 APOE4 Gene and Your Risk of Alzheimer’s
APOE4 Gene and Your Risk of Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia. It’s a progressive disease that causes memory issues, cognitive impairment, issues with language, and a loss of independence. To understand your risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease, it’s important to look at your genetics. Carrying the APOE4 gene may increase your risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
In this article, you will learn what the APOE gene is. I will discuss the connection between APOE4 gene and Alzheimer’s disease and the role of the gene in the disease. You will understand the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.
I will recommend a genetic test to test your genes for brain health and other labs to consider to check for risk factors. Finally, I will recommend my best natural strategies for APOE4 gene carriers.
What is the APOE Gene?
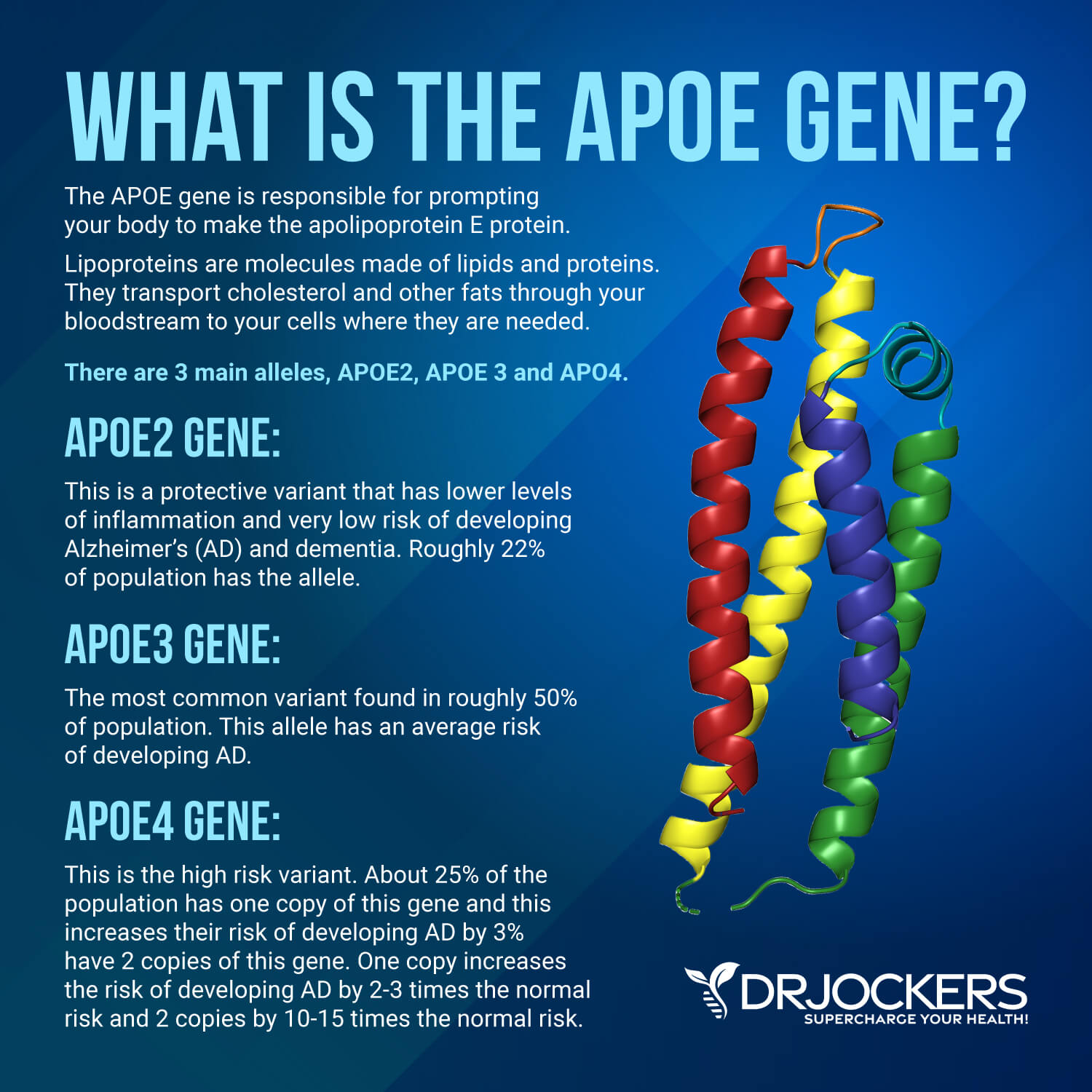
The APOE gene is responsible for prompting your body to make the apolipoprotein E protein. APOE helps to blend lipids (fats) to make lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are molecules made of lipids and proteins. They transport cholesterol and other fats through your bloodstream to your cells where they are needed.
Healthy levels of cholesterols are critical for reducing your risk of any diseases that affect your blood vessels or heart, including heart disease, heart attacks, and stroke. Research suggests that a genetic variation of the APOE gene on chromosome 19 may play a role in developing Alzheimer’s disease.
There are three different main variations (alleles) of the APOE gene: the APOE2, the APOE3, and the APOE4. The APOE4 gene is connected to the increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. APOE3 may play a neutral role and APOE2 may reduce your risk factors. In the next section, I will discuss the connection between each variation and Alzheimer’s (1, 2).

The APOE4 Gene and Alzheimer’s
Each variation of the APOE gene has a different relationship with Alzheimer’s disease.
- APOE2: This is a rather rare gene that may help to protect you from Alzheimer’s disease. When people with the APOE2 gene develop Alzheimer’s disease, it usually develops later in life.
- APOE3: This is the most common type of APOE gene, found in about half of the population. Having this gene seems to have a neutral role in the risk and development of Alzheimer’s disease. It doesn’t seem to reduce or increase the risk of the disease.
- APOE4: This gene can increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. It is mainly linked to early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. If you have one or two of these genes, it can increase your risk of developing the disease. About 25 percent of the population carries one, and 2 to 3 percent has two copies of the APOE4 gene. Having one copy of APOE4 increases one’s risk of developing Alzheimer’s by 2-3 fold. Having 2 copies of this gene increases the risk by 10-15 times.
Inheriting the APOE4 gene doesn’t necessarily mean that you will develop Alzheimer’s disease for certain. Many people with this gene never develop Alzheimer’s. Dietary, lifestyle, health, and other factors may also play a role in the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Later in this article, I will discuss how to improve your health and reduce your risk if you carry the APOE4 gene (1, 2).
Role of APOE4 Gene
The reason why the APOE4 gene may increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease is not completely understood and is under research. Some studies suggest that the connection may be connected to how the APOE4 gene may affect lipid metabolism in the brain cells.
A 2021 study published in the Science Translational Medicine has found that disruptions in lipid metabolism may increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in those with APOE genotypes (3). They found that improving lipid metabolism may be beneficial for those with the APOE4 gene.
Moreover, the APOE4 genotype may also increase inflammation through NLRP3 activation and other mechanisms you can discuss. According to a 2021 study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, the APOE4 gene may possess inflammatory properties (4). A 2019 study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology has found that the APOE4 may activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and may increase the inflammatory response (5).
This is important in that it helps the individual resist parasites and other infections better than other APOE genotypes, which was important for our ancestors. However, it is also associated with higher levels of inflammation which long-term may increase the risk of neurodegeneration. According to a 2020 study published in Frontiers in Immunology, the APOE4 gene may increase neuroinflammation and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease (6).

Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease
Your brain is full of specialized cells that transport and process information through chemical and electrical signals. These specialized cells are called neurons. Your brain is literally the home of millions of them.
Your neurons move information across your brain and between your brain and other parts of your body. If you have Alzheimer’s disease, it means that neural communication is interrupted. This will lead to a loss of function, cellular death, and neurodegeneration.
The function, health, and survival of neurons depend on:
- Communication: Your neurons are constantly communicating with other brain cells and cells in the rest of your body through synaptic connections.
- Metabolism: Metabolism is an essential function needed for cellular health and survival. It is the breakdown of chemicals and nutrients within a cell that need lots of energy through oxygen and glucose supplied by your blood moving through your brain.
- Repair and regeneration: Unlike other cells, neurons can live for a very long time. However, to stay healthy and function for a long time, they need to maintain, repair, and regenerate themselves on an ongoing basis. For example, synaptic connections may strengthen or weaken throughout your life, affecting cognition, memory, and brain health.
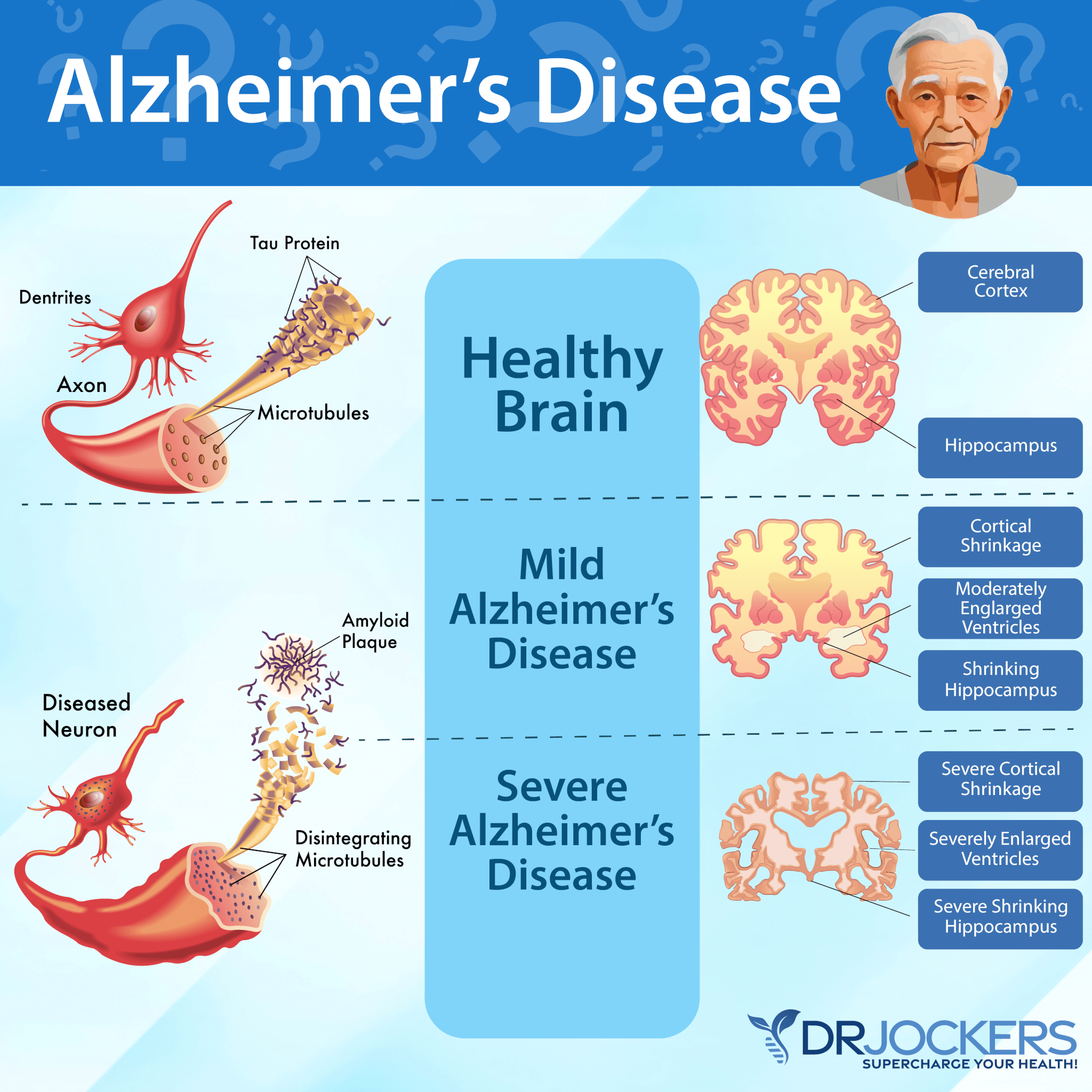
Your neurons play a key role in the function of your nervous system and brain. If you have Alzheimer’s disease, these functions are greatly affected.
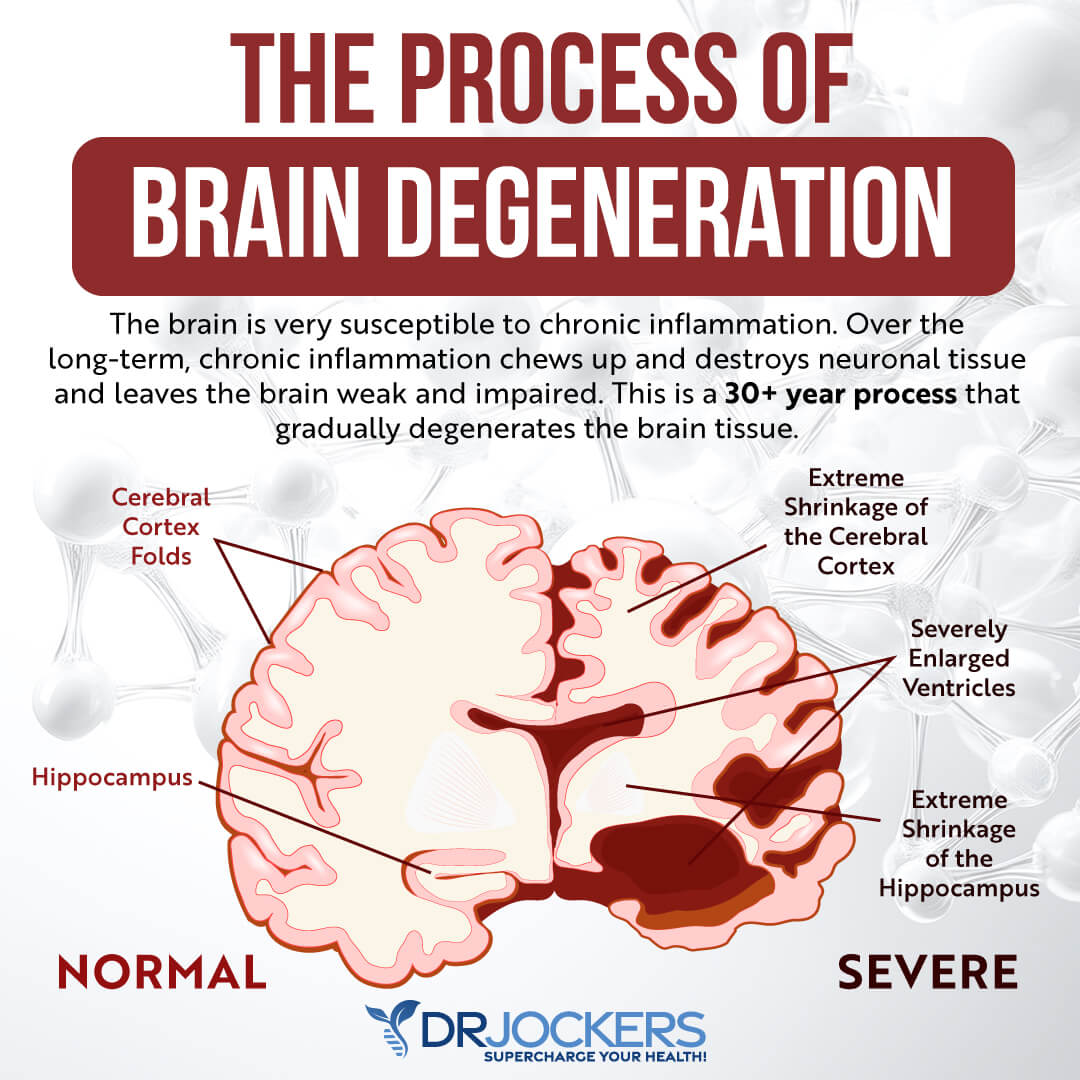
Though everyone’s brain shrinks and loses some neurons as we age, losing them in large numbers is not normal, even in older people. In Alzheimer’s disease, this neural damage and loss are widespread. Neurons increasingly start to lose connections. They stop functioning properly. And eventually, they will start dying in large numbers.
This will disrupt proper communication, metabolism, repair, and regeneration. This will lead to memory issues, the loss of cognitive abilities and function, and eventually, the ability to function and live your life independently. As a progressive disease, Alzheimer’s ultimately ends with death.
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by cellular and molecular changes. Beta amyloid plaques are among these changes that play a role in Alzheimer’s. Beta amyloids are proteins that are involved in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Beta amyloid is made through the breakdown of the amyloid precursor protein. Beta amyloid 42, a particularly toxic type, is found at abnormal levels in Alzheimer’s, clumping together and causing plaques that interrupt communication between neurons and cellular function.
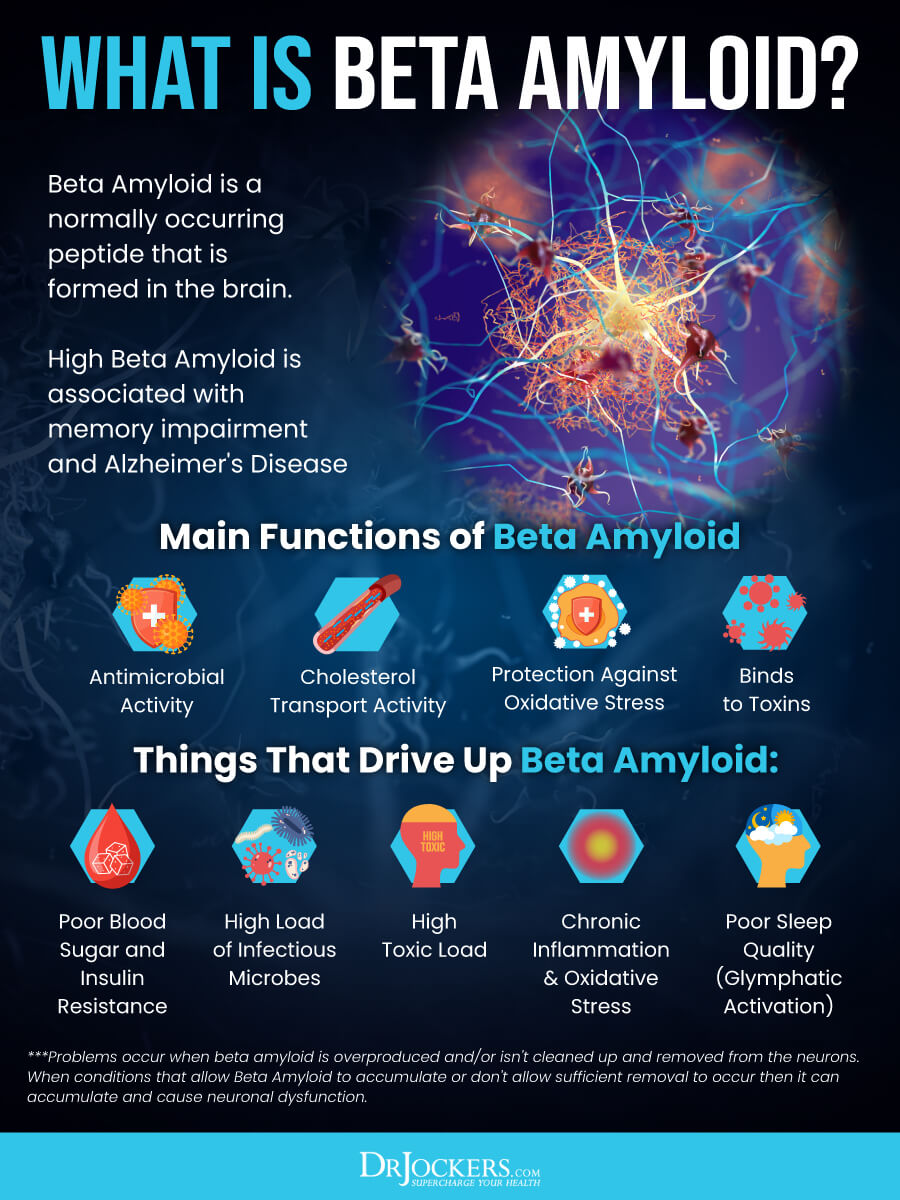
Other characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease include neurofibrillary tangles, chronic inflammation, and vascular issues that may all play a role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurofibrillary tangles are an abnormal buildup of the tau protein inside the neurons that may block the neuron’s transport system and synaptic communication. They may increase due to high levels of beta amyloids.
Chronic inflammation is also a common issue in Alzheimer’s. It happens when the microglia cannot clean up waste, debris, beta amyloid plaques, and other protein buildups. Chronic inflammation and neuroinflammation can lead to further neuron damage.
Moreover, beta amyloid buildup in the brain arteries may increase the risk of vascular problems, atherosclerosis, and mini-strokes in people with Alzheimer’s disease. Over time, Alzheimer’s disease causes brain atrophy or loss of brain volume, brain function, and eventually death (7, 8, 9, 10).
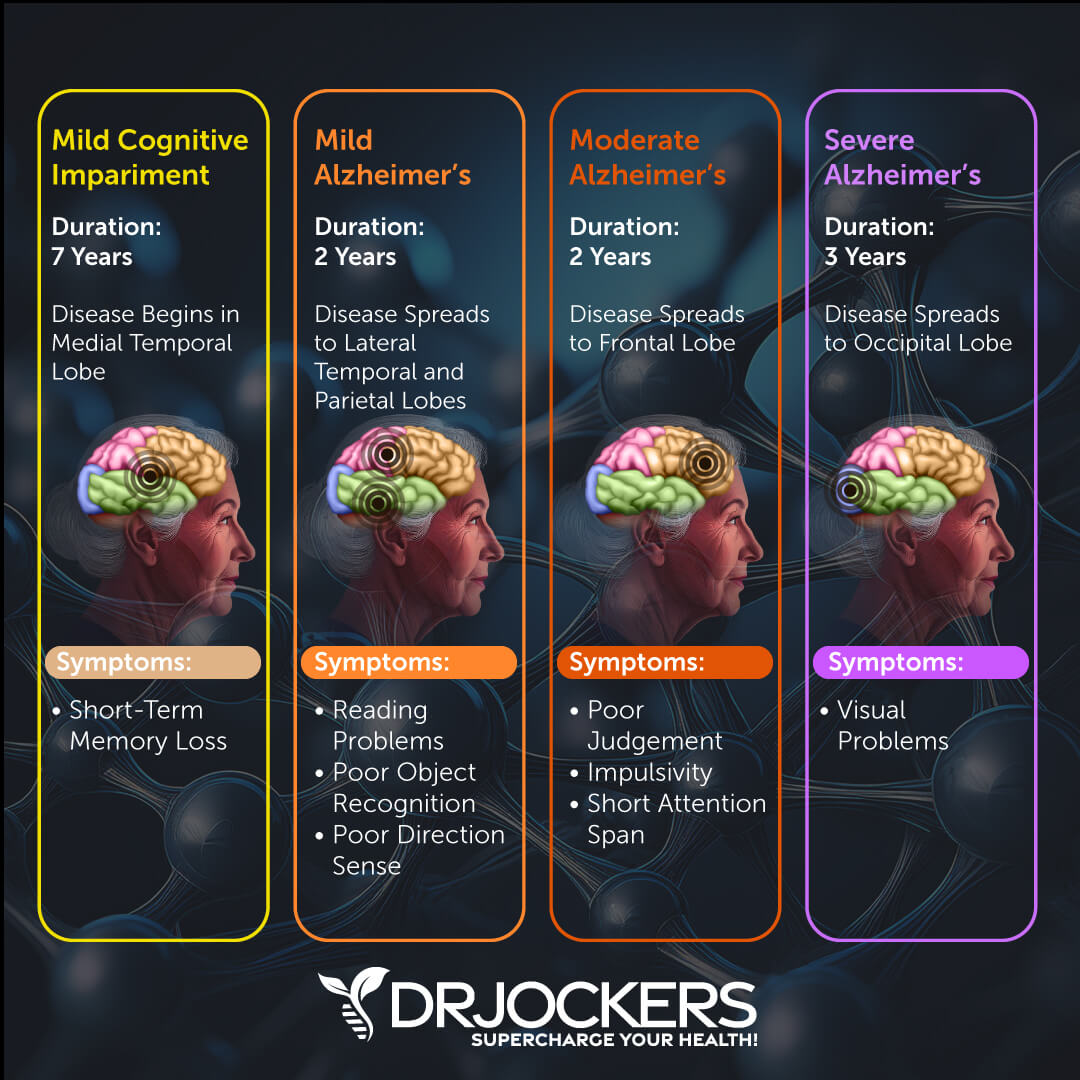
Labs to Consider
There are a few lab tests I recommend to test your risk factors for Alzheimer’s and your overall health markers. Here is what to consider:
Fasting Insulin & HbA1C
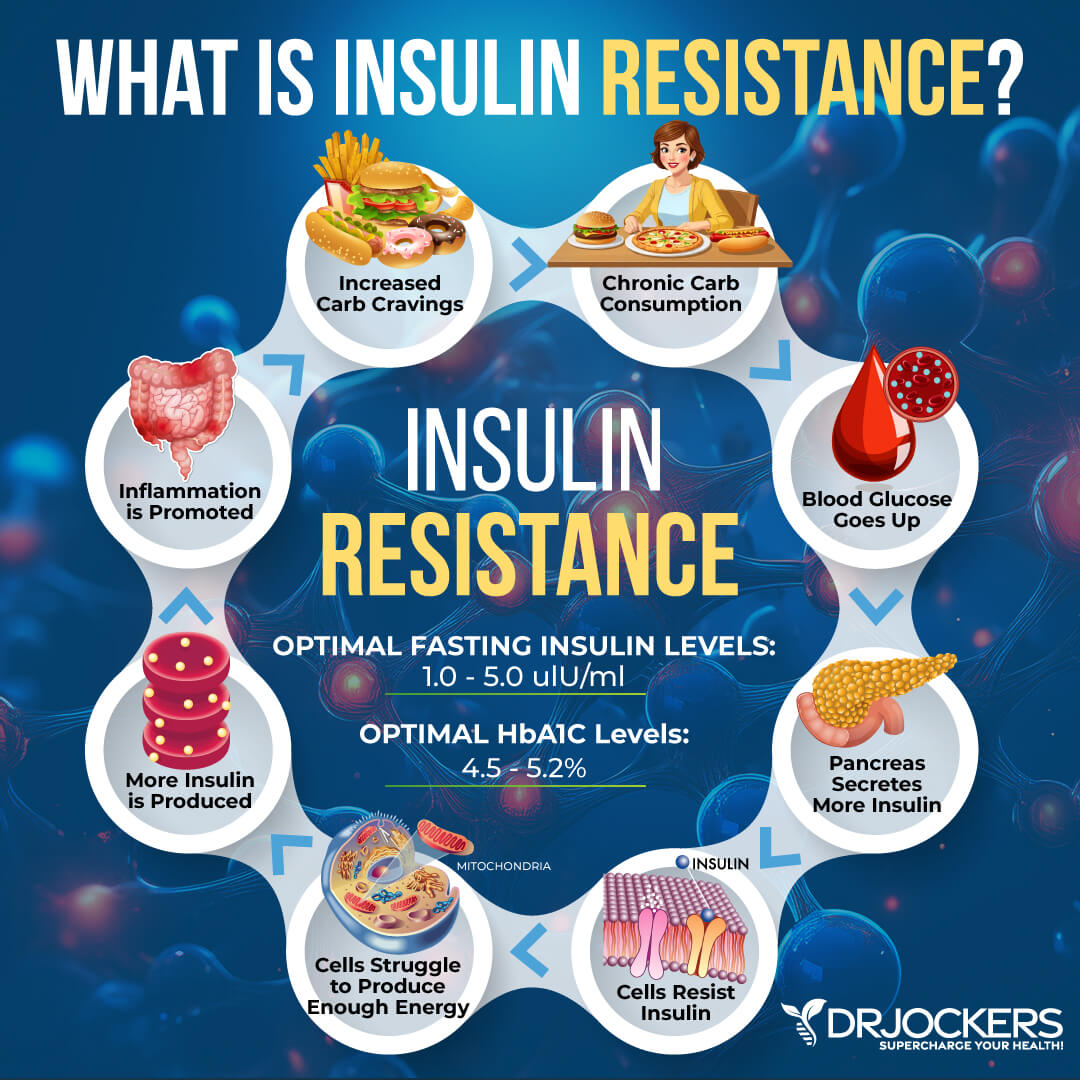
Blood sugar imbalances are one of the main causes of inflammation, so I recommend checking your hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) levels. Your HbA1C levels measure your average blood sugar over the past 2 to 3 months. Hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) gives the average amount of glucose in your blood or blood sugar over the past 3 months, making it one of the top tests for inflammation and diabetes. The clinical range is between 4.8 and 5.6, while the optimal range is 4.5 – 5.2.
Blood sugar imbalances may increase your risk of inflammation. In addition to testing your HbA1C levels, I recommend checking your fasting insulin levels.
Testing your fasting insulin can recognize elevated blood sugar levels and can detect inflammation, insulin resistance, blood sugar issues, and diabetes. The clinical range for fasting insulin is 2.6 – 24.9 uIU/ml, and the optimal range is 1.0 – 5.0 uIU/ml.
Lipid Panel
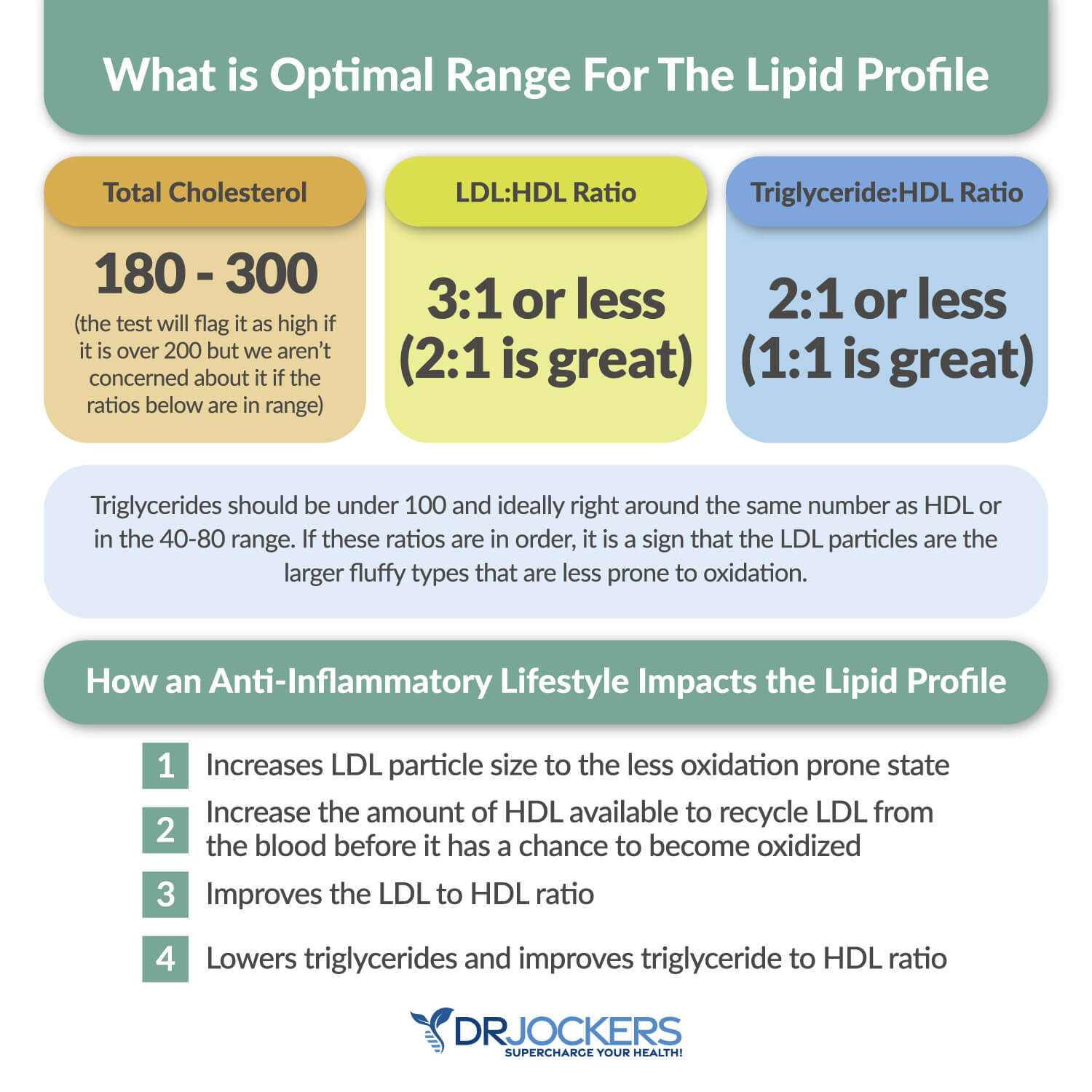
Your lipid panel may be another indication of inflammation and related issues, such as clogged arteries and cardiovascular issues, as well as insulin resistance. We are looking for low HDL or high triglycerides as a sign of insulin resistance.
Having a balanced ratio of LDL to HDL and triglycerides to HDL is essential for your health. Ideally, we are looking for an LDL: HDL ratio: 3:1 or less, 2:1 being optimal. For triglycerides, we are looking for an HDL ratio: 2:1 or less, 1:1 being optimal. Higher rates may indicate insulin resistance and inflammation. Optimal levels:
- VLDL cholesterol: The ideal range is 5 to 30 mg/dl.
- HDL cholesterol: The ideal range is 55 to 80. Levels above 100 can indicate chronic inflammation or active infection in the body.
- Triglycerides: The ideal range is 40 to 80.
Hs-CRP
The C-Reactive Protein or CRP test is a key test I recommend. It measures a protein (CRP) produced in your liver that indicates inflammation levels in your body. The clinical range is between 0 and 3 mg/L, while the optimal range is 0 to 1 mg/L.
When I see levels over 1 mg/L, I know the individual has an inflammatory response that could be due to acute trauma or chronic conditions. Ideally, we want to see the CRP levels as low as possible, certainly under 1 mg/L and more like .01 mg/L.

