise and moving your body are critical.
I recommend incorporating movement into your daily life throughout the day. Start your day with a stretch and some sort of movement. It may be a short walk, a quick yoga session, or a rebounding session.
Get up and move around throughout the day. Take a walk with your family or friends. Play with your kids and pets. Exercise at least five times a week for 20 to 30 minutes each session. Incorporate both cardiovascular exercise and strength and resistance training.

Reduce Stress & Improve Sleep
Chronic inflammation may increase your risk of poor circulation (1). Chronic stress and poor sleep both may contribute to chronic inflammation and circulatory issues. I recommend reducing your stress levels and improving your sleep.
Incorporate meditation, breathwork, gratitude, and relaxation strategies into your life. Spend time with supportive people. Spend time in nature and move your body regularly. Avoid electronics, heavy foods, sugar, caffeine, alcohol, and stress before bedtime.
Engage in relaxing activities that wind you down. Drinking herbal tea, reading, listening to calming music, and family time are great ideas. Support your sleep with supportive bedding, an eye mask, and blackout curtains.

Improve Air & Water Quality
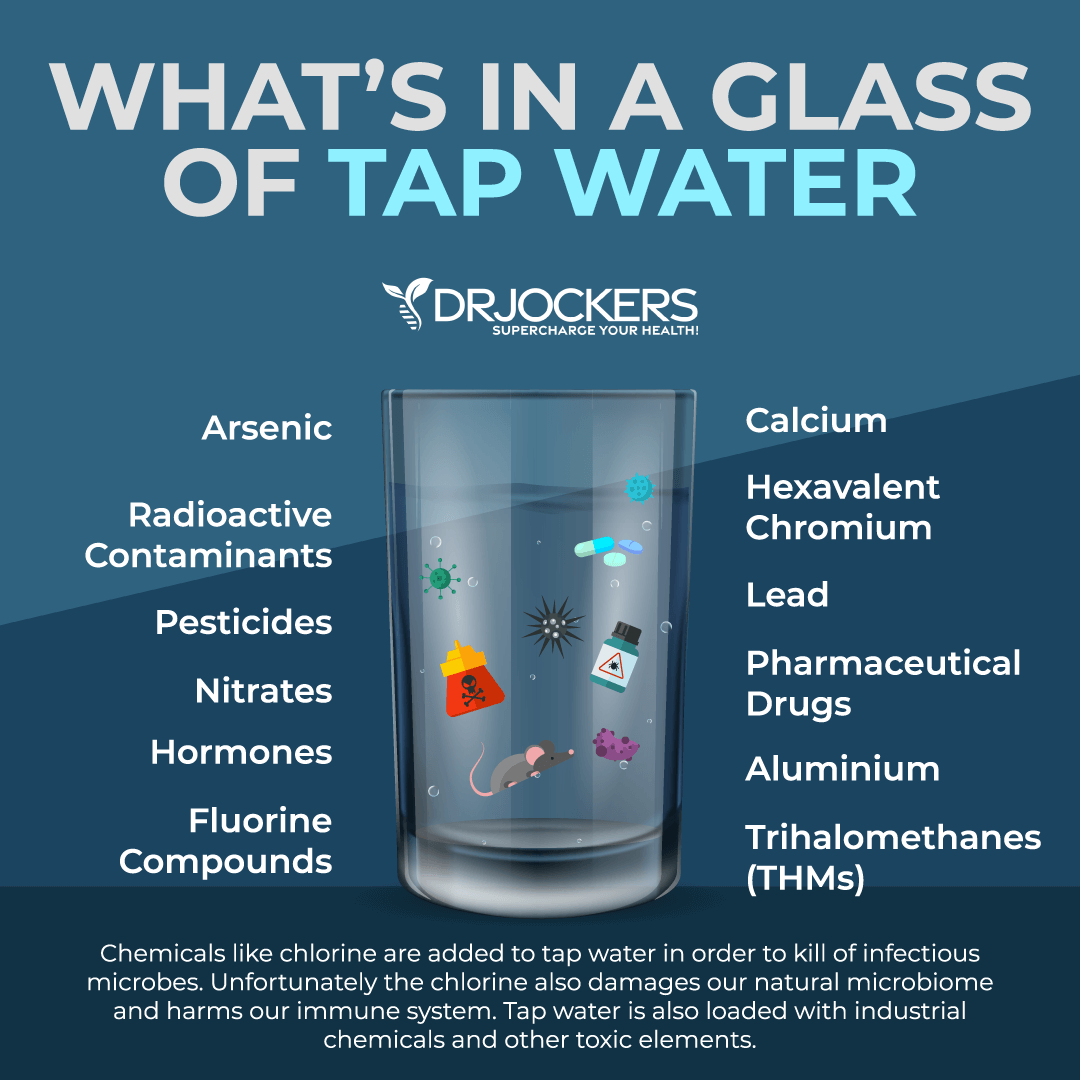
Environmental toxins may increase your risk of poor circulation (6, 7). Improving your air and water quality is just two important way to reduce environmental toxin exposure. Invest in a HEPA air-filtration system to improve your indoor air quality. I have and use the Air Doctor, and you can learn more about the Air Doctor air filtration system in my review article here.
I recommend using a water purification system and drinking purified water instead of regular tap water, and using glass or stainless-steel bottles instead of plastic. (Avoid bottled water or unfiltered tap water.). You may add some lemon juice, cucumber slices, basil, mint, other herbs, or berries for taste.
I recommend systems like Aquatrue or the Berkey system for low-cost filtration. The best water is the UltraLux Triple Action Hydrogen Water Machine, which is what I use at home, as it is powered by molecular hydrogen, which reduces oxidative stress in the body and improves immune function.
Reduce Mold & Mycotoxin Exposure
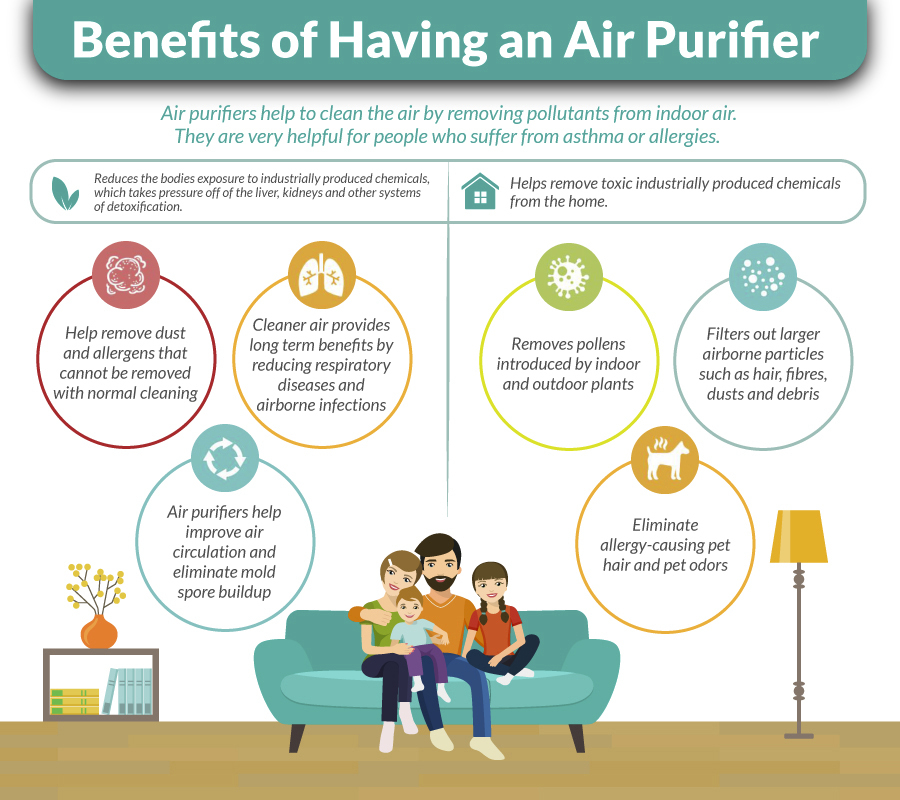
Mold and mycotoxin exposure may also increase your risk of poor circulation (5). Check for mold issues around your home and work with professional mold remediation to take care of any mold issues. Take care of any leaks and water damage in your home. Use a dehumidifier.
Take care of any high-risk areas, such as your bathroom: clean them regularly and keep them dry. Use a high-quality HEPA filter to remove any mycotoxins in your indoor air. You may learn more about the problem of mold exposure and what to do about it from this article. I have and use the Air Doctor, and you can learn more about the Air Doctor air filtration system in my review article here.