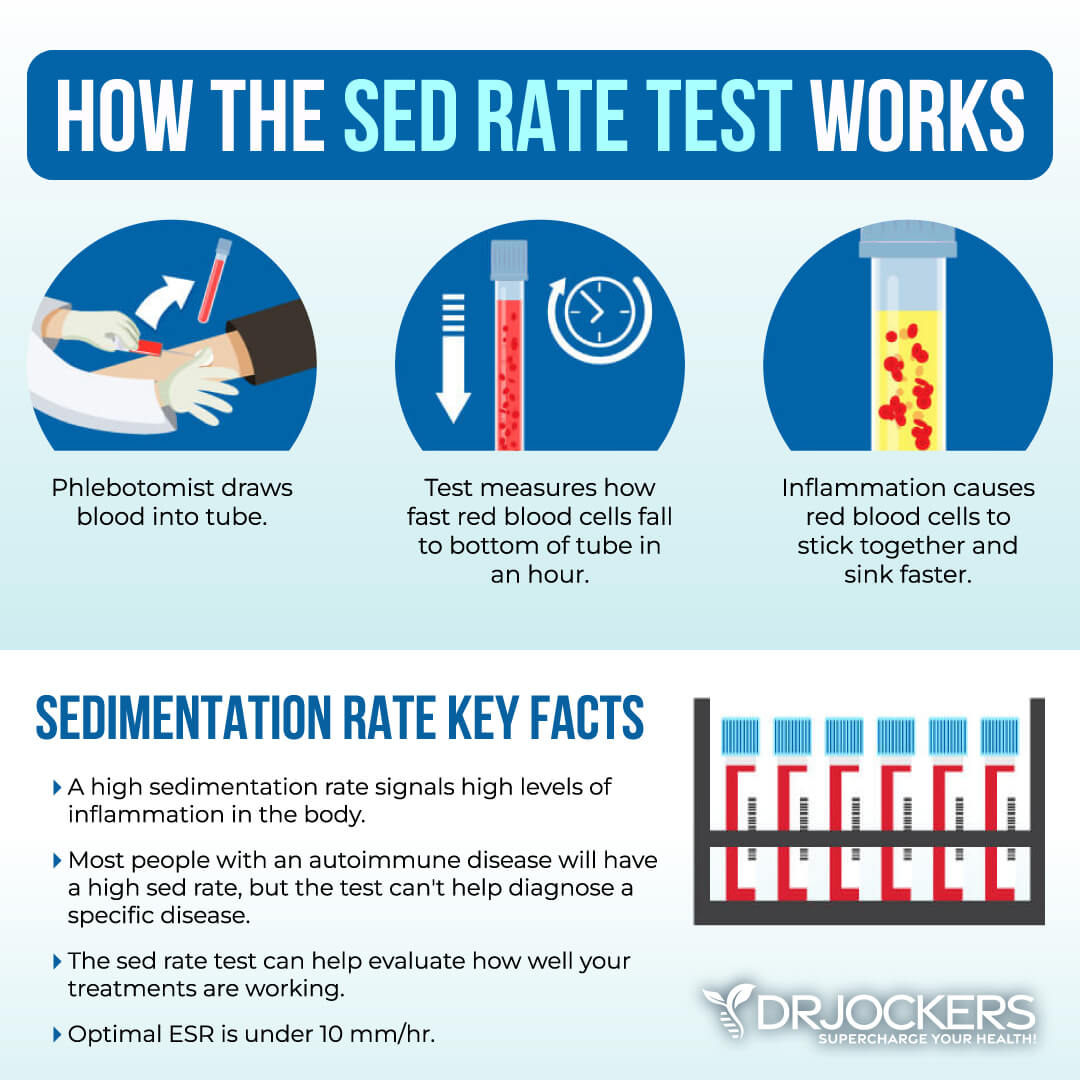
ESR, Fibrinogen, and Platelets
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a common hematology test to look for inflammation It refers to the rate at which your red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood go down in a standardized tube over a period of one hour. Anything over 20 mm/hr is a sign of significant inflammation, and optimal results should be under 10 mm/hr.
Fibrinogen is a protein produced by the liver. This protein helps stop bleeding by helping blood clots to form. High levels of fibrinogen can indicate chronic inflammatory conditions and increased blood clotting formation. The optimal level should be between 150 and 285 mg/dL.
As a signaling molecule for tissue repair, fibrinogen is a good marker for how well your body is able to repair itself. If your fibrinogen is optimal, your repair and recovery are probably meeting or outpacing wear and tear, allowing you to properly heal and recover.
Above 285, you are probably deteriorating more rapidly than you’re repairing. Fibrinogen is also a clotting factor marker, so in viral or bacterial infections, for example, high fibrinogen is indicative of a cytokine storm. Pre-cytokine storm levels are also indicative of several chronic diseases, including heart attack and cancer.
You can also look at platelets as a measurement tool for inflammation and the stickiness of blood. Platelets elevated above 250 are a sign of inflammation. The sweet spot for platelets is between 175 and 250. Below 175, immune function and blood clotting are compromised; the same is true for levels above 250.
Homocysteine Levels
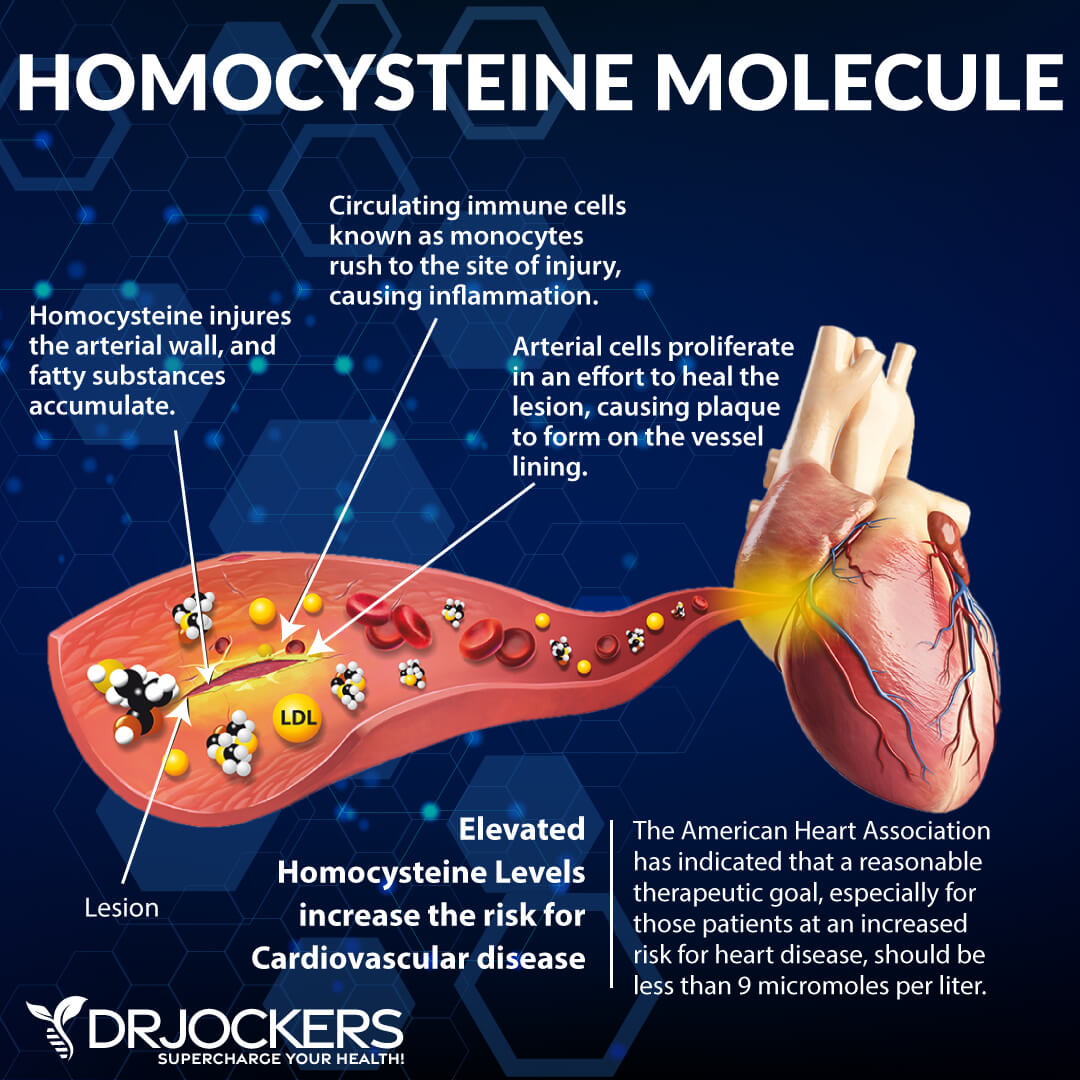
Homocysteine is a common amino acid in your blood that you mostly get from eating meat. Homocysteine is particularly a good marker for cardiovascular issues.
The optimal range for homocysteine is between 6 and 9 umol/L. Some practitioners like to see it under 8 umol/L.
Serum Ferritin
Serum ferritin measures the level of ferritin in your body to detect iron deficiency anemia and other health issues. Elevated serum ferritin levels may indicate inflammation, liver disease, autoimmune disease, or even cancer.
The optimal range is 30 to 400, and the optimal range is 50 to 150 for females and 75 to 150 for males.