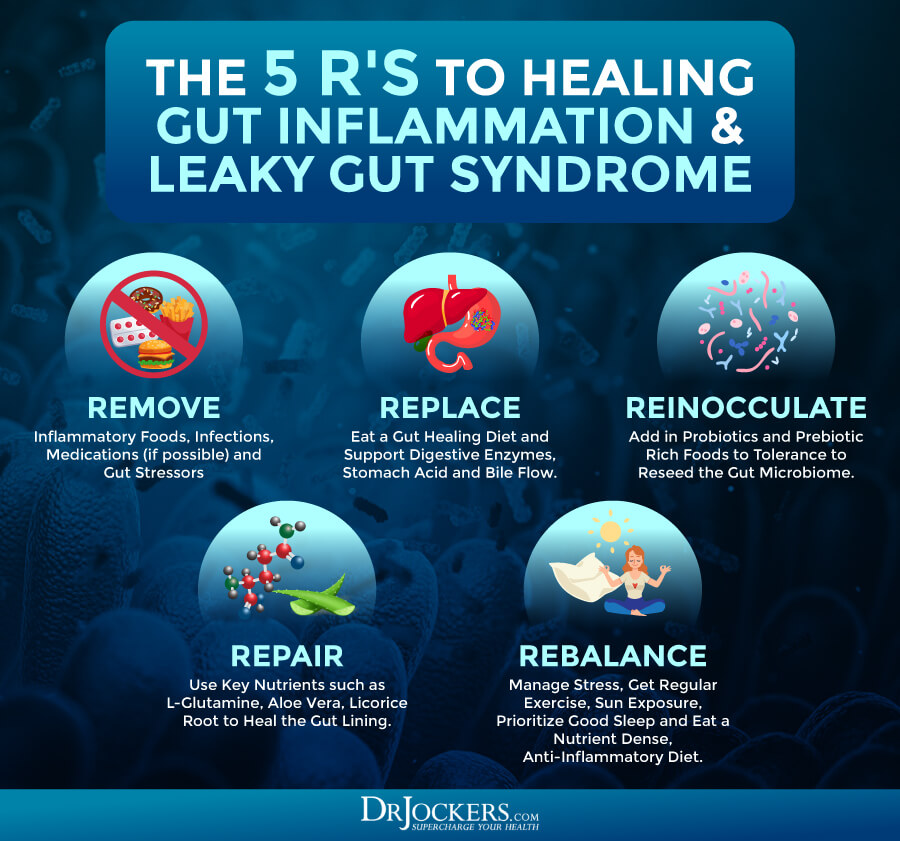
Support Gut & Immune Health
Gut and immune health issues may increase your risk of chronic inflammation and related circulatory issues (1). Supporting your gut health and immune health may help improve bad circulation. You can read about how to reduce gut inflammation in this article.
Follow a gut-friendly, immune-supporting, nutrient-dense, and antioxidant-rich diet as outlined earlier. Eat plenty of fermented foods, such as kimchi, sauerkraut, kefir, and kombucha.
Take a daily probiotic supplement to support a healthy gut microbiome. I also recommend Gut Repair for gut dysbiosis and gut health issues. Support your immune system with ImmunoCharge and Zinc Charge.
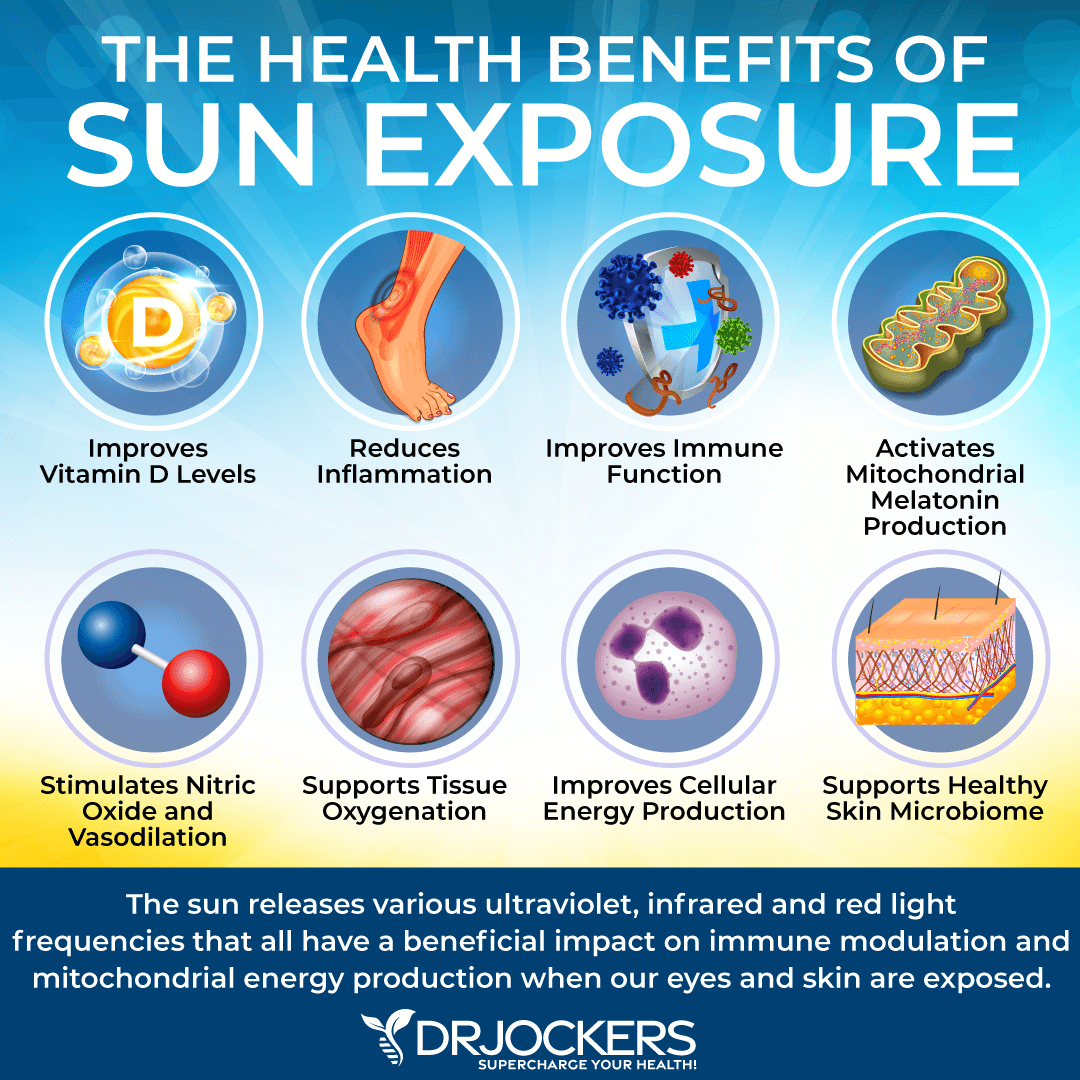
Regular Sun Exposure
We discussed earlier that vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of cardiovascular issues (12). Sunshine helps your body to produce vitamin D and reduces the risk of deficiencies.
Moreover, according to a 2021 review published in Nitric Oxide, the UVA rays from the sun may help to increase nitric oxide levels (15). Research has shown that endothelial dysfunction and poor nitric oxide levels may increase the risk of circulatory health issues and poor outcomes (13).
Regular sun exposure may help to improve your vitamin D levels and enhance blood nitric acid levels. I recommend daily sun exposure for at least 15 to 30 minutes each day, whether provided.
Ideally, you want to expose as much of your skin as possible. This may not be possible in colder months, but do your best based on the situation. To avoid sunburn, avoid the midday sun, and you may break this down into smaller sessions.