LDH and RDW
Lactate dehydrogenase (LD or LDH) is a critical enzyme for energy production in your cells. LDH is found in the highest levels in your liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, muscles, and blood cells.
Some bacteria may also produce LDH. LDH testing may be used to detect liver problems, liver disease, tissue damage, inflammation, and anemia. It may also help to determine the prognosis of certain cancers, including lymphoma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, and testicular cancer.
LDH levels can be measured in the blood (blood LDH) and as fluid LDH around an infection or area of inflammation. Normal LDH levels are between 140 U/L to 280 U/L or 2.34 mkat/L to 4.68 mkat/L. However, in functional medicine, we like to see these numbers lower rather than higher. Over 180 is a sign of inflammation, often impacting the liver.
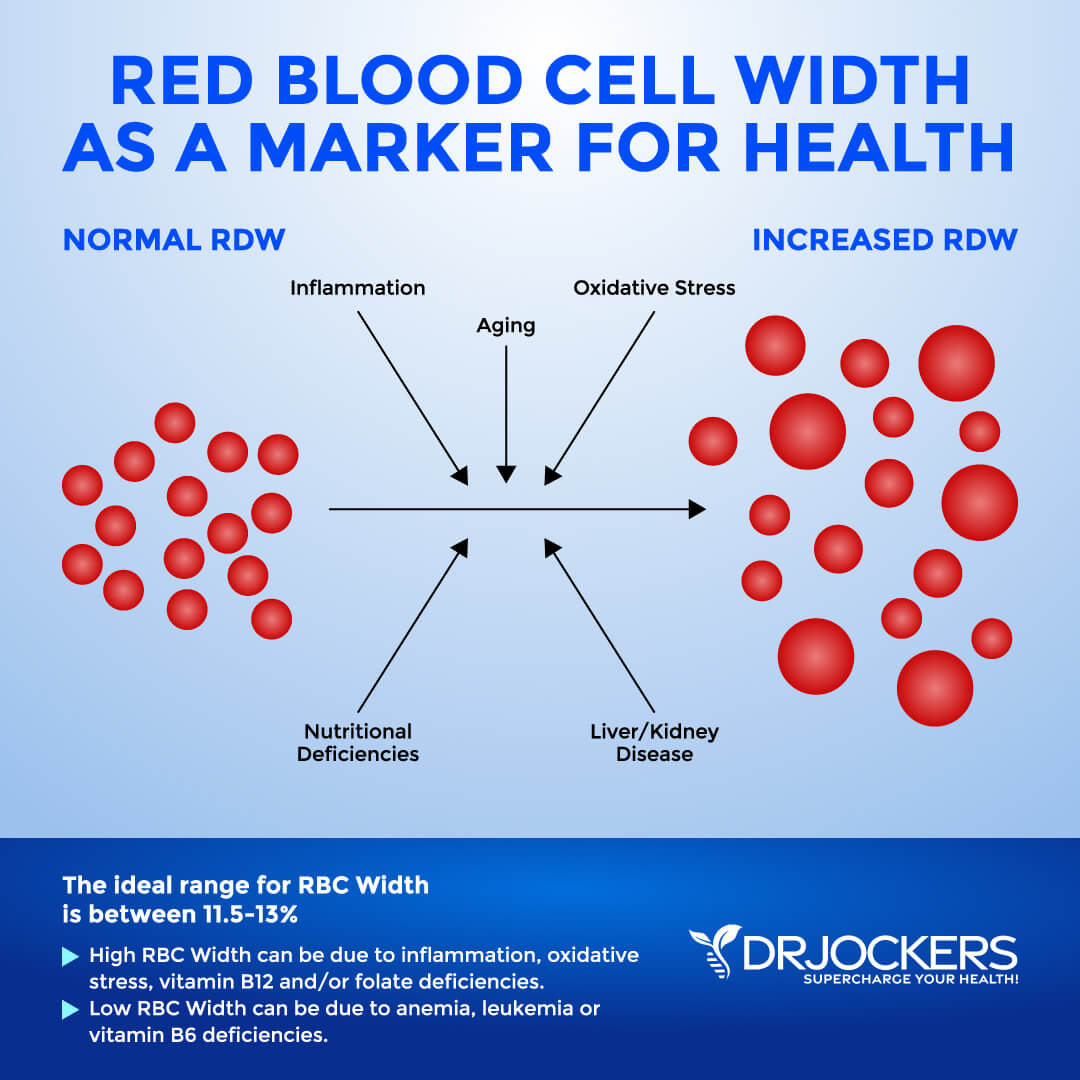
The size of your blood cells has to do with maturation and also depends on methylating agents, such as folate and vitamin B12. Red Blood Cell Distribution (RDW) markers are a great way to detect underlying inflammation in your body. The clinical range is between 12.3 and 15.4 percent while the optimal range is 11.5 and 13 percent.
Vitamin D Levels
Vitamin D3 is an important vitamin that most of our population is deficient in. Poor levels may indicate inflammation.
Optimal healthy levels of vitamin D are between 50 ng/mL and 70 ng/mL, while therapeutic levels are over 70 ng/mL up to 100 ng/mL