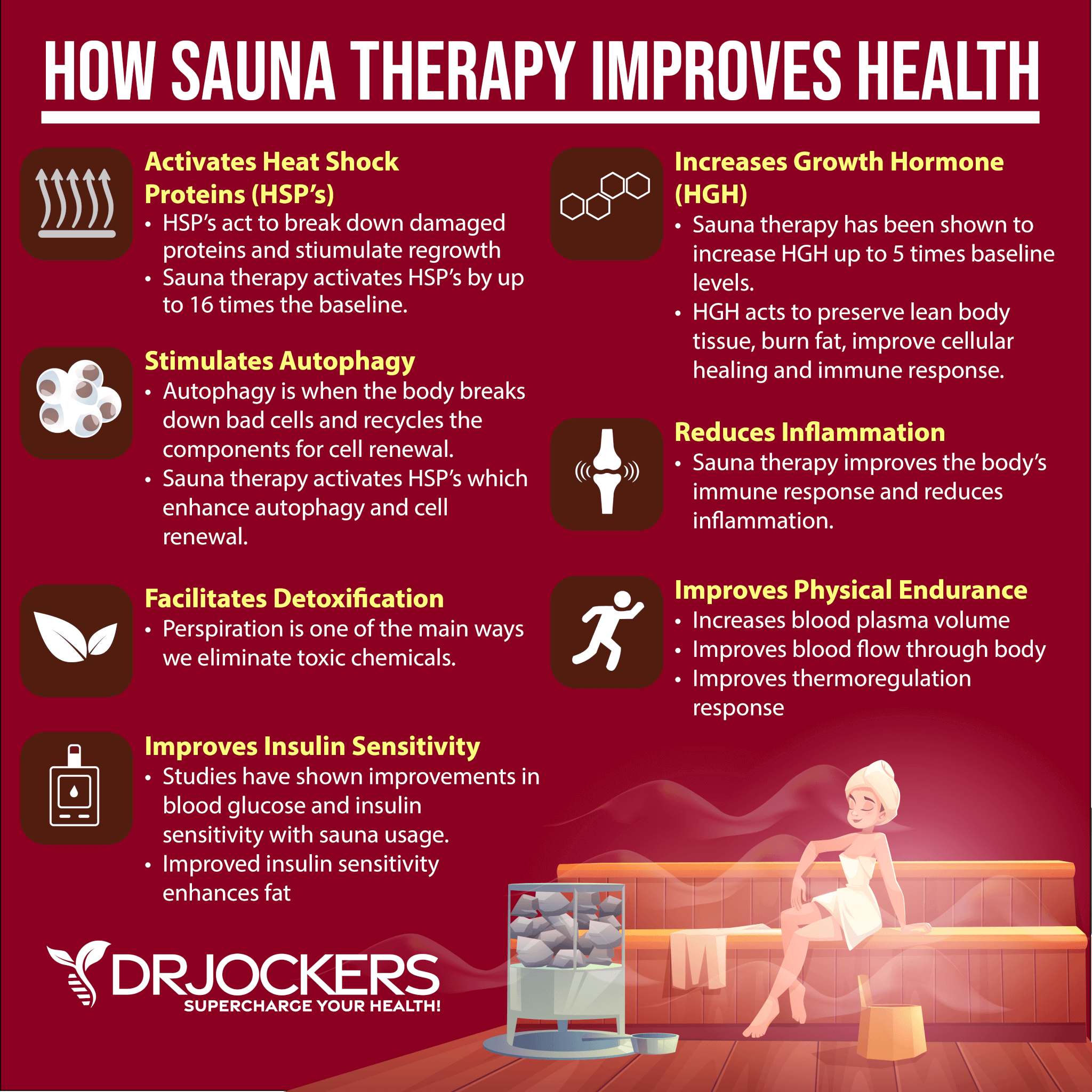
Use an Infrared Sauna
Infrared sauna therapy is a form of sauna that uses infrared heaters that release infrared light you experience as heat, as it gets absorbed through the surface of the skin. Infrared sauna therapy uses Far Infrared Technology (FIR), which is a non-invasive light therapy that can penetrate your body as much as three inches. It used FIR wavelengths between 5.6 and 20 microns.
Through this process, infrared sauna therapy heats your muscle tissues and internal organs without heating the surrounding air. This heat helps your organs and tissues to detoxify by pushing toxins out of your bloodstream to be eliminated by perspiration or sweating. This supports your immune system, circulation, metabolic pathways, kidney filtration, weight loss, stress reduction, and more.
According to a 2013 study published in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, far-infrared (FIR) radiation in infrared sauna may help to mobilize Ca (2+) and synthase Ca (2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide and, as a result, increase nitric oxide production (16).
Poor nitric oxide levels may increase the risk of circulatory health issues and poor outcomes (13). According to a 2018 study published in the Journal of Human Hypertension, using a sauna may improve cardiovascular function (17).
I recommend using an infrared sauna daily. You may learn more about the benefits of an infrared sauna in this article.