Zinc:Copper Ratio
Zinc and copper compete against one another as antagonists in order to properly regulate the physiological pathways in your body. The proper balance between the two trace minerals is critical to maintaining health.
Unlike zinc, copper can readily accumulate in the body in toxic concentrations. In order to maintain adequate zinc levels, a higher dose of zinc compared to copper is required daily. Zinc is only stored for short durations in the blood and bone and is quickly excreted through our urine and fecal matter.
Ideally, the proper intake of copper to zinc should be a 1:8 ratio. Fortunately, the foods that are high in zinc, such as meat, seafood, nuts and pumpkin seeds, are also very high in copper, so you get both of these together in your diet.
We test plasma zinc and serum copper levels, and the ideal ratio is roughly 1-1.2, meaning you should have equal or slightly higher levels of plasma zinc than you have serum copper.

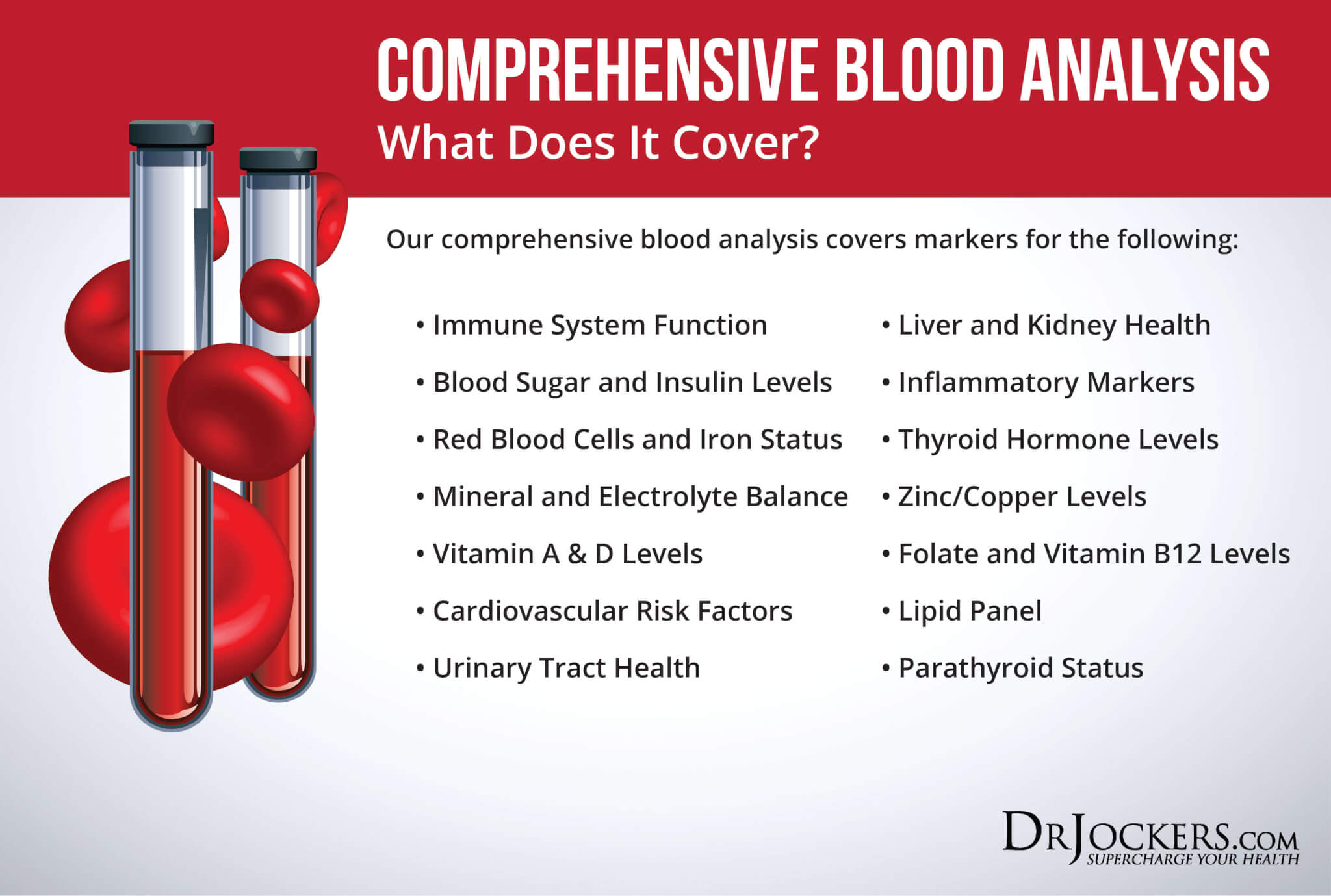
Comprehensive Blood Analysis
To receive a functional blood analysis and look at the optimal ranges of these markers, I recommend and regularly use a Comprehensive Blood Analysis (CBA), which is a very detailed blood test that looks at all of these markers of inflammation and other health functions.
This test is more sophisticated than most conventional doctors run. It looks at everything that a CBC and CMP do and more. It examines all parameters for inflammation, blood sugar levels, insulin levels, immune system function, thyroid function, parathyroid hormone levels, mineral and electrolyte balance, zinc and copper ratio, vitamin A and D levels, folate and vitamin B12 levels, a complete metabolic panel, complete blood count, liver function, kidney function, urinary tract health, nutrient deficiencies, and more.
I recommend getting the Comprehensive Blood Analysis done regularly both as a preventative measure and to monitor your inflammation levels and progress if you are on a treatment plan. Remember, our team is always happy to help to understand your results and create a personalized treatment protocol to regain your health and well-being naturally.
Best Natural Strategies for APOE4 Gene Carriers
If you carry the APOE4 gene, are otherwise under an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease, or simply want to support your brain health, I recommend the following natural strategies:
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition Plan
Eating too many inflammatory processed foods may increase your risk of neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. A 2018 study published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia (NY) has found a link between diet and Alzheimer’s disease (11).
A 2019 study published in Current Nutrition Reports has also found that an inflammatory diet may impact neuroinflammatory processes and may increase the risk and progression of Alzheimer’s disease (12). A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that a nutrient-dense diet rich in vitamins and minerals is critical for those carrying the APOE4 gene (13).
I recommend following an anti-inflammatory diet high in nutrient-dense foods for your brain health. Remove all inflammatory foods, including refined sugar, gluten, refined oils, deep-fried and processed foods, conventional dairy, grain-fed meat and eggs, soda and sugary drinks, and foods that you are sensitive to.
Instead, follow an anti-inflammatory diet and load up on greens, vegetables, low glycemic index fruits, herbs, spices, healthy fats, grass-fed meat, and wild-caught fish. To learn more about an anti-inflammatory diet, read this article as well.

Focus on Healthy Fats
I recommend that you focus on eating lots of healthy fats, including avocados, coconut oil, coconut butter, extra-virgin olive oil, olives, and high-quality animal fats. A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that APOE carriers may benefit from higher-fat diets (13).
APOE2 carriers do great on high fat, including saturated fat, including butter, ghee, sausages, bacon, and cheese. APOE4 carriers should, however, limit saturated fats and focus on monounsaturated fats, including olives and macadamia nuts and omega-3 fats, such as fish, seafood flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnut. According to a 2018 systematic review published in Nutritional Neuroscience, omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial for Alzheimer’s disease (14).
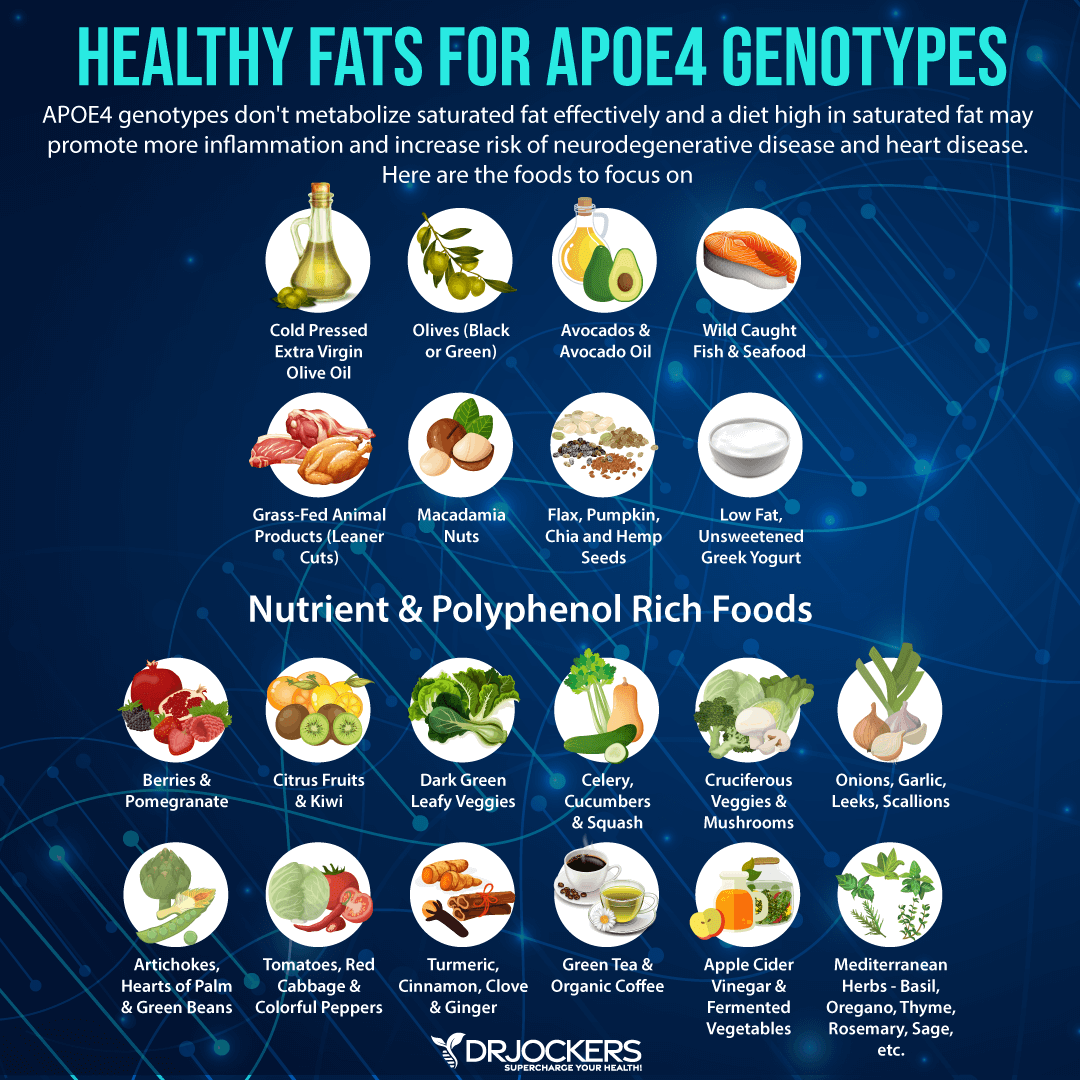
Rich in Polyphenols
I also recommend that your diet is rich in polyphenols, such as quercetin, catechins, kaempferol, and anthocyanins. According to a 2018 systematic review published in Alzheimer’s and Dementia, polyphenols may have protective effects on neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease (15).
A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that polyphenols may increase ABCA1 levels (13). Foods rich in polyphenols include apples, onions, garlic, spinach, red cabbage, berries, olives, herbs, spices, celery, broccoli, grapes, tomato, lettuce, and flaxseeds.
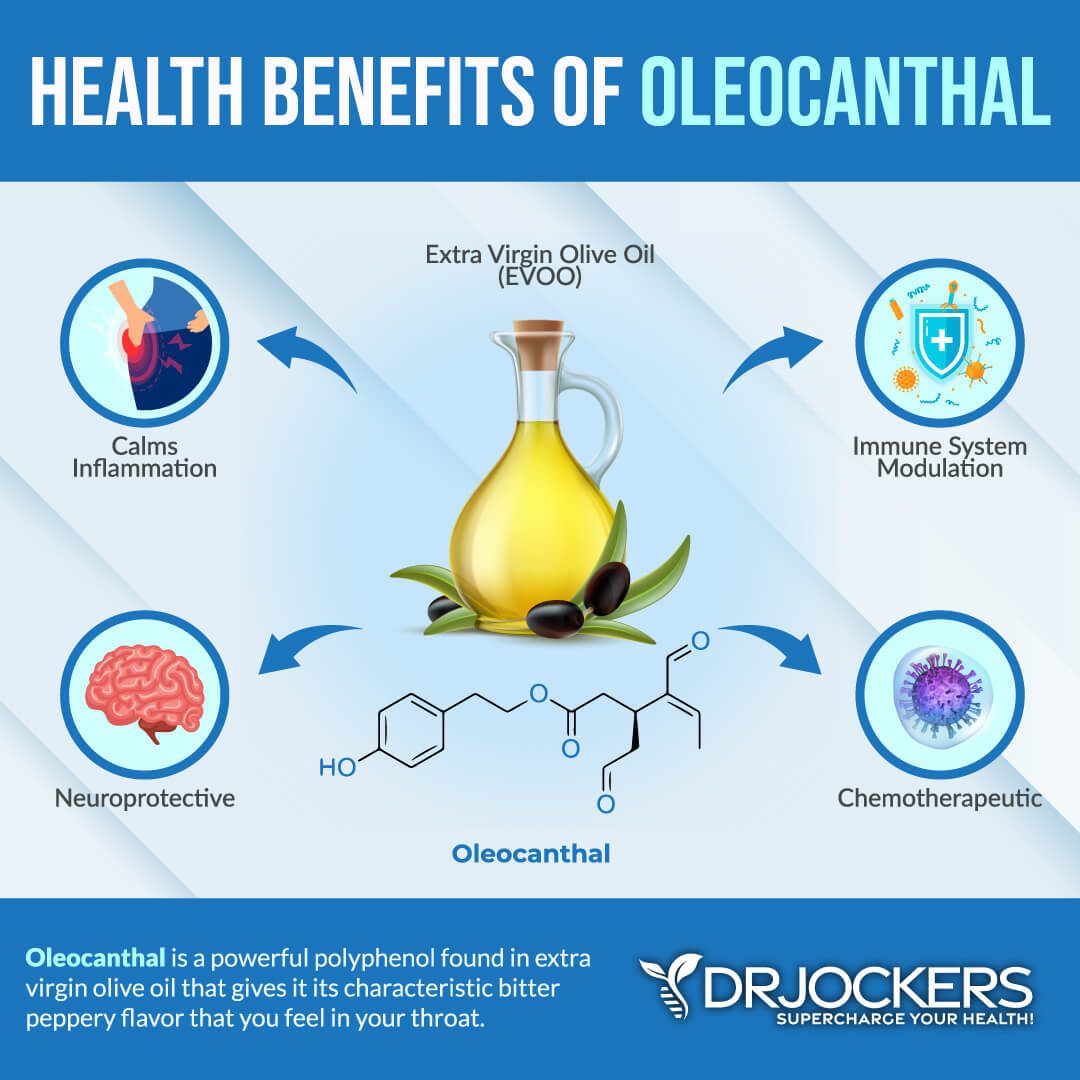
Extra virgin olive oil is one of the best polyphenol rich foods to consume and is especially good for reducing brain inflammation. It contains oleocanthal and hydroxytyrosol as well as vitamin E that all help reduce inflammation in the brain and support optimal neurological function. You may learn more about olive oil and the Fresh-Pressed Olive Oil I recommend from this article.
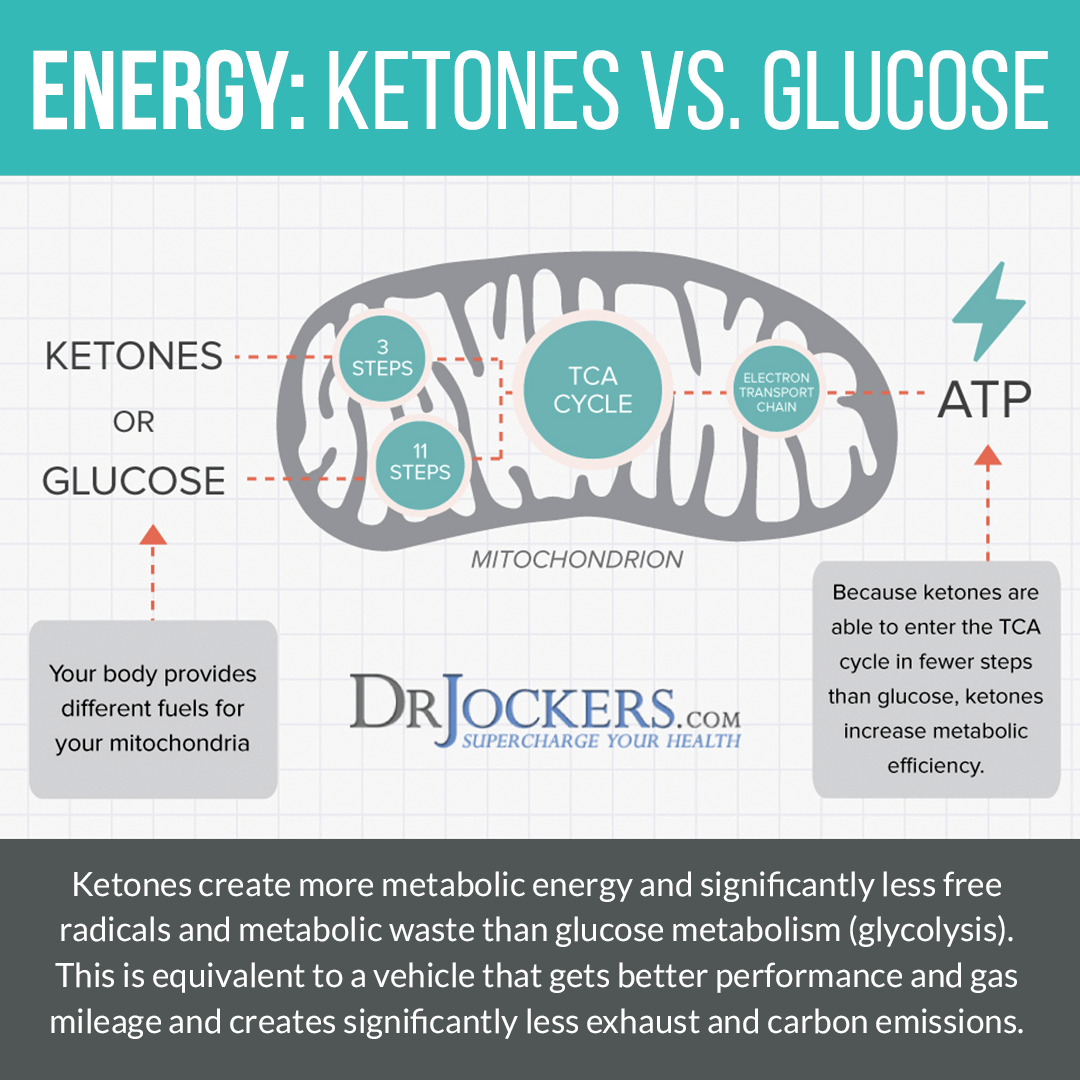
Get Into Ketosis
Under ordinary circumstances, the body relies on glucose for energy. This is what happens in most people since most people tend to follow a diet that is heavy or moderate in carbohydrates. However, this doesn’t always have to be this way. If you are following a high-fat diet, fasting, or restricting your calories, your body won’t receive enough glucose for energy. As a result, your body will turn to dietary or stored fat for energy. When this happens, fats get converted in the liver into ketones. Then it will enter your mitochondria inside your cells to get turned into energy.
The benefits of ketosis include reducing neuroinflammation and chronic inflammation, improved brain health, improved autophagy, and better mental sharpness. A 2021 study published in AIMS Public Health has found that a ketogenic diet may help to reduce cognitive decline in those with Alzheimer’s disease (16). A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that a ketogenic or low-carb diet may be beneficial for those carrying the APOE4 gene (13).
The ketogenic or keto diet is one of the best ways you can get into ketosis. It is a very low-carb, high-fat, and moderate-protein diet. If you are following a keto diet, I recommend focusing on nutrient-dense foods with lots of micronutrients instead of only focusing on your macros. I recommend that you eat plenty of healthy fats, including avocados, avocado oil, coconut oil, coconut butter, coconut milk, olives, extra virgin olive oil, organic butter and ghee, seeds, and fatty fish and meat.
Another great option is intermittent fasting, which you will learn about in the next section. One of the most effective options, though, is the combination of the keto diet and intermittent fasting. To learn more about ketosis, I recommend reading this article, and to learn more about the keto diet, I recommend this one.
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is a type of fasting that cycles between not eating (fasting) and eating (feasting) over a period of time. Intermittent fasting may improve cellular repair, autophagy, immune regulation, inflammation levels, and insulin sensitivity. It also helps to lower the risk of chronic diseases, including neurodegenerative conditions, such as dementia and Alzheimer’s. A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that intermittent fasting may be helpful for those carrying the APOE4 gene (13).
If you are new to intermittent fasting, start with a 12-hour fast. Stop eating after 7 pm dinner and don’t eat until breakfast the next day at 7 am. Increase your fasting window gradually by pushing breakfast to a later time and/or eating dinner earlier.
Most people feel their best doing a 16-hour fast. But listen to your body and figure out what works for you. To learn more about the benefits of intermittent fasting and best intermittent fasting practices, I recommend this article.