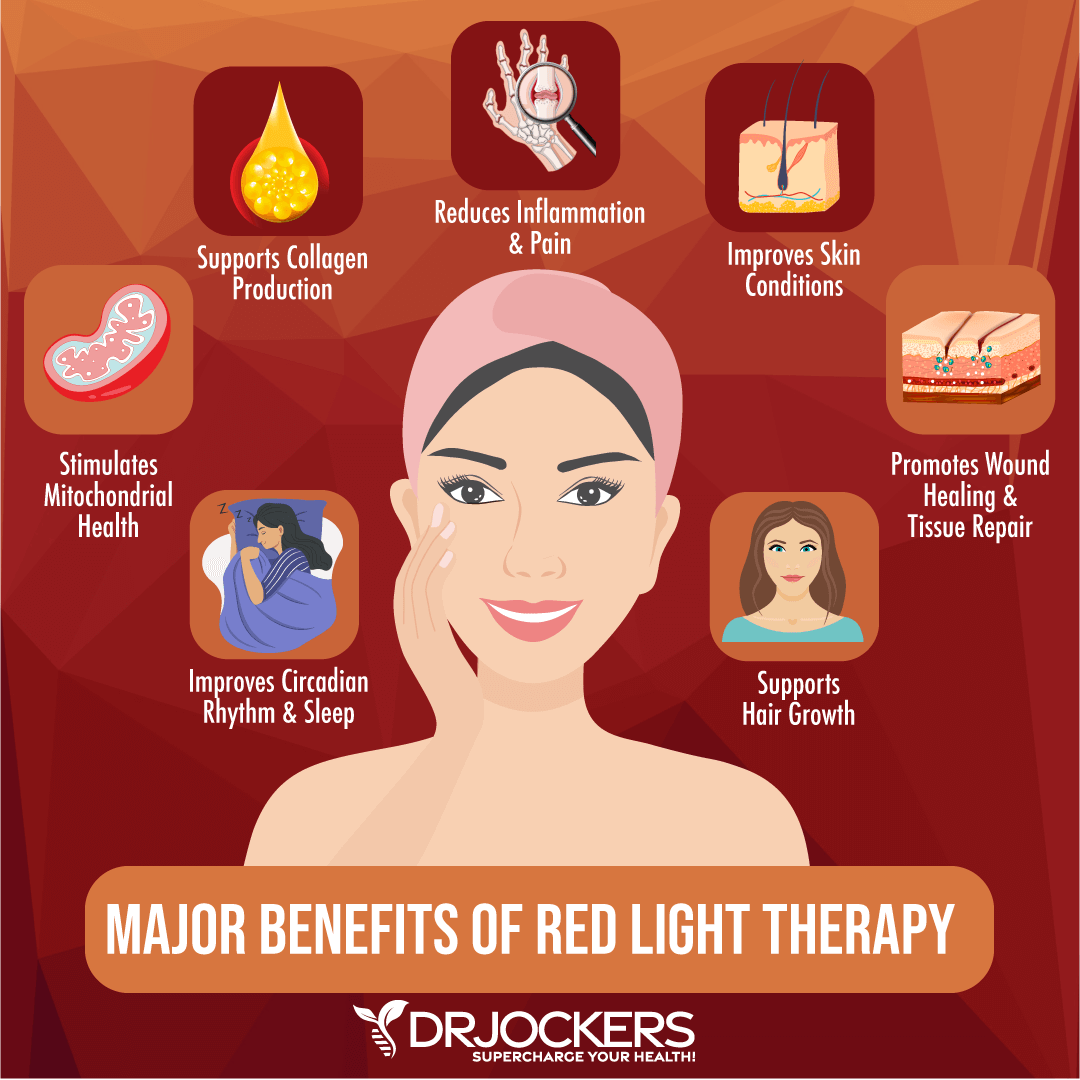
Use a Red/Infrared Light Panel
I also recommend using red or infrared light therapy. Red light therapy uses red low-level wavelengths of light, which are on the “long end” of the visible spectrum and have wavelengths of 630 nm to 700 nm. Red light therapy is most effective when used on the surface of the skin.
Infrared light therapy can penetrate deeper. Infrared light is invisible with 800 nm to 1000 nm wavelengths. It can be used at the surface of the skin, but it can also penetrate deeply, about 1.5 inches into your body, for deeper cellular support.
Unlike ultraviolet (UV) lights from the sun, red light therapy and infrared light therapy don’t burn your skin. There is no UV damage or sunburn. There is no suntan either.