Reduce Stress and Optimize Sleep Quality
Reducing stress is essential if you have the APOE4 gene. According to a 2021 study, chronic stress may increase your risk of Alzheimer’s disease (17). A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that getting enough sleep and reducing stress are both critical for APOE4 carriers (13).
To lower your stress levels, I recommend regular movement, meditation, breathwork, journaling, relaxation recordings, nature walks, positive self-talk, affirmation, daily gratitude, and prayer. Practice daily gratitude by keeping a daily gratitude journal and stopping to appreciate the small things throughout the day.
Sleep is necessary for rest, repair, and cellular rejuvenation, which means that sleep allows your brain cells to regenerate and new brain cells to form. According to a 2021 study published in Nature Communications, a lack of sleep may increase the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (18).
Sleeping enough is particularly important if you are an APOE4 carrier. To improve your sleep, avoid sugar and caffeine throughout the day, especially in the evening, try not to eat late at night, reduce stress, and turn off electronics several hours before bedtime. Wind down using relaxing activities, such as reading, crossword puzzles, healing baths, journaling, meditation, and prayer. Invest in a comfortable bed, bedding, pillows, black-out curtains, and a sleep mask.

Improve Air Quality
Improving your air quality is another important idea if you are an APOE4 carrier. According to a 2021 study published in Toxins (Basel), mycotoxins may play a role in Alzheimer’s disease (19). Other indoor air toxins and allergens may also increase inflammation and your risk factors.
I recommend getting a high-quality air filtration system. They can help to remove mold mycotoxins, microbes, allergens, and toxins from your indoor air. I recommend the Air Doctor. You can learn more about it here. You may learn more about mold toxicity here.

Optimize Your Microbiome
Your gut microbiome health is closely connected to your brain health. According to a 2017 review published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, poor microbiome health may increase neurodegeneration and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease (20). I recommend following a gut-friendly, anti-inflammatory, and nutrient-dense diet high in greens, vegetables, herbs, spices, healthy fats, and clean animal protein.
Unless you are following a low-FODMAPS or carnivore diet, eat plenty of prebiotic-rich foods, including apples, onion, garlic, leek, asparagus Jerusalem, artichokes, and jicama. Unless you have histamine intolerance, eat plenty of probiotic-rich fermented foods, including sauerkraut, kimchi, fermented vegetables and herbs, coconut kefir, coconut yogurt, and kombucha. Additionally, I recommend taking a daily probiotic supplement.

Optimize Vitamin D Levels
According to a 2018 study published in Alzheimer’s Research and Therapy, vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (21). A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that the combination of vitamin D3 and K2 may be beneficial for those with the APOE4 gene (13).
They recommend higher doses. I recommend taking a vitamin D3 supplement with at least 3,000-5,000 IU’s of vitamin D3 and at least 90 mcg of vitamin K2. I highly recommend this Vitamin D3/K2 Power. This supplement supports your brain, immune, skin, cardiovascular, and bone health.
Typically, taking 1,000 IU per 25 lbs. of body weight will help you get your levels into a healthy range. You want to test your vitamin D levels at least 1-2 times each year and get your levels between 50-100 ng/ml. It has been hypothesized that a therapeutic level for major health conditions is going to be between 70-100 ng/ml.
In addition to vitamin D3/K2 supplementation, I recommend spending time outside in the sun daily. Eating foods rich in vitamin D, such as cod liver oil, fatty fish, and beef liver, can help too.