They offer a safe way to receive health benefits on a cellular level when standing or sitting several inches from a red light therapy device without risks. Red light therapy may offer many health benefits, including reduced inflammation, lower pain levels, better sleep, improved immune health, better brain and mental health, and better circulation and cardiovascular health.
According to a 2017 study published in Free Radical Biology & Medicine, red/near-infrared light therapy may help to stimulate vasodilation in animal models (18). This happens due to the release of nitric oxide-bound substances from the endothelium. This may help to improve endothelial function, nitric oxide levels, and mitochondrial function, and may offer a new treatment option for diabetic vascular disease.
I recommend using infrared light therapy daily. You may learn more about red light therapy in this article.
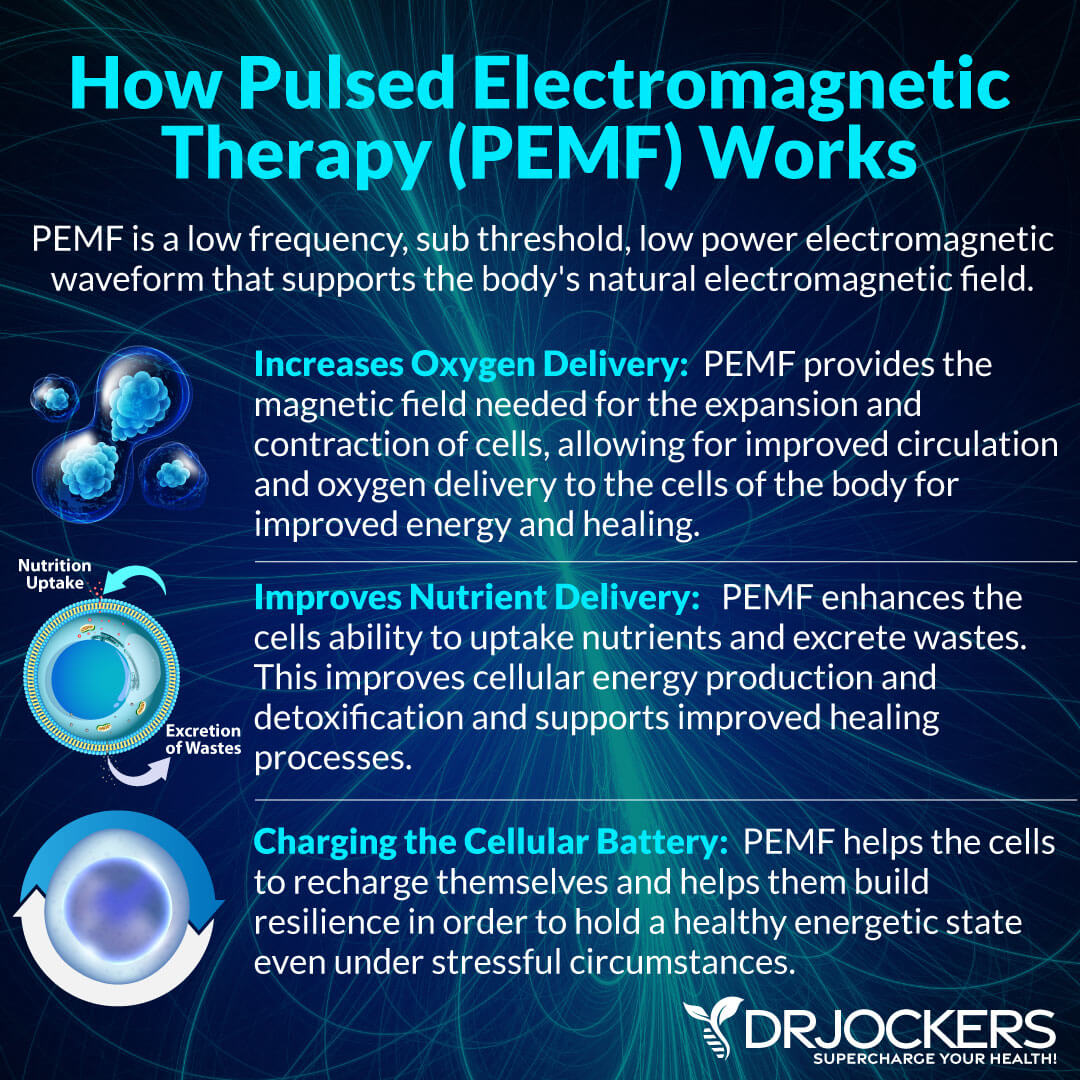
Pulsed Electromagnetic Therapy
Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMF) therapy is an increasingly popular alternative healing method that uses pulsed electromagnetic fields to stimulate your body on a cellular level. It may help to improve your energy, support circulation, aid detoxification, improve your sleep, reduce inflammation, lower pain, support your immune function, aid cognitive function, and boost your mood.
A 2019 study published in Blood Pressure looked at the potential benefits of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy over 12 weeks of treatment (19). They found that it may improve nitric oxide levels, blood pressure, and circulation in people with metabolic syndrome.
A 2020 study published in the Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich) has also found that 12 weeks of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy may improve blood pressure and vascular function, in this case, in hypertensive individuals (20).
I recommend pulsed electromagnetic therapy for poor circulation. You may learn more about it in this article.
Take a Magnesium Supplement
Earlier, we discussed that magnesium deficiency may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (11). Magnesium-rich foods include fatty fish, avocados, nuts, seeds, cacao, Swiss chard, spinach, and amaranth.
However, due to our poor soil quality, even these foods can’t provide enough magnesium in many cases. I recommend taking a magnesium supplement to support your circulation and overall health. I recommend Brain Calm Magnesium and CalMag Support.
Optimize Vitamin D Levels
We discussed earlier that vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of cardiovascular issues (12). Sunshine helps your body to produce vitamin D and reduces the risk of deficiencies. Eating vitamin D-rich foods, including fatty fish, fish liver oils, egg yolk, and mushrooms, may also help boost your levels. But it’s not enough. Most of us need supplementation.
Pairing vitamin D3 with vitamin K2 helps improve calcium absorption and control inflammation. I recommend taking a vitamin D3 supplement with at least 3,000-5,000 IU’s of vitamin D3 and at least 90 mcg of vitamin K2. I highly recommend Vitamin D3/K2 Power. Both of these supplements support your immune, skin, cardiovascular, and bone health.
Typically, taking 1,000 IU per 25 lbs. of body weight will help you get your levels into a healthy range. You want to test your vitamin D levels at least 1-2 times each year and get your levels between 50-100 ng/ml. It has been hypothesized that a therapeutic level for major health conditions is going to be between 70-100 ng/ml.

Consider Using Resveratrol and Quercetin
You already learned about how polyphenols may help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (14). Quercetin and resveratrol are powerful polyphenols you may benefit from. According to a 2019 study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, it may help to improve autophagy, reduce vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, and improve vascular function (21).
According to a 2021 review published in Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, quercetin may help to reduce endothelial dysfunction and improve cardiovascular health (22). It may help to reduce the risk of “hypertension, atherosclerosis, accumulation of senescent endothelial cells, and endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT)” (22).
I recommend using Resveratrol Power for the circulatory benefits of resveratrol and quercetin. This amazing combination of two major antioxidants delivers support to mitochondrial health by reducing free radical damage contributed by a variety of influences, including the aging process alone. In nature, resveratrol defends the plant against pests and environmental stressors.
Resveratrol is the reason why grapes that are grown in harsh climates have a higher concentration of resveratrol produced in the skin. In combination with quercetin, Resveratrol Power supports the aging process, improves skin health, provides protection against cardiovascular damage, and reduces free radical damage to neurons and mitochondria.
This product is fantastic for down-regulating inflammation and improving anti-aging characteristics. As a dietary supplement, take one capsule per day, or as directed by your health care practitioner.
Final Thoughts
Your circulatory system is a system in your body that includes your heart and blood vessels. Good circulation is critical for heart health, immune health, brain function, wound healing, and other important functions. It supports your organs, tissues, and health, and helps your body to stay alive and thrive.
Bad circulation may increase your risk of some serious health issues, including serious cardiovascular problems. I recommend supporting your circulation with the help of the natural support strategies outlined in this article.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. On our website, we offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!






Your articles are the best.
Which ingrédients are good to dissolve arteries ´ plaques?
No no one talk about that! why?
Of course, there is something (s)
Thanks a lot.
There is one God— so there is one truth —so why are so many différent religions?
Romans 10: 2-5
👍👍😀❤️