Key Supplements
In addition to these support strategies, I recommend a number of key supplements that may support your brain health if you have the APOE4 gene.
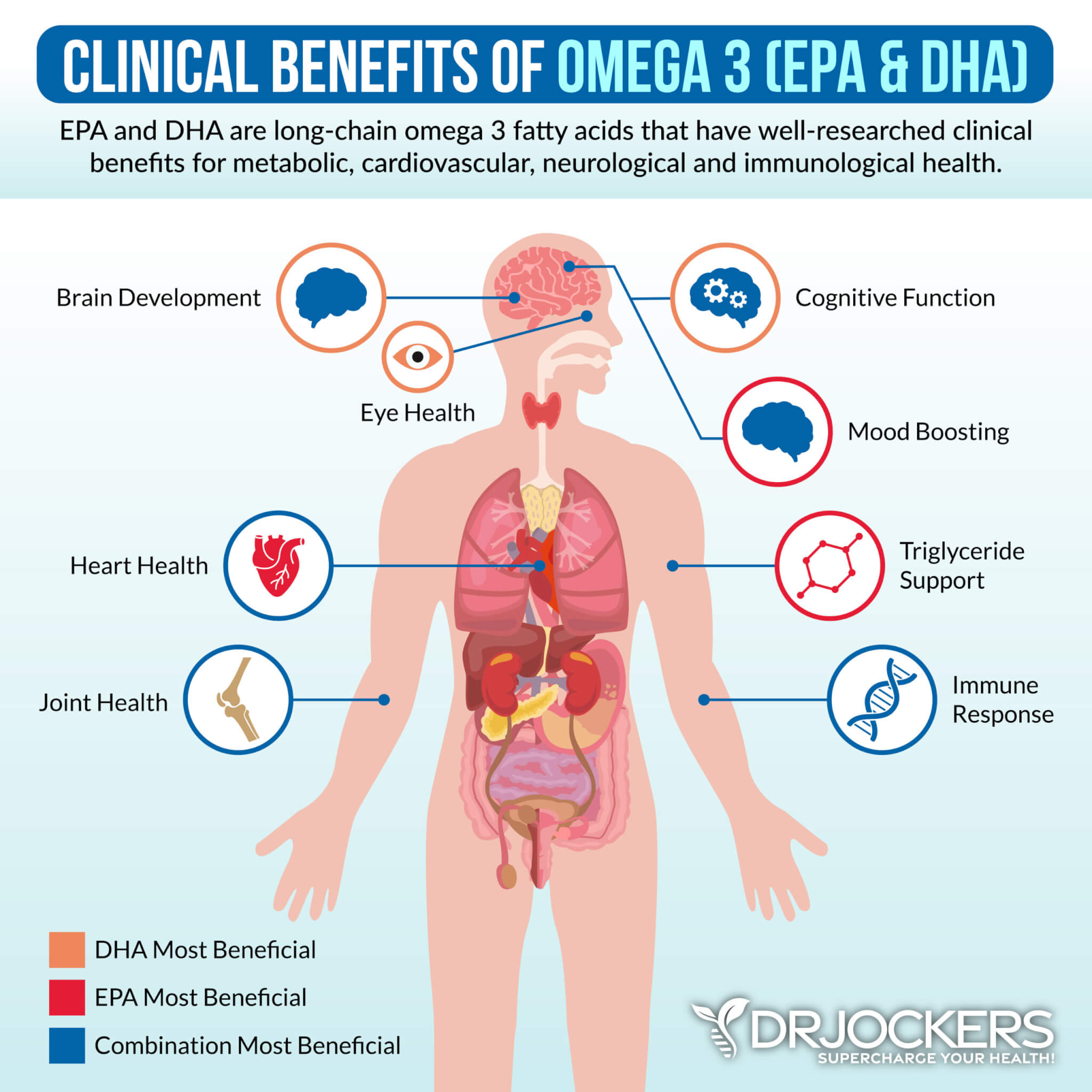
Omega 3 Fatty Acids
A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that taking omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial for those carrying the APOE4 gene (13).
They found that omega-3 fatty acids may help to reduce brain atrophy and may improve brain health. To improve your omega-3 levels, I recommend Pro Omega Curcumin.
Turmeric or Curcumin
Curcumin, the active ingredient of turmeric, offers anti-inflammatory and countless other health benefits. A 2020 study published in the Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling has found that curcumin may help to reduce neurodegeneration (22).
I recommend using turmeric in your cooking and taking a high-quality curcumin supplement, such as Ancient Nutrition Turmeric Once Daily.

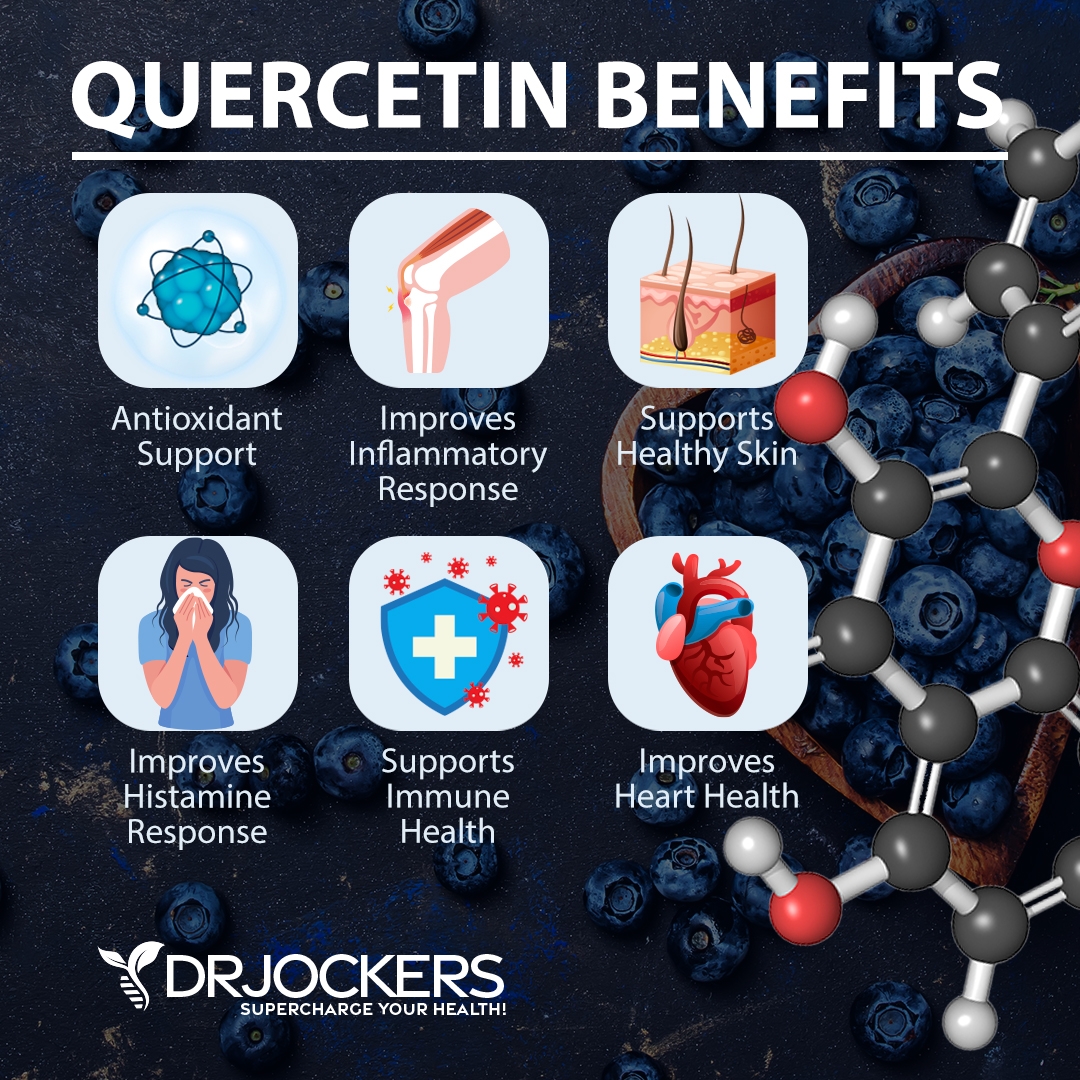
Quercetin
A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that quercetin may be beneficial for those carrying the APOE4 gene (13). They found that quercetin may help to inhibit NFκB and MMP9 activity.
I recommend eating plenty of quercetin-rich foods, including berries, grapes, black plums, cranberries, grapes, apples, cherries, black currants, broccoli, other cruciferous vegetables, peppers, chicory greens, raw kale, red leaf lettuce, romaine lettuce, cabbage, raw asparagus, raw red onion, snap peas, sprouts, and many herbs. I recommend taking a quercetin supplement.
Resveratrol
A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that resveratrol may be beneficial for those carrying the APOE4 gene (13). They found that it may help to reduce cognitive decline and support mitochondrial biogenesis.
I recommend eating resveratrol-rich foods, such as grapes, berries, and cacao, and taking a high-quality resveratrol supplement, such as Resveratrol Power which contains both resveratrol and quercetin.
B Vitamins
A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that B vitamins may be beneficial for those carrying the APOE4 gene (13).
They found that B vitamins may help to improve homocysteine levels, which may improve metabolic deficiency, cholesterol transport, and brain health. I recommend taking a high-quality B vitamin supplement, such as B Strong.

Lithium
A 2021 study published in Nutrients has found that lithium may be beneficial for those carrying the APOE4 gene (13). They found that lithium may help to improve Aβ clearance from the brain and may support brain health in APOE4 gene carriers. I recommend trying Stress Relief.
Zinc
According to a 2020 study published in Neurobiology of Disease, zinc may also be helpful for those with the APOE4 gene (23). Researchers found that zinc may help to alter NLRP3 inflammasome activity and reduce NLRP3-related inflammation.
Thus it may help to slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. I recommend taking a high-quality zinc supplement, such as Zinc Charge.

Brain Regeneration Guide:
If you have struggled with your mood, memory or had trouble concentrating…we have good news!
In the last 10 years, there has been several amazing breakthroughs in neuroscience that are showing that we can actually heal and regenerate our brain cells and improve our neurological health with healthy lifestyle practices.
There are scientifically validated strategies to improve your mood, memory and cognition no matter how old you may be! You can get immediate access to this life changing science and strategies today in the Brain Regeneration guide!
—>Download the Brain Regeneration Guide Today!
Final Thoughts
Carrying the APOE4 gene may increase your risk of Alzheimer’s disease. To reduce your risk factors for the disease and to protect your brain health, I recommend following my best natural strategies for APOE4 gene carriers.
If you want to work with a functional health coach, I recommend this article with tips on how to find a great coach. On our website, we offer long-distance functional health coaching programs. For further support with your health goals, just reach out—our fantastic coaches are here to support your journey.
Inflammation Crushing Ebundle
The Inflammation Crushing Ebundle is designed to help you improve your brain, liver, immune system and discover the healing strategies, foods and recipes to burn fat, reduce inflammation and Thrive in Life!
As a doctor of natural medicine, I have spent the past 20 years studying the best healing strategies and worked with hundreds of coaching clients, helping them overcome chronic health conditions and optimize their overall health.
In our Inflammation Crushing Ebundle, I have put together my very best strategies to reduce inflammation and optimize your healing potential. Take a look at what you will get inside these valuable guides below!